Session 1: DNA Replication, Mitosis and Meiosis
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Aneuploidy
Abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell.
Anueploid cells have chromosome number that is greater or smaller than a normal cell.
Polyploidy
Condition in which the cells of an organism have more than two paired sets of chromosomes.
Aneuploidy and polyploidy are generally ___
Lethal
Semi-conservative DNA replication
Each daughter DNA double-helix is composed of one strand from the original (one conserved), and one newly synthesized
DNA replication begins at the ___ of ____
origin of replication
Origins of replication are usually marked by particular sequence of nucleotides to which ___ proteins bind to open the double helix
initiator proteins
There are ___ origins of replication in the human genome
10,000
DNA ligase
enzyme which mediates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of phosphodiester bonds
DNA polymerases
group of polymerase enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA from mono-deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs)
DNA helicase
enzyme which separates double-stranded DNA into single strands
DNA topoisomerase
enzyme which unwinds overwound DNA ahead of the replication fork
DNA primase
catalyses the synthesis of short RNA primers complementary to a single-strand DNA template
DNA primase is a type of ___ polymerase
RNA polymerase
DNA is synthesised in what direction?
5' to 3'
The difference in the leading and lagging strand in DNA replication
Leading strand → synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 3' end - synthesized continuously as it grows.
