RCC 1003
1/224
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
225 Terms
Inlay vs Onlay
Inlay fits inside the cusp
Onlay is larger and restore cusp
Finish Line vs Margin
Finish line is most external of margin (Where tooth meet crown) (point of failure)
Margin is outer edge of crown
Facebow vs Centric Relation
Facebow: Transfer maxillary to articulator
Centric Relation: Maxillo-Mandible relationship independent of tooth contact
What is the impression material for bite registration
Polyvinyl Siloxane (PVS)
True or False: The path of insertion should encroach upon the pulp or adjacent teeth
False (it should not)
Taper is ______ of two opposing external walls of a tooth
convergence
Extension form angle of convergence
What is the ideal taper
6 degrees
A complete straight will have undercut (too much retention)
What must be resolved prior to treatment
Perio issues
Interocclusal record is a registration of the positional relationship of the ______ teeth or arches
opposing
Impression tray must have adequate _______ to avoid distortion
rigidity
Resin thickness of ______ is needed for adequate rigidity. Clearance between the tray and the teeth should also be ______.
Elastomeric impression materials are considered most stable when they have a uniform thickness of _______
2 to 3 mm
2 to 3 mm
What is tissue stop for?
Ensure impression seat at same place everytime
Uniform thickness
What is marginal percolation
Leakage of salviary and microbial products via the restorative margins
Which stress breaks most restoration
shear stress (not along straight line)
Galvanic reaction/shock: Pain sensation caused by the electrical current generated when two ______ metals are brought into contact in the oral environment
dissimilar
What is the minimally required clearance of following
Buccal cusp
Lingual cusp
Marginal ridges and fossae
1.5 mm
1.0 mm
1.0 mm
What type of gold alloy is for crown
Type 3 or 4
Type 1 and 2 is too soft
What metal ceramic alloy is similar to type IV gold
High Noble
What is the reduction of functional and nonfunctional cusp
Functional: 1.5 mm (lingual of maxillary) (buccal of mandibular)
Nonfunctional 1.0 mm
What is crown lengthening
cutting gingival tissue to expose more tooth
If the occlusal width of the preparation exceeds ______ to ______ the buccolingual intercuspal distance, a restoration offering more protection such as an onlay should be planned
1/3 to 1/2
Can you have convergent walls for indirect restoration?
No it has to be divergent for insertion
What kind of characteristic do gold restoration need
bevel so that gold can flow through
When is chamfer indicated and when is shoulder
Chamfer: FCG and Ligual of PFM (850 bur)
Shoulder: PFM and All ceramic (847 bur)
What burs are shoulder and what is chamfer
Chamfer 850
Shoulder 847 and 848
What does gold look like in radiograph?
What does porcelain look like?
Amalgam (zirconia look like metal)
Resembles normal tooth structure can see through
_______ cannot be used as Fixed partial denture (bridge)
Onlays
Porcelain is a ceramic that contains a _______ matrix
glass
Un-bonded restoration are _______
brittle
Try-in can result in fracture
Porcelain is etched with _______ acid
Increases micromechanical retention
hydrofluoric
Silane is a ________ agent
