Ch 4: Eukaryotic Cells
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Phagocytosis is defined as
- the feeding of protozoans
- the uptake of liquid material by a eukaryotic cell
- the ingestion of solid material by a eukaryotic cell
- cells of the immune system that ingest pathogens
the ingestion of solid material by a eukaryotic cell
How is phagocytosis in the immune system different from protozoan phagocytosis?
- protozoan phagocytosis is used for feeding; phagocytosis by immune cells is used to fight infection
- protozoan phagocytosis is used to fight infection; phagocytosis by immune cells is used to feed the cells
- there is no difference between the two
protozoan phagocytosis is used for feeding; phagocytosis by immune cells is used to fight infection
Which of the following is mismatched?
- Pinocytosis: endocytosis of dissolved substances in small vesicles
- Phagocytosis: clathrin mediated endocytosis
- Exocytosis: an exportation process involving vesicles delivering their contents to the plasma membrane
- Receptor mediated endocytosis: a highly specific importation tool
Phagocytosis: clathrin mediated endocytosis
Which grouping of parasitic helminths includes hookworms?
- roundworms
- cestodes
- flukes
- flatworms
roundworms
Which of the following is mismatched?
- Basidiospores: sexual spores found in mushroom
- Zygospores: sexual reproduction
- Sporangiospores: asexual spores
- Ascospores: asexual reproduction
Ascospores: asexual reproduction
Choose the TRUE statement(s) about protists.
- Protists can be photosynthetic or heterotrophic
- The term protozoan describes animal-like protists but is not a true taxonomic ranking
- Protists only reproduce by asexual means
- Protozoans are mostly multicellular protists
- Protists can be photosynthetic or heterotrophic
- The term protozoan describes animal-like protists but is not a true taxonomic ranking
Protozoans are mainly grouped by their _____
- nutritional requirements
- spore-forming potential
- mode of reproduction
- means of motility
means of motility
Choose the TRUE statement(s) concerning the eukaryotic glycocalyx.
- It promotes or prevents cell adhesion where appropriate
- It plays a role in cell communications
- It is mainly made of lipids
-It is only in cells that have a cell wall
- It promotes or prevents cell adhesion where appropriate
- It plays a role in cell communications
Choose the TRUE statement about cilia and flagella.
- While both cilia and flagella are surrounded by a membrane and sprout from centrioles, they have different types of movement
- Cilia are not found in multicellular Eukaryote species, while Flagella may be found at some stage in the life of a multicellular Eukaryote
- Cilia and flagella can be found in eukaryotes and prokaryotes
- Both cilia and flagella tend to be the same length
While both cilia and flagella are surrounded by a membrane and sprout from centrioles, they have different types of movement
Choose the FALSE statement about the cell's nucleus.
- Unless the cell is dividing, the DNA of the nucleus is loosely organized as chromatin
- The nucleus contains a region called the nucleolus, where DNA is copied
- The nucleus is typically visible with a light microscope
- The nucleus has a membrane that gives rise to the endoplasmic reticulum
The nucleus contains a region called the nucleolus, where DNA is copied
Choose the TRUE statement(s) about the structure and function of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
- The ER is a key site of RNA production
- Vesicles that bud off the ER are often shuttled to the Golgi apparatus
- The smooth ER is involved in lipid production and detoxification
- The endoplasmic reticulum modifies and packages cellular proteins
- Vesicles that bud off the ER are often shuttled to the Golgi apparatus
- The smooth ER is involved in lipid production and detoxification
- The endoplasmic reticulum modifies and packages cellular proteins
Which of the following vesicles is incorrectly matched with its function?
- Secretory vesicles: ferry digestive enzymes to the endoplasmic reticulum
- Transport vesicles: move substances around the cell
- Lysosomes: contain hydrolytic enzymes and act as garbage disposal tools for the cell
- Peroxisomes: contain enzymes that break down fats and amino acids and protect the cell from hydrogen peroxide
Secretory vesicles: ferry digestive enzymes to the endoplasmic reticulum
Where is the genetic information of the cell stored?