Lagging strand → synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 5' end - synthesized in short fragments (Okazaki fragments) that are ultimately stitched together.
- synthesised discontinuously.
Fragments of the lagging strand
Okazaki fragments
Replication forks are ___
asymmetrical
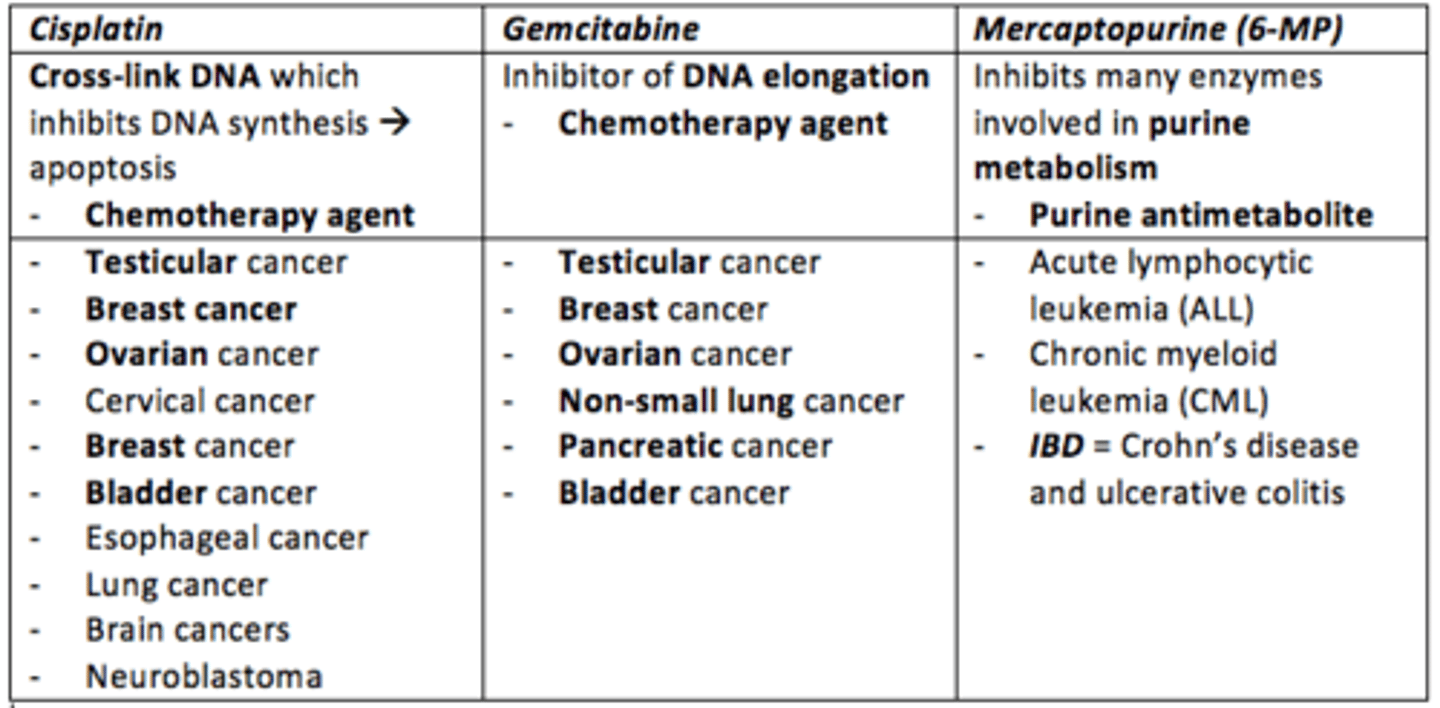
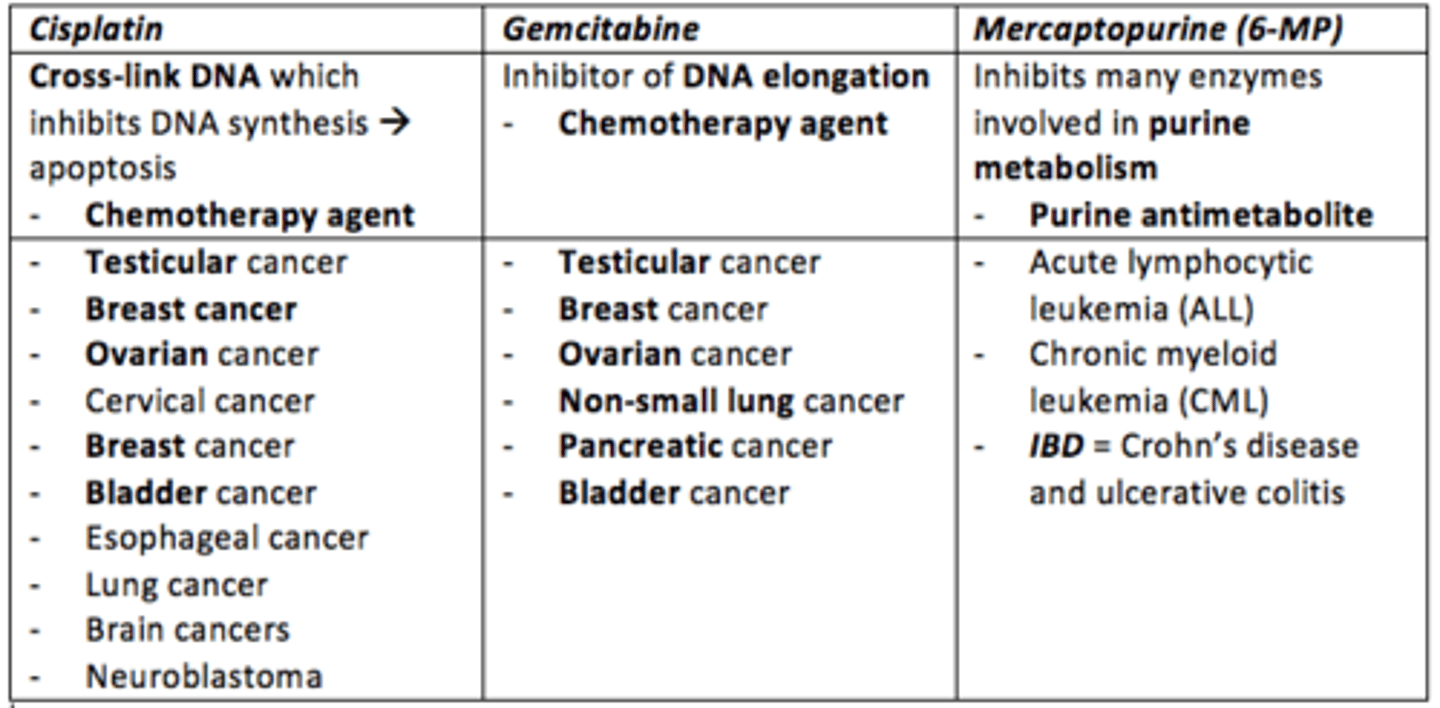
Cisplatin
- Chemotherapy agent
- Cross-links DNA which inhibits DNA synthesis leading to apoptosis
- Treats: testicular, ovarian, cervical, breast, bladder, esophageal, lung, brain cancers and neuroblastoma
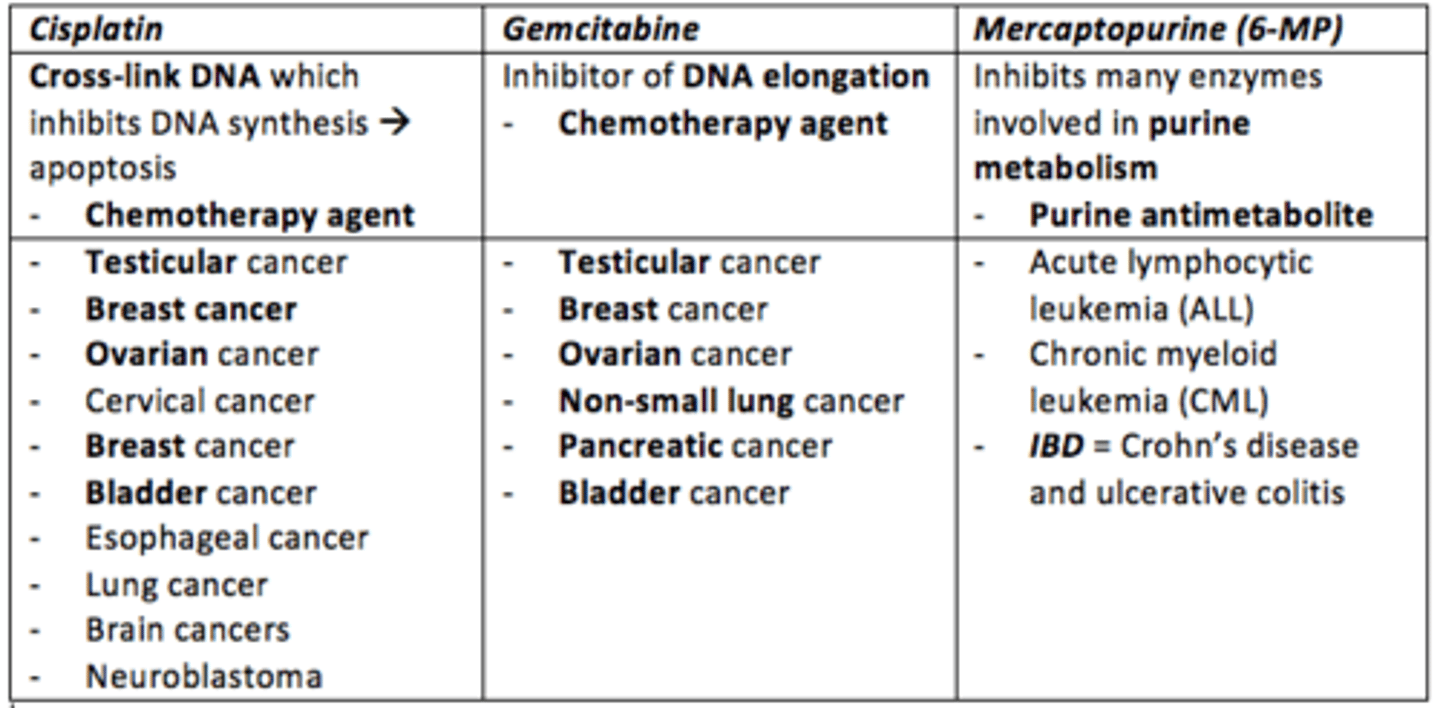
Gemcitabine
- Chemotherapy agent
- Inhibitor of DNA elongation
- Treats: testicular, breast, ovarian, non-small lung, pancreatic and bladder cancer
