Orgo 1 reactions and reactants
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Elimination reactions to prepare alkenes
E2 and E1 reactions
Hydrohalogenation
Reagents: HX
- Markovnikov product
- watch for carbocation rearrangements

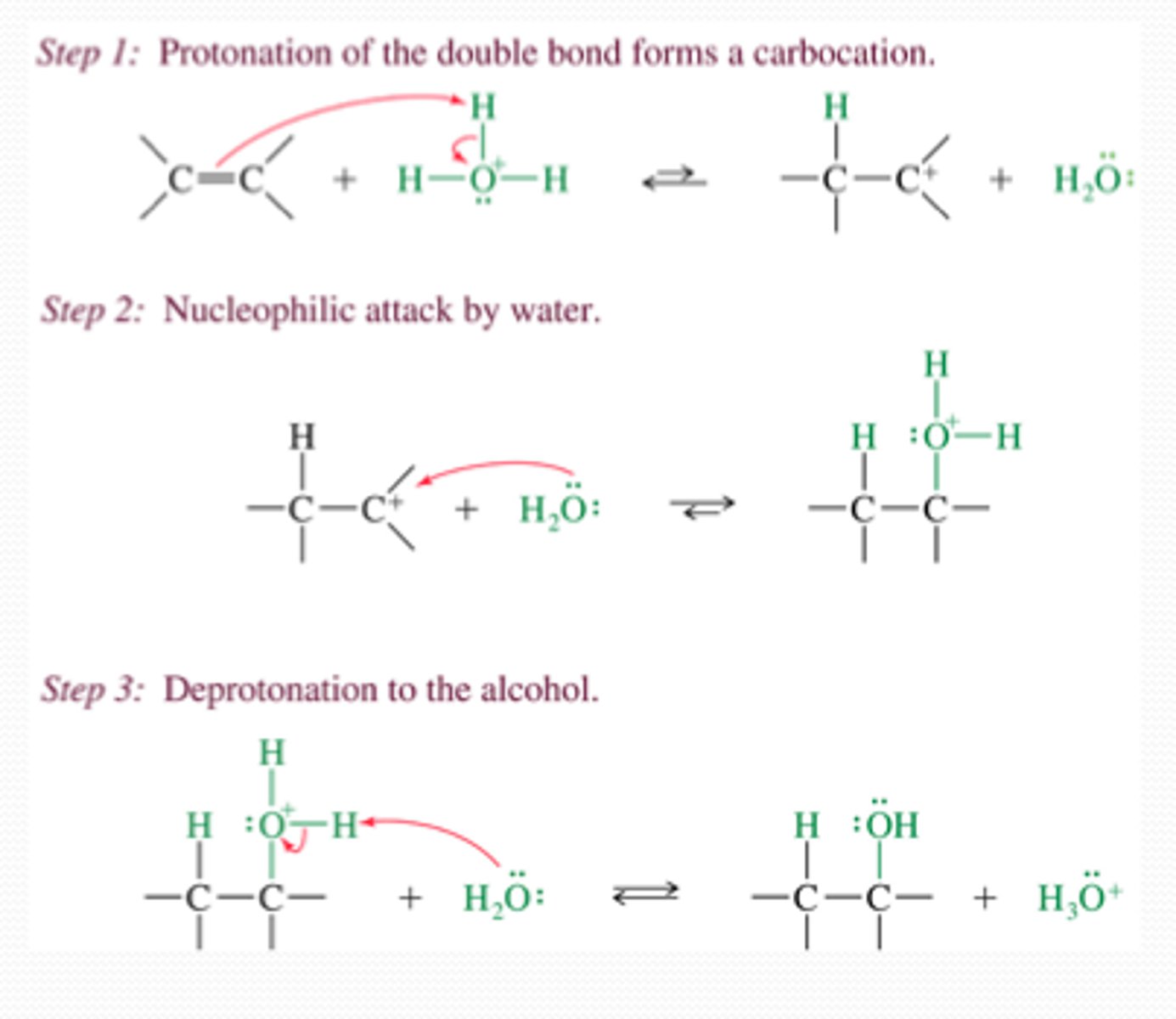
Hydration (acid-catalyzed)
Reagents: H2O, H2SO4
Stereochem: racemic
- Markovnikov product (rearrangements possible)
Hydration (oxymercuration)
Reagents: 1) Hg(OAc)2, H2O 2) NaBH4
- Markovnikov product (no rearrangement)
Halogenation (w/o peroxides)
Reagents: X2
- anti addition of X2
Sterochem: anti addition

Halohydrin formation
Reagents: X2 + H2O
- H2O on more substituted
- Anti addition

