M2 S4: sexaul intercourse btw males and females
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
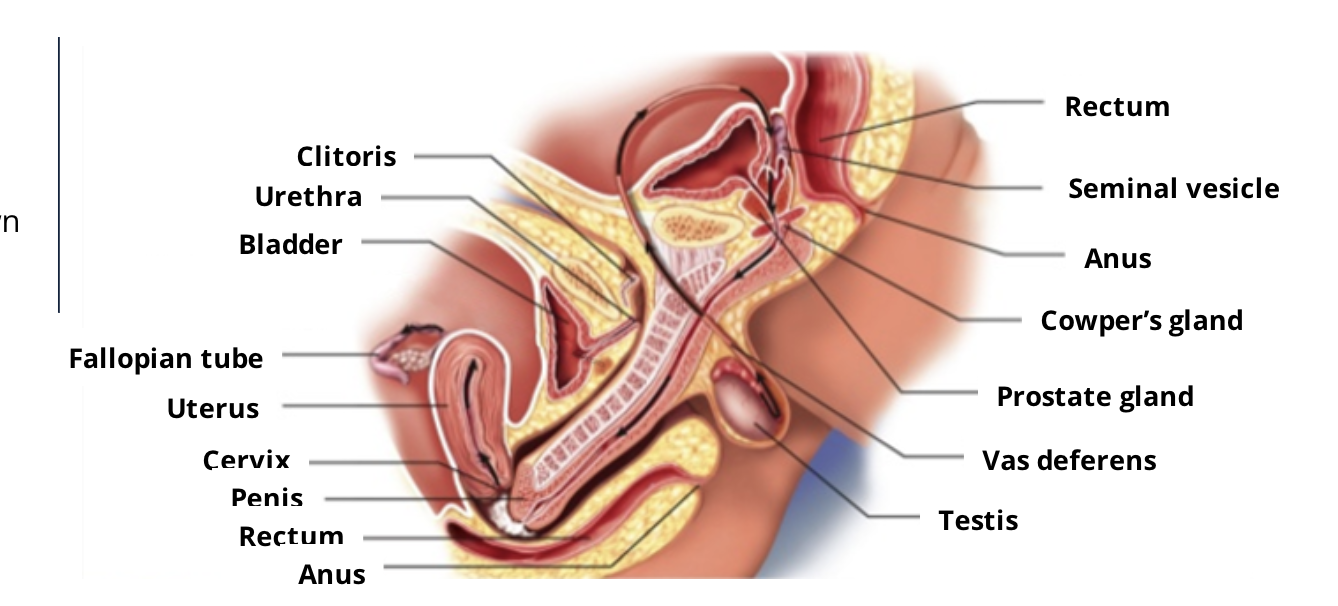
Sexual reproduction in humans requires the delivery of sperm into the female vagina through the sex act, which is also known as
sexual intercourse, coitus, or copulation.
what are the two parts of the male sex act
erection and ejaculation
what casues an erection
penis fills with blood allowing the penis to become ridgi and permit entry into the vagina
what is the erectile tissue of the penis
The erectile tissue of the penis is made up of three columns of sponge-like vascular spaces. These columns are known collectively as the corpora cavernosa.
