UCM Basic Genetics Final
1/285
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
286 Terms
Which fallacy uses personal attacks to argue a conclusion/statement is false?
ad hominem
|
If I hear a statement from three different sources, I know it is a fact.
opinion
Which of the following is deductive reasoning?
making sound conclusions using logical reasoning and true premises
Science is a solitary pursuit and is best performed without discussion from others.
false
When one makes sound conclusions from true premises and logical reasoning, one is performing ___
deductive reasoning
Earth is round (a sphere) because pictures from the space station show it to be round. |
fact
Which fallacy accuses a person of holding a position they do not hold but is often an exaggeration of their argument?
strawman
In the modified Bloom's taxonomy of learning, what is the lowest level of learning?
remember
Is the following statement a fact, inference, or opinion?
In spite of what the pundits thought, Donald Trump was elected President of the United States.
fact
Earth is round (a sphere) because pictures from the space station show it to be round. |
fact
What is inductive reasoning?
the process to come up with a generalization that is supported by facts
According to Bloom's taxonomy of learning, which of the following represents a basic level of learning?
remembering
Is the following statement a fact, inference, or opinion?
The best college sports teams are the UCM Mules
opinion
| ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
answered above
|
abductive reasoning
Is the following statement a fact, inference, or opinion?
I got 90% on the last 4 exams, but only got 60% earlier when I did not study. I need at least 80% on the next exam to get an A in the course. If I study, I can get the 80% I need.
inference
When one makes highly probable conclusions from true premises, one is performing __
inductive reasoning
Which fallacy argues something caused something else because they both occur together?
post hoc ergo propter hoc
Which of the following is(are) included in the actual process scientists apply to their work? Check all that apply
They generally work by themselves. |
They use creative solutions to overcome road blocks. |
Their work involves many people so they are social |
not all the way correct 0.1666
Match the argument with the fallacy it makes.
I'm correct because mom said so. | B. appeal to authority |
If you say killing a fertilized egg is okay, then you are just as bad as the school shooter who massacred innocent children. | E. ad hominem |
The sky is blue because it is blue. | A. circular argument |
A wife says, "I rather have a cat over a dog." The husband argues, "Why do you hate dogs?" | C. post hoc ergo propter hoc |
Vaccines cause autism. | D. straw man |
not all the way correct 0.6
The phenotype is
the expression of a trait in an organism
In his monohybrid crosses, Mendel deduced that one trait was recessive because
that trait was not present in the F1 and reappeared in the F2
If plants, one with white flowers and the other with purple flowers, are crossed and all of the progeny have purple flowers, then which of the following statements is true?
The allele determining purple flower color is dominant.
Stem length in pea plants is controlled by a single gene where long stems are completely dominant. Consider the cross between a true-breeding long-stemmed plant with a true-breeding short-stemmed plant. If 120 F1 plants are examined, what are the likely stem lengths of these plants?
20 F1 plants are long stemmed
What Mendel called "factors" we now call
genes
Which of the following refers to visible traits?
phenotypes
Which of the following refers to pairs of factors that determine traits?
genotypes
An unspecified characteristic controlled by a single gene is examined. Only two phenotypic states exist for this trait. One phenotypic state is completely dominant to the other. A heterozygous plant is crossed with another heterozygous plant. What proportion of the progeny exhibiting the dominant phenotype is homozygous?
1/3 of dominant progeny
Is Aa a genotype or phenotype?
genotype
A genotype is
a combination of two alleles a person has for a gene
match the description with the term
visible traits | D. phenotypes |
pair of factors that determine a trait | A. alleles |
variants of a gene | E. genotype |
macromolecules that carry out cellular functions | B. proteins |
macromolecule that carries a gene's code | C. DNA |
0.3 not all the way correct
Recessive traits are expressed only in the homozygous state.
true
Wet ear wax (W) is dominant over dry ear wax (w).
A 3:1 phenotypic ratio of children indicates that the parents are what genotype? Choose all answers that are correct. Incorrect answers have a negative penalty.
heterozygous (Ww)
Two black female mice are crossed with the same brown male mouse. In a number of litters, female mouse #1 produced 9 black and 8 brown mice while female mouse #2 produced 14 black mice. What is the genotype of female mouse #2?
AA
A 1:1 phenotypic ratio of children indicates that the parents are what genotype? Choose all answers that are correct. Incorrect answers have a negative penalty. |
heterozygous (Ww) |
homozygous recessive (ww) |
This is problem #18 from chapter 3.
