Exam Two - notes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/178
Earn XP
Last updated 1:55 AM on 3/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
179 Terms
1
New cards
obligatory Intracellular Parasites require what to multiply
a living host cell
* there are some bacteria such as chlamydia and rickettsia that require living host to multiply
* there are some bacteria such as chlamydia and rickettsia that require living host to multiply
2
New cards
why do doctors sometimes give us antibiotics when we have a different infection"?
to treat possible secondary infections
* hospital settings are teeming with microbes, so just being there with a weakened immune system makes us susceptible to other infections, so they preemptively give us antibiotics to treat them
* hospital settings are teeming with microbes, so just being there with a weakened immune system makes us susceptible to other infections, so they preemptively give us antibiotics to treat them
3
New cards
True or False: viruses DO NOT posses both DNA and RNA
TRUE
4
New cards
general characteristics of Viruses
* obligatory Intracellular Parasites
* contain DNA OR RNA
* contain a protein coat
* they have No Ribosomes
* they have no ATP
* contain DNA OR RNA
* contain a protein coat
* they have No Ribosomes
* they have no ATP
5
New cards
host range
the spectrum of host cells a virus can infect; determined by specific host attachment sites and cellular factors
6
New cards
bacteriophages are…
viruses that infect bacteria
7
New cards
virion
complete, fully developed viral particle
* nucleic acid
* capsid
* envelope
* spikes
* nucleic acid
* capsid
* envelope
* spikes
8
New cards
capsid
protein coat made of capsomeres (subunits)
9
New cards
spikes
projections from outer surface
10
New cards
what is the very FIRST thing a pathogenic organism must do?
attach
11
New cards
Due to the fact that we cannot grow a virus itself in order to observe its metabolic pathways or other characteristics, what must we do?
we can look at what they infect and learn things about them that way
12
New cards
viroid
composed solely of a short strand of circular, single-stranded RNA that has no protein coating
* the smallest infectious pathogens known
* the smallest infectious pathogens known
13
New cards
viral species
a group of viruses sharing the same genetic information and ecological niche (host)
* descriptive common names are used for species
* subspecies are designated by a number
* descriptive common names are used for species
* subspecies are designated by a number
14
New cards
bacteriophages form BLANK
plaques- clearings on a lawn of bacteria on the surface of agar
15
New cards
how can we grow animal viruses in a lab?
in living animals, in embryonated eggs, in cell structures
16
New cards
when growing animal viruses in embryonated eggs, how do we know if there is viral growth?
by changes or death of the embryo
17
New cards
with animal viruses growing in cell structures, how are they detected?
via their deterioration, or cytopathic effect (CPE)
* they make the stuff inside the host cell divide over and over again, until it bursts, spreading the Virus
* they make the stuff inside the host cell divide over and over again, until it bursts, spreading the Virus
18
New cards
one-step growth curve
the top is where we either die or defeat the virus
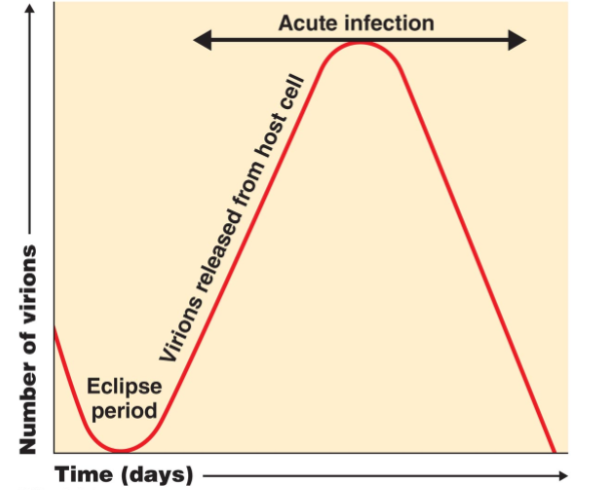
19
New cards
steps of the lytic cycle (multiplication of bacteriophages)
* attachment
* penetration- phages lysozyme opens the cell wall; the tail sheath contracts to force the tail core and DNA into the cell
* biosynthesis
* maturation
* release
* penetration- phages lysozyme opens the cell wall; the tail sheath contracts to force the tail core and DNA into the cell
* biosynthesis
* maturation
* release
20
New cards
TRUE or FALSE bacteriophages never actually enter the cell, but instead inject the information
TRUE
21
New cards
animal viruses are pulled in the cell by what mechanisms?
