Astr 1210 Quiz 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/129
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:39 AM on 2/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
1
New cards
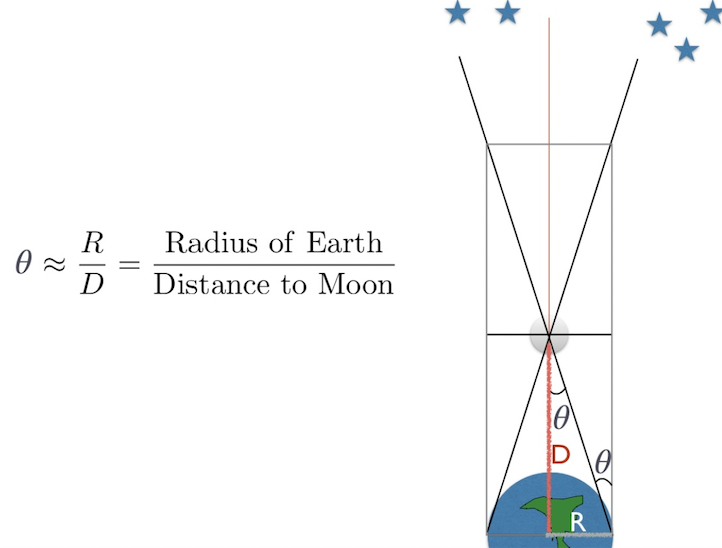
Small angle formula
angle(θ)(radians)=Size/distance
2
New cards
Degrees=
radians x 180/π
3
New cards
Angle(arcsec)=
1/distance(parsec)
4
New cards
Distance(parsec)
1/angle(arcsec)
5
New cards
Angle of parallax(radians)=
Distance between observers or to center of Earth/vertical distance
6
New cards
Parallax
the apparent displacement of an object due to the position of the observer
7
New cards
Angular size of Moon/Sun
1/2°
8
New cards
Movement of objects through the sky
Rise in East, set in West
9
New cards
Origin of Constellations
Discovered by a society at 36° N latitude(Babylonia)
10
New cards
Circumpolar
Stars visible year-round (none at equator)
11
New cards
Polaris
closest star to North Pole(North Star)
12
New cards
(T or F) All constellations can be seen from the equator at some point in a year
T
13
New cards
How many stars are visible?
6000
14
New cards
Which way do stars move?
Clockwise in Southern Hemisphere(or facing South)/Counter-clockwise in Northern Hemisphere(or facing North)
15
New cards
How long are constellations recognizable?
About 500,000 years
16
New cards
(T or F) Stars visible vary by time of day
T
17
New cards
How many official constellations are there?
88
18
New cards
Pointer star of Little Dipper
Polaris
19
New cards
Apparent magnitude
Brightness of stars(lower is brighter)
20
New cards
Relative magnitude
magnitude=2.5^difference in magnitude
21
New cards
Zodiac
set of 12 constellations through which the Sun appears to move over a year (originated 2500 years ago, now 10% off)
22
New cards
Ophiuchus
13th constellation left out of Zodiac
23
New cards
Aries
Zodiac of vernal equinox
24
New cards
Almagest
most important astronomy text prior to the Renaissance
25
New cards
Asterism
small part of a constellation (ex: Little Dipper)
26
New cards
Prime meridian
Longitude which passes through Greenwich, England (0°)
27
New cards
Arcsecond
1/60 of an arcminute or 1/3600 of a degree
28
New cards
Arcminute
1/60 of 1°
29
New cards
Constellation
a region of the sky with well-defined borders
30
New cards
Speed of Earth’s orbit
100,000 km/hour
31
New cards
Our solar system’s orbit of the Milky Way
800,000 km/hour, every 230 million years
32
New cards
Speed of Earth’s rotation
1000 km/hour (counterclockwise)
33
New cards
Speed of Milky Way towards Andromeda
300,000 km/hour
34
New cards
Speed of solar system relative to other stars
70,000 km/hour
35
New cards
Position of solar system in Milky Way
Halfway between the center and visible edge (26,000 LY from center)
36
New cards
Ecliptic plane
flat plane on which Earth orbits around the Sun
37
New cards
Local solar neighborhood
neighboring stars
38
New cards
Axis tilt
23\.5° from perpendicular to ecliptic plane (towards Polaris)
39
New cards
When was our solar system formed?
