Bio 101 Exam 1
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
143 Terms
Two adjacent carbon atoms share a pair of electrons. This bond
is a nonpolar covalent bond
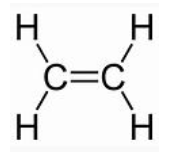
Ethylene is a hydrocarbon, it is a colorless flammable gas with a faint odor when pure. Based on the information in your videos, which of the following with accurate of ethylene?
It is water soluble, contains all nonpolar covalent bonds, it is nonpolar
You add an methyl group (-CH3) to a hydrocarbon. What affect will this likely have on how this molecule interacts with water?
None, it will still be water soluble
List the order of macromolecules from largest to smallest
Polymer, dimer, monomer
Dehydration Synthesis
Connects monomers to make larger molecules
What is the correct sequence of life’s hierarchy, most complex to least complex
Ecosystem, community, population, organism
What is the lowest level of biological organization that shows evolutionary adaptations, order, energy processing, regulation (homeostasis), reproduction, growth/development, and response to the environment?
Cells
How many eukaryotic kingdoms are there?
Four
What are the different types of eukaryotic kingdoms?
Fungi, protists, animals, plants
What is the importance of basic research?
Basic research can be used to drive applied research
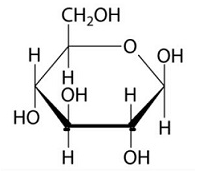
What is this molecule?
Glucose
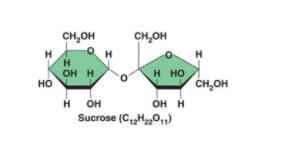
What is sucrose? and how is it formed?
Disaccharide, monosaccharides
What is the difference between starch and glycogen
Starch is produced by plants, glycogen is produced by vertebrae animals
Hydrophilic
Water loving
Hydrophobic
Water fearing
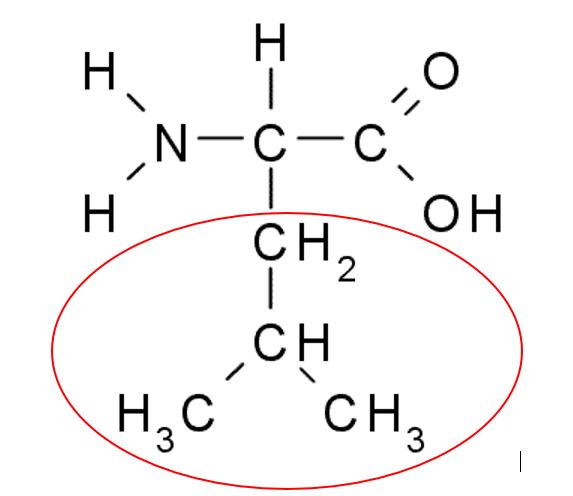
How can this amino acid be classified?
Hydrophobic, uncharged, nonpolar
Peptide bonds…
Link the amino acids found in a polypetide chain
Primary (Protein Structure)
The amino acid sequence of a protein from beginning to end
Secondary (Protein Structure)
Segments of the polypeptide chain are repeatedly folded or coiled due to hydrogen bonding between repeated sequences in the polypeptide chain
Tertiary (Protein Structure)
Overall shape of protein resulting from interactions between R groups
Quaternary (Protein Structure)
Assembly of multiple polypeptides into a functional protein
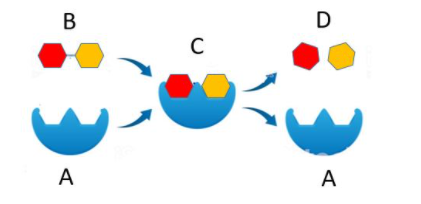
What is A?
Enzyme
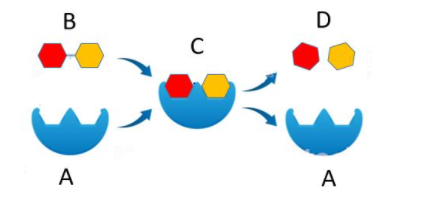
What is B?
