Runway/Taxiway Lights, Communications
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
https://pilotinstitute.com/atis-vs-awos-vs-asos/ https://pilotinstitute.com/runway-lights-explained-colors-spacing-types/
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
CTAF common traffic advisory frequency
is what you use when operating at a nontowered airport
(used in the air to talk to other pilots)
turn your CTAF on 10miles inbound
UNICOM universal integrated community
air/ground radio
Unicom can be identified as the CTAF
will find this information in the chart supplements
How high must you remain before crossing midfield and being out of the pattern
500ft agl or 2000ft agl if large turbine airplanes operate at your airfield
When crossing midfield how far out should you go?
two miles out then descend to altitude and enter the pattern
ATIS - automated terminal information system
updates once an hour at controlled airports
AWOS - automated weather observation system
updates every minute and is ran by the Federal aviation administration
can be at towered or nontowered
ASOS - automated surface observation system
more advanced than AWOS and is ran by the national weather service
updates every minute
can be at towered or nontowered
ATIS vs AWOS and ASOS
ATIS - updates every hour only at controlled airports. Most detailed. Tells weather and runway/airport information. Stops when tower closes and turns over to AWOS/ASOS
AWOS and ASOS - updated every minute at both controlled and noncontrolled towers. Only focuses on weather.
Runway distance remaining signs
black background with a white number telling you in thousands of feet how much runway is left
when you get to the last number you have 950ft left
enhanced taxiway centerline
yellow line outlined in black to tell you, you are 150ft approaching a runway
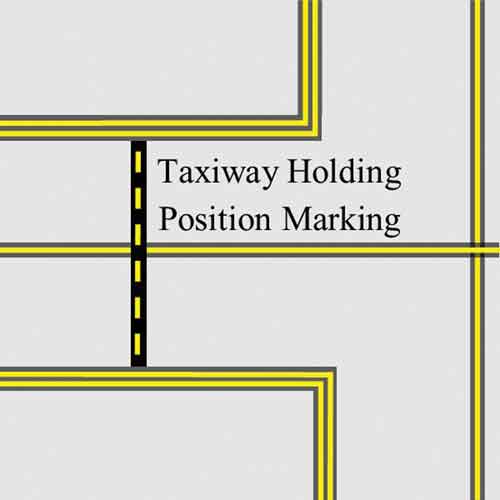
a holding position on a taxiway looks like
a solid black line with yellow dash in the middle
omnidirectional and unidirectional
unidirectional can only see from one side (approaching area)
omnidirectional can be seen from all sides
In chart supplement what does HIRL, MIRL, and LIRL mean?
High intensity runway lights
Medium Intensity runway lights
Low intensity runway lights
on a runway

What is this runway?
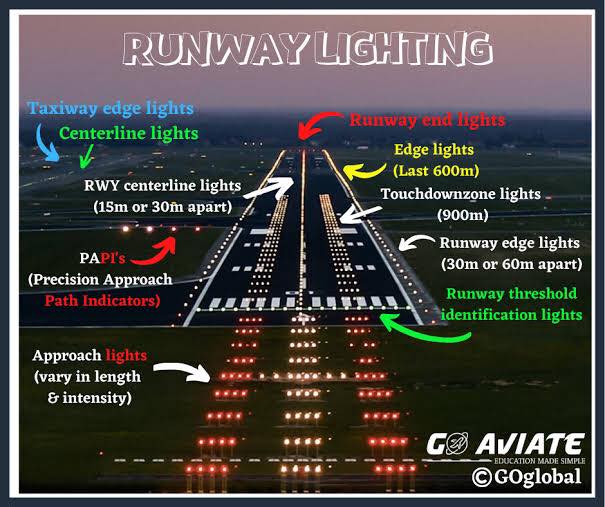
Runways without instrument approach visuals, just white lights?
Runways with instrument approach
Red lights before green lights indicate displaced threshold
Greenlights indicate threshold and where you can start to land
Two symmetrical strips of white lights in rows indicate the Touchdown Zone (TDZLs)
-this is where the pilot must aim in order to have enough runway left to stop
White lights indicate the side of the runway
-starts 100ft beyond the landing threshold and extends 3,000ft or to the runway midpoint, whichever is less
Yellow lights on the side of the runway indicate that there are 200ft of runway left or half the runway is left whichever is less
White center line is beginning of runway
Red and white centerline alternating lights indicate 3000-1000ft left of runway
Red centerline indicates 1000ft left of runway
Taxiway lights
Blue lights are the sides of taxiway
Green lights is the center of the taxiway
Altering green and yellow lights are at the beginning and end of taxiway
All yellow lights will be in the center to alert that you are entering a runway

ALS means
approach lighting system
ASL (Approach lighting system) lengths
Approach lights start at the landing threshold. Precision approach runways have lights that extend 2,400 – 3,000 feet. Non-precision approach lights only extend 1,400 – 1,500 feet.
See ASL before runway in bad weather
allows to descend no less than 100ft
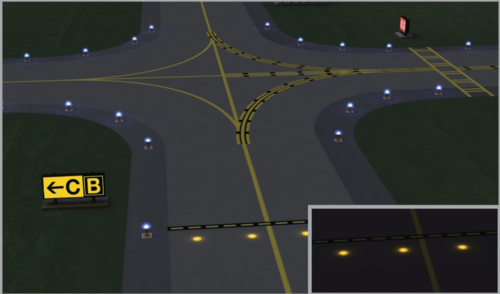
image shows
clearance bar lights
three in pavement steady burning yellow lights
Your radio is malfunctioning, and you lost your receiver what should you do?
remain outside of airspace D until the direction of flow is determined. Then advice the tower of aircraft type, position, altitude, and intent to land.
What to do if your transmitter malfunctions
Monitor that you’re on the right ATC frequency
remain outside of airspace D until the direction of flow is determined. Then advice the tower of aircraft type, position, altitude, and intent to land.
Monitor that you’re on the right ATC frequency
During daylight, rock wings back and forth to alert ATC
At night, blink the landing lights
What to do if both transmitter and receiver are inoperative
remain outside of airspace D until the direction of flow is determined
Look for light signals
What does dashed lines along the center double yellow parallel lines indicate to a pilot?
There is 150ft remaining before you approach a runway holding position marking.
How to operate lights at night?
Set radio to appropriate frequency (usually CTAF) then click radio microphone for frequency
When should you turn on landing lights?
Under 10,000ft msl
What is 1090MHz and 980MHz
radio frequency for ADSB out
1090 is a frequency required for flying 18,000ft above or outside US
980Mhz is a less congested version of reporting altitude/information