carboxylic acids
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
what is the functional group of carboxylic acids? (1)
-COOH
how are carboxylic acids made? (2)
by oxidising a primary alcohol to an aldehyde
it is then further oxidised to form the carboxylic acid
write the general reaction for the oxidation of a primary alcohol to an aldehyde (1)
RCH2OH + [O] → RCHO + H2O
provide an example of a primary alcohol being oxidized to an aldehyde (1)
CH3CH2OH + [O] → CH3CHO + H2O
write the general equation for the oxidation of an aldehyde to a carboxylic acid (1)
RCHO + [O] → RCOOH
provide an example of an aldehyde being oxidised to a carboxylic acid (1)
CH3CHO + [O] → CH3COOH
write the overall reaction for the formation of a carboxylic acid from a primary alcohol (1)
CH3CH2OH + 2[O] → CH3COOH + H2O
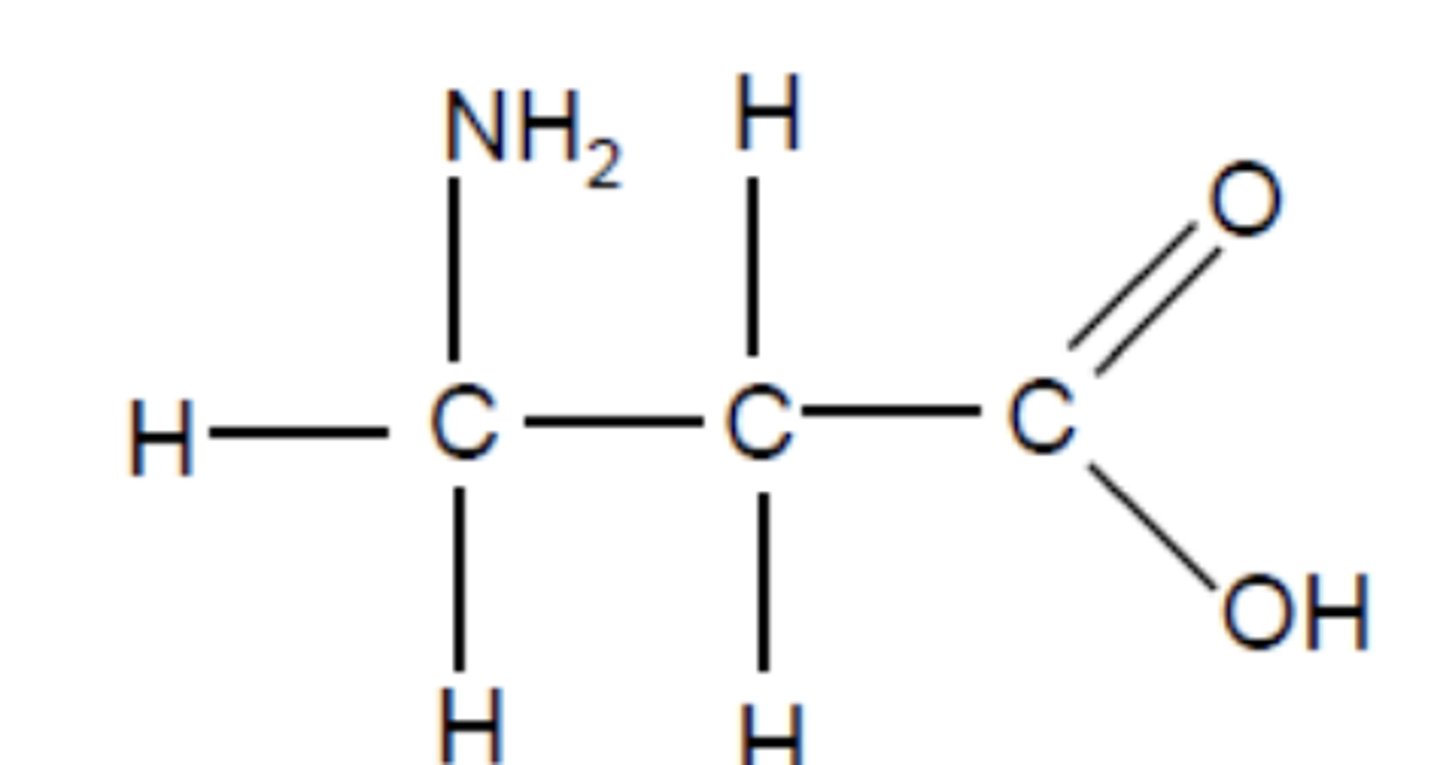
draw the structure of 3-aminopropanoic acid (3)
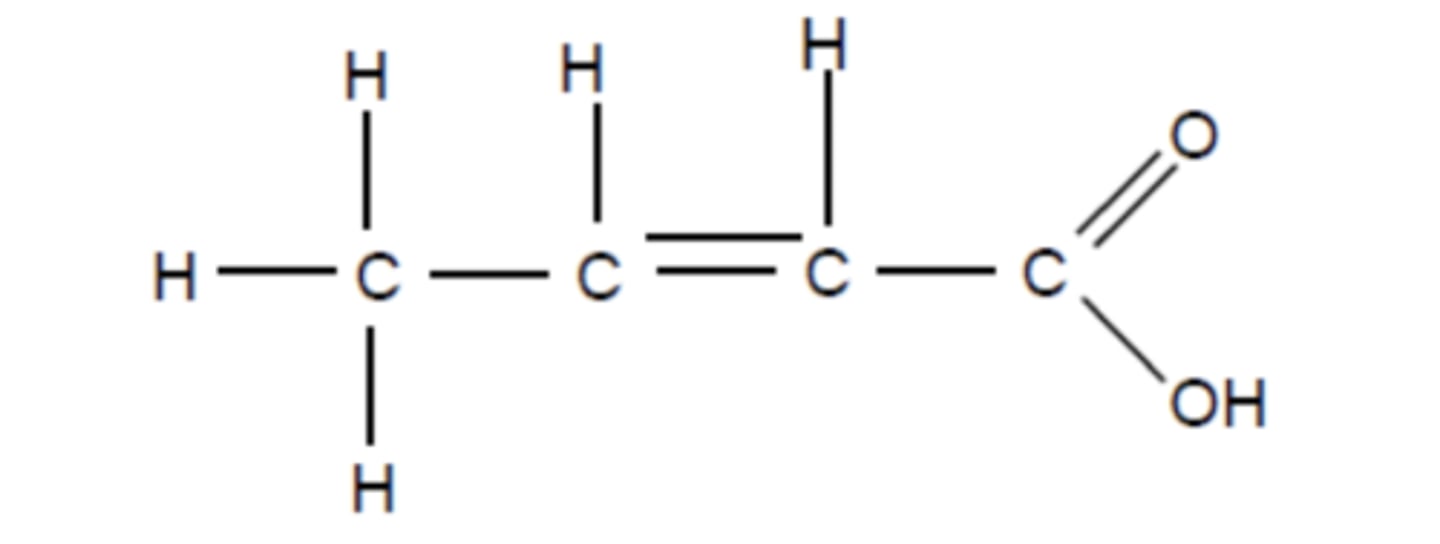
draw the structure of but-2-enoic acid (3)
why are carboxylic acids with a low molecular mass very soluble in water? (1)
the -COOH group forms hydrogen bonding with water
why are carboxylic acids considered weak acids despite being very soluble in water? (1)
they are only slightly dissociated in water
write the dissociation equation for ethanoic acid in water (1)
CH3COOH (aq) ⇌ CH3COO⁻ (aq) + H⁺ (aq)
what is the role of the carbonyl group in the dissociation of a carboxylic acid in water? (2)
the carbonyl group attracts electrons away from the -OH group
