FINAL
1/434
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
435 Terms
What does HIPAA stand for?
Health Information Portability and Accountability Act
What must be used when handling someone with a wound?
Probe covers
Sterile gel
Airborne Precautions
Used when patients have or are suspected to have diseases that are transmitted via the air
Examples
Measles
Tuberculosis (TB)
Varicella
Droplet Precautions
Used when patients have diseases that are borne on droplets
Heavier; don’t travel more than 3 ft.
Examples
Diphtheria
Influenza
Mumps
Pertussis
Adenovirus
Meningitis
Contact Precautions
Used when patients have diseases that are spread by direct contact with the germ
Examples
MRSA
VRE
E. coli
Draining wounds
Impetigo
Pinkeye
Blood-Borne Transmission
Falls under standard precautions because we treat all body fluids and blood as if they were infected
Examples
Hepatitis B & C
HIV
Subjective Health Assessment
Information patient gives about how they FEEL
Qualitative information
Objective Health Assessment
Information obtained through observation
Quantitative information
Examples
Blood pressure
Weight
Bradycardia
Below 60 bpm
Tachycardia
Above 120 bpm
Normal Respirations
16-20 per min
Systolic Pressure
Top number (100-130)
Left ventricle max contraction
Diastolic Pressure
Bottom number (60-80)
Left ventricle relaxation
Acidosis
Blood pH of 6.8 or less
Alkalosis
Blood pH of 7.8 or more
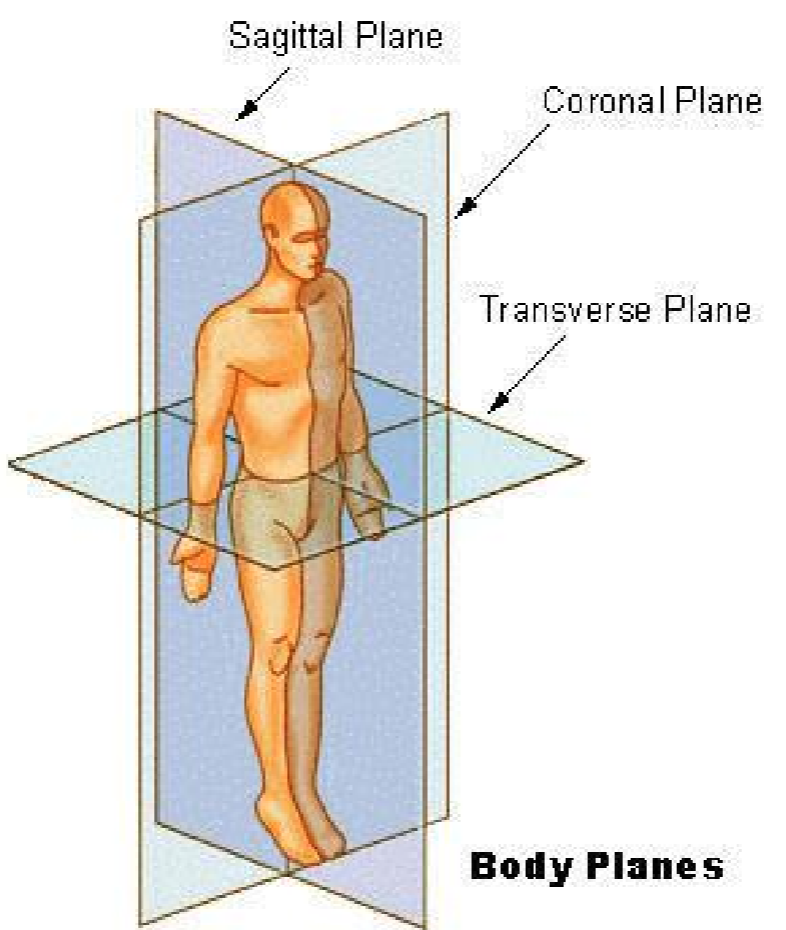
Sagittal
AKA Longitudinal
Divides body into left and right
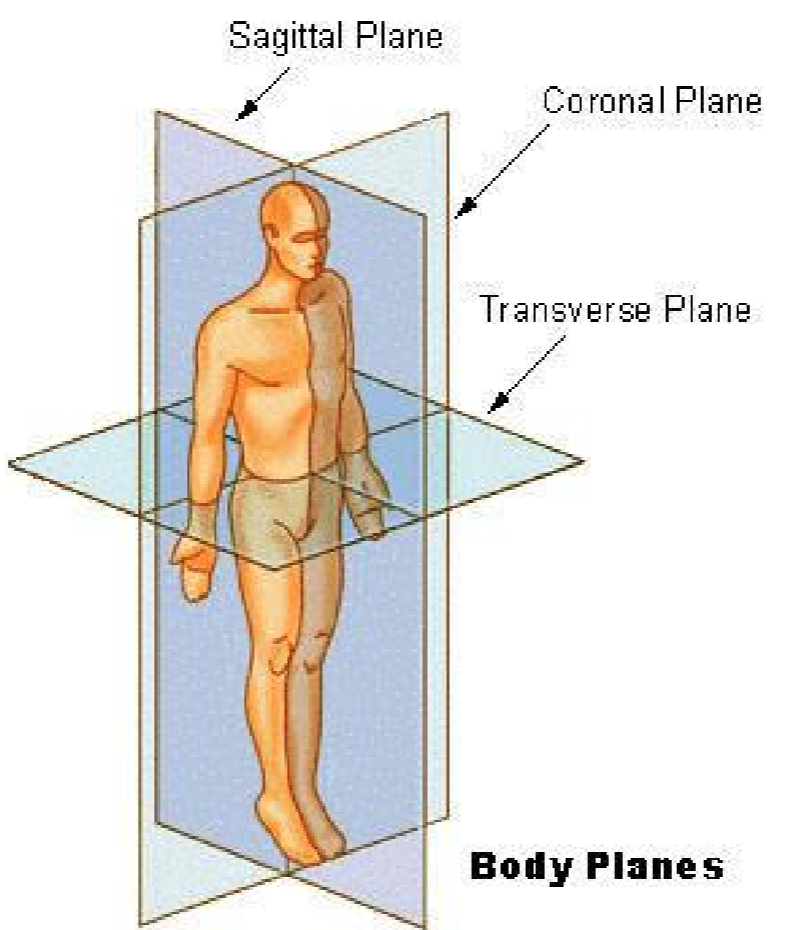
Transverse
Divides body into superior and inferior
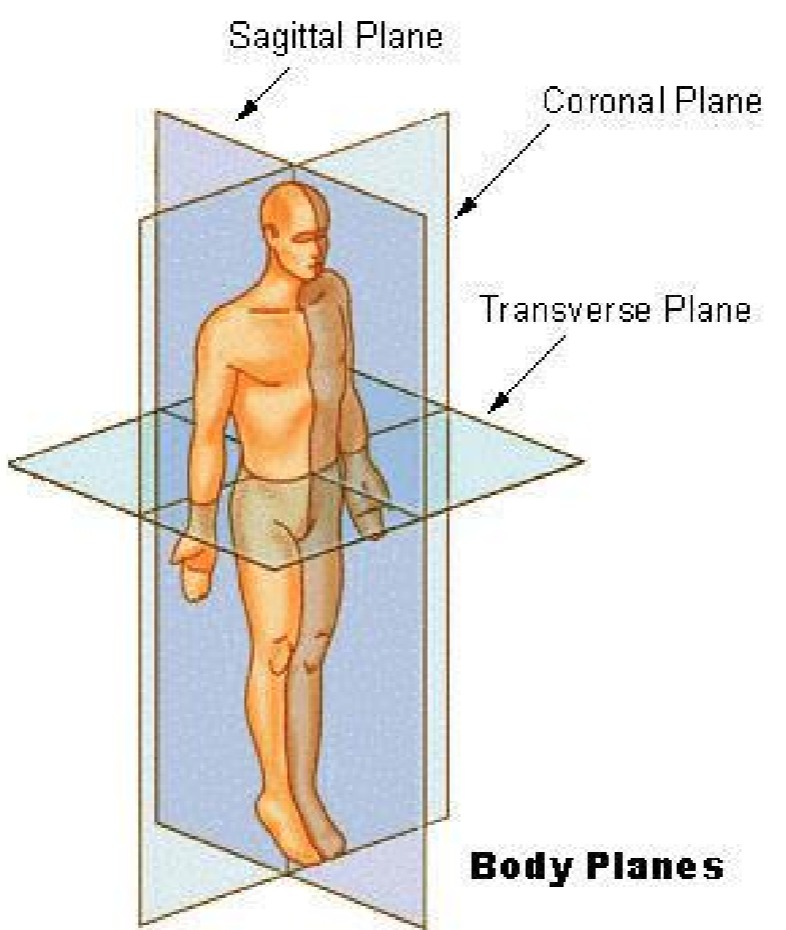
Coronal
Divides the body into anterior and posterior
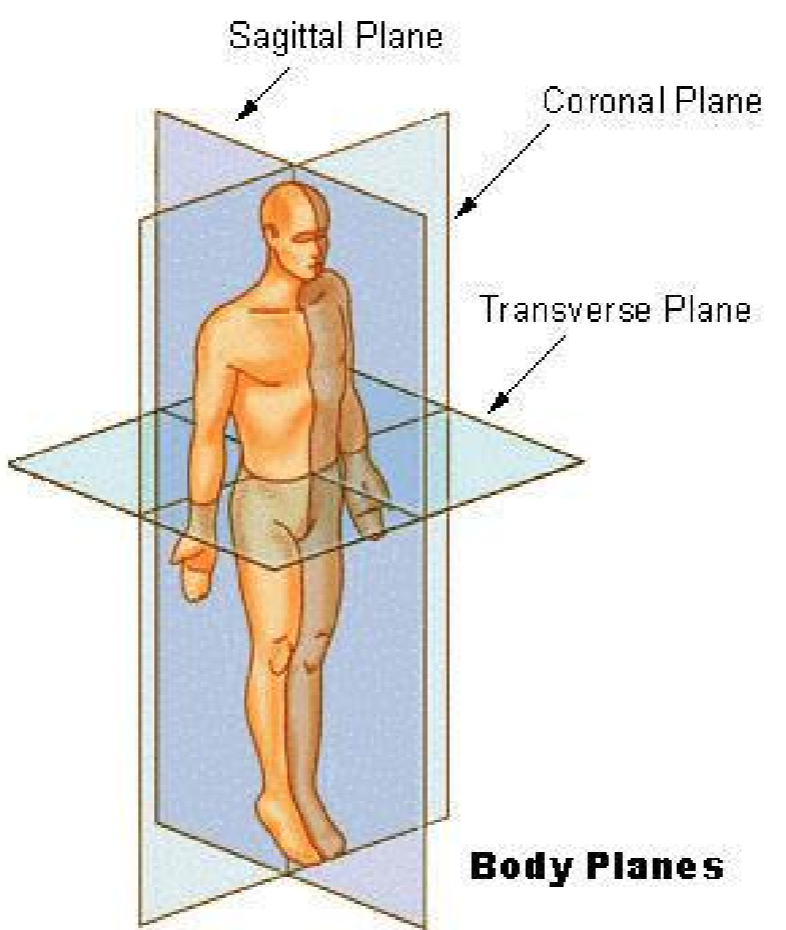
Oblique
Any scan plane between longitudinal and transverse planes
Supine
Laying flat on back