Hydroboration-oxidation
Reagents: 1) BH3 2) H2O2, NaOH
- Anti Markovnikov product
- Syn addition of H and OH
Reduction of alkenes to give alkanes
- Hydrogenation
Reagents: H2 + metal catalyst (Pd, Pt, Ni)
- alkene -> alkane
- syn addition of H2
Oxidative cleavage of alkenes
- Ozonolysis
Reagents: 1) O3 2) DMS or Zn
- breaks double bond into 2 carbonyls (aldehydes or ketones)
Epoxidation of alkenes
Reagent: mCPBA (or peracids like RCO3H)
- alkene -> epoxide
- Syn addition of oxygen
Reduction of alkynes to give alkanes
Reagents: H2 + metal catalyst (Pt, Pd, Ni)
- alkyne -> alkane
- adds 2x equiv of H2
Reduction of alkynes to give alkenes
Reagent: H2 / Lindlar catalyst
- Cis (Z) alkene
Reagent: Na or Li metal / NH3 (l)
Oxidative cleavage of alkynes
Reagents: O3 / H2O or KMnO4 (hot, conc.)
- internal alkyne -> 2 carboxylic acids
- terminal alkyne -> carboxylic acid + CO2
Hydration of alkynes
Reagents: HgSO4, H2SO4, H2O
- Markovnikov ketone
- first enol -> tautomerizes -> ketone
- terminal alkyne -> methyl ketone
- internal alkyne -> mixture of ketones
Hydroboration/oxidation of alkynes
Reagents: 1) BH3 2) H2O2, OH(-)
- Anti Markovnikov
- Terminal alkyne -> anti mark aldehyde (always aldehyde, never ketone)
- internal alkyne -> mixture of ketones
- enol -> tautomerizes -> aldehyde
Addition of HX to alkynes
Reagents: HX
- 1 equiv -> vinyl halide (Markovnikov)
- 2 equiv - geminal dihalide (both halogens on same C) (Markovnikov)
Addition of X2 to alkynes
- Halogenation
Reagents: X2
- 1 equiv -> Trans dihalide alkene (anti addition)
- 2 equiv -> tetrahalide
Alkynes homologation (with alkyl halides)
1) Reagent: NaNH2
- forms acetylide anion
2) Reagent: R-X (primary)
- extends carbon chain (SN2)
Alkynes homologation (with alkyl tosylates)
1) Reagent: NaNH2
- forms acetylide anion
2) Reagent: R-OTs (primary)
- extends carbon chain (SN2)
Alkynes homologation (with epoxides)
Reagents: 1) Acetylide anion 2) H2O
- forms alcohol after ring opening
- attack happens at less substituted carbon
NaH
- strong base (non nu)
- Deprotonates alcohols (ROH -> RO-)
- Deprotonates terminal alkynes
H2SO4
- Acid catalyst / dehydrating acid
- Alcohol -> Alkene (E1; rearrangements possible)
- hydration of alkenes (alkene + H2O -> alcohol) (E1 or acid-catalyzed addititon - Zaitsev, rearrangements possible)
TsOH
- strong acid like H2SO4
- Dehydrates alcohols -> alkenes (E1)
POCl3, pyridine
- dehydration of alcohols w/o rearrangement
- Alcohol -> Alkene (E2; Zaitsev)
HX
- Alcohol + HX -> Alkyl halide (SN1 or SN2)
- Alkene + HX -> Markovnikov alkyl halide
- Alkyne + HX -> vinyl halide or geminal dihalide (Markovnikov)
ZnCl2
- alcohols -> alkyl halides
- makes OH a good LG
SOCl2
- OH -> Cl
- alcohol -> alkyl chloride
- usually with pyridine
PBr3
- OH -> Br
- alcohol -> alkyl bromide
- usually with pyridine
TsCl
- makes tosylate
- ROH -> ROTs (good LG)
H20/H2SO4
-Hydration
- Alkene + water -> alcohol (Markovnikov)
X2, H2O
- halohydrin formation
- anti addition (Markovnikov OH)
1) BH3, 2) H2O2, OH(-)
- Hydroboration-oxidation
- Alkene -> alcohol (anti-Markovnikov, syn add.)
- Alkyne -> aldehyde (anti-Markovnikov hydration, syn add.)
NaNH2
- very strong base
- alkyne deprotonation -> acetylide ion
- double elimination of vicinal/geminal halides -> alkyne
- E2 and deprotonation
KOC(CH3)3 in DMSO
- t-BuOK
- bulky base -> Hofmann elimination
- E2 elimination (Hofmann)
H2O, H2SO4, HgSO4
- oxymercuration for alkynes
- Markovnikov hydration of alkynes
- terminal alkyne -> ketone
- enol -> keto tautomerization
1) R2BH 2) H2O2, HO(-)
- Hydroboration-oxidation of alkynes
- anti-Markovnikov hydration
- terminal alkyne -> aldehyde (via enol -> keto) (syn add.)