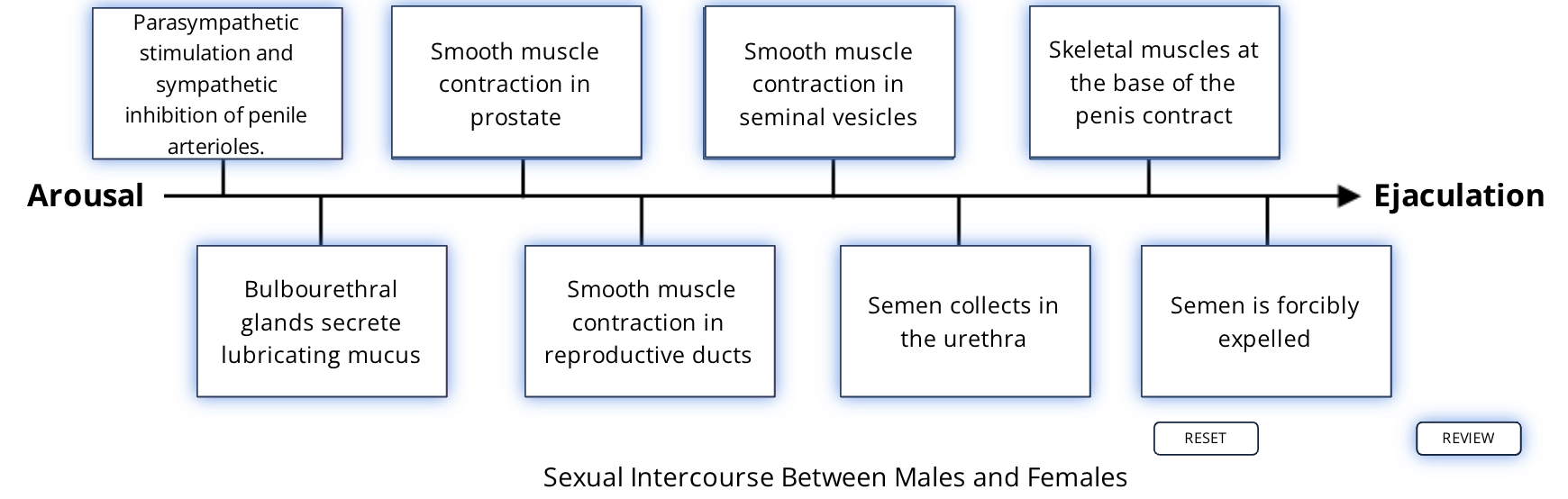
during arosual the arterioles that supply corpora cavernosa dialate or constrict
aterioles dialte = enlargement and rigidity of penis
Glans penis:
The sensitive bulbous structure at the end of the human penis. Also known as the head of the penis.
T or F: Thoughts about sex or stimulation of mechanoreceptors in the glans penis initiate the erection reflex. This is a spinal reflex and the erection generating centre lies in the lower spinal
T
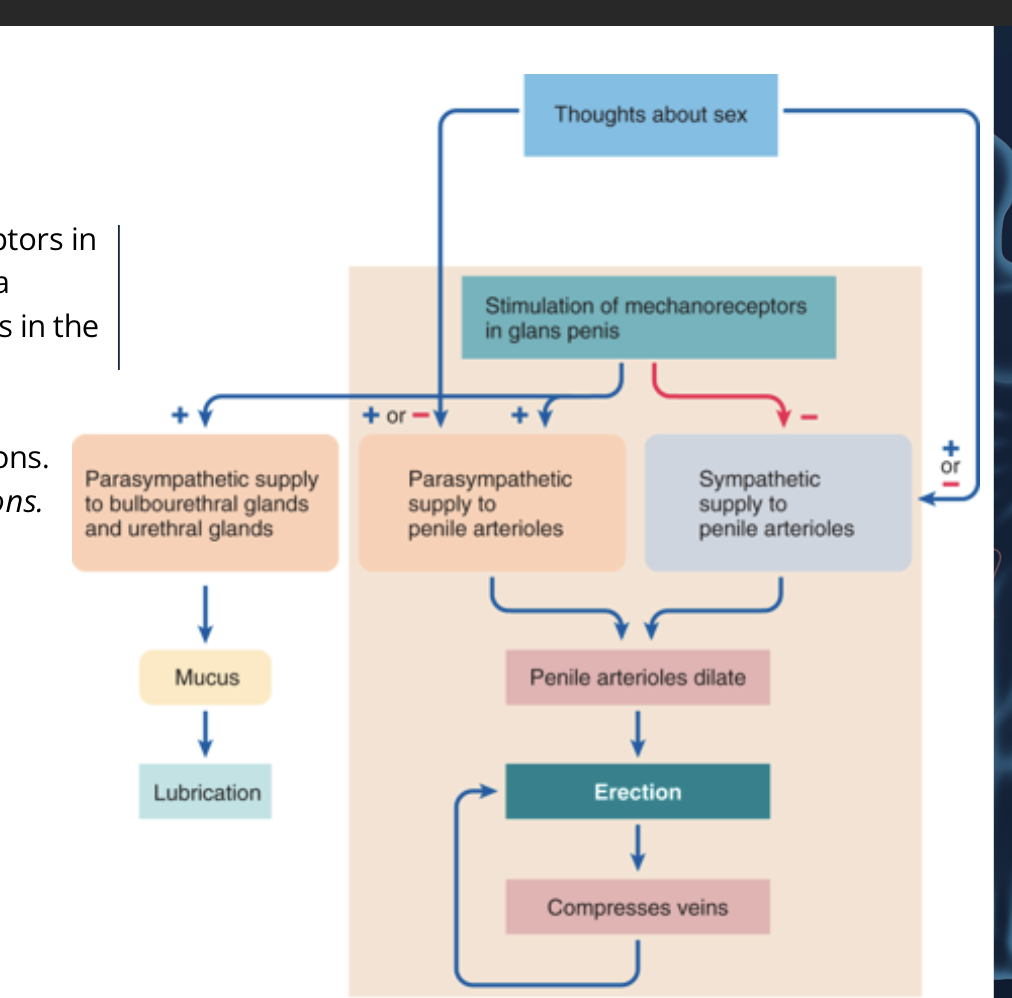
what are the three main actions of the activation of the erection reflex
Inhibiting the sympathetic supply to the penile arterioles. This removes the tonic vasoconstrictor actions of the sympathetic system.
Activates the parasympathetic supply to the penile arterioles to cause vasodilation via a NO-mediated mechanism.
Activates the parasympathetic supply to the bulbourethral glands to secrete mucus for lubrication.
what is erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (impotence) is referred to as the inability to obtain and maintain an erection rigid enough for sex. If erectile dysfunction is an ongoing issue, it could be a sign of an underlying health condition that requires treatment.
T or F : ejactilation is a spinal reflex
T: Ejaculation is also the result of a spinal reflex, and is mediated by the same tactile and psychological stimuli that cause an
2 steps of ejactulation
emission
