Skin overview
1/127
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
what are the functions of the skin?
physical barrier, immunologic functions, temperature regulation, protection from radiation, nerve sensation, injury repair
describe the function of the skin as a physical barrier
regulates water loss, protects against mechanical/chemical/microbial insults
dysfunction leads to: dehydration, injury, infection, and inflammation.
describe the skin’s immunologic functions
senses and responds to pathogens — Langerhans Cell in epidermis, part of cell mediated immune response
dysfunction leads to: infection, skin cancer, inflammation, allergy
describe the skin’s role in temperature regulation
insulation via fat and hair
cooling via sweat and superficial microvasculature
dysfunction leads to: overheating, hypothermia, Raynaud’s Phenomenon
describe how the skin provides protection from radiation and what dysfunction leads to
pigmentation (melanin)
dysfunction leads too:
Xeroderma Pigmentosum: decreased ability to repair DNA
Albinism: skin, hair, or eyes have little or no color
Vitiligo: white patches on skin
describe nerve sensations related to the skin
sensory receptors for physical interactions
dysfunction can lead too: pruritis, dysesthesia (painful, burning, itchy sensation), insensitivity to injury
describe how to skin repairs injuries
coagulation, inflammation, proliferative/migratory (tissue formation), and remodeling phases
dysfunction can lead to: delayed wound healing
describe the skin’s effect on quality of life
psychological aspects of damage or defects
dysfunction can lead to: anxiety, depression, etc
what is the endocrine role of the skin?
sun converts to vitamin D!
several hormones are activated or deactivated by skin
what is excreted through the skin?
water, ammonia, uric acid, alcohol, salicylic acid, heavy metals
methamphetamine/amphetamine in sweat
what is the largest organ of the body?
the skin
what are the three layers of the skin?
Epidermis, Dermis, and Hypodermis
what is the epidermis composed of?
consists primarily of keratinocytes
what is the dermis composed of?
fibroblasts, collagen, elastin
what is the hypodermis composed of?
fat, sweat glands, hair grows
what are filaggrin and keratin?
important proteins in barrier function
filaggrin protein mutations are thought to contribute to skin conditions such as _____________________
eczema and chronic dry skin
what is keratin’s role?
is a protein that helps protect the outer later of skin from water loss, UV radiation, and other skin stressors
which skin protein prevents the invasion of allergens/extrinsic stimuli?
filaggrin
what are melanocytic nevi?
Moles which are benign collections of melanocytes
what is the ABCDE rule for identifying melanomas?
A is asymmetry: one-half of mole doesn’t match other
B is for border: irregular borders
C is for color: not the same color or diff shades
D is for diameter: > 6 mm across
E is for evolving: mole is changing in size/shape/color
what is melanoma?
a malignancy of melanocytes
what are macules?
flat colored spots
what are papules?
raised colored spots
how can you differentiate between a macule and papule?
dim lights, shine pen light at right angle to lesion, if a shadow is cast, then it’s a papule (<1.5 cm diameter)
macules have no shadow and <1.5 cm diameter
nodule bump has shadow and > 1.5 cm diameter
what are patches or plaques?
patch is a colored spot (larger than papule)
plaque is a raised patch (larger than papule)
what are the different types of fluid filled lesions, “blisters”?
vesicles (fluid)
bullae (is vesicle > 2 cm diameter, fluid)
pustules (pus)
how do you decipher if a lesion is fluid filled or not?
place a tip of penlight against lesion — solid lesions do not transmit light, while fluid filled lesions fill with a red “glow”
which things have proliferation into the dermis?
cyst (liquid) and nodules (solid)
what is a fissure?
“crack” linear, cleavage
what is erosion?
loss of epidermis — weeping, crusting, and usually no scar
what is an ulcer?
loss of epidermis and part of dermis — can become infected, and often heal with scars
what is excortiation?
erosion or ulcer caused by scratching
what are wheals and flares?
may be from allergic reaction but can be from other causes: wheal is the swelling and release of serum in tissue (bump on skin), while flare is the dilation of blood vessels (erythema)
what is a burrow?
often seen with scabies — the trail they leave under the skin
what is a sinus?
hole in the skin (cutie cole’s ear)
what is striae?
basically stretch marks
what are petechiae?
round spots on skin when capillaries break open, pinpoint, < 4 mm, can be red/brown/or purple
negative diascopy (do not lose color when you press on them)
what is purpura?
when the petechiae dots combine into a big “dot” — 4-10 mm petechiae, can be red/brown/or purple
negative diascopy (do not lose color when you press on them)
what is telangiectasia?
small dilated blood vessels, red or purple, “spider veins,” or “broken blood vessels”
what is lichenification?
thickening of skin
what is ecchymosis?
discoloration of the skin (>10 mm)
what are scales?
fine and desquamation that occurs in cold weather, low moisture air, meds, and from soaps
what is ichthyosis?
hereditary, thick, dry, fish scale like
what are some of the causes for telangiectasia?
aging, rosacea, pregnancy, sun exposure/damage, and varicose veins
what are some of the causes for petechiae/purpura?
infection and reactions to medications (nitrofurantoin, penicillin)
what is a bruise?
falls under umbrella of ecchymosis — injury to small blood vessels under skin, also known as contusion
what is a hematoma?
falls under umbrella of ecchymosis — blood pools and is trapped outside blood vessels, may not be seen
which medications can cause desquamation?
phenytoin and sulfa drugs
what is diascopy?
test for blanchability by applying pressure with finger or glass slide
what is the diascopy of inflammatory lesions (psoriasis, urticaria, eczema)?
(+) diascopy
what is the diascopy of hemorrhagic lesions (petechiae-steroid induced atrophy of bv)?
(-) diascopy
what is the diascopy of nonvascular lesions (mole with distinct edges)?