endocytosis
22
New cards
lysogenic Cycle (multiplication of bacteriophages)
* attachment
* entry
* integration
* cell division
* entry
* integration
* cell division
23
New cards
phage conversion
when the DNA of the bacteriophage Becomes Part of the Host DNA
* we are pretty sure that the majority of our DNA is from various viruses because of being infected over time
* we are pretty sure that the majority of our DNA is from various viruses because of being infected over time
24
New cards
steps for multiplication of Animal Viruses
* attachment
* entry by receptor- by endocytosis or fusion
* uncoating
* biosynthesis
* maturation
* release by budding
* entry by receptor- by endocytosis or fusion
* uncoating
* biosynthesis
* maturation
* release by budding
25
New cards
poxviridae
* DNA virus
* double-stranded DNA, enveloped
* causes skin lesion
* ex. vaccinia and smallpox
* double-stranded DNA, enveloped
* causes skin lesion
* ex. vaccinia and smallpox
26
New cards
Herpesviridae
* double-stranded DNA virus, enveloped
* HHV-1 and 2
* HHV-3
* HHV-4
* HHV-5
* HHV-6
* HHV-8
* HHV-1 and 2
* HHV-3
* HHV-4
* HHV-5
* HHV-6
* HHV-8
27
New cards
HHV-1 and HHV-2
simplexviruse; causes cold sores
28
New cards
HHV-3
causes chickenpox and shingles
29
New cards
HHV-5
ctyomegalovirus; important for OBGYN and PEDS
* torch test for different viruses and infections
* torch test for different viruses and infections
30
New cards
papovaviridae
* double-stranded, NON-enveloped
* papillomavirus- causes warts and HPV
* papillomavirus- causes warts and HPV
31
New cards
hepadnaviridae
uses reverse transcriptase to make DNA from RNA
32
New cards
rhinovirus
common cold
33
New cards
lyssavirus
rabies; a bullet-shaped virus
34
New cards
retroviridae
lentivirus (HIV)
* RNA virus that use DNA via reverse transcriptase
* RNA virus that use DNA via reverse transcriptase
35
New cards
sarcoma
cancer of connective tissue
36
New cards
oncogenes
transform normal cells into cancerous cells, if anything goes wrong with them in any way, a cancer state in the cell occurs
37
New cards
why cant we just Cure Cancer?
there are 217 different types of cancer because we have so many different tissue types in our bodies; melanomas tend to be very aggressive while nerve cell cancers are extremely slow
38
New cards
latent viruses
remain asymptomatic for long periods
may reactivate due to changes in immunity
may reactivate due to changes in immunity
39
New cards
persistent viral infection
occurs gradually over long periods and is generally fatal
40
New cards
prions
infectious proteins
41
New cards
etiology
the cause of a disease
42
New cards
pathogenesis
the development of disease
43
New cards
infection
invasion or colonization of a body by pathogens
44
New cards
disease
an abnormal state in which the body is not performing normal function
45
New cards
transient microbiota
may be present for days, weeks, or months
46
New cards
areas of normal microbiota
skin, eyes, nose and throat, mouth, large intestine, urinary and reproductive systems
47
New cards
skin microbiota
gram-positive
acinetobacter
candita-fungal (yeast)
acinetobacter
candita-fungal (yeast)
48
New cards
eye (conjunctiva) microbiota
tears and blinking also eliminate some microbes or inhibit others from colonizing
49
New cards
nose and throat microbiota
gram-positive
nasal secretions kill or inhibit many microbes, and mucus and ciliary action remove many microbes
nasal secretions kill or inhibit many microbes, and mucus and ciliary action remove many microbes
50
New cards
symbiosis
the relationship between normal microbiota and the host
* commensalism & mutualism
* commensalism & mutualism
51
New cards
Koch’s Postulates exceptions
some pathogens can cause several disease conditions
some pathogens cause disease only in humans (we cant exactly inject people with a virus and see what happens)
