3 - Regulating blood glucose
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What receptor does glucagon function by and what does it do?
G protein coupled receptors and increases blood glucose levels
What cells secrete glucagon?
α islet of langerhans cells
What receptor does insulin function by and what does it do?
enzyme linked receptors and decreases blood glucose levels
What cells secrete insulin?
β islet of langerhans cells
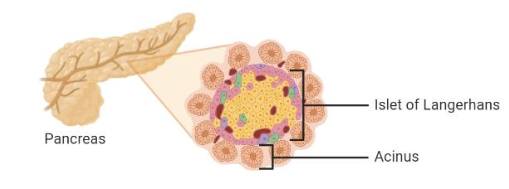
What is the funciton of pancreatic accini? (2 points)
exocrine tissue that secretes digestive enzymes which flow through the duodenum into a duct
these enzymes produce calcium carbonate to maintain alkaline environment
List the 4 main types of islet of langerhans cells
alpha
beta
delta
pp
What to delta islet of langerhans cells secrete and what is its purpose?
somatostatin which suppresses insulin and glucagon
What to PP islet of langerhans cells secrete and what is its purpose?
pancreatic polypeptides (leptin) which regulates widespread appetite control
What is normal blood glucose levels?
4-8 mmol/L of blood
State two effects of hyperglycaemia
causes brain function impairment if sustained
glucose can stick to lipids and proteins which cause kidney, nerve, and capillary damage
State one effect of hypoglycaemia
causes changes in osmolarity
Insulin and glucagon work…
antagonistically
List two ways in which β islet of langerhans cells measure blood glucose concentration
K+ channels close when ATP is bound
Voltage gated Ca2+ channels open when cell depolarises
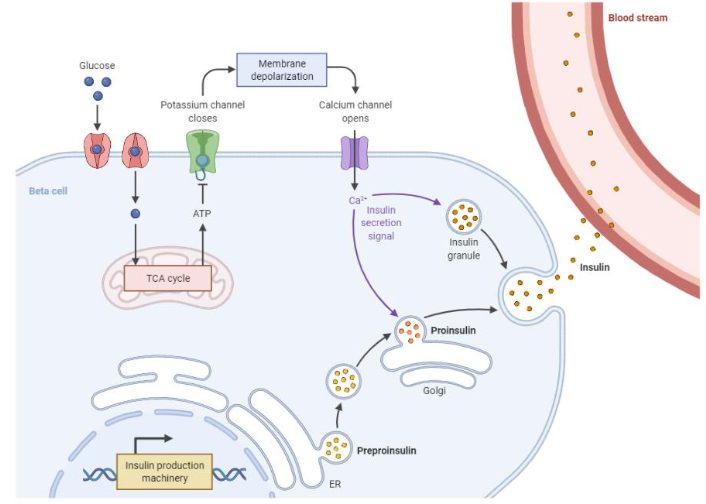
How do cells sense and respond to glucose? (4 points)
glucose is transported into cell via GLUT2 transporter
glucokinase converts glucose to glucose 6 phosphate (decreases glucose concentration = more can enter & can be used in glycolysis)
produced ATP binds to K+ channel so that they cant leave
depolarisation opens Ca2+ channels, its increase resulting in exocytosis of insulin granules

How do liver / muscle cells respond to insulin? (2 points)
insulin binds to tyrosine kinase receptor which initiates signal cascade
signal cascade results in exocytosis in GLUT4 receptors, inserting them into the membrane, facilitating glucose entry