33. Pharmacology
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Cardiac Drugs:
What drugs are:
Anti-arrhythmic Drugs + Antihypertensives (2)
Function:
ONLY Antihypertensives (3)
Function:
Anti-arrhythmic Drugs + Antihypertensives » Dec HR and BP
Beta Blockers
Ca Channel Blockers
ONLY Antihypertensives » Dec BP
Diuretics
ACE Inhibitors
ARB Blockers
Beta Blockers:
Suffix:
Common Drug Names:
Mechanism: (2)
Effects: (3)
Indications: (3)
Suffix:
“-olol”
Common Drug Names:
Atenolol, Metoprolol, Carvedilol, Labetalol, Propranolol
Mechanism:
Block Beta-Adrenergic Receptors
Block Action of SNS (Inc HR/BP, Bronchodilation, Vasoconstriction)
Effects:
Dec HR and BP
Bronchoconstricton
Vasodilation
Indications:
Coronary Artery Disease
HTN
Arrhythmia
Beta Blockers:
Adverse Effects: (6)
ECG Findings:
Considerations: (3)
Effects on Preload and Afterload:
Adverse:
Orthostatic Hypotension
Dizziness
Lightheadedness
Ringing of Ears
Venous Pooling
Blood accumulates in LE d/t Vasodilation
Bradycardia
ECG:
PR Interval Increases
Considerations:
Use RPE for exercise prescription
DO NOT use in Asthma, COPS, or any other Pulmonary Dx
D/t bronchoconstriction
No Abrupt Withdrawal
Effects on:
Preload: Slightly reduce
Afterload: Reduce
Ca Channel Blockers:
Suffix:
Common Drug Names:
Mechanism:
Effects: (2)
Indication: (3)
Suffix:
“-Pines and -Zems”
Common Drug Names:
Amlodipine, Verapamil, Diltiazem
Mechanism:
Blocks entry of Ca in cardiac tissue » reducing cardiac contractility and vasoconstriction
Effects:
Decrease HR and BP
Vasodilation
Indication:
CAD
HTN
Arrhythmias