Contributes to covalent and hydrogen bond
coupling
Can you bond gold
No
Sharp angles in preparation lead to ________ in restoration
fracture
Onlay longevity can be enhanced if the preparation allows for at least _______ occlusal ceramic thickness and incorporates additional retentive features
2 mm (magic number)
Which should be made first: Interim restoration or Final impression
Interim Restoration
________ ________ is the contour of a tooth or restoration, such as a crown on a natural tooth or dental implant abutment
Emergence profile
Gingival health is better maintained if the crown is slightly ________ rather than ________
________ causes plaque trapping and gingival inflammation
undercontoured, overcontoured
Overcontoured
Luting agent (cement) does/does not provide significant help with retention
does not
PMMA and PEMA
PMMA: Strong material but come with powder and liquid and very exothermic (very hot will fry pulp)
PEMA: Similar to PMMA, but has a slower setting time and less heat generation, improving usability in dental applications. (liquid is carcinogen)
Smell Terrible
PEMA can be attacked by _______
eugenol
Atundant (make pulp tissue feel better)
What is the material of provisa plus
Bis-acrylics
Less exothermic
Less shrinkage
Less odorous
Higher cost
Tine of Explorer
The tip of explorer
What is iatrogenic damage
Damage occurred during treatment
Biological width is defined as the dimension of soft tissue which is attached to the portion of the tooth coronal to the crest of ________ ________
alveolar bone
2 mm
Over Contour causes ________ disease
Under Contour causes ________
periodontal
recession
________ gingival margin is preferred
Supragingival
The margin of a ________ crown is to be hidden behind the labiogingival crest
metal-ceramic
A smooth margin is considerable ______ than a jagged one
shorter
What happens if chamfer is wider than half the bur used to form it
It causes J margin
Margin should be smooth and distinct and allow for approximately _______ of metal thickness at the margin
0.5 mm
(in lab is 1mm)
________ crown is considered a all ceramic
Zirconia
Zirconia requires ________ for it to density to crown
sintering (require high heat)
Cost of Zirconia compared to Full Cast Noble
Zirconia is cheaper
Having increased taper reduces ________ of the tooth
retention
Glass-based ceramics are etched with ________ acid and bonded with _______ coupling agent
hydrofluoric, silane
Does not work with zirconia
________- modified ________ allows zirconia to act like glass based ciramic
Silica, alumina
Sandblasting the ________ surface of zirconia crown develops the bond
intaglio (inside)
Coupling agent of zirconia
MDP (increase bond strength)
APC Concept
Method enhance bond strength of Zirconia
Step A: Air-particle abraded with alumina or silica-coated alumina (50 to 60 micron)
Step P: MDP (Primer) on tooth
Step C: Resin cement used to ensure polymerization
Which crown causes the least opposing wear
Zirconia Crown especially when polished
What is a Z bur
Bur to cut zirconia
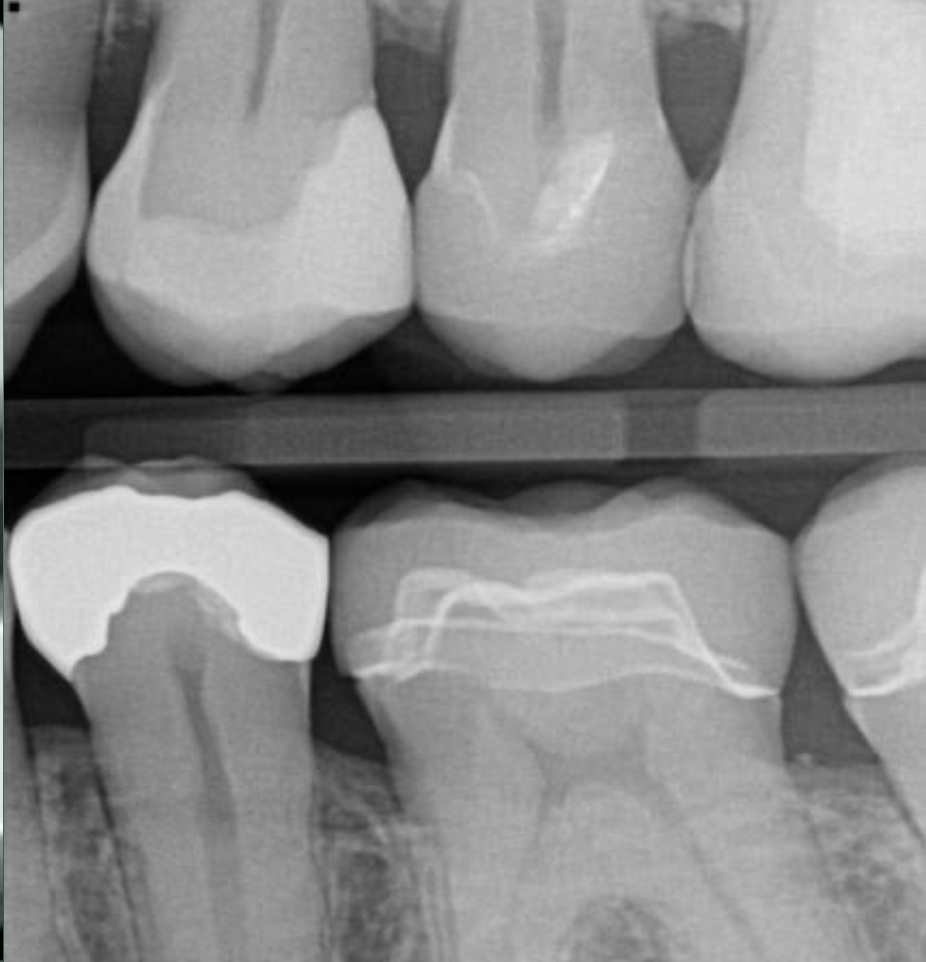
What restoration is the molar
Emax
What is a ferrule
A ferrule is a small metal band or ring used to reinforce a dental restoration, particularly at the cervical area of a crown, enhancing retention and stability.