Determine the possible genotypes of the following parents by analyzing the phenotypes of their children. We will assume that brown eyes (B) is dominant to blue eyes (b); right-handedness (R) is dominant to left-handness (r). Eye color and handedness are independently assorting genes.
Parent: brown eyes, right handed X brown eyes, right handed
Children: 3/4 brown eyes, right-handed and 1/4 blue eyes, right handed
Look at the trait that is different among the children. This trait accounts for the 3/4 and 1/4 probabilities. Then look at the phenotype of the parents. Which genotype matches the parents' phenotype and would give the probabilities of the children.
Next, decide how you can only get the trait that does not change.
BbRR X BbRR
|
false
Determine the possible genotypes of the following parents by analyzing the phenotypes of their children. We will assume that brown eyes (B) is dominant to blue eyes (b); right-handedness (R) is dominant to left-handness (r). Eye color and handedness are independently assorting genes. Parent: brown eyes, right handed X blue eyes, left handed Children: 1/4 blue eyes, right handed 1/4 blue eyes, left handed 1/4 brown eyes, right handed 1/4 brown eyes, left handed For this analysis, look at pairs of children where one trait is held constant, e.g., blue eyes, right handed and blue eyes, left handed. The probability can then be reduced. If it is 3/4 and 1/4, parents are heterozygotes. If it is 1:1 or the same probability, one parent is a heterozygote and the other one is recessive. Also, one parent has recessive traits. There is only one genotype for recessive traits. And, if there is a recessive trait among the children, then both parents must carry the recessive allele even though their phenotype is dominant |
BbRr X bbrr
|
1/8
|
The dominant allele determines the black coat color
Two black female mice are crossed with the same brown male mouse. In a number of litters, female mouse #1 produced 9 black and 8 brown mice while female mouse #2 produced 14 black mice. What is the genotype of the male parent?
aa
|
Aa
NOT → Determine the possible genotypes of the following parents by analyzing the phenotypes of their children. In this case, we will assume that brown eyes (B) is dominant to blue (b) and that right-handedness (R) is dominant to left-handedness (r). Offspring are ¼ brown eyes, right-handed; ¼ brown eyes, left-handed, ¼ blue eyes, right-handed, ¼ blue eyes, left-handed. One is parent is blue eyes, left-handed. What is the genotype of this parent?
NOT→ BbRr
NOT → This is problem #18 from chapter 3.
Determine the possible genotypes of the following parents by analyzing the phenotypes of their children. We will assume that brown eyes (B) is dominant to blue eyes (b); right-handedness (R) is dominant to left-handness (r). Eye color and handedness are independently assorting genes.
Parent: brown eyes, right handed X blue eyes, right handed
Children: 6/16 blue eyes, right handed
2/16 blue eyes, left handed
6/16 brown eyes, right handed
2/16 brown eyes, left handed
For this analysis, look at pairs of children where one trait is held constant, e.g., blue eyes, right handed and blue eyes, left handed. The probability can then be reduced. If it is 3/4 and 1/4, parents are heterozygotes. If it is 1:1 or the same probability, one parent is a heterozygote and the other one is recessive.
NOT → BBRr X bbRr
NOT → Wet ear wax is dominant over dry ear wax. A 3:1 wet:dry ear wax ratio in the offspring indicated that the parents are which phenotype?
NOT → homozygous wet ear wax and heterozygous dry ear wax
Which of the following are cellular structures that house genes where males are hemizygous for genes on this structure?
X
|
mitochondrial gene
What is the genotype of an affected person of a rare trait caused by an autosomal recessive allele?
homozygous recessive
If a pedigree tree shows an affected father with all of his daughters affected, but not of his sons, what is the likely mode(s) of inheritance for the trait/disease? Choose all correct answers.
X-linked dominant
|
autosomes
Which disease is caused by a mutation in opsin?
red/green colorblindness
Which disease contributed to the collapse of the Russian monarchy in the early 20th century?
hemophilia
|
hemophilia | B. clotting factor VIII |
sickle cell disease | C. hemoglobin |
Duchenne muscular dystrophy | H. dystrophin |
cystic fibrosis | E. CFTR |
colorblindness | A. opsin |
Marfan syndrome | G. fibrillin |
If a pedigree tree shows an affected child with two normal parents, what is the likely mode(s) of inheritance for the trait/disease? Choose all correct answers.