Substrate
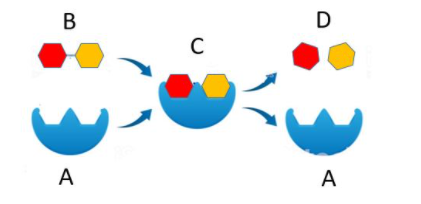
What is C?
Enzyme-substrate
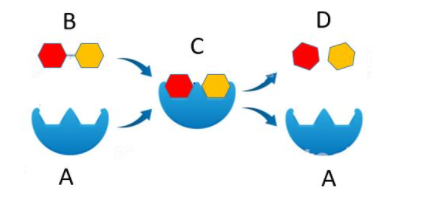
What is D?
Product
Why are lipids important in animal cells?
Component of cell membrane, energy storage molecule, and is a steroid and hormone
Unsaturated fatty acids…
are hydrocarbon chains that contain one or more double bonds between the carbon atoms that compose the chain
Phospholipids are NOT…
Hydrophobic
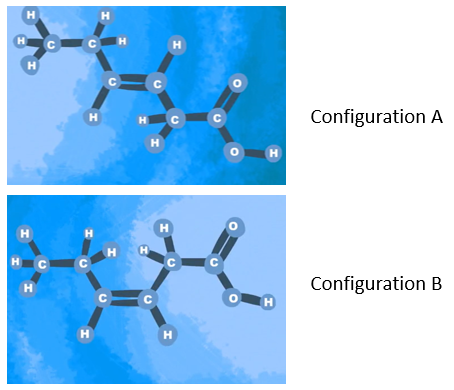
Which configuration would you rather have in your diet?
B
In the fluid mosaic model of biological membranes….
There is a phospholipid bilayer with a mosaic of proteins, both proteins and phospholipids move
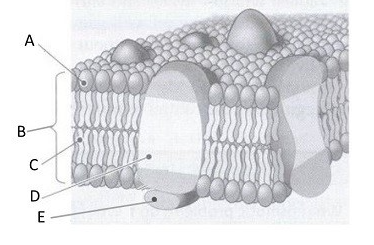
What is “a” showing?
Hydrophilic head of a phospholipid
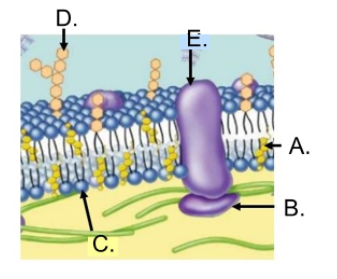
What is A?
Sterol
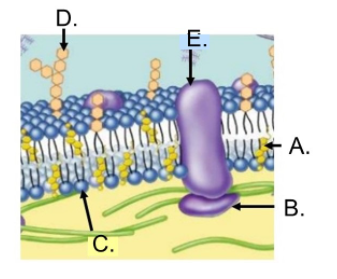
What is B?
Peripheral Membrane
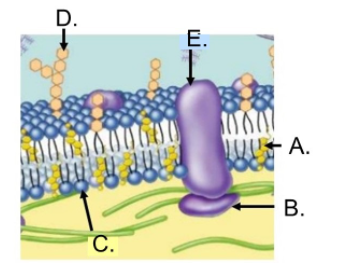
What is C?
Phospholipid
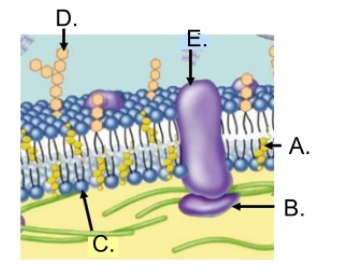
What is D?
Oligosaccharide (Carbohydrate)
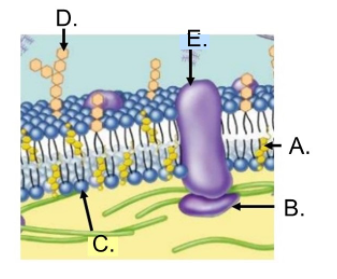
What is E?