- nucleus
- golgi apparatus
- smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
- rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
- lysosomes
nucleus
The structural framework in a cell is the
- extracellular matrix
- plasma membrane
- endomembrane system
- endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
- cytoskeleton
cytoskeleton
Where in a cell is ATP made?
- mitochondria
- ribosomes
- chloroplasts
- nucleus
- lysosomes
mitochondria
What carries instructions for making proteins from the nucleus into the cytoplasm?
- ATP
- DNA
- mRNA
- rough ER
- ribosomes
mRNA
One of the ways smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER) differs from rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is that rough ER is covered by
- ribosomes
- the extracellular matrix
- the cytoskeleton
- the golgi apparatus
- mitochondria
ribosomes
Which of the following is part of the endomembrane system?
- gogli apparatus
- flagellum
- ribosomes
- cytoskeleton
- mitochondria
golgi apparatus
Which of the following organelles breaks down worn-out organelles?
- golgi apparatus
- mitochondria
- rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
- lysosomes
- smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
lysosomes
Where are lipids made in the cell?
- ribosomes
- mitochondria
- rough ER
- golgi apparatus
- smooth ER
smooth ER
What structure acts as a selective barrier, regulating the traffic of materials into and out of the cell?
- plasma membrane
- endomembrane system
- nuclear envelope
- extracellular matrix
- cytoskeleton
plasma membrane
Meiosis starts with a single diploid cell and produces
- four diploid cells
- eight haploid cells
- two haploid cells
- two diploid cells
- four haploid cells
four haploid cells
A cell preparing to undergo meiosis duplicates its chromosomes during
- meiosis II
- prophase I
- metaphase I
- anaphase I
- interphase
interphase
During prophase I of meiosis,
- there are two daughter cells, each with 23 chromosomes
- there are four haploid daughter cells
- homologous chromosomes stick together in pairs
- chromosome pairs are positioned in the middle of the cell
- the homologous chromosomes separate and move towards opposite poles
homologous chromosomes stick together in pairs
The correct order of events during meiosis is
- prophase I, anaphase I, metaphase I, telophase I, meiosis II, cytokinesis
- prophase I, anaphase I, telophase I, metaphase I, meiosis II
- metaphase I, prophase I, telophase I, anaphase I, cytokinesis, meiosis II
- prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, cytokinesis, meiosis II
- metaphase I, prophase I, anaphase I, telophase I, cytokinesis, meiosis II
prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, cytokinesis, meiosis II
During meiosis, segments of nonsister chromatids can trade places. This recombination of maternal and paternal genetic material is a key feature of meiosis. During what phase of meiosis does recombination occur?
- meiosis II
- metaphase I
- anaphase I
- telophase I
- prophase I
prophase I
What must happen before a cell can begin mitosis?
- a mitotic spindle must form
- the nucleus must divide in two
- the nuclear envelope must break up
- the sister chromatids must be separated
- the chromosomes must be duplicated
the chromosomes must be duplicated
The centrosomes move away from each other and the nuclear envelope breaks up during which phase of mitosis?
- telophase
- anaphase
- interphase
- prophase
- metaphase
prophase
The chromosomes line up in the center of the cell during which phase of mitosis?
- metaphase
- anaphase
- prophase
- interphase
- telophase
metaphase
The sister chromatids separate and begin moving toward opposite poles of the cell during which phase of mitosis?
- metaphase
- interphase
- prophase
- anaphase
- telophase
anaphase
The chromosomes arrive at the poles and nuclear envelopes form during which phase of mitosis?
- telophase
- interphase
- anaphase
- prophase
- metaphase
telophase
An the end of the mitotic (M) phase, the cytoplasm divides in a process called _____
- replication
- cytokinesis
- meiosis
- telophase
- condensation
cytokinesis
Which of the following statements defines eukaryotic cells?
- they may contain 80S or 70S ribosomes in their cytoplasm
- they contain membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus
- they have a singular circular chromosome in the nucleus
- they may divide using binary fission, mitosis, or meiosis
- they may contain a cell wall made of peptidoglycan
they contain membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus
You have discovered a compound that inhibits the placement of sterols in the plasma membrane. What can you deduce about the efficiency of this drug?