NOTE: Can be given to pts c Pulmonary Conditions d/t not causing bronchoconstriction
Ca Channel Blockers:
Adverse Effects: (5)
Considerations:
ECG Changes:
Adverse Effects:
Orthostatic Hypotension
Dizziness
Lightheadedness
Ringing of the Ears
Venous Pooling
Considerations:
Use RPE for Exercise Prescription
ECG Changes:
Prolonged QT Interval
Practice Q 1:
A patient is taking B blockers for three years post myocardial infarction. Which of the following is the MOST LIKELY response to exercise seen in this patient?
A. Rapid increase in HR
B. Decreased exercise tolerance
C. Blunted response of HR with exercise
D. Increased BP
C. Blunted response of HR with exercise
B: Improves exercise tolerance

Duretics » LOOP DIURETICS
Suffix:
Common Drug Names:
Mechanism:
Use: (4)
Suffix:
“-Ide”
Common Drug Names:
Furosemide (Lasix)
Mechanism:
Inhibits reabsorption of water and electrolytes from Loop of Henle
Use:
HTN
CHF
Edema
Pulmonary Edema
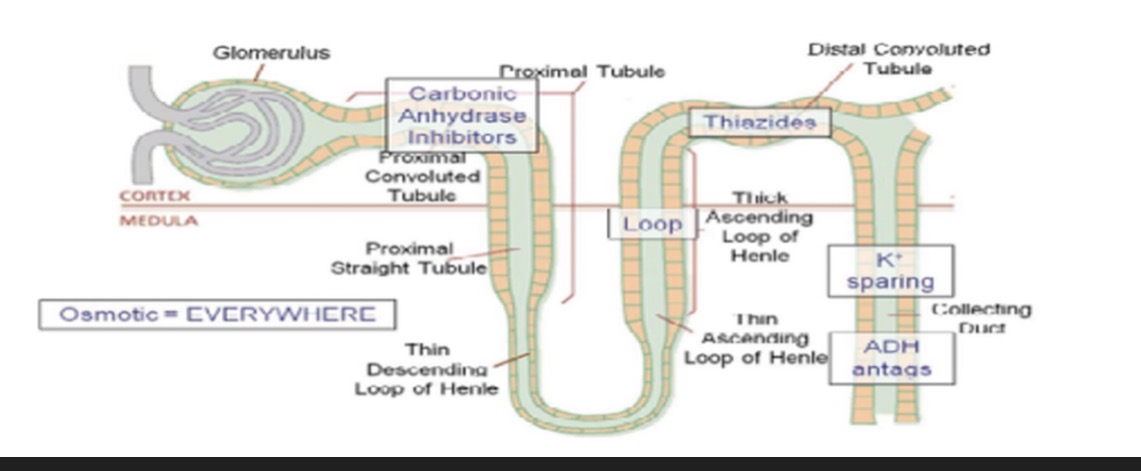
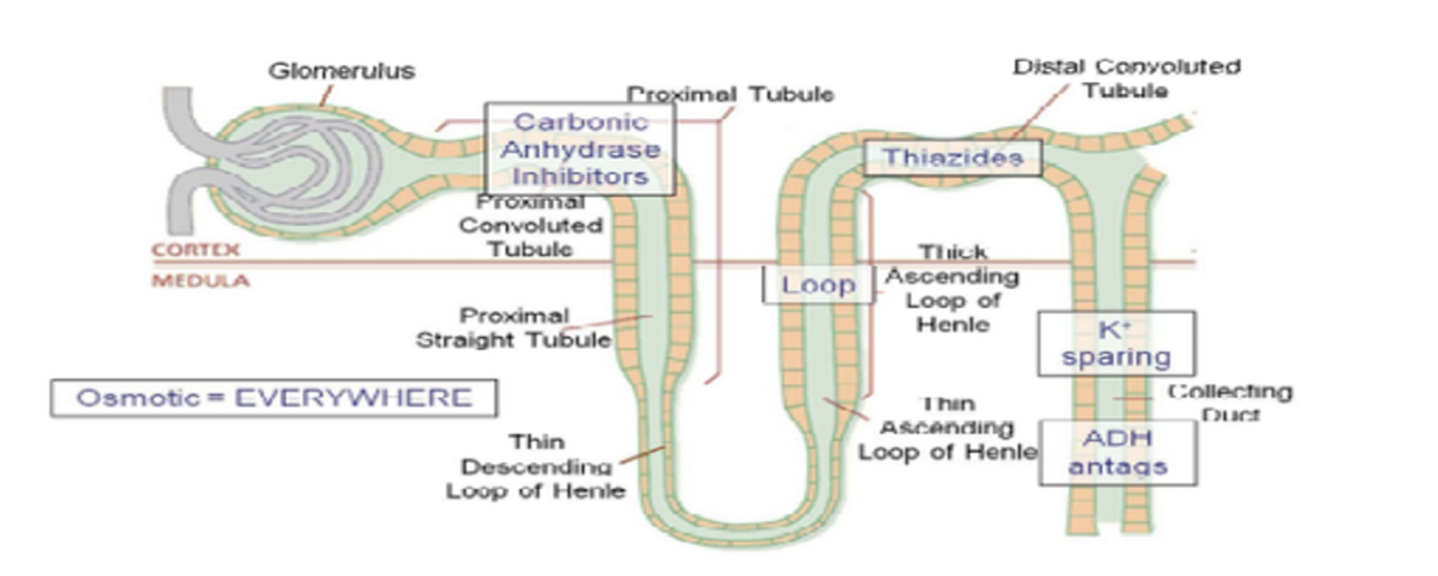
Duretics » LOOP DIURETICS
Side Effects: (8)
Effects on Preload and Afterload
Side Effects
REFLEX TACHYCARDIA
In response to Dec BP and Inc HR (Compensation)
Hypokalemia
Hypocalcemia
Hyponatremia
Dehydration
Orthostatic Hypotension
Dizziness
Lethargy
Effects on:
Preload: Dec
Afterload: Dec
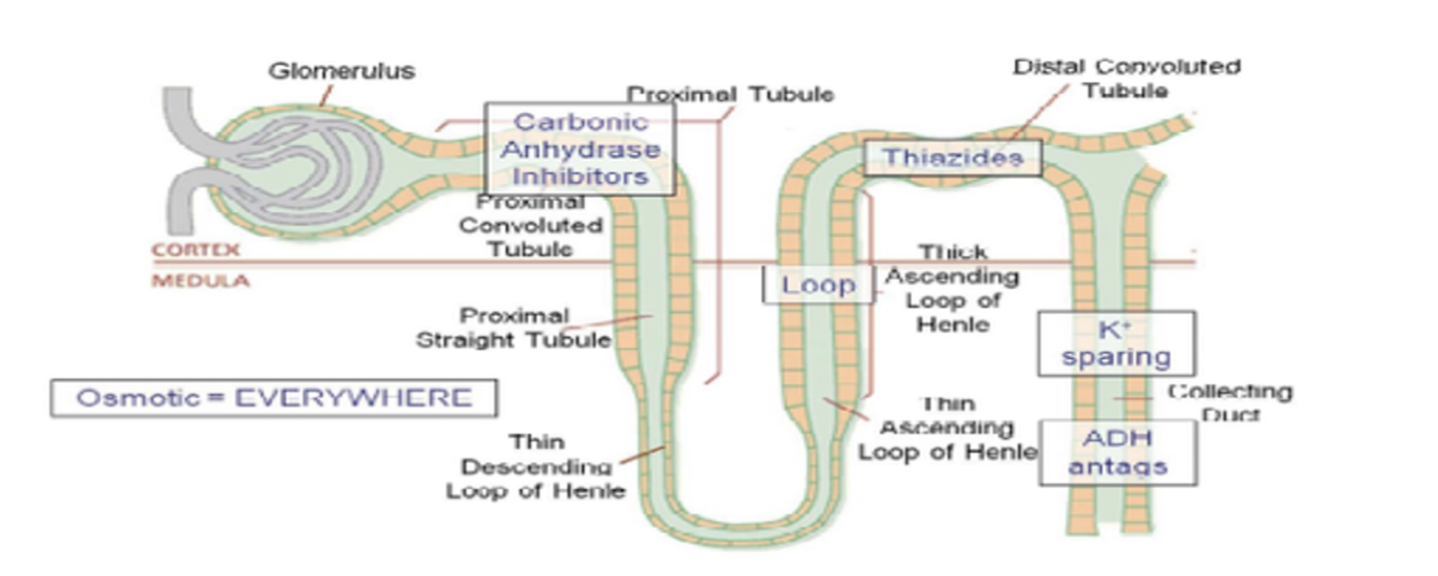
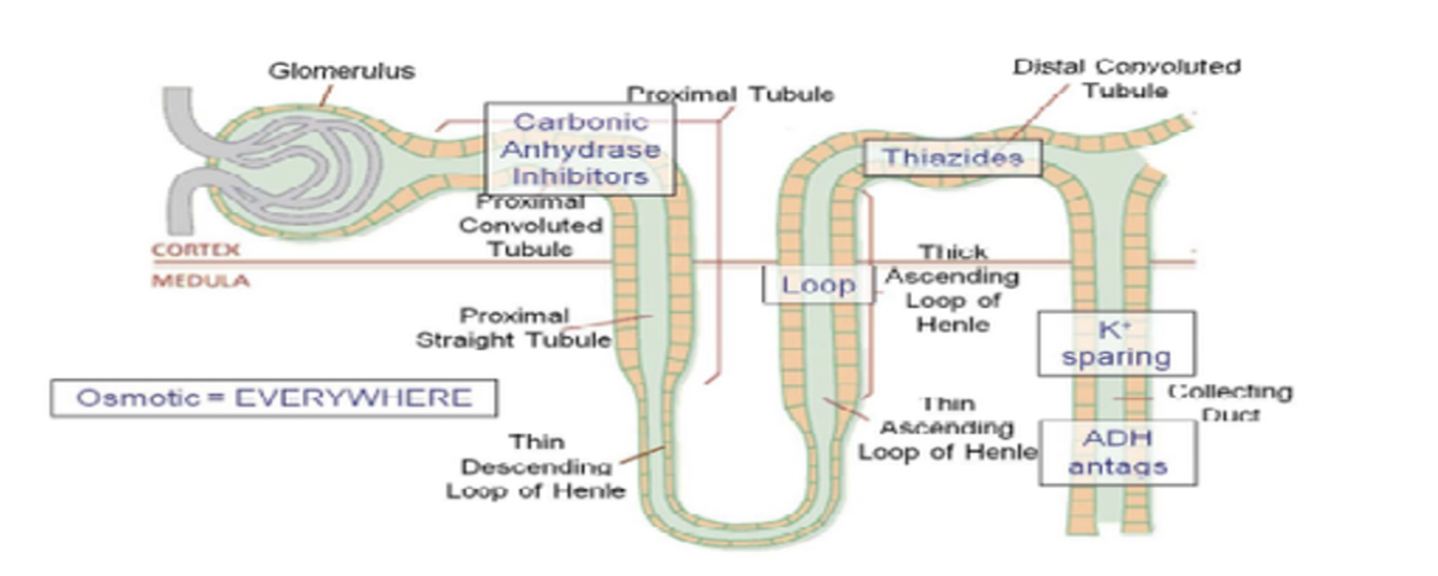
Diuretics: POTASSIUM SPARING DIURETICS
Suffix:
Common Drug Name:
Mechanism:
Through competitive binding of receptors at the aldosterone-dependent sodium-potassium exchange site in the…
Use: (3)
Potassium Sparing Diuretics are preferred over Loop Diuretics when?
