The Male Pelvis Prostate Gland and Seminal Vesicles Sonography: Guided Notes
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Prostate Gland: ____________ to the urinary bladder
inferior
Prostate Gland Surrounds the...
proximal urethra
Prostate Gland Lies posterior to the..
symphysis pubis
Prostate Gland: Separated posteriorly from the rectum by two layers of tissue called ______________________ fascia
Denonvilliers
Prostate Gland: Supported laterally by what two things?
obturator internus and levator ani muscles
Seminal Vesicles: ____________ to the urinary bladder
posterior
Seminal Vesicles Superior to the...
prostate
Seminal Vesicles Angle medially toward the ____ of the bladder
apex
Normal size for the Seminal Vesicles length
5.0 cm in length
Normal size for the Prostate length
3.8 cm in length
Prostate (cone shaped): _________: tip of the cone, inferior margin of the prostate
Apex
Prostate (cone shaped): Base: __________ margin of the prostate in contact with the _______ margin of the bladder
superior inferior
Prostate (cone shaped): Central core
prostatic urethra
Prostate (cone shaped): Perforated by the__ ___ which enter the prostate on the posterior margin, coursing obliquely and anteriorly to enter the ___ ___
ejaculatory ducts prostatic urethra
Prostate (cone chaped): Divided into two main parts
Small, anterior fibromuscular region or stroma
Large, posterior glandular region
Prostate (cone shaped): Small, anterior fibromuscular region or stroma is located anterior to the...
prostatic urethra
Prostate (cone shaped): Small, anterior fibromuscular region or stroma is less important due to...
pathology occurring primarily in the glandular region
Prostate (cone shaped): Large, posterior glandular region
Prostate (cone shaped): Large, posterior glandular region is divided into four zones
Peripheral zone
Central zone
Transition zone
Periurethral glandular zone
Peripheral zone: ________, making up approximately __% of the glandular prostate
Largest
70
Peripheral zone: Occupies the area lateral and posterior to the...
distal prostatic urethra
Central zone: _____% of the glandular prostate
20
Central zone: Located at the superior edge bordering the __ and ___
bladder and seminal vesicles
Central zone: __ ___ course through this zone
Ejaculatory ducts
Transition zone: __% of glandular prostate
5
Transition zone: Two lobes situated on the lateral aspects of the proximal
prostatic urethra superior to the _____________________
verumontanum (area close to the center of the prostate that splits proximal and distal)
Transition zone: Borders the central zone ___ and ___ as well as the fibromuscular tissue ___
posteriorly laterally anteriorly
Periurethral glandular zone: Tissue that lines the _____________ prostatic urethra
Proximal (lining of the urethra)
Seminal Vesicles: Paired glands, each encapsulated by __ __
connective tissue
Seminal Vesicles: Convoluted, __________________ structures emptying into the distal portion of the ductus (vas) deferens to form the __ __
pouchlike
ejaculatory ducts
Prostate Physiology: Secretes a...
milky, alkaline fluid that contains enzymes like prostate specific antigen (PSA)
and fibrinolysin, as well as nutrients like citric acid, zinc, and spermine
Prostate Physiology: Constitutes __ - __% of the total volume of semen
13-33%
Prostate Physiology: Semen is fluid that consists of...
sperm and secretions of the prostate, seminal vesicles and other glands associated with the male urogenital tract
Prostate Physiology: Semen fluid helps with... (4)
o Liquefy semen
o neutralize acidic vaginal environment
o Protect and nourish sperm
o Enhance motility and survival
Seminal Vesicles Physiology: Secrete a ______________, alkaline fluid rich in fructose, prostaglandins and various proteins
Viscous
Seminal Vesicles Physiology: Constitutes __ - __% of the total volume of semen
50-80
Seminal Vesicles Physiology: __ fluid helps (4)
o Provide energy for sperm motility
o Provide hormones which trigger smooth muscle contractions in the female reproductive system to help move sperm forward
o Semen Coagulate (thicken) after ejaculation which is critical for semen to remain in the female reproductive tract
o Protect and nourish sperm (This will help it stay stuck)
Seminal Vesicles Physiology: Prostatic and seminal secretions are conveyed through numerous ducts to the__ __
prostatic urethra
Seminal Vesicles Physiology: The
fluids are then carried outside the body through the penis via the__ __ and finally exit through the __ __ __.