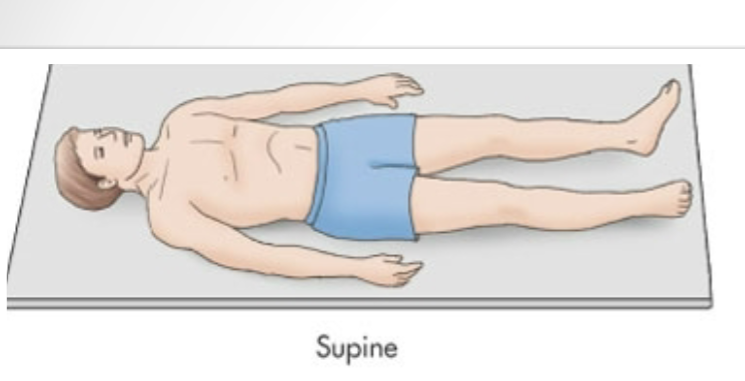
Prone
Laying flat on stomach
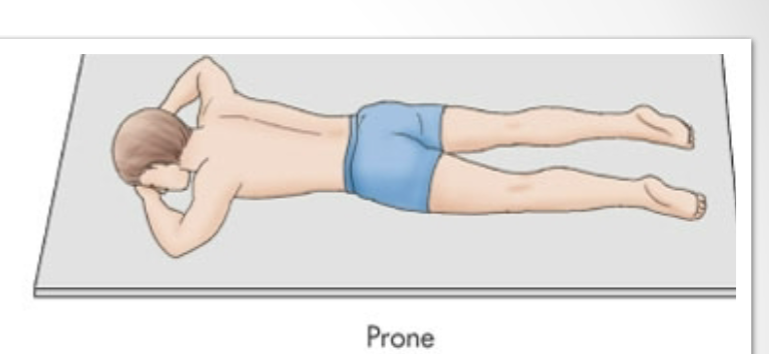
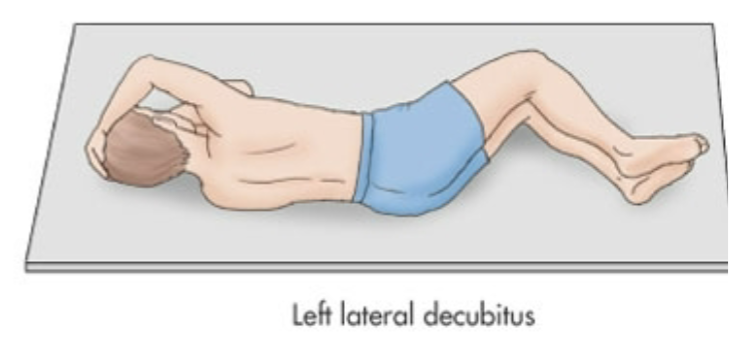
Left Lateral Decubitus
Laying directly on left side
90 degrees
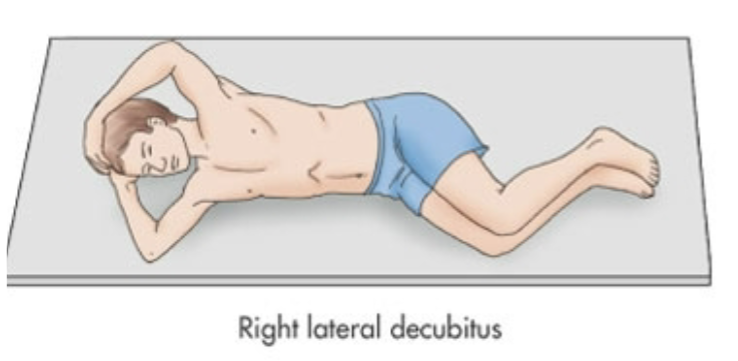
Right Lateral Decubitus
Laying directly on right side
90 degrees
Left Posterior Oblique
Laying on left side but more tilted on their back
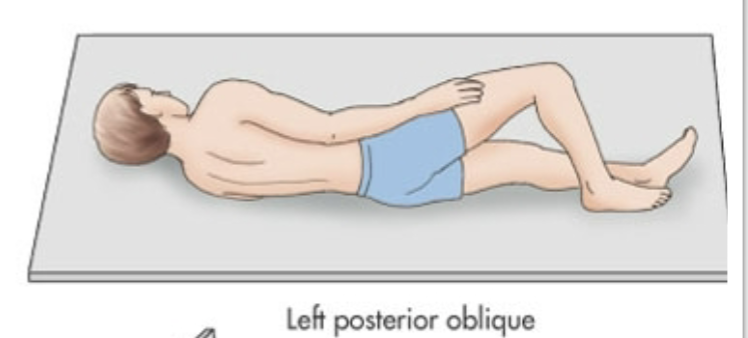
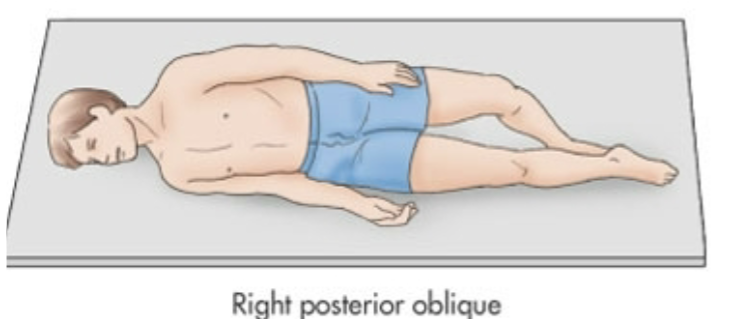
Right Posterior Oblique
Laying on right side but more tilted on their back
What does right or left in the name of a patient position indicate?