4\.5 billion years ago
40
New cards
Early universe only contained:
hydrogen and helium
41
New cards
Supernovae
large explosion which occur when a star dies
42
New cards
When was the Big Bang?
14 billion years ago
43
New cards
Local Group
Group of 40-70 galaxies including the Milky Way (Milky Way is one of the two biggest)
44
New cards
Galaxy
collection of stars held together by gravity and orbiting a common center
45
New cards
Supercluster
Largest known structures in the universe-cluster of galaxy clusters
46
New cards
Oort Cloud
theoretical cloud of small icy objects on the outskirts of our solar system
47
New cards
Galaxy cluster
group of galaxies help together by gravity
48
New cards
1 light year
10 trillion km
49
New cards
Alpha Centauri
Nearest star system to us (4.4 light years away)
50
New cards
Speed of light
300,000 km/second
51
New cards
AU
Earth’s distance from the sun (150 million km)
52
New cards
Width of Milky Way
100,000 light years
53
New cards
How many stars are in the Milky Way?
100 billion
54
New cards
Number of stars in the observable universe
100 billion x 100 billion
55
New cards
Distance of Sirius from Sun
8 LY
56
New cards
Distance of Jupiter from Sun
5\.2 AU
57
New cards
Sun’s diameter
1 million km
58
New cards
Distance of Mars from Sun
1\.5 AU
59
New cards
Distance of Pluto from Sun
39\.5 AU
60
New cards
Vega
Star towards which our solar system is moving at 70,000 km/hour
61
New cards
Distance to Orion Nebula
1500 LY
62
New cards
Nearest stellar neighborhood
Proxima Centauri(4.2 LY away)
63
New cards
Distance between Earth and Moon
384,400 km
64
New cards
Perihelion
Nearest point in a planet’s orbit to the Sun
65
New cards
Aphelion
Farthest point in a planet’s orbit from the Sun