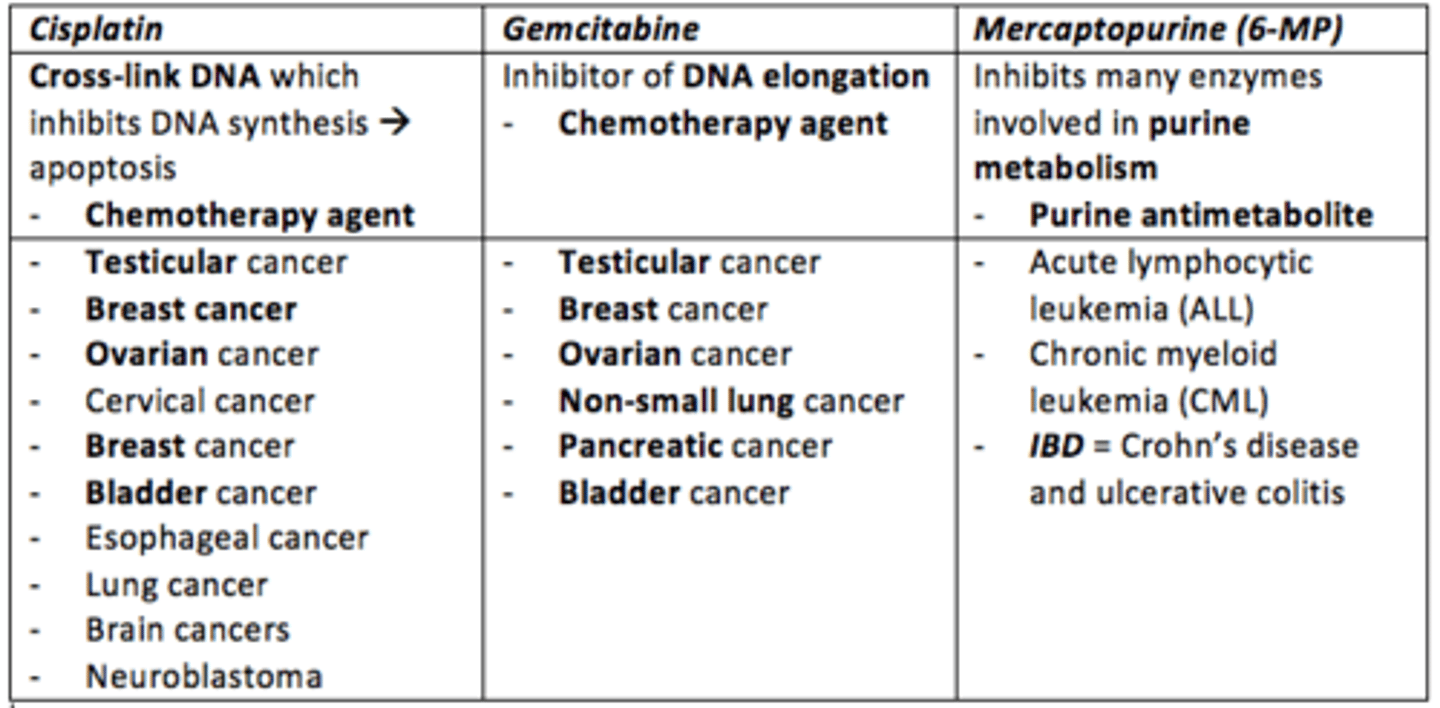
Mercaptopurine (6-MP)
- Inhibits many enzymes involved in purine metabolism (purine antimetabolite) during DNA replication
- Treats: acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
- Also can be used to treat Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis
Name three therapeutic agents which inhibit DNA synthesis (replication) process
- Cisplatin
- Gemcitabine
- Mercaptopurine (6-MP)
Stages of mitosis in order
PPMAT-C
Prophase
Prometaphase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokinesis
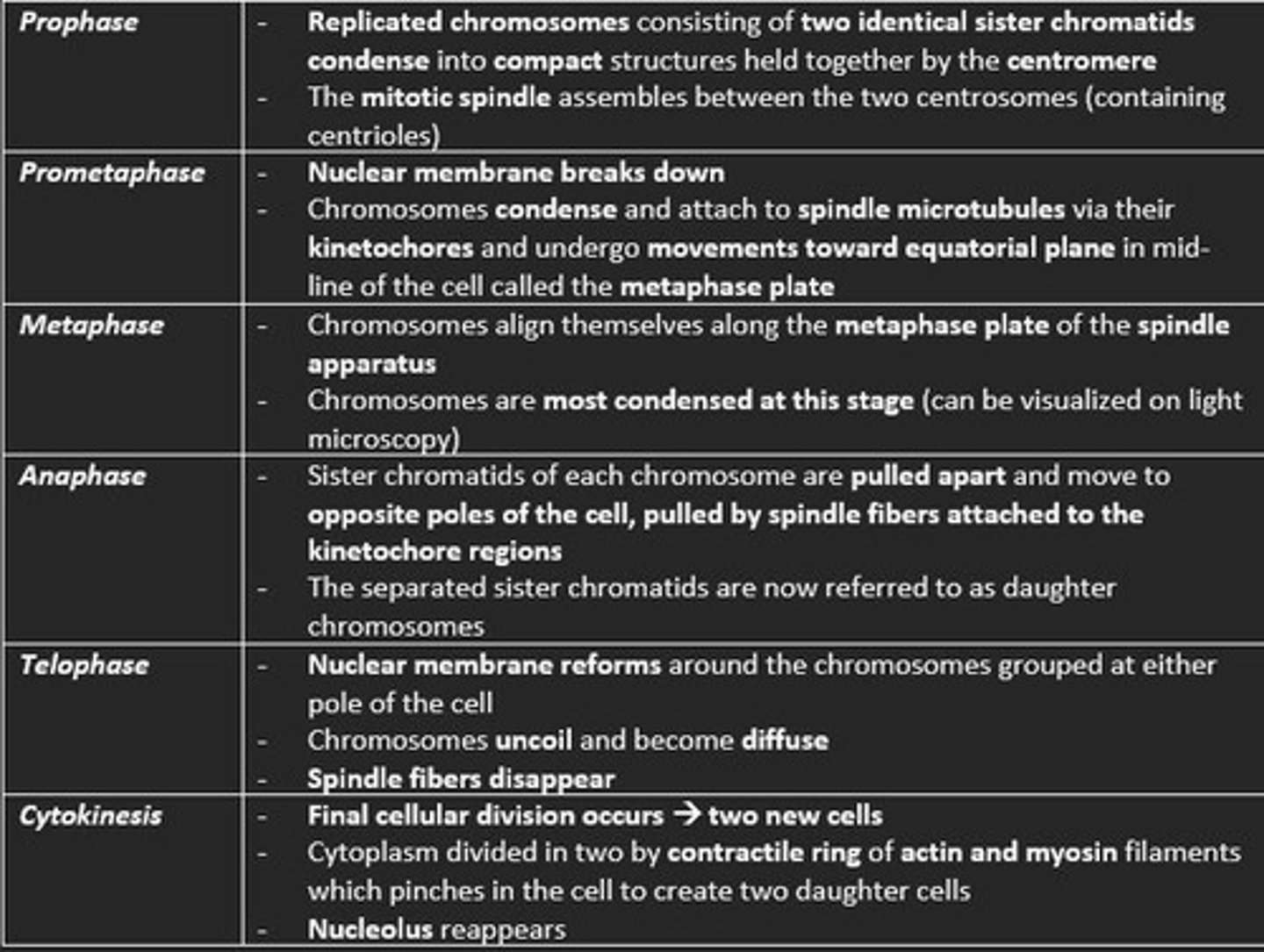
The contractile ring which forms in the cytokinesis stage of mitosis is made of ___ and ___ filaments
actin and myosin filaments
What does mitosis produce
2 genetically identical diploid daughter cells.
These cells have the same chromosome content as the parental cell (2n).
Why are metaphase and anaphase important stages of mitosis?
Ensure that each daughter cell receives a copy of every chromosome
Meiosis
Specialised cell division of germline cells to produce oocytes (eggs) and spermatozoa (sperm). Consists of one round of DNA replication followed by two rounds of division: meiosis I and meiosis II.
What does meiosis produce
Four genetically different haploid cells
Meiosis is a ___ division - resulting in production of four non-identical ___ cells in which the chromosome number is halved from diploid (46) to haploid (23)
reduction, haploid cells
Describe what occurs during meiosis 1 - prophase 1
'Lazy Zebra Push Dumb Donkey'
Leptotene
Zygotene
Pachytene
Diplotene
Diakinesis

Which stage of prophase 1 in meiosis produces genetic variation?