0.125 → autosomal recessive
What is the genotype of an affected person of a rare trait caused by an autosomal dominant allele?
heterozygous
If a pedigree tree shows affected mothers and all of her children affected, what is the likely mode(s) of inheritance for the trait/disease? Choose all correct answers
0.2 → autosomal dominant, mitochondrial inheritance
Which disease is caused by a mutation in hemoglobin?
sickle cell disease
Match the disease with its mode of inheritance. |
hemophilia | C. X-linked recessive |
sickle cell disease | D. autosomal recessive |
Duchenne muscular dystrophy | C. X-linked recessive |
cystic fibrosis | D. autosomal recessive |
colorblindness | C. X-linked recessive |
Marfan syndrome | A. autosomal dominant |
Huntington disease | A. autosomal dominant |
polydactyly | A. autosomal dominant |
Which of the following describes the cellular structures that contain all of the genes of a person? It is made up of DNA and proteins.
chromosomes
What is the genotype of an affected son with a trait caused by an X-linked recessive allele?
hemizygous
Which disease is caused by a mutation in clotting factor VIII? |
hemophilia
NOT → Which of the following is NOT a reason that makes interpreting pedigree trees difficult
NOT → A recessive trait is common in the family so it looks dominant
The trait has variable expressivity so it is difficult to count everyone with the trait
View the following pedigree tree.
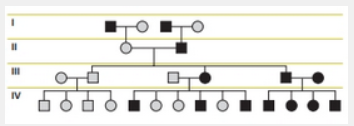
Which of the following modes of inheritance CANNOT account for the pattern seen
Y-linked |
mitochondrial inheritance |
|
Answer: Allows tissues to grow because the two cells at the end has the exact same chromosomes as the cell at the beginning
Allows the mixing the genes during crossing over. |
Allows recombination because some chromosomes from mother segregate with chromosomes from father. |
Allows gametes to form with half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. |
Which of the following organelles stores linear, chromosomal DNA?
nucleus
In the cell cycle, the G1 phase represents ___.
a period of growth
What occurs during anaphase I?
Homologous chromosomes separate to opposite poles
Which of the following statements does NOT describe a part of the Cell Theory?
All cells have a nucleus
|
anaphase I
|
3
In the cell cycle, which phase(s) is(are) part of interphase?
0.1875 → G2, S, G1
Which of the following elements are found in biologically important molecules? | ||
H, O, N, S, P, C
|
ribosomes
The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is made up of which of the following?
phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins
|
The chromosomes are duplicated.
A chromosome whose centromere is close to the end of the chromosome is called _____
acrocentric
The region that divides a chromosome into two arms is the _____
centromere
What is a reversal of the order of a chromosomal segment?
inversion
Which disease is caused by the destruction of the myelin sheath of neurons? This condition is due to a duplication within chromosome 17.
Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A
Which of the following disorders results from a deletion in chromosome 5? The disorder results from the deletion of genes involved in the development of the larynx and brain.
cri-du-chat
If nondisjunction takes place in one of the cells of the second meiotic division, the four products of meiosis will include
two normal and two abnormal karyotypes
Cytogenetics is the study of normal and abnormal chromosomes in cells. What is the pictorial array of chromosomes from a person’s cell called.
karyotype
In this type of prenatal diagnosis, karyotype analysis can be performed as early as 8 weeks.
Chorionic villus sampling
Amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling are two methods of prenatal diagnosis. One important difference between these techniques is that
chorionic villus sampling can be performed earlier than amniocentesis
The risk for Down syndrome increases in situations where the
mother is 35−45 years old
|
Yes, but the cat has to be an aneuploid of the sex chromosomes, XXY, and heterozygous for the orange gene
NOT → Which of the following disorders results from a copy number variant?
NOT → cri-du-chat
Which of the following is not a part of determining gender in the embryo?
X chromosome produces Xist and inactivates itself by condensing
A Barr body is a(n) ___
inactivated X chromosome
A zygote is a(n) ___ |
diploid cell
The process of ___ equalizes the dosage of functional genes carried on the X chromosome in males and females.
X-chromosome inactivation
Complete androgen insensitivity causes XY males to become phenotypic females.
true
Because females carry two X chromosomes and males carry only one, females have higher levels of all products encoded by genes on the X chromosome |
false
A blastocyst ___
implants in the endometrium
|
testosterone, AMH, and DHT
NOT → Teratogens can cause birth defects especially when the mother is exposed when the embryo is developing organs. When is this sensitive period?
NOT → 2 weeks
The female oocyte completes meiosis II upon
fertilization
How long does it take for a zygote to travel down the uterine tubes to the implant into the uterus?
1 week
The brain and nervous system of a developing embryo can only be damaged during the very early stages of development.
false
Polynucleotide chains (DNA or RNA) have a 5' and a 3' end. Which groups are found at each end?
5' phosphate and 3' OH of the sugar