Increased sympathetic activity causes smooth muscle contractions in the prostate, reproductive ducts, and seminal vesicles. The timing is coordinated such that prostatic fluid, then sperm, then seminal vesicle fluid is delivered into the urethra. Collectively, this mixture is called semen. The sphincter at the neck of the bladder is also contracted to prevent urine release.
expulsion
The filling of the urethra with semen triggers the activation of skeletal muscles at the base of the penis. This increases the pressure and forcibly expels the semen.
This changes the pressure within the urethra and forcibly expels the semen
what happens during emmison
emission
Increased sympathetic activity causes smooth muscle contractions in the prostate, reproductive ducts, and seminal vesicles. The timing is coordinated such that prostatic fluid, then sperm, then seminal vesicle fluid is delivered into the urethra. Collectively, this mixture is called semen. The sphincter at the neck of the bladder is also contracted to prevent urine release.
what happens during expulsion
expulsion
The filling of the urethra with semen triggers the activation of skeletal muscles at the base of the penis. This increases the pressure and forcibly expels the semen.
This changes the pressure within the urethra and forcibly expels the semen
what are the four stages of the male sexual response
The excitement phase: This includes a heightened sexual awareness and erection.
The plateau phase: This has more generalized responses such as increased heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate.
The orgasmic phase: This includes ejaculation as well as other physical and emotional responses.
The resolution phase: The return of the body to its pre-arousal stage.