Pachytene = crossing over between pairs of homologous chromosomes to form chiasmata

What occurs during metaphase 1 of meiosis
- Homologous pairs of chromosomes arranged as double row along metaphase plate
- Alignment of maternal and paternal homologues along the metaphase plate is random = source of genetic variation through random assortment

What occurs during anaphase 1 of meiosis
- Homologous chromosomes in each bivalent are separated and move to opposite poles of the cell
- Sister chromatids remain attached and some of the chromatids have exchanged genetic material at this stage

What occurs during telophase 1 of meiosis
- Chromosomes become diffuse
- Nuclear membrane reforms

What occurs during cytokinesis 1 of meiosis
Final cellular division to produce two new haploid cells

What occurs during meiosis II
Mitotic division of each of the haploid cells produced in meiosis I

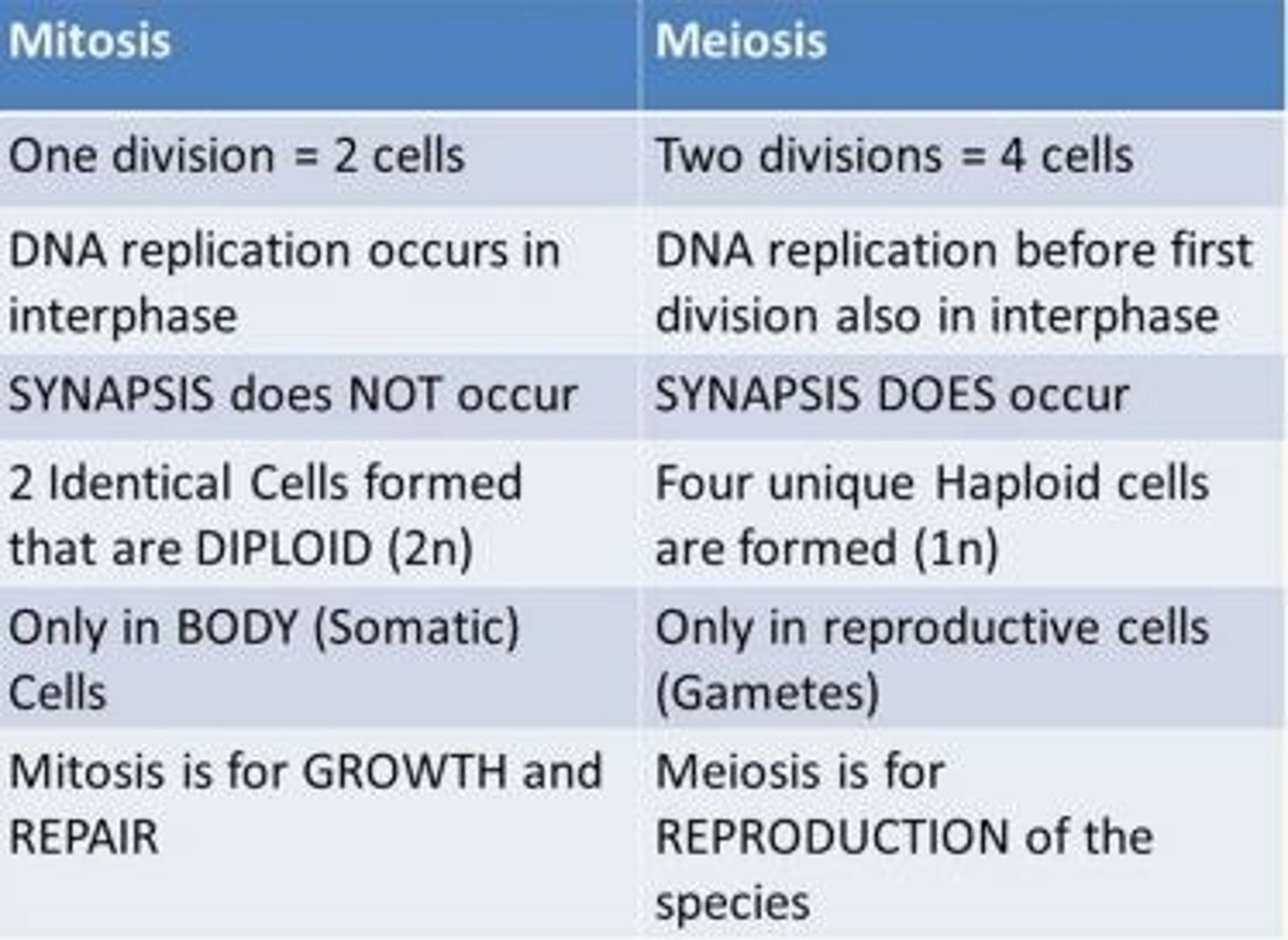
Compare mitosis and meosis
MITOSIS:
1 div = 2 cells
DNA replication occurs in interphase
Synapsis DOESN’T occur
2 identical cells formed that are diploid (2n)
Only in body (somatic) cells
for GROWTH and REPAIR
MEIOSIS:
2 div = 4 cells
DNA replication before first div in interphase
Synapsis DOES occur
4 unique haploid cells (1n)
Only in reproductive cells (gametes)
for REPRODUCTION
Sources of genetic variation in meiosis
Crossing-over, independent assortment, random fertilization

Genotype
- Genetic make-up of an individual
- Inherited
Phenotype
- Observable characteristics of an individual resulting from interaction of its genotype with the environment
- Not inherited