Transmembrane protein
Fluidity of an animal cell membrane is affected by…
Degree of saturation and length of phospholipid tails, cholesterol, protein density, and temp
What is found in a prokaryotic cell?
Plasma membrane, cell wall, DNA/chromosome, ribosomes
The nucleoid region of a prokaryotic cell…
Is the region in the cell where DNA is concentrated
The cell wall of a bacterium is composed of
Peptidoglycan
What is the function of ribosomes?
Protein production
How do bacteria “talk” and launch a virulent attack overcoming a large host?
Quorum sensing
Quorum sensing…
Requires signals and receptors, is a system of stimulus and response correlated to population density, can be species specific
What is accurate about the tertiary structure of proteins?
Stabilized by H bonds, ionic bonds, covalent bonds (disulfide bridges) and hydrophobic interactions, overall shape is from interactions between R groups
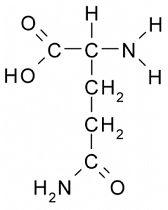
Where would you expect to find this amino acid in its tertiary structure?
On the exterior of the protein because it can form H bonds with water
Changing a single amino acid in a polypeptide chain can…
Affect protein function, sometimes change tertiary structure of a protein, sometimes change secondary structure of a protein, and always change the primary structure of a protein
What is the 1st step of enzyme action?
Substrate enters the active site of enzyme
What is the 2nd step of enzyme action?
Induced fit
What is the 3rd step of enzyme action?
Substrates converted to products
What is the 4th step of enzyme action?
Products are released
What is the 5th step of enzyme action?
Enzyme returns to its original tertiary structure and can bind another substrate molecule
How is cholesterol(hydrophobic) carried in our bloodstream?
As part of lipoprotein complexes
Apolipoproteins are found…
In lipoprotein complexes
What is a glycoprotein?
A protein with a covalently attached oligosaccharide that often serves as a cellular identification tag
What is true about triglycerides?
Mainly function as energy storage molecules, their fatty acids can be saturated or unsaturated, constructed from glycerol and three fatty acids, assembled from smaller molecules by dehydration reactions, and they are hydrophobic
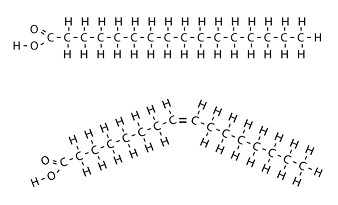
If the molecule on top is found in a triglyceride, what would it be at room temp?
Solid
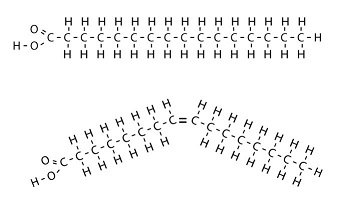
Where would the top molecule most likely be found?
Animal fats
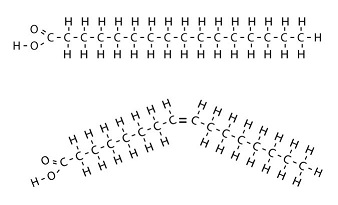
Where would the bottom molecule most likely be found?
Plant fats
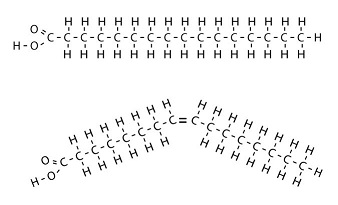
What is the molecule on top?
Saturated fatty acid
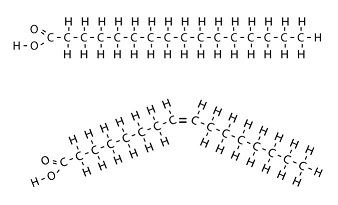
What is the molecule on bottom?
Unsaturated fatty acid
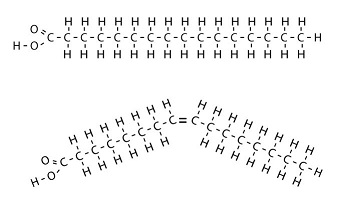
What is true about both molecules?