some microbes have never been cultured
some pathogens cause disease only in humans (we cant exactly inject people with a virus and see what happens)
some microbes have never been cultured
52
New cards
symptoms
changes in body function that are felt by a patient as a result of disease
* subjective
* like a pain scale
* subjective
* like a pain scale
53
New cards
signs
changes in the body that can be measures or observed as a result of a disease
54
New cards
syndrome
a specific group of signs AND symptoms that accompany a disease
55
New cards
communicable disease
a disease that is spread from one host to another
56
New cards
contagious disease
diseases that are easily and rapidly spread from one host to another
57
New cards
noncommunicable disease
a disease that is not spread from one host to another
58
New cards
incidence
number of people who develop a disease during a particular time period
* number is important here
* they take a snapshot of the number infected week to week for example and determine spread, only looking at new data and disregarding old
* number is important here
* they take a snapshot of the number infected week to week for example and determine spread, only looking at new data and disregarding old
59
New cards
prevalence
number of people who develop a disease at a specific time, regardless of when it first appeared
* takes in to account new and old cases
* takes in to account new and old cases
60
New cards
sporadic disease
a disease that occurs only occasionally
* every once in a while
* like the flu
* every once in a while
* like the flu
61
New cards
endemic disease
disease constantly present in a population
* in a certain area that is always present
* the bubonic plague in the US (Arizona)
* in a certain area that is always present
* the bubonic plague in the US (Arizona)
62
New cards
epidemic disease
a disease acquired by many people in a given area in a short time
* when the endemic level goes above baseline
* when the endemic level goes above baseline
63
New cards
pandemic disease
worldwide epidemic
64
New cards
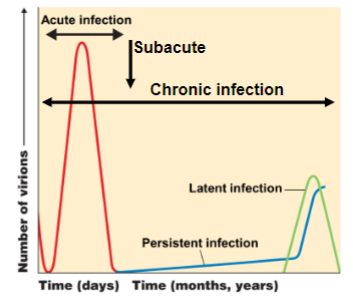
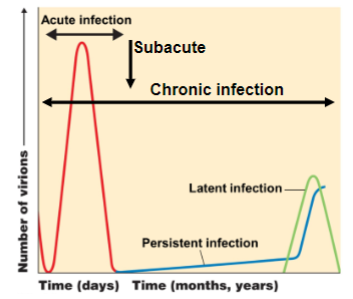
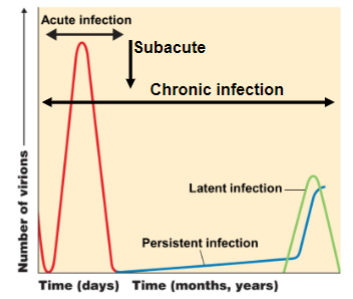
acute disease
symptoms develop rapidly but the disease lasts only a short time
65
New cards
chronic disease
symptoms develop slowly
66
New cards
subacute disease
intermediate between acute and chronic
67
New cards
latent disease
causative agent is inactive for a time but then activates and produces symptoms
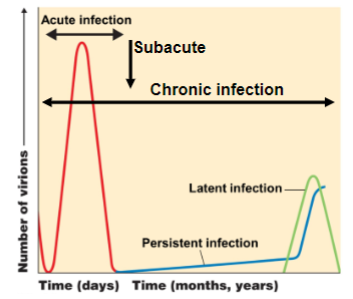
68
New cards
herd immunity
immunity on most of the population
* what we could have if people weren’t selfish and stupid
\
* what we could have if people weren’t selfish and stupid
\
69
New cards
focal infection
systemic infection that began as a local infection
70
New cards
sepsis
toxic inflammatory condition rising from the spread of microbes, especially bacteria or their toxins, from a focus of infection
71
New cards
bacteremia
bacteria in the blood
* the bacteria is just kinda there, floating around
* the bacteria is just kinda there, floating around
72
New cards
septicemia
also know as blood poisoning; growth of bacteria in the blood
* the bacteria are actually doing something
* the bacteria are actually doing something
73
New cards
secondary infection
opportunistic infection after a primary infection
* why we give antibiotics to prevent the secondary infection (not so much anymore)
* why we give antibiotics to prevent the secondary infection (not so much anymore)
74
New cards
subclinical disease
no noticeable signs or symptoms
* the problem with a lot of diseases is that they dont know they have and are just spreading the infection
* the problem with a lot of diseases is that they dont know they have and are just spreading the infection
75
New cards
development of disease
* incubation period
* prodromal period