- this drug may be broadly effective against prokaryotic cells
- this drug may be broadly effective against eukaryotic cells but may be toxic in human patients
- this drug may be broadly effective against both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells but may be toxic in human patients
- this drug may be broadly effective against eukaryotic cells
- this drug may be broadly effective against both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
this drug may be broadly effective against eukaryotic cells but may be toxic in human patients
True of False:
Binary fission, mitosis, and meiosis all produce genetically identical daughter cells.
False
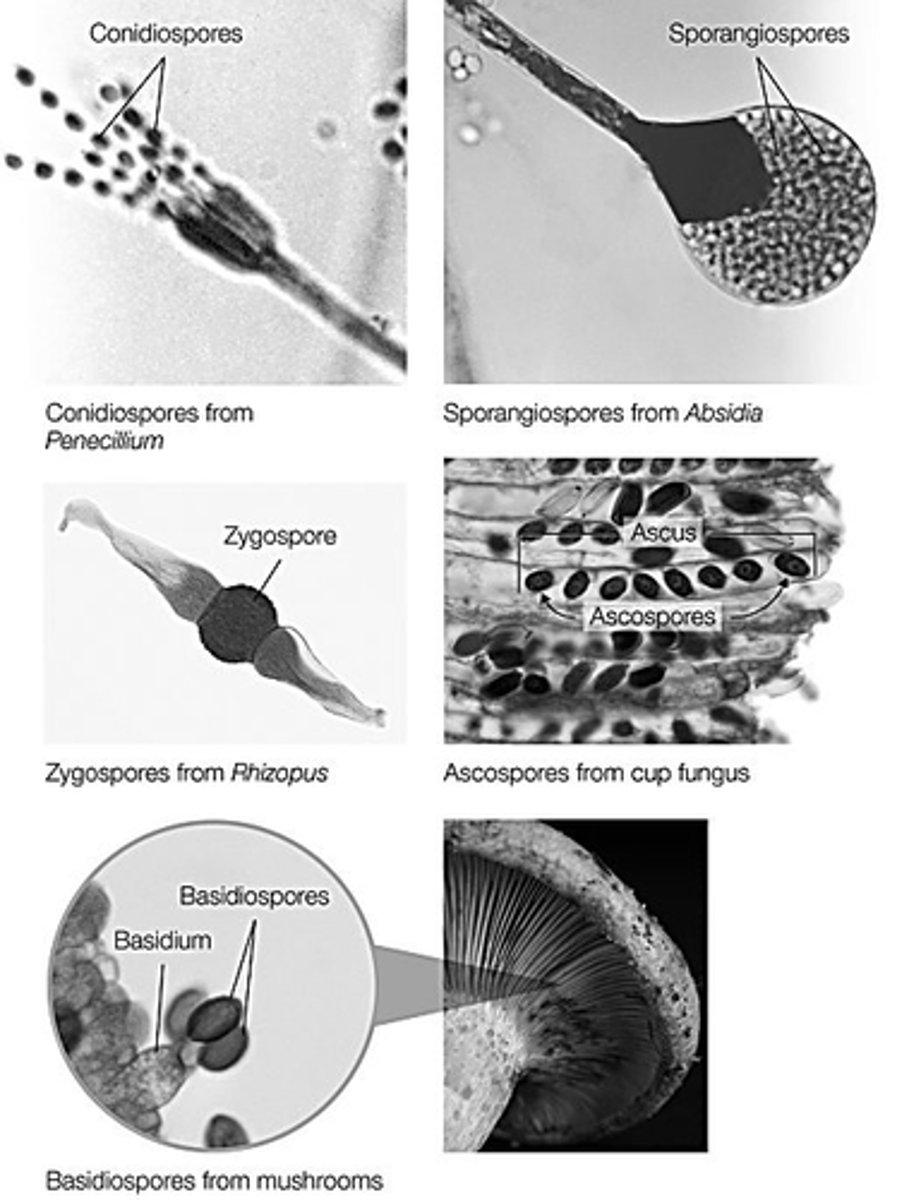
Which of the following are asexual fungal spores?