Both can be found in triglycerides and in phospholipids
Plasma membranes are selectively permeable. This means that…
They allow some substances to cross more easily than others
If you want to make a membrane fluid at LOW TEMPS, you should…
Increase amount of cholesterol, make more active desaturase enzymes, and increase number of unsaturated fatty acids in membrane phospholipids
How do substances diffuse across the membrane?
Substances move down their concentration gradient
WHich of the following would have the most trouble crossing a biological membrane composed of only a phospholipid bilayer?
Na+
How is facilitated diffusion similar to active transport?
Both processes require transmembrane proteins
Cells that have lots of aquaporins transport lots of….
Water across their membranes
Carrier proteins, channel proteins, and pumps are all…
Transmembrane proteins
Exocytosis is a process by which cells
Release substances via vesicles
In which of the following would you expect to find cells with organelles?
Protists, plants, animals, eukaryotic organisms, and fungi
A eukaryotic cell is_______than a prokaryotic cell
Larger
What is the outermost boundary of an animal cell?
Plasma membrane
How does surface area to volume ratio affect the rate of diffusion?
As a cell gets larger, the volume increases faster than the surface area, so diffusion cannot meet the needs of the cell
In eukaryotic cells, organelles…
Provide additional membrane surfaces for the cell and provide compartments for specialized reactions/processes
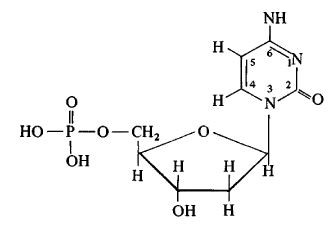
What does this image depict?
Single nucleotide
What best describes RNA?
Its nucleotides contain the sugar ribose, which usually exists and functions as a single polynucleotide strand, copy of instructions in DNA; is used to make proteins that run the cell, and is found in the nucleus and cytosol
How are the two polynucleotide strands of the double helix connected?
Hydrogen bonds
How are nucleotides within a single polynucleotide strand connected?
Phosphodiester bonds
In DNA, T goes with
A
In DNA, C goes with
G
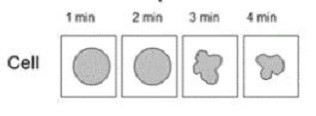
What is true about this figure?
The solution is hypertonic to the cytosol, water is moving across the membrane by facilitated diffusion via aquaporins and by simple diffusion
When an individual cannot remove LDL from her bloodstream and has high cholesterol, which is a potential explanation?
Misfolded LDL receptors and a defect in apolipoproteins in her LDL complexes
Why does amoxicillin kill bacterial cells and not yours?
We do not have a cell wall
An archaea living in a hot spring can be described as…
Extreme thermophiles
What is true about nuclear envelope?
Nuclear side is lined with a nuclear lamina, encloses the nucleus (separating it from the cytoplasm), and it contains pores
What happens if you genetically modify an organism to produce DNA polymerase with no nuclear localization signal (NLS)?
Cells will not be able to replicate DNA
What best describes the golgi apparatus?
In the endomembrane system, a warehouse for receiving, sorting, and shipping proteins made in the rough ER
What best describes the lysosome?
Contains functional hydrolytic enzymes
What best describes the nucleus?
Contains most of the cell’s DNA
What best describes the ribosomes?
Synthesis of proteins; subunits of this structure are made in the nucleolus
What best describes the rough ER?
Proteins that will be secreted from the cell are made in this endomembrane compartment
What best describes smooth ER?
Synthesis of oils, phosphates, and steroids
A mouse that does not make lamin has…
Abnormally shaped nuclei and disorganized chromatin (DNA)C
Cells that secrete motilin are likely to have lots of…
Rough ER
Cells that produce lots of oil are likely abundant with…
Smooth ER
WBC are abundant with…
Lysosomes
Where is the 1st place BGH goes as it leaves the pituitary gland?
Rough ER
Where is the 2nd place BGH goes as it leaves the pituitary gland?
Transport Vesicle
Where is the 3rd place BGH goes as it leaves the pituitary gland?
Smooth ER
Where is the 4th place BGH goes as it leaves the pituitary gland?
Lysosome