66
New cards
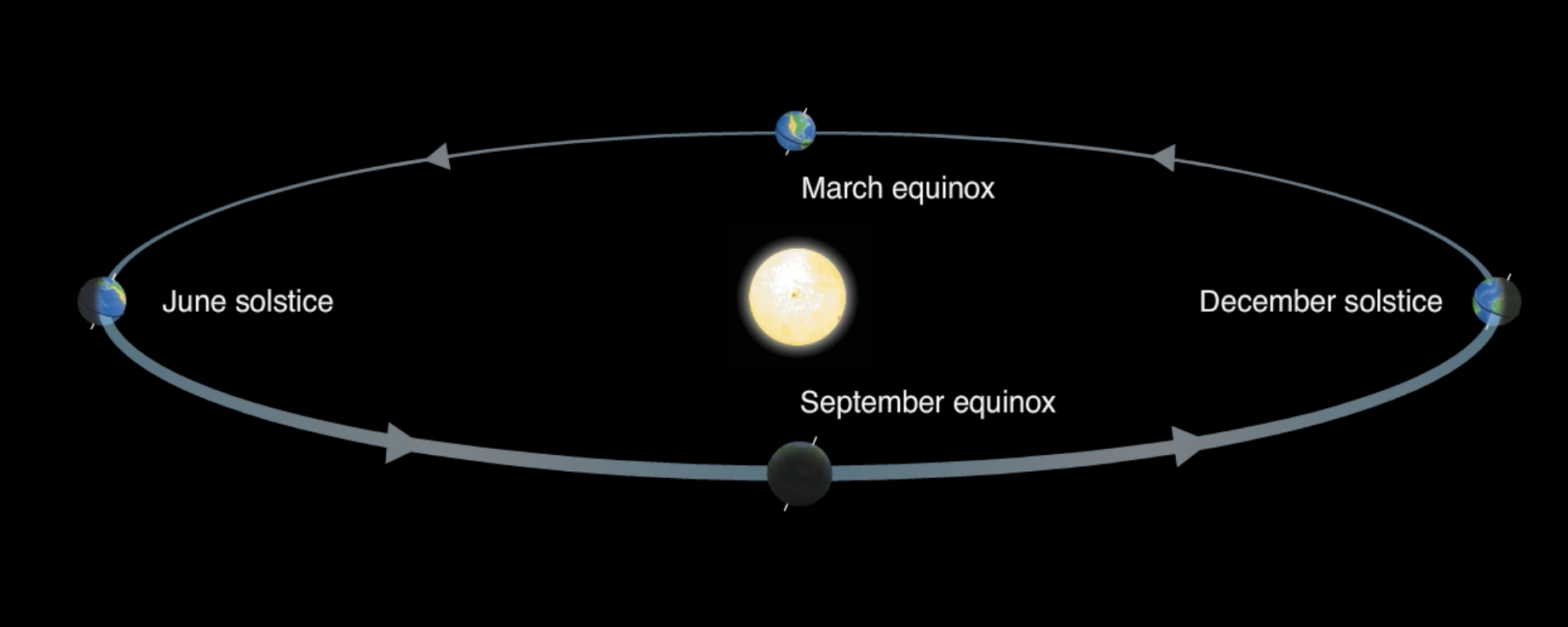
Summer solstice
When the Northern hemisphere is most tipped towards the Sun (June 21)
67
New cards
December solstice
When the Northern hemisphere is tipped furthest away from the Sun (December 21)
68
New cards
Vernal equinox
When the Northern hemisphere becomes tipped towards the Sun + the moment when the Sun’s path crosses the celestial equator (March 21)
69
New cards
Autumnal equinox
When the Northern hemisphere starts to be tipped away from the Sun (September 22)
70
New cards
Precession
a gradual wobble of the Earth’s axis’ orientation in space caused by gravity, affects timing of the seasons
71
New cards
Equinox
Day where most locations have equal amounts of daylight and night
72
New cards
Cause of seasons
Change in Earth’s axis tilt relative to the Sun and its effect on the angle at which sunlight hits the ground
73
New cards
How much does Earth’s distance from the Sun vary over a year?
3% (closest in January)
74
New cards
Cycle of Earth’s precession
26,000 years
75
New cards
What is the purpose of leap years?
To keep the dates of solstices/equinoxes about the same
76
New cards
When does the equator get the least direct sunlight?
The solstices
77
New cards
When is the Sun at peak height in the sky for someone on the equator?
Equinoxes
78
New cards
Tilt of the Moon
5° from ecliptic
79
New cards
Globular cluster
cluster of stars
80
New cards
Betelgeuse
Star 1000x the size of the Sun, 8 million years old
81
New cards
What causes apparent retrograde motion?
Earth surpassing other planets in its orbit
82
New cards
What planets are visible from Earth?
Mercury, Venus, Mars, Saturn, Jupiter
83
New cards
How old is the Sun?
4 billion years