distal urethra and external urethral orifice
Sonographic Appearance Prostate: ___ with medium-level echoes
Heterogeneous
Sonographic Appearance Prostate: ___ in shape and size
Symmetric
Sonographic Appearance Prostate: __________________ when compared to the
seminal vesicles
hyperechoic
Sonographic Appearance Prostate: In a normal prostate, the _________ & ________ zones cannot be differentiated from one another
Central and transition
Sonographic Appearance Prostate: The peripheral zone appears ___ and ___
hyperechoic and homogenous
Sonographic Appearance Seminal Vesicles: _______ structures with low-level echoes superior to prostate gland
ovoid
Sonographic Appearance Seminal Vesicles: Low gray, __ structures
hypoechoic
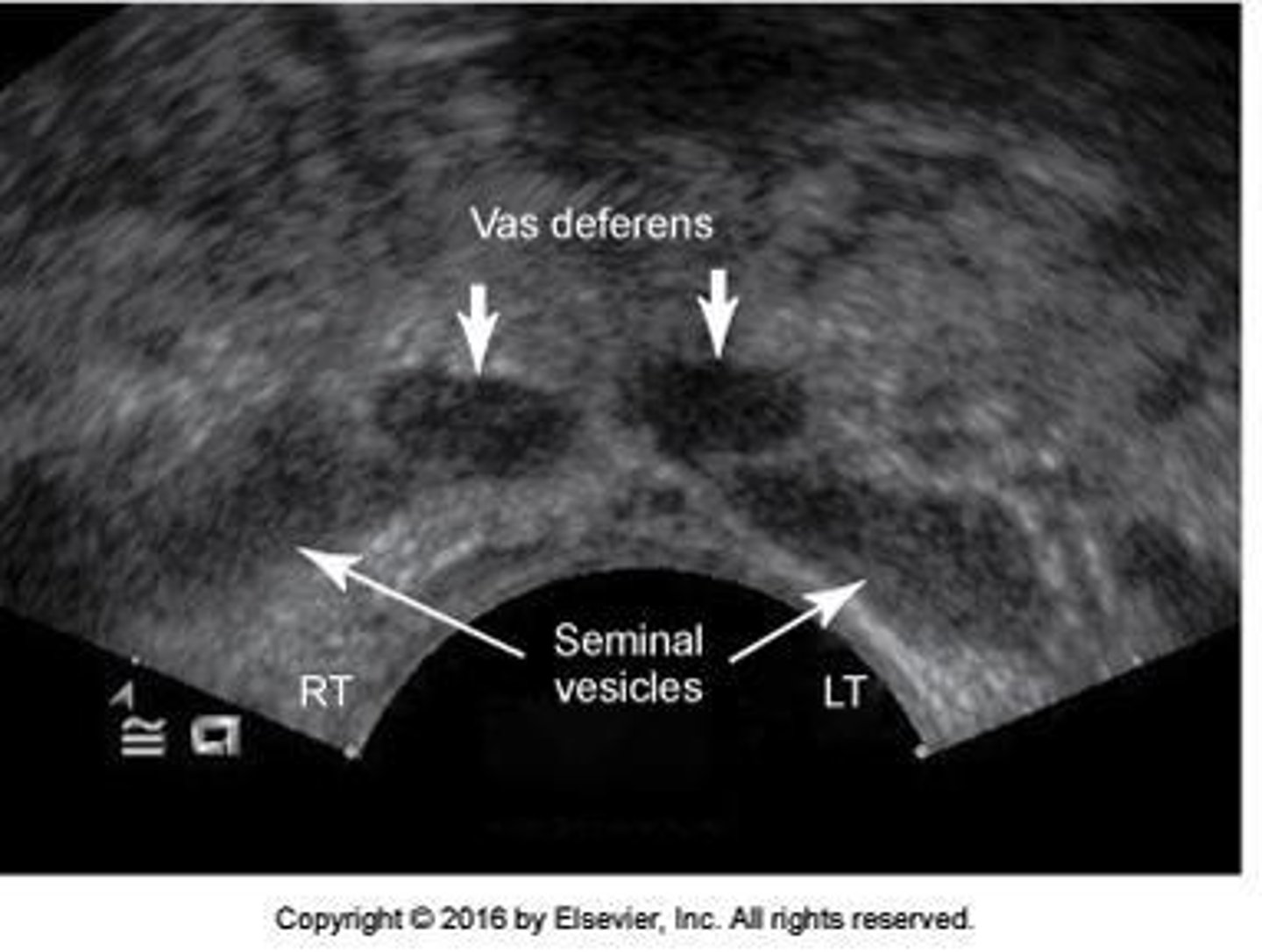
Sonographic Appearance Seminal Vesicles: ___ in size and shape
Symmetric
Sonographic Appearance Seminal Vesicles: When scanning in the transverse plane, the seminal vesicles will be ___________________
elongated
Sonographic Appearance Seminal Vesicles: When scanning in the sagittal plane, the seminal vesicles will be ___________________
Round
The prostate can be evaluated transabdominally through a distended bladder to assess ________ only.
size
Ultrasound examinations of the male pelvis are indicated for: Prostate (9)
• size and echotexture
• Prostatitis (infection)
• Detection of masses • Evaluation of benign prostatic hypertrophy (enlarged prostate) (BPH)
• Sonographic correlation of findings on a digital rectal examination
• Sonographic correlation of evaluated serum prostatic specific antigen (PSA)
• Evaluation of extracapsular spread of prostatic carcinoma
• Evaluation of postoperative transurethral resection (TURP)
• Ultrasound-guided biopsies of prostatic lesions
Ultrasound examinations of the male pelvis are indicated for: • Seminal Vesicles (4)
• Evaluation of size, symmetry , and echotexture
• Ruling out presence of cysts or calculi
• Inflammatory processes
• Congenital anomalies
Lab Values: PSA
Serum prostatic specific antigen
Lab Values: Serum prostatic specific antigen (PSA): Used to evaluate the function of the ___
prostate
Lab Values: Serum prostatic specific antigen (PSA): Normal serum PSA is..
less than 4.0
Associated Diagnostic Imaging Exams - Prostate biopsy
a procedure to remove small tissue samples from the prostate gland to check for signs of prostate cancer. It is performed by a urologist using a thin needle, often guided by an ultrasound probe, to collect samples for laboratory analysis
Lab Values: Serum prostatic specific antigen (PSA): Elevated serum PSA may indicate...
presence of disease but is not specific for carcinoma
Associated Diagnostic Imaging Exams: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
A noninvasive imaging modality that is very useful in identifying soft tissue structures.
Associated Diagnostic Imaging Exams: Sonography
As a method of evaluating the structures of the male genitourinary system, ultrasonography is second only to direct physical palpation of the prostate by a urologist.