Indicated what side they are LAYING on, not what side you are scanning
Sitting Semi-Erect
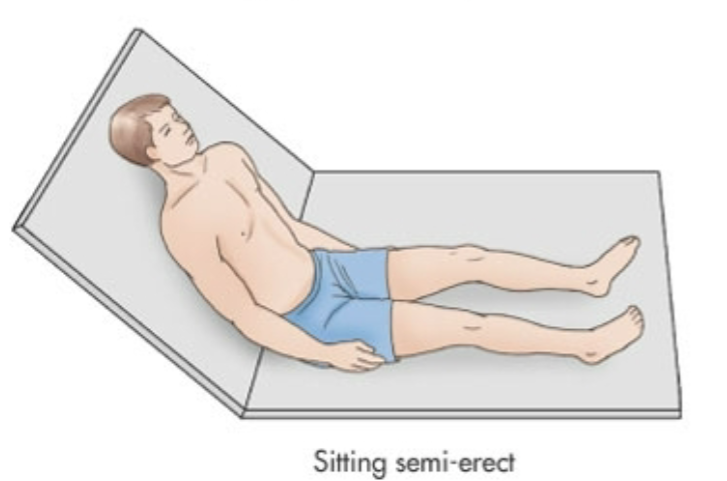
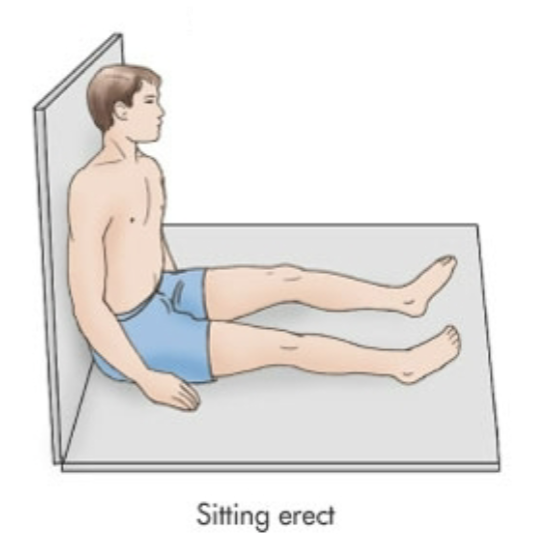
Sitting Erect
How do you label a coronal image?
Superior/inferior
Lateral/medial
How do you label a sagittal image?
Superior/inferior
Anterior/posterior
How do you label a transverse image?
Anterior/posterior
Laterals (right/left)
What is the most common site of pain for a sonographer?
Shoulder of scanning arm
AKA “sonographer’s shoulder”
What are the most common causes of WRMSDs?
Holding arm away from body for long periods of time
Maintaining constant pressure
Standing with back twisted
Holding neck in an awkward position
Rotator Cuff Syndrome
Multiple micro tears that result in weakness/tears of rotator cuff
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Repetitive motion injury involving thickening of fascia at neuromuscular outlet of wrist resulting in hand and wrist pain and numbness
de Quervain Syndrome
Tenosynovitis of wrist/thumb caused by repetitive motion
How do we prevent WRMSDs?
Transducer grip
Wrist position
Neck position
Shoulder abduction
Spine alignment
Don’t hang yourself on a cross
Crucifixion
Exercise
What degree should sonographers shoulders be abducted to?
30 degrees or less
Anechoic
Black structures
No internal echoes
Echogenic
Reflects sound with brighter intensity (white)
Posterior Enhancement
Brighter area behind a fluid structure due to low attenuation
Fluid Level
Difference in echogenicity of two fluids in same structure
Loculated Mass
Compartments within a mass or fluid collection
Septations
Shadowing
Failure of echoes to pass through a dense structure
Heterogenous
Not uniform in texture/composition
Homogenous
Smooth uniform texture/composition
Hypoechoic
Darker than adjoining tissues/reference tissue
Infiltrating
No discrete borders
Diffuse disease process
Irregular Borders
Borders absent or not well-defined
Isoechoic
Same echogenicity as adjoining tissues
Sound
A mechanical longitudinal wave
Phased Array
Small footprint probe
Used for abdominal organs from between ribs
Curved Array
Larger footprint probe
Larger field of view than linear or phased arrays
Better resolution than phased array
Used for abdominal imaging and OB/GYN
Linear Array
Rectangular footprint probe
Used for superficial and peripheral vascular structures
What is ALARA?