(-) diascopy
what is a positive diascopy?
skin blanches
what is a negative diascopy?
skin does not blanch
what are the different shapes of papules?
dome shaped, flat topped, umbilicated, acuminate, verrucous, pedunculated
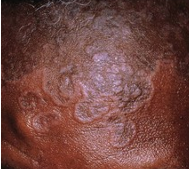
what is this image?
annular/polycyclic/grouped
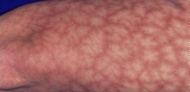
what is this image?
reticular (can occur from minocycline or amantadine)
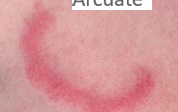
what is this image?
arcuate
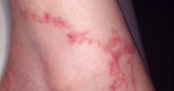
what is this?
serpiginous
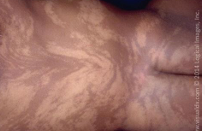
what is this image?
whorled
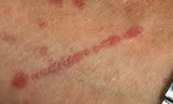
what is this image?
linear
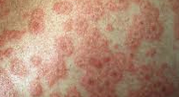
what is this image?
targetoid
what does intertriginous mean?
skin folds
what does acral mean?
peripheral
what are dermatomes?
an area of skin that is supplied by a single nerve
what is lymphangitic?
transport WBCs in the body, rid body of toxins (something follows the lymph nodes)
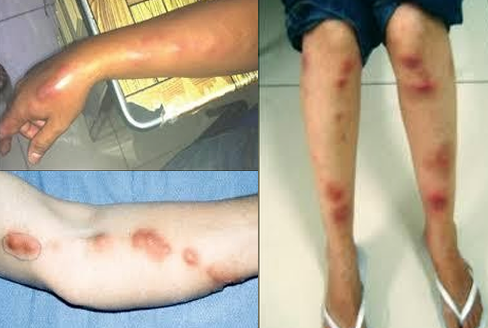
what is cellulitis?
skin infection — red, swollen, warm to touch, painful, pus
what is impetigo?
group A b-hemolytic Streptococcus pyogenes (presents with yellow, silver grey/honey colored crust)
what is folliculitis?
infected hair follicle (not cellulitis)
what is furuncle?
(boil) cellulitis arising from single hair follicle
what is carbuncle?
large furuncle with cellulitis contains multiple hair follicles that has connecting around cuticle
what is paronychia?
cellulitis around cuticle
what is necrotizing fasciitis?
“flesh eating bacteria,” multi-organism, aerobic/anaerobic, often GABHS, may lose soft tissue
what evaluation/questions should be done to describe skin integrity?
intact or presents with injury? classify the type of injury, describe the type/shape/arrangement and distribution of injury/lesion
types of wounds (puncture/hole, abrasions, laceration, contusion, burns)
what are the pressure ulcer scale stages?
Stage 1: just erythema of the skin
Stage 2: erythema with the loss of partial thickness of the skin including epidermis and part of the superficial dermis
Stage 3: full thickness ulcer that might involve the subcutaneous fat
Stage 4: full thickness ulcer with the involvement of the muscle or bone
what is edema?
swelling d/t excess fluid (note location), pitting vs. non-pitting (grade 4 is deeper than grade 1)
what evaluation/questions should be done to review sensory status?
determine if intact or altered
if issues, not where: loss of protective sensation, two-point discrimination (touch test), temperature (can pt discriminate warm/cold), deep pressure, pin prick
how does dry skin present?
flaking, scales, fissures, cracks
how does moist skin present?
sweat, incontinence, weeping, exudate
what do atrophic changes of the skin look like/mean?
shiny or hairless extremities “tobacco paper skin”
might indicate vascular compromise (or age, or excessive topical steroid use)
what can effect skin turgor/texture?
Skin that isn’t intact may be caused by irritation or trauma. Rough skin may be caused by dermatologic or systemic conditions (eczema, psoriasis)
define turgor
elasticity of skin (poor marker in dehydrated or edematous patients, or in the elderly but not reliable marker of hydration)
what is skin texture?
scar tissue forms when wound heal, different texture/quality than normal skin, may cause cosmetic concerns/patient distress
what are acne scars?
pitting, sunken recesses
what are contracture scars?
tightening of skin may impede mobility
what are hypertrophic scars?
red, raised bump does not exceed wound boundaries (surgery scars)
what are keloid scars?
overgrowth of colloid/granulation tissue results in benign tumorous growth (trauma, piercings, ance, surgery)
what evaluation/questions should be done to describe nails and hair?
nails — reflect patients health (color, shape, contour, clubbing, texture, thickness)
hair:
too much in females? hirsutism
too little? alopecia
brittle, dry hair? sx of underlying disease or excess care
what evaluation/questions should be done when evaluating skin color?
normally smooth, slightly most, and same tone throughout
tone = melanocyte concentration
note color of skin and uniformity (color may serve to confirm diagnosis, or may be diagnostic)
hypopigmented or hyperpigmented
what is the distribution of absent color?
small, circumscribed areas, generalized
what are the possible causes/terminology for absent color?
vitiligo - loss of skin color in blotches
albinism - genetic, partial, or complete loss of color in skin, eyes, and hair
what is the distribution of blue colored skin?
around lips, buccal mucosa, or generalized
what are the possible causes/terminology for blue skin?
cyanosis (in African Americans, blue gingivae are normal)
what is the distribution for deep red colored skin?
generalized
what are the possible causes/terminology for deep red colored skin?
polycythemia vera — type of cancer that makes too many RBCs
what is the distribution of pink skin?
local or generalized
what are the possibel causes/terminology for pink skin?
erythema
what is the distribution of tan/brown colored skin?
facial patches
what are the possible causes/terminology for tan/brown skin?
chloasma, butterfly rash (SLE)