Lesson 5.2 Newton’s law of universal gravitation
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
1
New cards
State Newton's law of universal gravitation in words and as a formula.
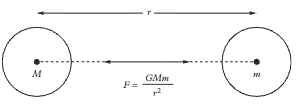
The gravitational force between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centres. Formula: F = GMm/r²
2
New cards
What does each symbol represent in F = GMm/r² and what are their units?
F = gravitational force (N). G = universal gravitational constant (6.67 × 10⁻¹¹ N m² kg⁻²). M and m = masses of the two objects (kg). r = distance between centres of mass (m).
3
New cards
What are the key properties of gravitational force?
Always attractive (points inward between objects). Acts as equal and opposite forces on both objects (Newton's third law). Is a vector quantity with magnitude and direction. Applies to ALL objects with mass regardless of size.
4
New cards
Why is gravitational force called an "inverse square law" and what does this mean practically?
Force is proportional to 1/r². If distance doubles force becomes 1/4. If distance triples force becomes 1/9. If distance halves force becomes 4 times greater.
5
New cards
When can objects be treated as point masses in gravitational calculations?
When the separation distance is very large compared to their diameters OR when objects are spherically symmetrical. In these cases all mass can be assumed to be located at the centre of mass.
6
New cards
When calculating gravitational force for an object on Earth's surface what value should be used for r?
r = radius of Earth (6.37 × 10⁶ m) because r is measured from centre to centre. For objects at altitude add the altitude to Earth's radius: r = rₑ + altitude.
7
New cards
What is "order of magnitude" and how is it used?
The power of 10 in scientific notation ignoring the coefficient. Example: 3.18 × 10²⁶ m has order of magnitude 10²⁶ m. Useful for comparing very large or very small quantities and checking if answers are reasonable.
8
New cards
How did Cavendish experimentally determine the value of G?
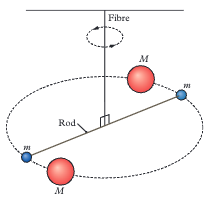
Used a torsion balance with small lead spheres on a rod suspended by a fibre. Large lead balls attracted the small ones causing the fibre to twist. The twist angle was proportional to gravitational force allowing G to be calculated.
9
New cards
How can you linearise gravitational force vs distance data to verify the inverse square relationship?
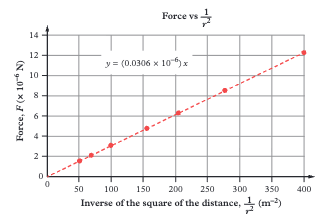
Plot F versus 1/r² instead of F versus r. This gives a straight line through the origin. The gradient equals GMm confirming F ∝ 1/r².
10
New cards
What happens to the gravitational force when: (a) one mass is doubled (b) distance is halved?
(a) If one mass doubles force doubles (direct proportion). (b) If distance halves force increases by factor of 4 (inverse square: 1/(0.5)² = 4). Combined: if mass doubles AND distance halves force increases by factor of 8.
11
New cards
Three asteroids A B and C are in a line. A has mass 3.8 × 10⁹ kg and is 1600 m from B. C has mass 5.1 × 10⁹ kg and is 2400 m from B. B has mass 8.5 × 10⁹ kg. Determine the net force on B.
Fₐ on B = GMₐMᵦ/r² = (6.67×10⁻¹¹ × 3.8×10⁹ × 8.5×10⁹)/(1600)² = 0.84 N toward A. Fᶜ on B = (6.67×10⁻¹¹ × 5.1×10⁹ × 8.5×10⁹)/(2400)² = 0.50 N toward C. Forces oppose so Fₙₑₜ = 0.84 - 0.50 = 0.34 N toward A (2 s.f.)