Usually 1.5 to 2 mm
Multi-functional vs Mono-functional
Linear Branched Cross-linked
Multi-functional stronger
Cross-linked stronger
Polymer are _______
crosslinked
Are ceramic composites?
Yes
Methyl Methacrylate vs Higher Alkyl Methacrylate
Higher Alkyl (Ethyl and Isobutyl Methacrylate) overcome drawback of MMA (high level of monomer release and high exothermic)
_______ can break the bond of higher alkyl methacrylate
Eugenol (found in temporary cement and IRM)
What is Bis-Acryl
Composite based provisional material
Doughy vs Rubbery Stage of acrylic
Doughy: No more monomer on surface (take impression)
Rubbery: Polymerization continues
Fiber-reinforced Provisional
For longer-term bridges
Multiple layers of Ribbond “Fiberglass”
Very strong but Ribbond prevents failure
PMMA vs Bis-acryl
PMMA is stronger
Can PMMA be used directly on tooth?
No it has strong exothermic reaction
Which technique is better: Direct or Indirect
Indirect
Don’t heat pulp
Better restoration
Disadvantage is require a good stone cast
An impression is an imprint or ______ likeness
A ______ reproduction, or cast will be made from the impression
negative
positive
What is HIRD
Hemostasis (Control bleeding)
Isolation (No saliva)
Retraction (Retract Gingival tissue)
Directions
Local anesthesia may help with saliva control by blocking nerve impulses from the ______
PDL
Atropine, Dycyclomine, and propantheline are _________
anticholinergics
Inhibit parasympathetic innervation and reduce saliva
What is the caution of glaucoma pt
No anticholinergics or will cause permanent blindness
What is another drug to reduce saliva that is safer than anticholinergics?
Clonidine (Antihypertensive)
Avoid in pt taking other antihypertensive
Not recommended
Mechanical, Chemical, and Surgical Displacement of Gingival Tissue
Mechanical: Retraction Cord
Chemical: Astringent (aluminum or iron salt) cause transient ischemica shrinking gingival tissue
Double cord technique
Thin cord placed without overlap at bottom
Second cord placed to to for lateral tissue displacement
Latter is removed immediately before impression making and initial cord left in place
Astringent contain aluminum or iron salts and cause a ______ _____, shrinking the gingival tissue
transient ischemia
Impression must be taken immediately upon removal
Repeated use should be avoided (can cause gingival recession)
What is ferric sulfate gel
Viscostat for hemorrhage control
What is aluminum chloride
Hemostatic agent and promote tissue shrinkage
What material is needed to use reversible hydrocolloid
Water cooled trays
Inhibition of Reversible Hydrocolloid
Displacement of one fluid by another immiscible fluid
Polysulfide as Final Impression
Takes time to set
Smell bad
Need to mix (error)
Not dimensionally stable
Condensation Silicone as final impression
Poor wetting characteristics (need very dry)
Not as good
Polyether vs Polyether with silicone
Polyether is very stiff
Addition of silicone (poly vinyl siloxane)
What is the final impression material we use
Polyether with addition of silicone
Latex glove inhibit the setting of what impression material?
PVS with silicone
Vinyl Siloxane
Closed-Mouth Impression Technique is made at _______
MICP (Maximum intercuspation)
No eccentric relationships recorded so need to be adjusted
Retraction for Impression vs Digital Impression
Impression: Tissue retracted vertically and laterally
Digital: Laterally
What is the disadvantage of digital impression
Problematic in subgingival cases
Must have clear margin and finish line
PFM require _______ tooth reduction compared to FCM and Zirconia
More
Two material both need sufficient thickness
Sufficient thickness needed to mask color of metal
Clearance vs Reduction
Clearance is difference between opposing tooth
Reduction is how much tooth you actually cut off
You may have enough visual clearance but reduction is what matters to success of restoration
Which restoration can pt have nickel sensitivity
PFM with nickel (cause most allergy)
Can have dramatic gingival response
Pt that can’t have costume jewelry
What kind of margin is for periodontally involved cases where gingival health is important
Shoulder beveled
Beveled shoulder only works on what kind of crown?
Metal cermic crown
Do not work on ceramic