* period of illness
* period of decline
* period of convalescence
* prodromal period
* period of illness
* period of decline
* period of convalescence
76
New cards
incubation period
the interval between initial infection and first signs and symptoms
77
New cards
prodromal period
short period after incubation; early and mild symptoms
78
New cards
period of illness
when the disease is most severe
79
New cards
period of decline
when signs and symptoms subside
80
New cards
period of convalescence
when the body returns to its pre-diseased state
81
New cards
fomite
nonliving object that can be used as a means to spread disease
* doorknob that an infected person touches
* doorknob that an infected person touches
82
New cards
vectors
arthropods; fleas, ticks, and mosquitoes
* mechanical transmission
* biological transmission
* mechanical transmission
* biological transmission
83
New cards
contributing factors to emerging infectious diseases
* genetic recombination
* evolution of new strains
* widespread use of antibiotics and pesticides
* changes in weather patterns
* modern transportation
* ecological disasters, war, and expanding human settlement
* animal control measures
* public health failure
* evolution of new strains
* widespread use of antibiotics and pesticides
* changes in weather patterns
* modern transportation
* ecological disasters, war, and expanding human settlement
* animal control measures
* public health failure
84
New cards
epidemiology
the study of where and when diseases occur and how they are transmitted in populations
85
New cards
CDC roles and measurements
collects and analyzes epidemiological information in the US
publishes morbidity and mortality weekly report (MMWR)
* morbidity
* mortality
* notifiable infectious diseases
* morbidity rate
* mortality rate
publishes morbidity and mortality weekly report (MMWR)
* morbidity
* mortality
* notifiable infectious diseases
* morbidity rate
* mortality rate
86
New cards
morbidity
incidence of a specific notifiable disease
87
New cards
mortality
deaths from notifiable disease
88
New cards
notifiable infectious diseases
diseases in which physicians are required to report occurrence
89
New cards
morbidity rate
number of people affected in relation to the total population in a given time period
90
New cards
mortality rate
number of deaths from a disease in relation to the population in a given time period
91
New cards
virulence
the degree of pathogenicity
92
New cards
TRUE or FALSE: doctors don’t need to report certain diseases to the CDC
FALSE
93
New cards
portals of entry
mucous membranes
* resp. tract
* GI tract
* genitourinary tract
* placenta
conjunctiva of the eye
parental route (other than the alimentary canal)
* broken skin
* bites
* injection
* puncture
* resp. tract
* GI tract
* genitourinary tract
* placenta
conjunctiva of the eye
parental route (other than the alimentary canal)
* broken skin
* bites
* injection
* puncture
94
New cards
alimentary canal
digestive tract
95
New cards
TRUE or FALSE: endospores, which enter through the skin, are the most virulent form of anthrax
TRUE
96
New cards
TRUE or FALSE: botulinum is so potent that only 0.03 ng/kg is a lethal dose
TRUE
97
New cards
how do pathogens penetrate Host defenses?
* capsules to impair phagocytosis
* cell wall components such as M proteins, Opa proteins, and waxy lipids
* enzymes
* coagulation
* kinases
* hyaluronidase
* collagenase
* IgA proteases
* cell wall components such as M proteins, Opa proteins, and waxy lipids
* enzymes
* coagulation
* kinases
* hyaluronidase
* collagenase
* IgA proteases
98
New cards
strep pyogenes use what to resist phagocytosis
M proteins
99
New cards
neisseria gonorrhea use opa proteins which allow them to..
attach to host cells
100
New cards
which disease uses a waxy lipid (mycolic acid) to resist digestion?
mycobacterium tuberculosis