respiratory system part 2
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Gas Transport
Oxygen is carried by Hemoglobin in RBCs
Only a small amount of CO2 is carried by hemoglobin.
Most is converted into Bicarbonate by the enzyme Carbonic Anhydrase in RBCs
CO2 + H2O ↔ H2CO3 ↔ HCO3⁻ + H⁺
Reaction reverses in the lungs, allowing for the release of CO2
Acid
substance that donates a proton (H+)
Base
substance that accepts proton (H+)
pH
a scale to measure how acidic or basic a substance is.
Related to the concentration of H+ in the solution.
the lower the pH
the greater the [H+] = more acidic
the higher the pH
the lower the [H+] = more basic
Equilibrium reaction
a reaction in which the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. No net change in amounts of reactants or products
Forward reaction
reactants to products
Reverse reaction
products back to reactants
Le Chatelier's Principle
You can manipulate the direction of an equilibrium reaction by adjusting amounts of reactants or products.
Shift right
forward reaction progresses more.
Reactants used up, products made
Shift left
reverse reaction progresses more.
Products used up, reactants made.
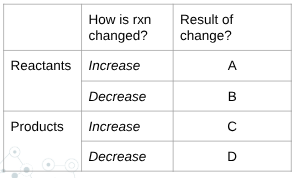
what is A?
shift right
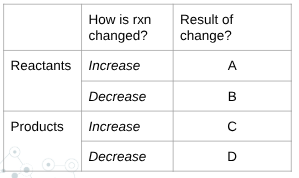
what is B?
shift left
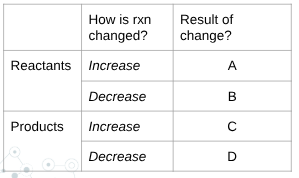
what is C?
shift left
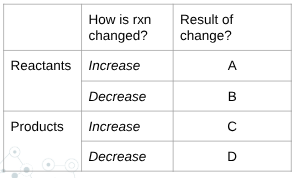
what is D?
shift right
pH Regulation
The Bicarbonate buffer system allows for regulation of blood pH
The production of Bicarbonate also produces H⁺ which makes the blood more acidic
Therefore, by controlling the amount of CO2, the body can control the pH of the blood.