weakening the bond and allowing it to release a proton
how does the addition of a halogen atom, such as chlorine, affect the acidity of a carboxylic acid? (3)
the halogen atom withdraws electron density away from the carbonyl carbon
making the O-H bond more polar and easier to break
this increases the acid's ability to release a hydrogen ion
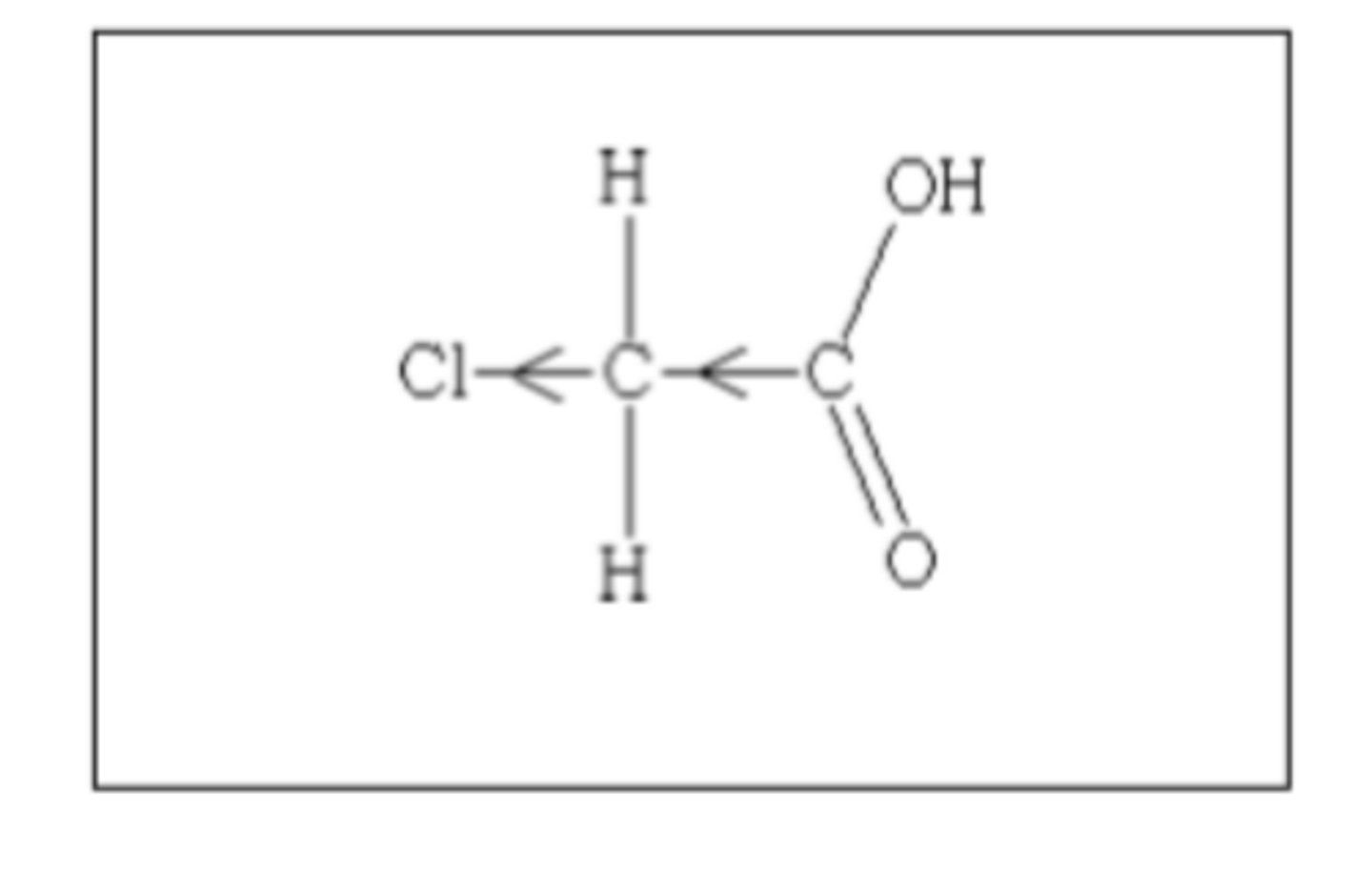
draw the structure of chloroethanoic acid (2)
how can you test for carboxylic acids? (2)
react the carboxylic acid with sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃)
effervescence occurs due to the production of carbon dioxide gas
write the balanced equation for the reaction of ethanoic acid with sodium carbonate (1)