Side Effects: (3)
Effects on Preload and Afterload:
Suffix:
“-Tone”
Common Drug Name:
Spironolactone (Aldactone)
Mechanism:
Distal Convoluted Renal Tubule
Sparing Potassium
Use:
CHF
HTN
Combined with other drugs causing Hypokalemia
Preferred when pt already has Hypokalemia
Side Effects:
HYPERKALEMIA
Gynecomastia
Similar to Loop Diuretics
Effects on:
Preload: Dec
Afterload: Dec
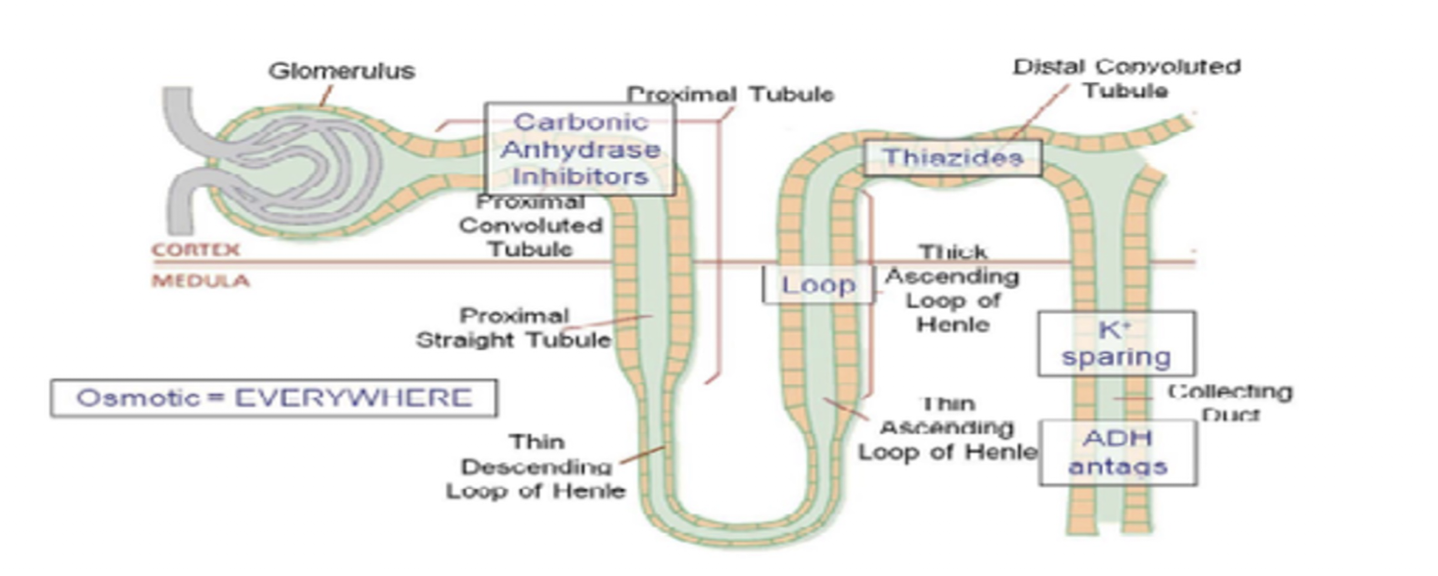
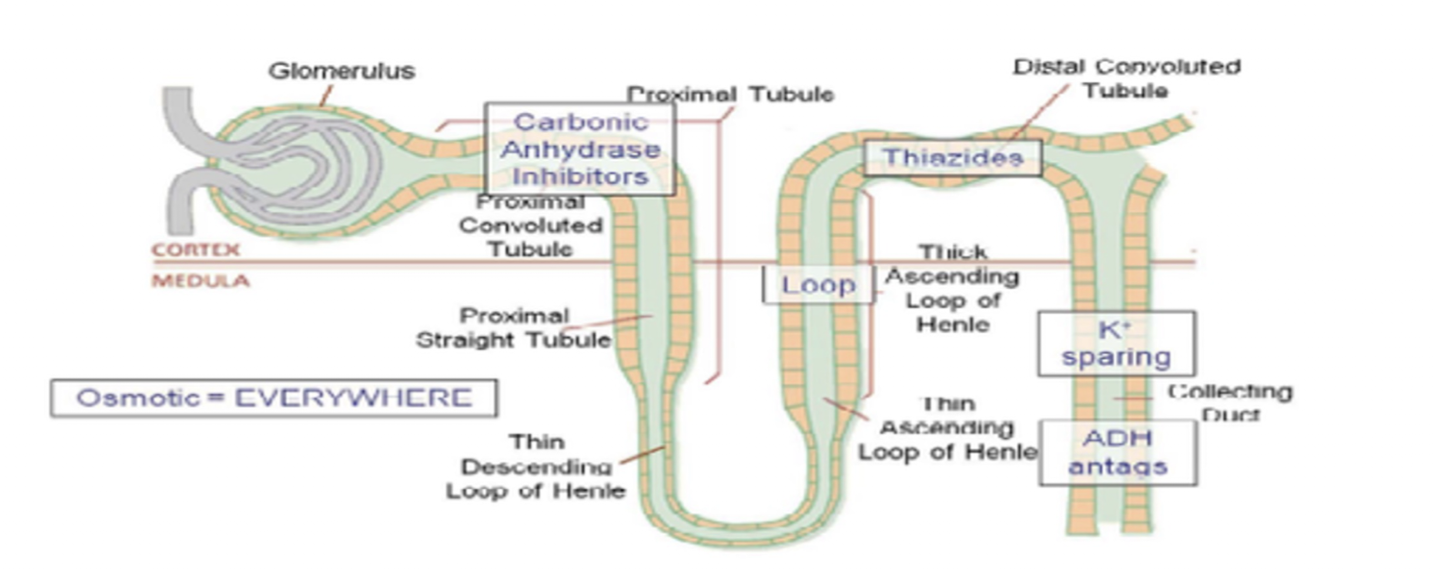
Diuretics: THIAZIDES
Suffix
Common Drug Names:
Mechanism:
Use: (3)
Side Effects: (5)
Thalazides must be avoided in what pop? (5)
Effects on Preload and Afterload:
Suffix:
“-Thiazide”
Common Drug Names:
Hydrochlorothiazide (HCT)
Mechanism:
Blocks Sodium and Chloride Channels in Distal Convoluted Tubule
Inhibit Reabsorption of Sodium and Water
Use:
HTN
CHF
Edema
Side Effects: CLUG
Hypercalcemia
Hyperuricemia
Hyperlipidemia
Hyperglycemia
Same as Loop Diuretics
Avoided:
Elderly
DM
Renal Dysfunction
Gout
Hyperlipidemia
Effects on:
Preload: Dec
Afterload: Dec
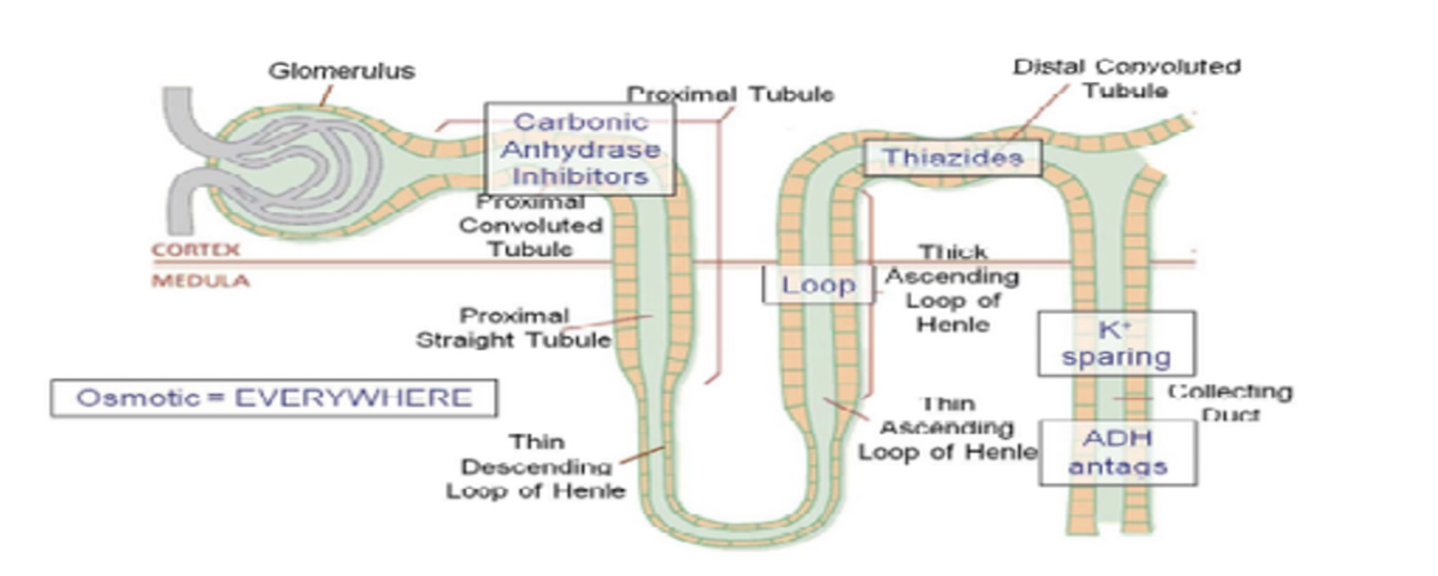
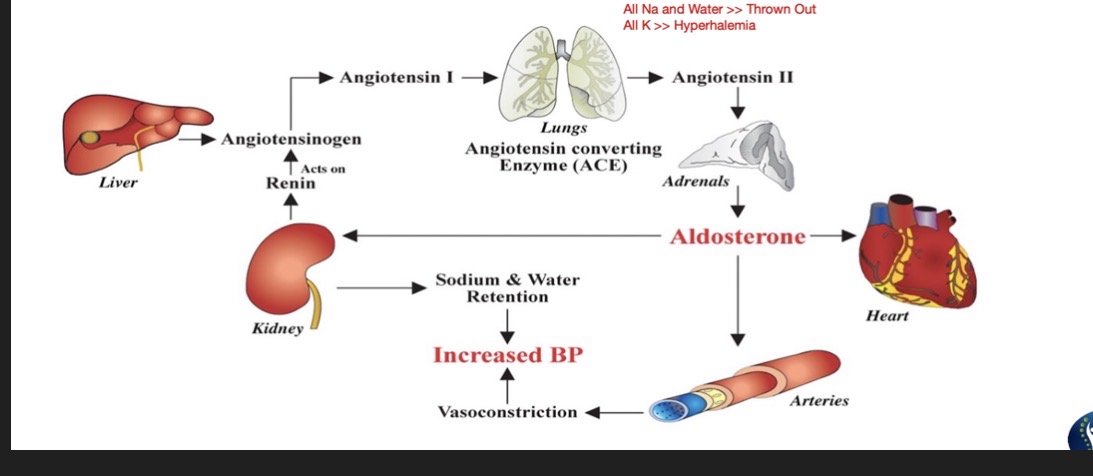
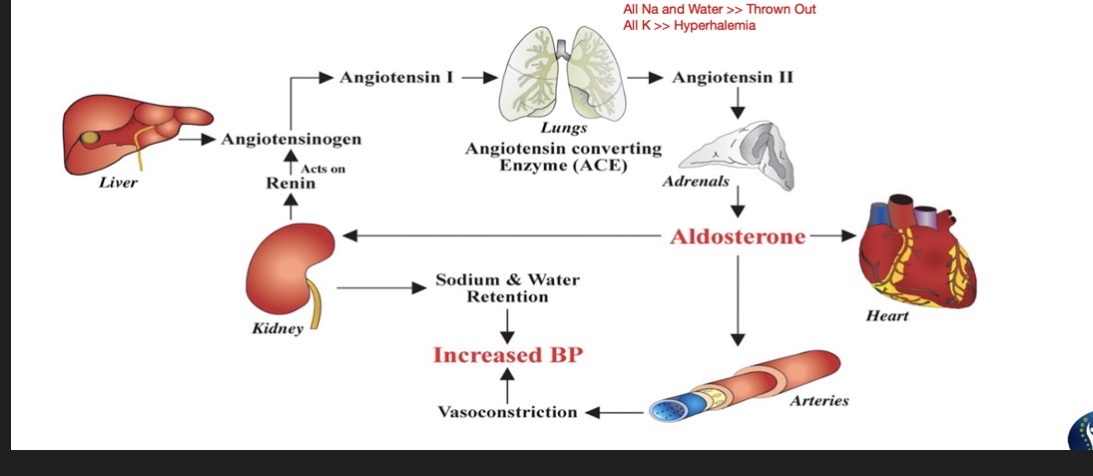
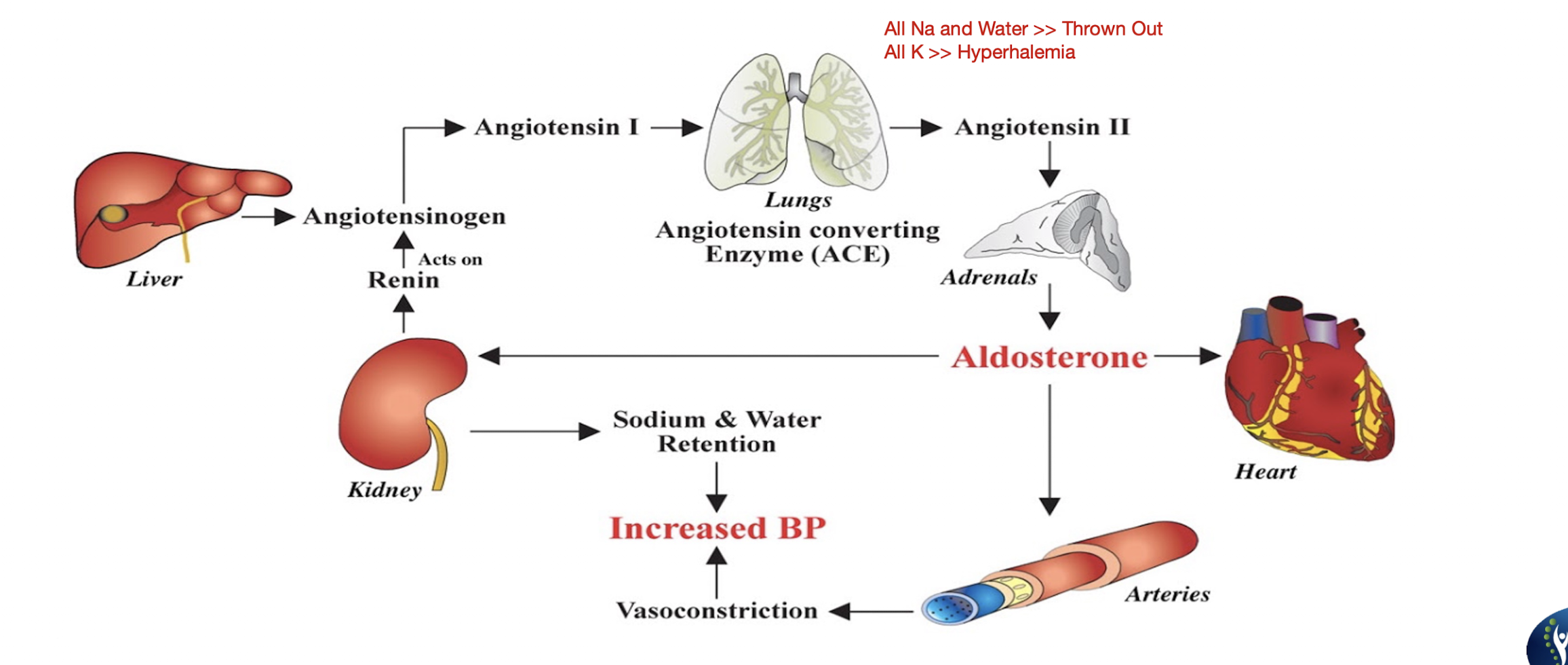
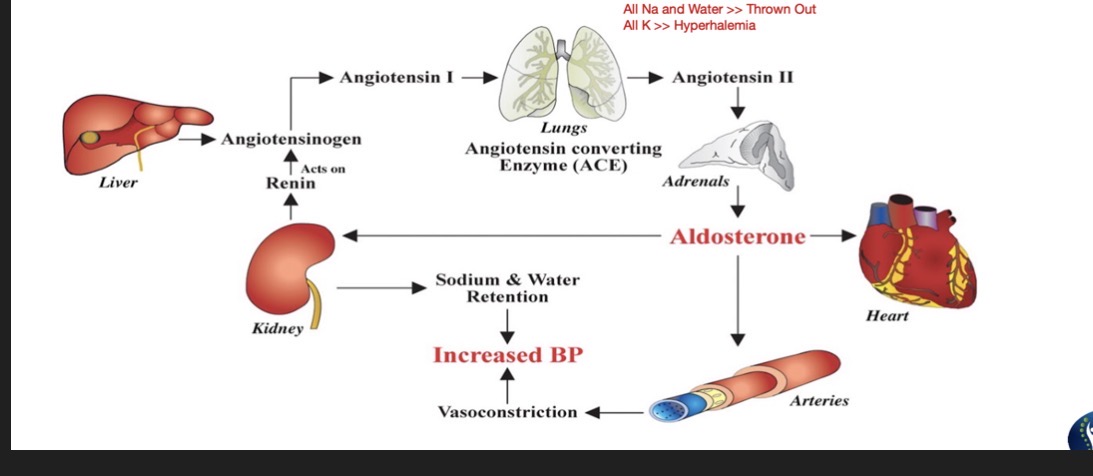
ACE Inhibitors:
Suffix:
Common Drug Names:
Mechanism:
Use: (4)
Administered:
Suffix:
“-Pril”
Common Drug Names:
Captopril, Enalapril, Lisinopril
Mechansim:
Blocks ACE » Reducing BP
Use:
CHF
HTN
Edema
Pulmonary Edema
Administered:
Orally
ACE Inhibitors:
Side Effects: (6)
ACE may react c Diuretics and cause…
ACE may react c Potassium Sparing Diuretics and cause…
