3. metallic bonding
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bonding
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
metal elements exist as…
…giant metallic lattice structures
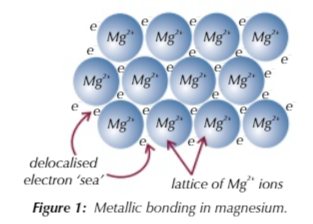
the outermost shell of electrons for metal atoms is delocalised…
leaving a positive metal ion like Na+ which are attracted to the negative delocalised electrons
metallic bonding is when
the positive ions and sea of delocalised electrons form a lattice
metallic bonding properties
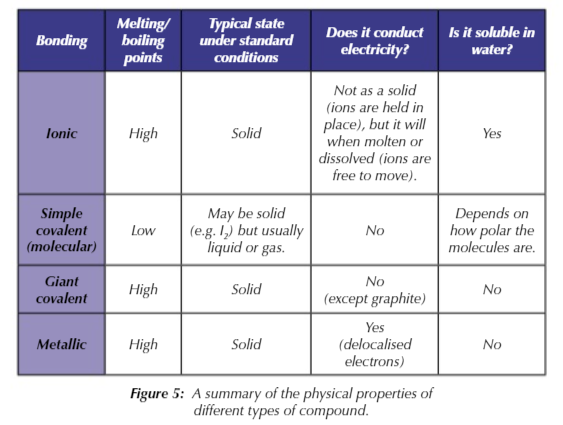
high melting point
ability to be shaped
conductivity
solubility
metals have a high melting point
because of strong electrostatic attraction between the positive metal ions and sea of delocalised electrons.
the more delocalised electrons per atom the stronger the bonding will be
therefore the higher the melting point that’s why Mg2+ has a higher melting point that Na+
there are no bonds holding specific ions together
so the metal ions can slide over each other when the structure is pulled making metals malleable and ductile (can be drawn into wires)
metals are good thermal and electrical conductors
sea of delocalised electrons can pass kinetic energy to each other AND they are free to carry the flow of charge
metals are insoluble apart from liquid metals
due to the strength of the metallic bonds
solids
high density which makes them incompressible. solid particles vibrate in a fixed position and cant move freely
liquids
similar density to solids and virtually incompressible. particles flow freely and randomly
gases
particles have loads of energy and are much further apart, density is generally low and its very compressible
in simple covalent substances the covalent bonds DONT break during melting/ boiling
you only have to overcome the weak intermolecular forces that hold the molecule together

in giant covalent substances you DO need to break the covalent bonds holding the atoms together
that’s why giant covalent compounds have very high melting and boiling points


✍(◔◡◔)✍(◔◡◔)
✍(◔◡◔)✍(◔◡◔)

(✿◕‿◕✿)
(✿◕‿◕✿)