2CH₃COOH + Na₂CO₃ → 2CH₃COO⁻Na⁺ + CO₂ + H₂O
why are ionic salts formed in the reaction between carboxylic acids and sodium carbonate? (2)
the reaction forms carboxylate salts
which are ionic and soluble in water
what is the reaction called when carboxylic acids react with alcohols to form esters? (1)
esterification
what are the products of an esterification reaction? (1)
an ester and water
what catalyst is used in the esterification reaction? (1)
concentrated sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄)
give the general reaction equation for esterification (1)
RCOOH + ROH ⇌ RCOOR + H₂O
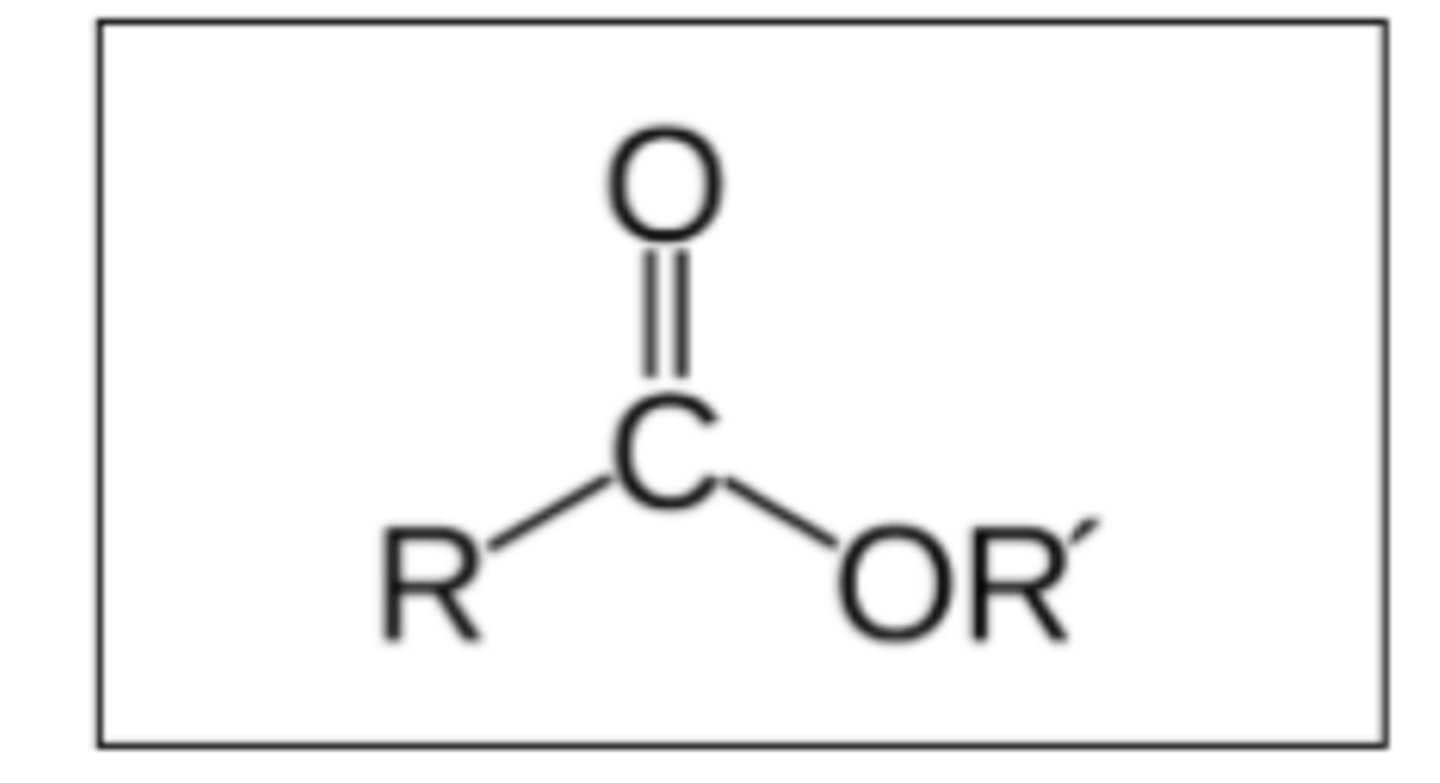
draw the structure of an ester functional group (2)
what is the functional group isomer of esters?