Effects on Preload and Afterload:
Side Effects:
HYPERKALEMIA
DRY HACKING COUGH
Orthostatic Hypotension
Hyponatremia
Decreased Taste Perception
Angioedema
Hypotension
Hyperkalemia
Effects:
Preload: Dec
Afterload: Dec
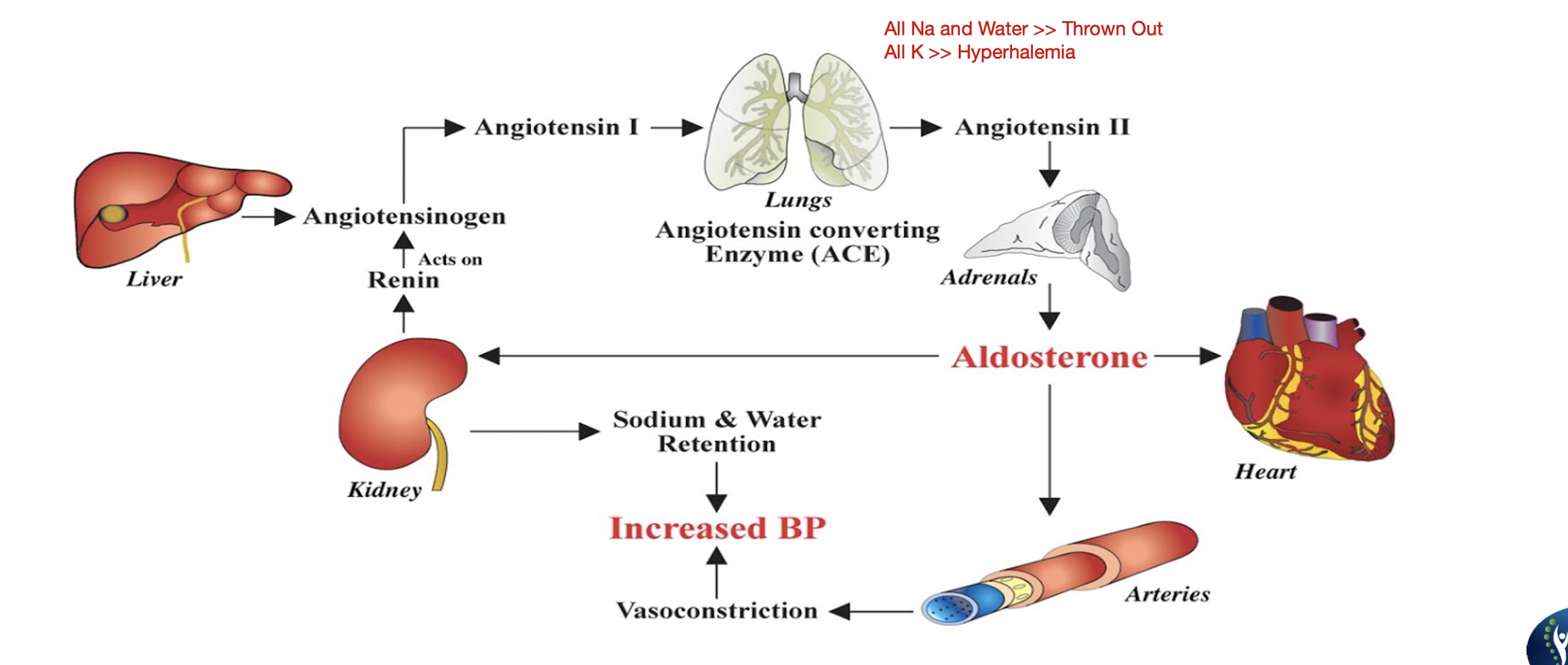
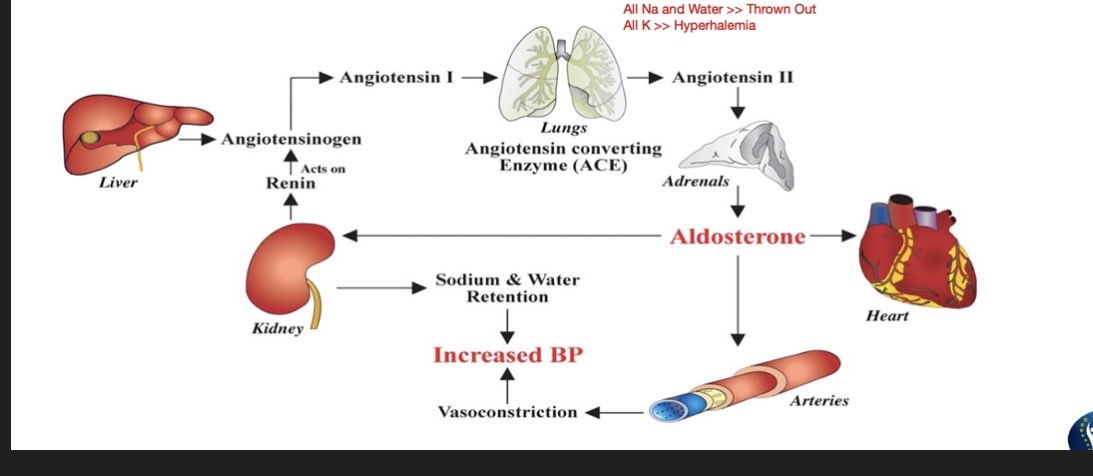
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARB) Blockers:
Suffix:
Common Drug Names:
Mechanism: (2)
Use: (3)
Administered:
Side Effects: (6)
Effects on Preload and Afterload:
Suffix:
“SARTANS”
Common Drug Names:
Losartan, Telmisartan, Candesartan
Mechanism:
Blocks Angiotensin 2 receptors » Decreasing effects of Angiotensin 2
Decreased Angiotensin 2 will decrease BP
Use:
HTN
CHF
Intolerant to ACE
Administered:
Orally
Side Effects:
HYPERKALEMIA
Hyponatremia
Orthostatic Hypotension
Dizziness
Lightheadedness
Fatigue
Effects:
Preload: Dec
Afterload: Dec
NOTE: ARB does NOT produce Dry Hacking Cough like ACE
Practice Q 2:
The physical therapist is educating a patient on the potential side effects from the medication Ramipril. Which of the following side effects will MOST LIKELY correlate with this drug?
A. Increased fluid retention
B. Causes hyperkalemia
C. Increases blood Pressure
D. Enhanced myocardial contractility
B. Causes hyperkalemia
D. ACE has no effect on heart

Practice Q 3:
The physical therapist is educating a patient on the potential side effects from the medication Candesartan. Which of the following side effects will MOST LIKELY correlate with this drug?
A. Hypokalemia
B. Dry hacking cough
C. Hypotension
D. Prevents the recurrence of atrial fibrillation