Once ejaculation has occurred, a temporary refractory period occurs in which further sexual stimulation cannot trigger another erection.
what are the 4 stages of the females sexual response
excitment
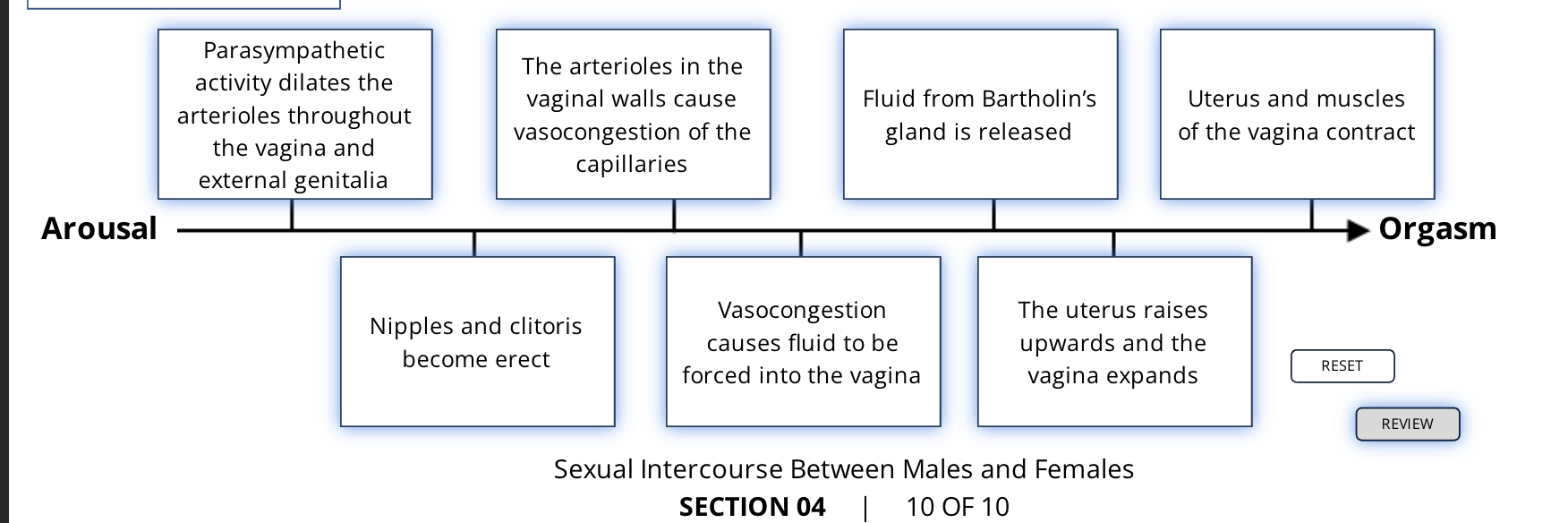
Excitatory stimuli can be both psychological or physical stimuli. Stimulation of the clitoris and the surrounding area activates a spinal reflex that activates the parasympathetic system to dilate the arterioles throughout the vagina and external genitalia. The nipples also become erect and there is an increase blood supply to the skin. The clitoris, like the penis, contains erectile tissue and becomes erect. Dilation of arterioles in the vaginal walls causes vasocongestion of the capillaries, which forces fluid out of the vessels and into the vagina. This fluid, along with secretions from Bartholin's gland, serves as the primary lubricant for intercourse.
plateau
During the plateau phase, the uterus raises upward, lifting the cervix and enlarging the upper portion of the vagina. This tenting effect creates space for ejaculated semen.
Breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure of the female also continue to increase.
orgasm
If erotic stimulation continues, the sexual response culminates in orgasm, as sympathetic impulses lead to rhythmic contractions of the pelvic musculature.
There is no female equivalent to ejaculation.
resolution
After orgasm, heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing return to normal. This phase is marked by a general sense of well-being, enhanced intimacy, and, often, fatigue.
Some women are capable of a rapid return to the plateau phase with further sexual stimulation.