carboxylic acid
how is the name of an ester derived from its alcohol and carboxylic acid? (2)
alcohol part (e.g. ethanol -> ethyl) + acid part (e.g. ethanoic acid → ethanoate)
what is the ester formed from ethanol and propanoic acid? (1)
ethyl propanoate
What is the ester formed from propan-1-ol and ethanoic acid? (1)
propyl ethanoate
what happens when esters are hydrolysed using water and a dilute acid catalyst? (1)
esters are broken down into their carboxylic acid and alcohol components
what catalyst is used for the hydrolysis of esters with water? (2)
dilute H₂SO₄ or HCl
why does hydrolysis of esters using water result in a low yield of carboxylic acid and alcohol? (1)
the reaction is reversible, so only partial hydrolysis occurs
what is the first step in the alternative 2-step method for hydrolysing esters with alkali? (1)
add NaOH to hydrolyse the ester into an alcohol and a carboxylate salt
what happens during the second step of the alternative 2-step method for ester hydrolysis? (2)
add an acid such as H₂SO₄ or HCl
to convert the carboxylate salt into a carboxylic acid
Write the reaction for the hydrolysis of methyl ethanoate with NaOH. (2)
CH₃COOCH₃ + NaOH → CH₃COO⁻Na⁺ + CH₃OH