C. Hypotension

Cardiac Glycosides:
Common Drug Names:
Mechanism: (2)
ECG Changes: (2)
Use: (3)
Common Drug Names:
Digitalis, Digitoxin, Digoxin (Lanoxin)
Mechanism:
Decreases HR BUT Increases Strength of Contraction (Increase CO)
Fewer and better contractions/beats
ECG Changes:
Prolonged PR Interval
Shortened QT Interval
Use:
Systolic Dysfunction in patients c Congestive Heart Failure
Acute Signs of Decompensated HF
Short Term Drug
EF < 55%
Cardiac Glycosides:
Side Effects: (9)
DIGOXIN TOXICITY
Arrhythmias
Palpitations
Fatigue
GI Disturbances
Visual Disturbances
Hyperkalemia
Confusion
Delirium
Practice Q 4:
A patient with congestive heart failure is taking Digoxin since the last few weeks. Which of the following is an EXCEPTION to common side effects of digoxin toxicity?
A. Disorientation and delirium
B. Ringing in the ears
C. Fatigue and palpitations
D. Gastrointestinal disturbances
B. Ringing in the ears

Nitrates:
Common Drug Name:
Mechanism:
Use:
Administered:
Dose/Position:
If there is no relief, patient may be having…
Common Drug Name:
Nitroglycerin (NTG)
Mechanism:
Vasodilation of Arterial and Venous Vessels
Use:
Angina Pectoris
Levine Sign
Administered:
Sublingually
Dose/Position:
Dose: 3 doses every 5 min
Pos:
Must sit/lay when taking NTG
MI » Call EMS
Nitrates:
Side Effects: (7)
Only used ___ term
What 2 drugs are appropriate long term drugs to prevent angina?
Side Effects:
Dizziness
Lightheadedness
Orthostatic Hypotension
HA
Flushing
Reflex Tachycardia
Venous Pooling
Short term
Beta Blockers and Ca Channel Blockers
Nitrates:
Call EMS if: (3)
Angina:
Stable:
Unstable:
Variant (Pizmental):
Angina:
Stable: Exercise (YES NTG)
Unstable: Rest (NO NTG)
Variant (Pizmental): Vasospasm (YES NTG)

Practice Q 5:
A patient with angina pectoris has been advised to use sublingual nitroglycerin for stable angina. This drug will MOST LIKELY cause which of the following?
A. Lower preload and afterload
B. Increase myocardial oxygen demand
C. Increase preload and afterload
D. Hypertension and bradycardia
A. Lower preload and afterload
Blood Thinners » ANTICOAGULANTS
Common Drug Names:
Mechanism:
Use: (3)
Side Effects: (5)
Common Drug Names:
Warfarin (Coumadin), Heparin
Mechanism:
Inhibits Vitamin K formation » Prevents synthesis of clotting factor
Heparin: Inhibits formation of clotting factor
Use » Immediate resolution of blood clot
DVT
MI
CVA
Side Effects:
Bleeding
Easy bruising
Hemorrhage
Hemarthrosis (Bleeding in Joints)
Lightheadedness
Blood Thinners » ANTICOAGULANTS
Internatonal Normalized Ration:
Normal:
Taking Anticoagulants:
> 2.5:
> 3.0:
> 4.0:
> 6.0:
Avoid what foods when taking Warfarin: (2)
Avoid:
High in Vitamin K
High Sugar Food/Drink

Blood Thinners » ANTIPLATELET
Common Drug Name:
Mechanism:
Use:
Side Effects: (3)
Common Drug Name:
Aspirin, Clopidogrel
Mechanism:
Prevents Aggregation of Platelets
Use:
Prevent CVA and MI
Side Effects
Peptic Ulcers
Gastritis
Risk of Internal Bleeding
NOTE: Antiplatelets are not as strong as Warfarin and Heparin
Can be taken to prevent blood clot formation
Practice Q 6:
Which of the following is an INAPPROPRIATE statement regarding the drug Coumadin?