Radiation safety principle for minimizing radiation doses
A regulatory requirement for all radiation safety programs
Universal Precautions
Treat blood and any bodily fluid as if they were infected with HIV, Hep B/C
Standard Precautions
Treat everyone the same regardless of symptoms
What three characteristics does a simple cyst have?
Anechoic
Smooth borders
Posterior enhancement
Complex
Both fluid and solid areas within same mass
Solid
Mass with internal echoes
No posterior enhancement
Lobulated
Bumpy border
Bunch of grapes
Sustained awkward positioning can cause what?
Muscle spams
Misalignment of joints
Most sonograms are performed under which condition?
Indirect supervision by physician
What four things is it important for sonographers to know when looking at artifacts?
Recognize artifacts
Causes of artifacts
How to compensate artifacts
How to use artifacts to aid in making a diagnosis
What are the artifacts that correspond with improper equipment settings/technique caused by?
The sonographer
What are the artifacts that correspond with the interaction of sound with the tissues caused by?
The sound beam traveling through and interacting with other tissue in its path
What key things does the ultrasound machine always assume?
Sound travels in a straight line down beam axis
Echoes originate from structures along beam axis
Amplitudes of returning echoes directly correspond to \n echogenic nature of structure producing echo
Distance to reflectors corresponds to round-trip travel time
What distance does the ultrasound machine automatically assume tissues are at?
13 us/cm
Propagation Artifact
The result of the way sound passes through tissue
What two things does speckle come from?
Constructive interference
Destructive interference
What does speckle artifact result in?
The light and dark spots seen in tissue
When does reverberation occur?
Echoes “bounce” between transducer and strong reflector
Sound bouncing between two strong reflectors within tissues
What is mirror-image caused by?
Caused by sound interaction with large, curved reflector like the diaphragm
What does a mirror-image artifact result in?
An additional depiction of object deep to the strong reflector
What does a comet tail artifact result in?
Short-path reverberations
Series of small bands distal to reflector
Where does a comet tail artifact occur?
Behind a very strong interface
Air bubble
Metallic object (suture or bullet)
When does resonance (ring-down) occur?
Sound striking a gas bubble and causing it to vibrate
What is the chief characteristic that distinguishes ring-down from comet tail?
Comet tail = banding
Ring down = NO banding
What is refraction?
Bending of sound beam
What does refraction result in?
Reflectors to be displaced laterally on image
Leads to distortion of
Size
Shape
When does ghost-image occur?
When scanning through rectus abdominus muscles due to fat and rectus sheath
What does ghost-image result in?
Duplication of structures posterior to rectus muscles
What structures are typically seen as ghost-images?
Vessels
Aorta
IVC
Gestational sacs
When does a dirty shadow occur?
When sound beams hits air or bowel
Creates snowy gray
When does sharp shadow occur?
When sound strikes a calcified object
Bone
Mineral salts
Metal
Creates black area posterior to object
When does posterior enhancement occur?
When sound passes through poorly attenuating structure
When can posterior enhancement be useful?
Proving that structures are cystic
Slice Thickness Artifact
AKA
Section Thickness
Partial Volume Artifact
Loss of lateral or axial resolution
What does a slice thickness artifact result in?
Blurring of the image
Two structures blended to display as one
What does an elevation resolution/slice thickness artifact result in?
Appearance of echoes within an otherwise anechoic structure, like a blood vessel or cyst
When does an absence of focusing artifact occur?
When narrow part of beam is not at area of interest
What transducers are side lobes present in?
ALL
When do side lobe artifacts occur?
Off-axis lobes of energy are created outside the main ultrasound beam, resulting in artificial display of echoes along the main beam path
What does a side lobe artifact result in?
Linear echoes that can mimic dissection in
Aorta
Amniotic sheets in OB scans
Streaky, linear echogenic artifact
When does a grating lobe artifact occur?
Created by the way that elements are spaced in an array transducer
What is the difference between a side lobe and grating lobe artifact?
Side lobes
Arise from individual elements
Less bright
Grating lobes
Arise from multiple elements
Bright
When does propagation speed error occur?
When sound travels through tissue at a speed different from 1540 m/s assumed by machine
What happens if sound travels faster than assumed by the machine?
Object will be displayed more superficially than true location
What happens if sound travels slower than assumed by the machine?
Object will be displayed deeper than true location
Why does the range ambiguity artifact occur?
Ultrasound machine assumes that echoes received are generated by most recent transmitted pulse
Echoes are not received by transducer until after next pulse is transmitted