sodium ethanoate and methanol formed
what are the products of hydrolysing an ester with alkali followed by acid? (1)
a carboxylic acid and an alcohol
why is an excess of dilute acid required in the second step of the 2-step ester hydrolysis? (1)
to fully convert the carboxylate salt back into the carboxylic acid
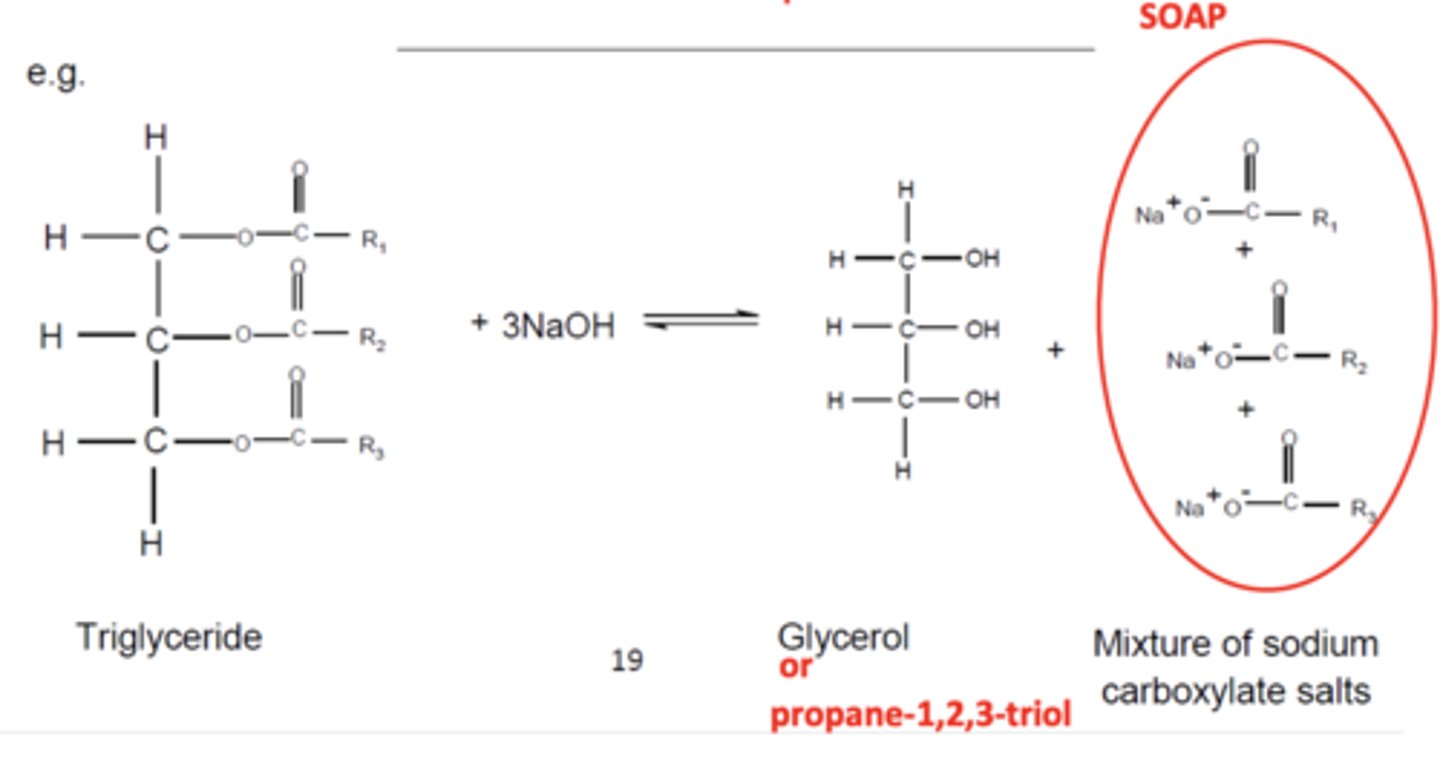
what are triglycerides? (1)
triglycerides are triesters of long-chain carboxylic acids (fatty acids) and propane-1,2,3-triol (glycerol)
how can triglycerides be hydrolysed and what are the products? (2)
using a hot NaOH solution
to form glycerol and sodium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids
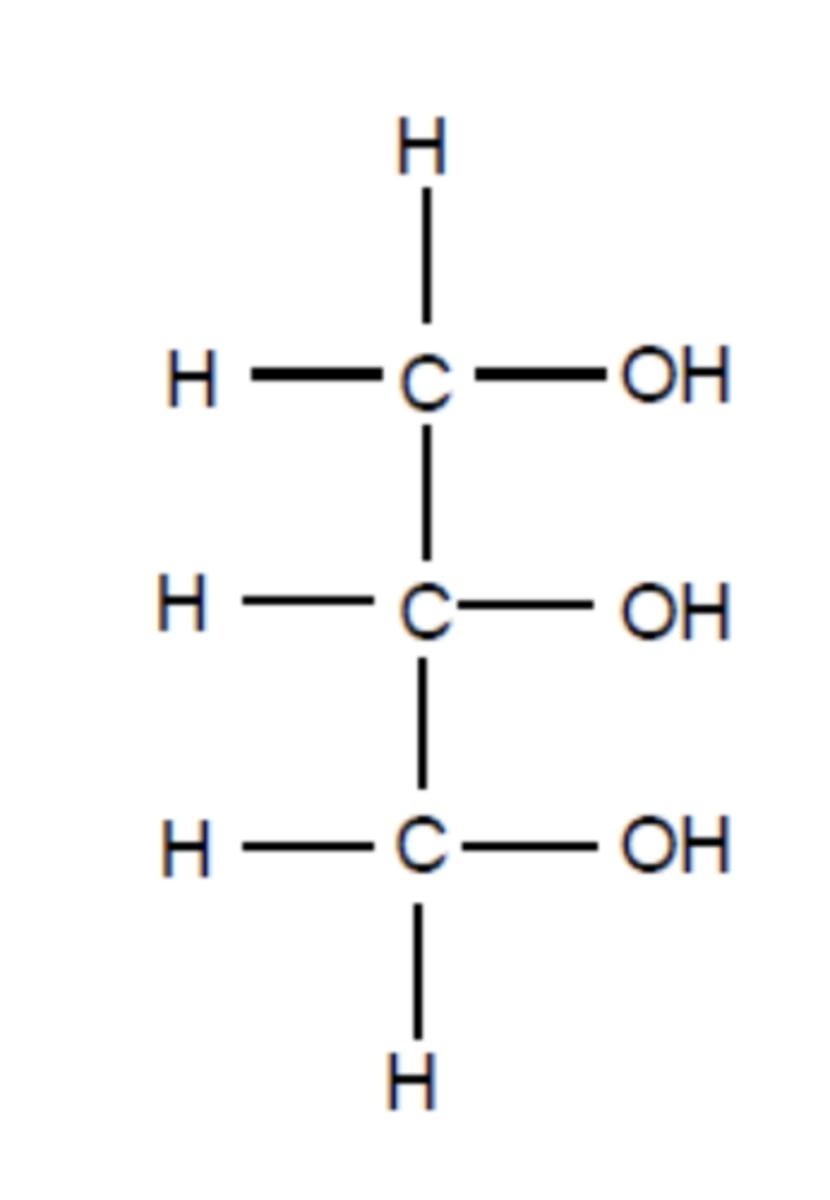
draw the structure of glycerol (1)
why are sodium carboxylate salts important? (1)
they are used in the manufacture of soaps
draw the equation for the reaction of the formation of soap (4)
why does glycerol dissolve easily in water? (2)
glycerol has three -OH bonds
which form hydrogen bonds easily with water
what are the uses of glycerol? (4)
cosmetics industry
food
glues (to prevent materials from drying too quickly)
wine
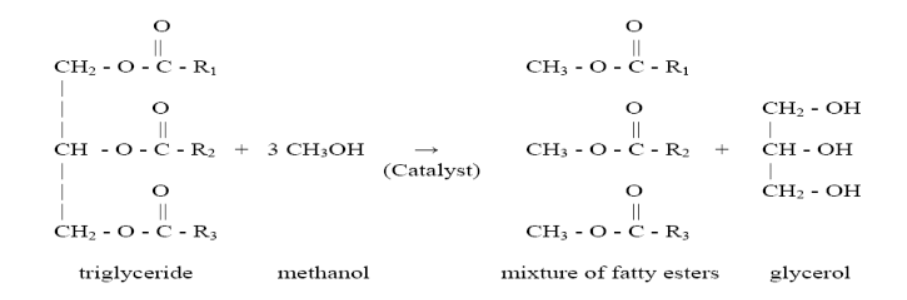
what is biodiesel? (2)
biodiesel is a liquid fuel consisting of a mixture of methyl esters of long-chain carboxylic acids
derived from vegetable oils
what is a biofuel? (1)
a fuel produced from renewable biological sources
how is biodiesel produced from vegetable oils? (3)
made by reacting vegetable oils (such as rapeseed oil)
with methanol (CH₃OH) in the presence of a strong acid or alkali catalyst
to form a mixture of methyl esters
why is biodiesel considered renewable? (1)
because it is made from oils derived from crops such as rapeseed
draw the equation for the reaction of the formation of biodiesel (5)
what are the raw materials used to make bioethanol? (1)
sugar cane and sugar beet
what are the raw materials used to make biodiesel? (1)
vegetable oil
how is bioethanol made? (1)
by fermentation
how is biodiesel made? (1)
by reacting vegetable oil with an alcohol and HCl
where is bioethanol commonly used? (2)
in cars as a mixture with petrol
widely used in Brazil
where is biodiesel commonly used? (3)
in cars, buses, and vans as a mixture with diesel
how widely available is bioethanol in the UK? (1)
increasingly available
how widely available is biodiesel? (1)
it can be home-made and is available from some petrol stations