84
New cards
Distance=
velocity x time
85
New cards
How far are we from Andromeda?
2\.5 LY
86
New cards
Angular size:
the angle created by an object’s linear boundaries when they reach the ground
87
New cards
Ecliptic path
path that the Sun traces around the Earth/Celestial sphere over its orbit (mirrors ecliptic plane)
88
New cards
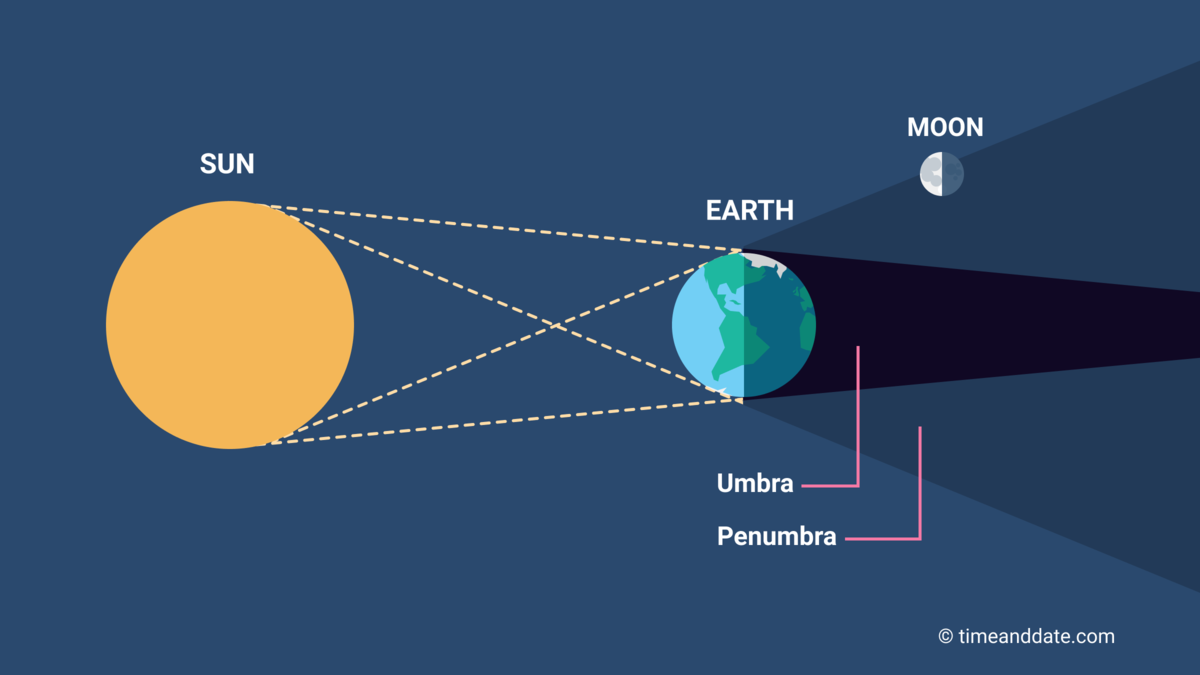
Lunar eclipse
When the Earth aligns between the Sun and Moon; two total eclipses every 3 years
89
New cards
Solar eclipse
When the Moon aligns between the Earth and Sun; total eclipse every 18 months
90
New cards
Umbra
Earth’s full shadow
91
New cards
Penumbra
Earth’s partial shadow
92
New cards
Penumbral lunar eclipse
When the Moon only passes within Earth’s penumbral shadow

93
New cards
Partial lunar eclipse
When the Moon is partially covered by Earth’s umbral shadow

94
New cards
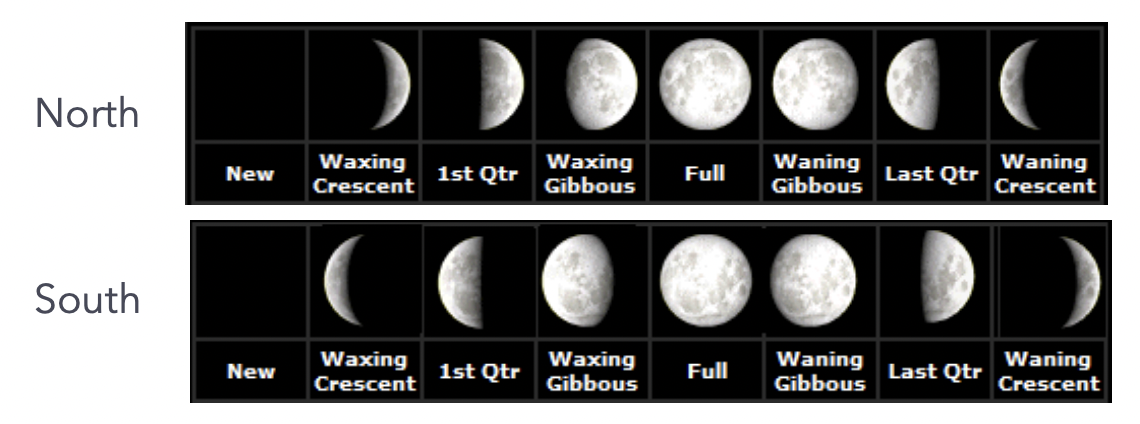
Moon phases
waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full, waning gibbous, third quarter, waning crescent, new (appears reversed in Southern hemisphere)
95
New cards
Length of cycle of phases
1 month/29.5 days (counterclockwise when facing Sun)
96
New cards
Moon rise/set times
Full: Rise-Sunset
Set-Sunrise
* Varies counterclockwise(sunset, —, midnight, —, sunrise, —, noon, —)
Set-Sunrise
* Varies counterclockwise(sunset, —, midnight, —, sunrise, —, noon, —)
97
New cards
Earthshine
subtle illumination of moon’s face by sunlight reflected off Earth
98
New cards
How long does solar totality last?
A few minute
99
New cards
How long does lunar totality last?
About an hour
100
New cards
Annular solar eclipse
Solar eclipse where moon is directly in front of Sun but not large enough to cover it completely