gonads and pancreas
1/13
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Alpha cells/ glucagon cells
Secrete glucagon between meals/ when blood glucose concentration falls below 100mg/dL
Glucagon
2 primary actions
1) glycogenolysis
2) gluconeogenesis
Both raise blood glucose level
Stimulates fat catabolism and release of free fatty acids in adipose tissue
Secreted in response to high protein meal
Promotes amino acid absorption provide cells raw material
Glycogenolysis
Breakdown of glycogen into glucose
Gluconeogenesis
Synthesis of glucose from fats and proteins
Beta cells/ insulin cells
Secrete 2 hormones
Insulin and amyloid
When blood nutrients increase, secrete insulin to help transport of nutrients into cells
Insulin hormone
Hormone of nutrient abundance
Secreted during and after meal when blood nutrient levels are srising
Osteocalcin and lipocalin 2
From osteoblasts of bone
Stimulate multiplication of beta cells
Insulin secretion, and insulin sensitivity of other body tissues
Pancreatic islet (islets of Langerhans)
Small cluster of endocrine cells in pancrease that secretes insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin
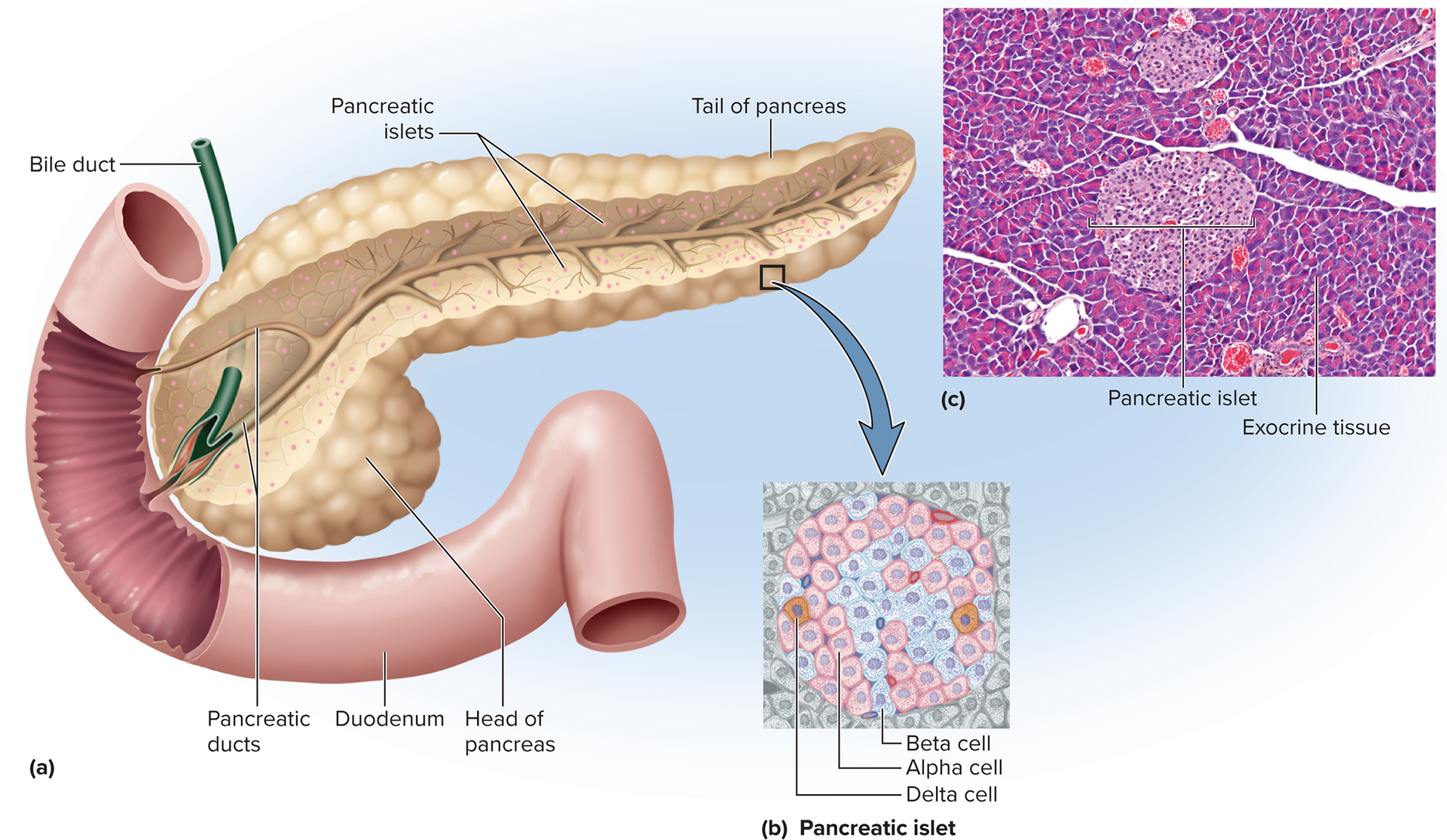
Pancreas
Endocrine gland also acts as exocrine gland
Posterior to stomach
Glycemic
Blood glucose concentration
Hypo-lower
Hyper-heighten
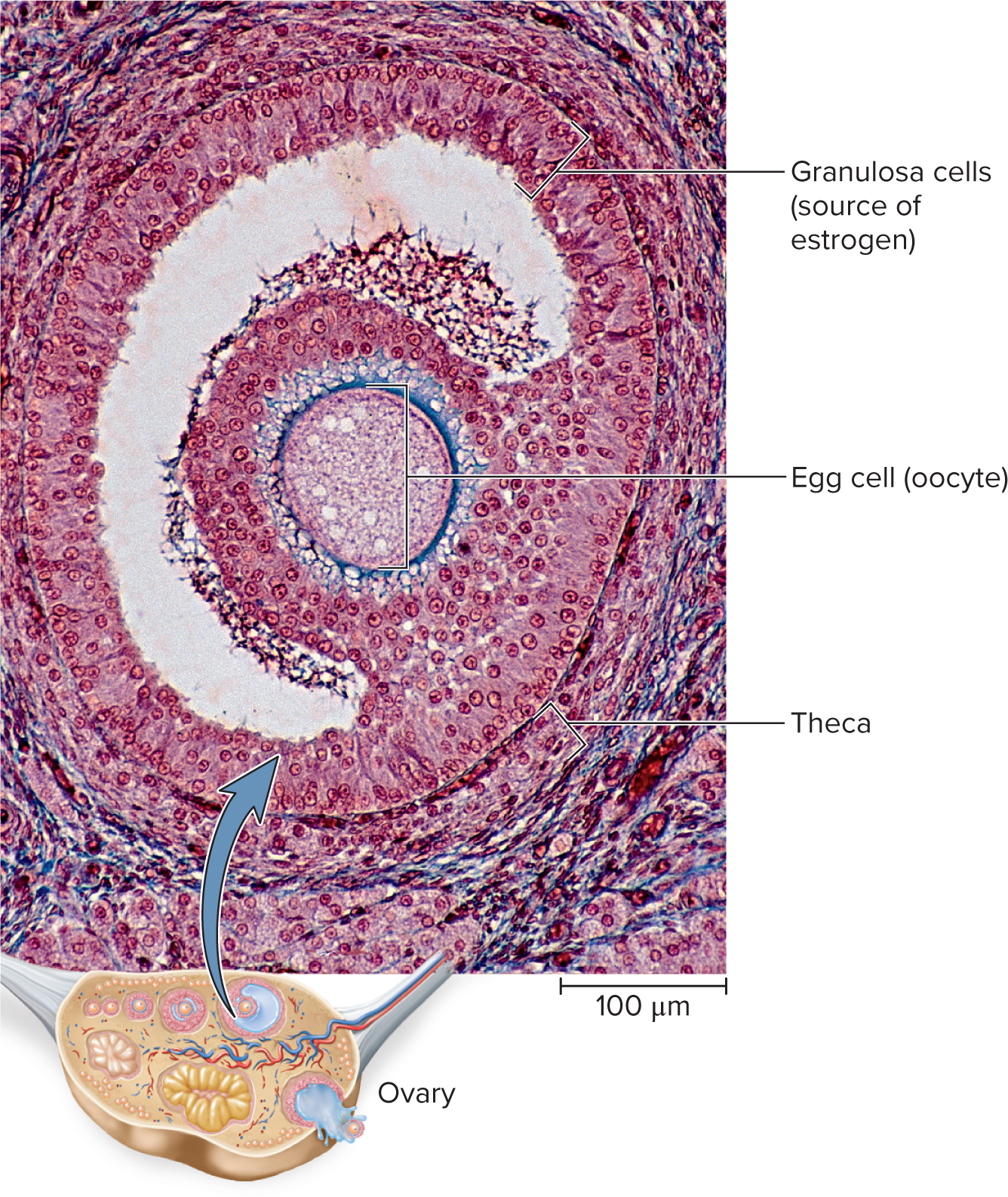
Ovary gland
Secrete progesterone and estrogen (estradiol and inhibit)
Corpus luteum: progesterone
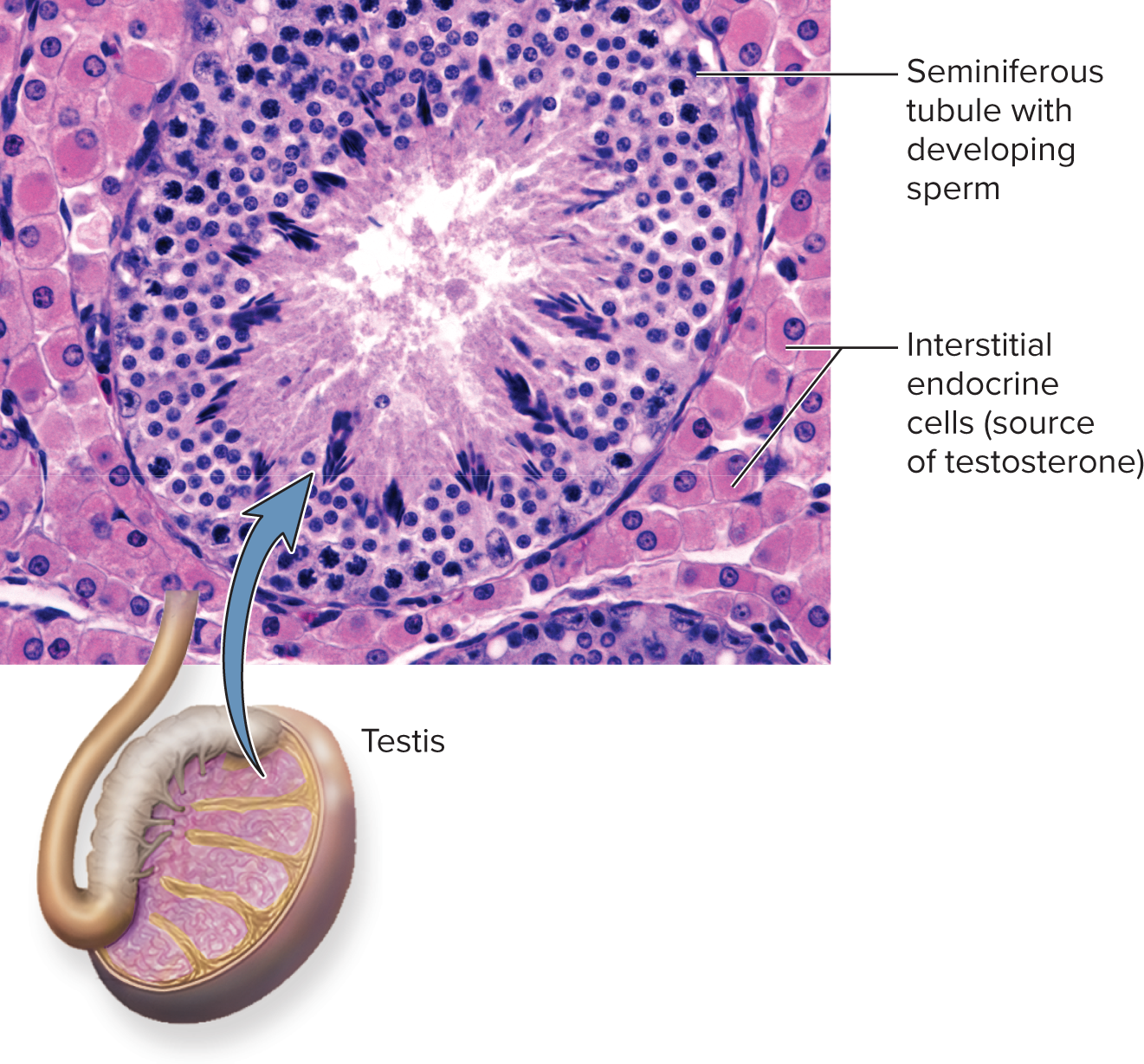
Testes
Have intestinal endocrine cells
Interstitial endocrine cells
Located between seminiferous tubules of testis
Endocrine that secrete testosterone
Gonads
Ovary
Testes
Both endocrine and exocrin glands