- conidiospores and sporangiospores
- ascospores, basidiospores, and conidiospores
- any type of fungal spore can be asexual or sexual depending on how it formed
- ascospores, basidiospores, and zygospores
- No types of fungal spores are asexual.
conidiospores and sporangiospores
Most helminthic parasites spend at least some part of their life cycle in the
- respiratory tract
- skin
- cardiovascular system
- gastrointestinal tract
- genitourinary tract
gastrointestinal tract
Fungal infections are called
- mycoses
- basidium
- sporangia
- coenocytic
- dimorphic
mycoses
Which persons may be at increased risk for mycoses?
- those with weakened immune systems
- those who have not received the recommended vaccine schedule
- those who have had their normal microbiome disrupted by antibiotic therapy
- either those with weakened immune systems or those who have had their normal microbiome disrupted by antibiotic therapy
- either those with weakened immune systems or those who have not received the recommended vaccine schedule
either those with weakened immune systems or those who have had their normal microbiome disrupted by antibiotic therapy
A patient presents with symptoms of severe gastrointestinal distress. Bacterial and viral pathogens are ruled out. A protozoan which moves via hair-like appendages is observed upon microscopic examination of the patient's stool. The most likely cause of the infection is
- Plasmodium, an apicomplexan
- ergot toxin, a fungal mycotoxin
- Balantidium coli, a ciliated protozoan
- Entamoeba histolytica, an amoeboid protozoan
- Giardia lamblia, a flagellated protozoan
Balantidium coli, a ciliated protozoan
True or False:
The four groups of protozoans are grouped by their mode of reproduction.
False
True or False:
Dimorphic pathogenic fungi exhibit a yeast-like growth in the environment and a hyphae growth form during an active infection in a human host.
False
A researcher discovers a chemical compound which prevents the incorporation of ergosterol in the plasma membrane We can predict that this compound would be toxic to which kinds of organisms?
- animals
- bacteria
- plants
- viruses
- fungi
animals
The primary function of the nucleus is
- housing the cell's DNA
- serving as the site of ribosome synthesis of protein
- production of the cell's energy molecule, ATP
- serving as the site of most of the cell's chemical reactions
- digestion and processing of nutrients