A. It should not be given to a patient with an active GI ulcer
B. Adverse effects of Coumadin can be hematuria and bleeding gums
C. It inhibits the formation of thrombin and fibrin in the clotting process
D. It should be given to a patient undergoing a surgery for liver transplant
D. It should be given to a patient undergoing a surgery for liver transplant


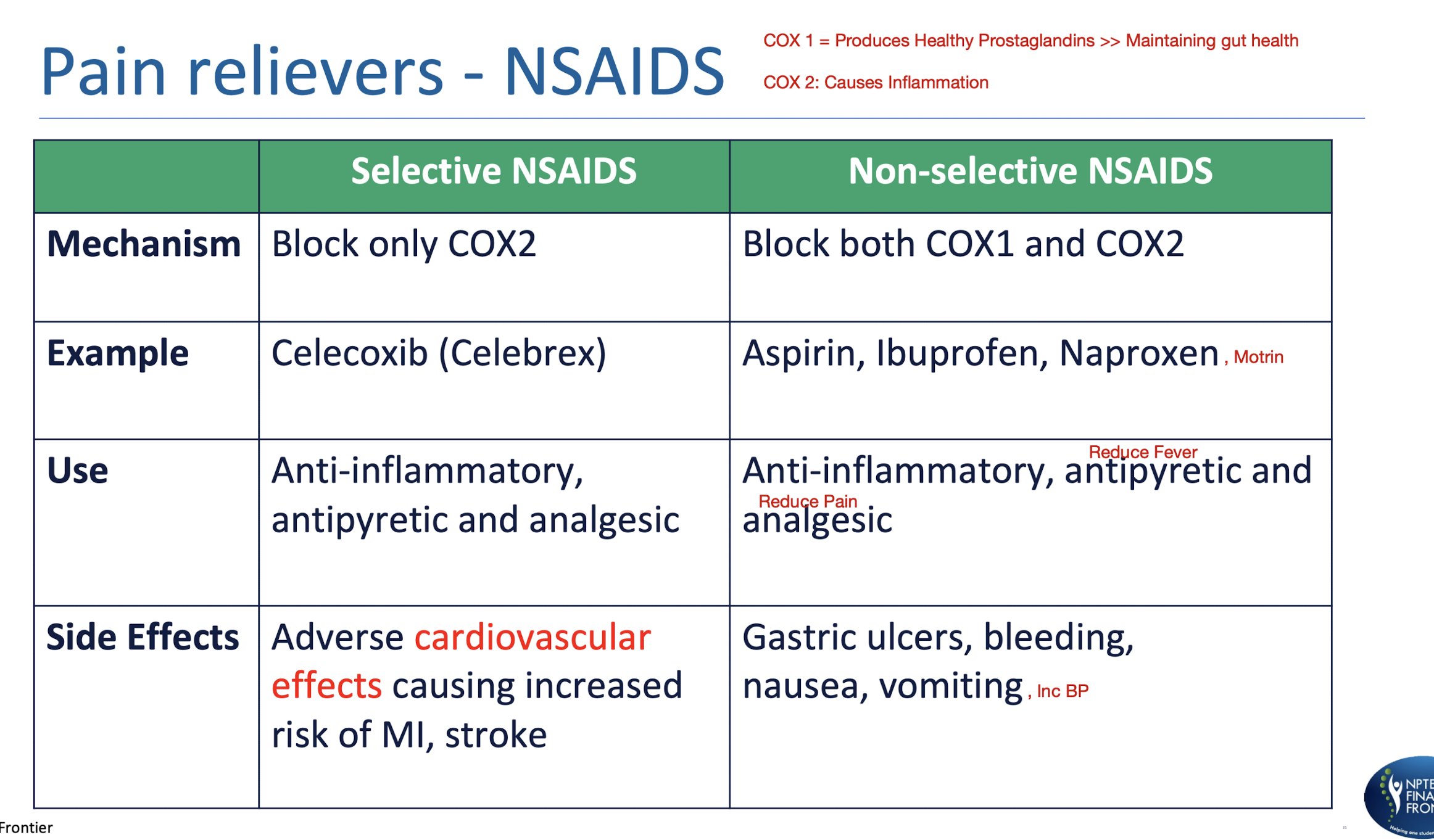
Pain Receivers » NSAIDS
COX 1 =
COX 2 =
Selective NSAIDS vs NON Selective NSAIDS:
COX 1 = Produces Healthy Prostaglandins >> Maintaining gut health
COX 2 = Causes Inflammation
Pain Receivers » ACETAMINOPHEN
Common Drug Name:
Mechanism:
Use: (3)
NOT…
Administered:
Side Effects: (2)
Common Drug Name:
Tylenol
Mechanism:
Block sensation of pain
Use:
Antipyretic
Analgesic
HA
NOT ANTI-INFLAMMATORY
Administered:
Orally
Side Effects:
Overuse can cause liver damage leading to Jaundice and Clay Colored Stools
No more than 6 Tablets (500mg)/day
Pain Relievers » OPIODS ANALGESICS
Common Drug Names:
Mechanism:
Works c ___
It interacts c receptors that causes… (2)
Use: (3)
Common Drug Names:
Morphine, Oxycodone, Hydrocodone, Fentanyl, Methadone
Mechanism:
CNS
Decreased Neuronal Excitability and Altered Synaptic Transmission in pain specific pathways
Use:
Severe Pain
Post Op Pain
Antitussive (Cough)
Pain Relievers » OPIODS ANALGESICS
Side Effects: (9)
Take Medication __ min prior to PT
Antidote for overdose is __
Side Effects:
ADDICTION
CONSTIPATION
Resp and CNS Depression
Bradycardia
Slowed Breathing
Slowness
Dizziness
Drowsiness
Tolerance
30 min
Naloxone (Narcan)
Benzodiazepines:
Suffix:
Common Drug Names:
Mechanism:
Use: (5)
Side Effects: (8)
Suffix:
“-Pams and “-Lams”
Common Drug Names:
Diazepam (Valium), Clonazepam (Klonopin), Alprazolam (Xanax)
Mechanism:
Potentiates inhibitory effects of GABA in CNS
Use:
Muscle Spasms
Anxiety
Alcohol Withdrawal
Acute Epileptic Attacks
Insomnia
Side Effects:
Tolerance
Dizziness
Hallucinations
Drowsiness
Sedation
Fatigue
Hypotonia
Increased Fall Risk
Skeletal Muscle Relaxant » CYCLOBENZAPRINE (FLEXERIL)
Mechanism: (2)
Administered:
Use: (3)
Side Effects: (10)
Mechanism:
Increases serotonin activity at the brainstem level
Increasing the inhibitory influence of serotonin on Alpha Motor Neuron Activity
Administered:
Orally
Use:
Reduce Muscle Spasms
Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Fibromyalgia
Side Effects:
N/V
DRY MOUTH
Tolerance
Dizziness
Hallucinations
Drowsiness
Sedation
Fatigue
Hypotonia
Increased Fall Risk
Skeletal Muscle Relaxant » BACLOFEN
Mechanism:
Use:
Administered:
Side Effects: (8)
Mechanism:
Works on CNS
Use:
Reduce muscle spasticity seen c SC lesions » MS, SCI vs Cerebral lesions
Administered:
Orally or Intrathecally
Side Effects:
Hypotonia
Hallucination
Confusion
Nausea
Dizziness
Drowsiness
Inc Fall Risk
Shallow Breathing
Skeletal Muscle Relaxant » BOTULINUM TOXIN (BOTOX)
Mechanism:
Use:
Mechanism:
Works on CNS
Blocks Release of Acetylcholine
Use:
Muscle Spasticity
Seen c CP
Practice Q 7:
An intrathecal Baclofen pump has been put for a child with spastic cerebral palsy. The physical therapist observes that the child is very drowsy, tone appears floppy and is not breathing well. What is the MOST LIKELY cause of the above symptoms?