housing the cell's DNA
Which of the following processes is
INCORRECTLY matched to its description?
- Endocytosis: Imports materials into a cell
- Receptor-mediated endocytosis: Uses specific binding between structures on the plasma membrane binding to ligands
- Phagocytosis: Imports undissolved substances but not whole cells or viruses
- Exocytosis: Exports materials out of a cell
- Pinocytosis: Imports dissolved substance using small vesicles
Phagocytosis: imports undissolved substances but not whole cells or viruses
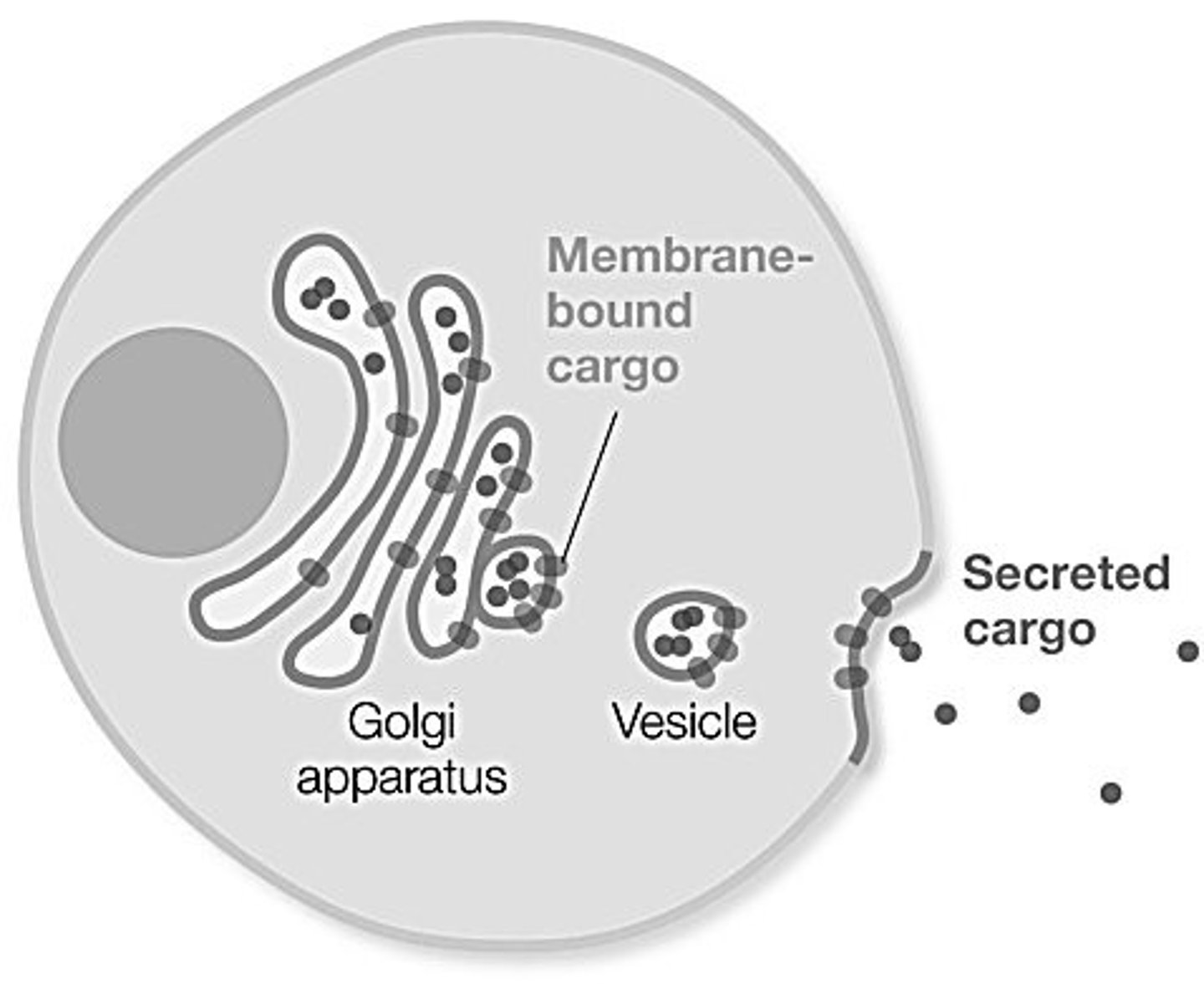
Which process is pictured?
- pinocytosis
- exocytosis
- phagocytosis
- receptor-mediated endocytosis
- endocytosis
exocytosis
Hyphae are
- the main growth form of pathogenic fungi when they are infecting humans
- a unicellular yeast-like form found in some fungi
- a collection of tubular structures that result from fungal growth
- collections of fungal growth on the skin
- reproductive structures in fungi
a collection of tubular structures that result from fungal growth
True or False:
Animal cells are unique among all other eukaryotic groups in that they universally lack a cell wall.
True
The rough ER and the smooth ER are distinguished from each other by
- synthesis of lipids by the rough ER and synthesis of proteins by the smooth ER
- the presence or absence of both DNA and membrane-bound ribosomes
- the presence or absence of DNA
- the presence or absence of membrane-bound ribosomes and the synthesis of lipids by the rough ER and the synthesis of proteins by the smooth ER
- the presence or absence of membrane-bound ribosomes
the presence or absence of membrane-bound ribosomes
Mitochondria do NOT participate in which function?
- regulation of cell division
- programmed cell death
- production of ATP
- production of amino acids and vitamins
- motility
motility
A similarity between mitosis and meiosis is
- production of genetically unique daughter cells
- sexual reproduction
- two sequential cell divisions
- production of daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent
- copying DNA before the cell divides
copying DNA before the cell divides
You have isolated a new organism which has eukaryotic cells, is multicellular, grows as hyphae, does not perform photosynthesis, and has a cell wall. This organism most likely belongs to which kingdom?
- Bacteria
- Protista
- Archaea
- Fungi
- either Fungi or Protista
Fungi