A. Overdose of Baclofen
B. Child is experiencing fatigue
C. Dosage of Baclofen is less
D. Child is not interested in therapy
A. Overdose of Baclofen

Bronchodilator Drugs:
Beta 2 Agonist:
Short Acting:
Long Acting:
Antimuscarinic (Cholinergic):
Short Acting:
Long Acting:
Corticosteroids:
(2)
Beta 2 Agonist:
Short Acting: Salbutamol, Albuterol (Ventolin)
Crisis Drug
Long Acting: Salmeterol, Formoterol
Maintenance Drug
Antimuscarinic (Cholinergic):
Short Acting: Ipratropium
Long Acting: Tiotropium
Corticosteroids:
Budensonide
Prednisolone
Bronchodilator Drugs:
Administered: (2)
Uses:
Side Effects: (4)
Administered:
Inhalation
Oral
Uses:
Bronchodilation in Bronchial Asthma and COPD
Side Effects:
Tremors
Palpitations (Inc HR)
GI Disturbances
Dry Mouth
Specifically Anticholinergic Drugs
NOTE: Works c SNS so symptoms will be similar to SNS function
Antibacterial Drugs:
Common Drug Names:
Use:
Administered:
Adverse Effects: (5)
Common Drug Names:
Penicilin. Cepalosporin, Vanomycin, Gentamicin
Use:
Treat Bacterial Infection
Administered:
Orally
Adverse Effects:
OTOTOXICITY (BPPV)
Hypersensitivity (Skin Rashes)
GI Disturbances (N/V)
Nephrotoxicity (Esp Gentamiacin)
CNS Confusion
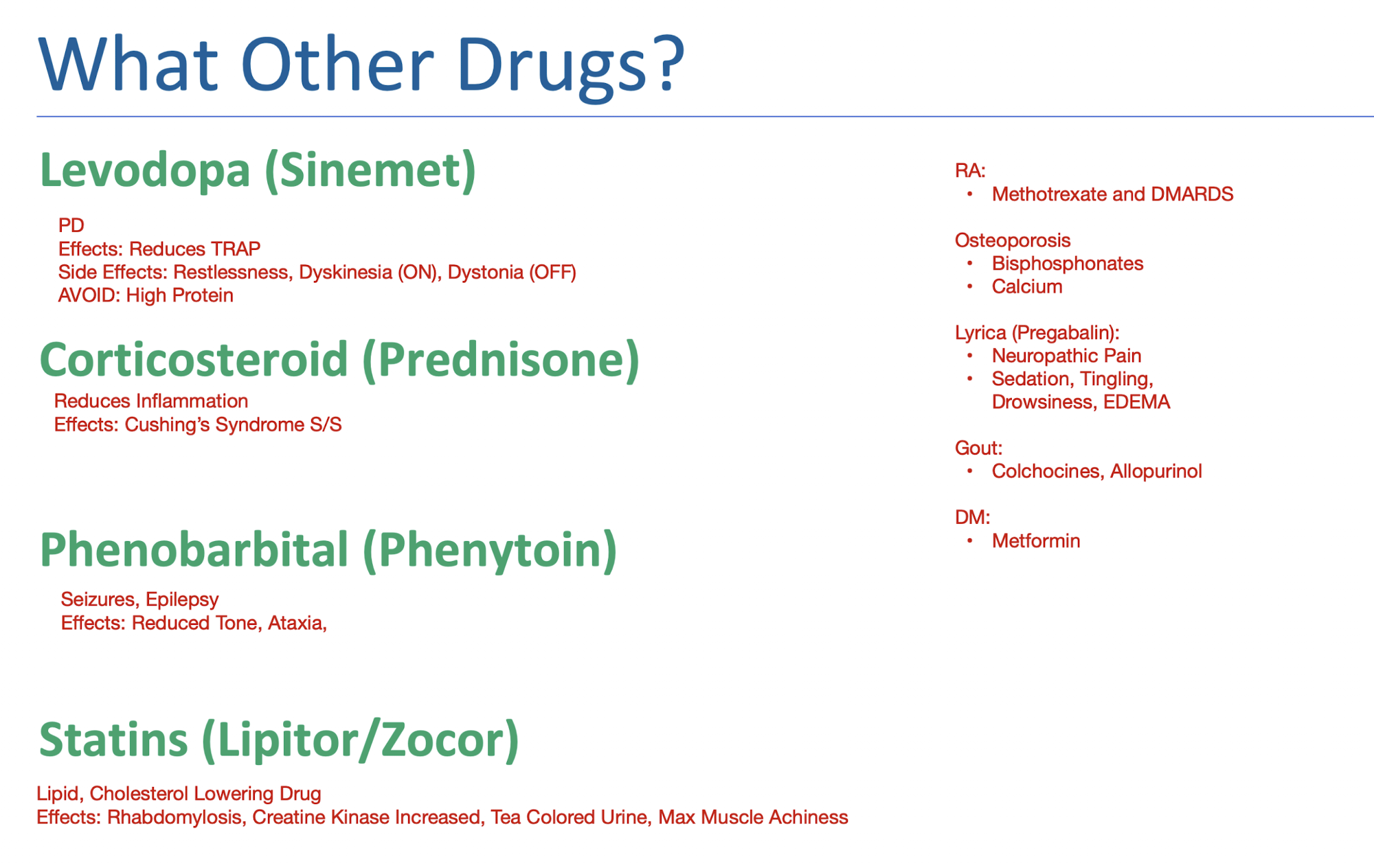
Other Drugs:
Practice Q 8:
Which of the following is an EXCEPTION to the medications commonly used to lower blood pressure in patients with hypertension?
A. Thiazide diuretics
B. ACE inhibitors
C. Calcium channel blockers
D. Digitalis
D. Digitalis

Practice Q 9:
A patient has just started using Ventolin for management of their condition. What is the patient MOST LIKELY to experience as a side effect of the drug?
A. Tachycardia
B. Hypotension
C. Lightheadedness
D. Increased risk of falls
A. Tachycardia

Practice Q 10:
A patient reports pain in the right groin and upper thigh region, which was gradual in onset. They have a medical history of ulcerative colitis for which they have been taking Prednisolone. Which of the following is MOST LIKELY diagnosis for this patient?
A. Meralgia paresthetica
B. Trochanteric bursitis
C. Osteomyelitis of hip
D. Osteoporosis of hip
D. Osteoporosis of hip
A. Lateral Cutaneous Nerve Compression
