recombinant DNA technology (making DNA fragments)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
what is the promoter region?
sits before a gene and controls gene expression, allowing transcription to occur
what is recombinant DNA technology?
(aspect of genetic engineering which involves) transferring a fragment of DNA from one organism to another (in order to give it desirable characteristics)
compare and contrast selective breeding and recombinant DNA technology (genetic engineering):
both increase desirable allele frequency
recombinant DNA technology involves directly transferring a fragment of DNA and allows cross species transfer
recombinant DNA technology is faster as you do not need to wait for alleles to become more frequent
in selective breeding other traits are also passed down
what is a transgenic organism?
organism containing transferred DNA
what is the significance of DNA being universal in recombinant DNA technology?
allows cross species DNA transfer
give 2 uses of recombinant DNA technology:
to produce a genetically modified organism e.g. Bt corn has a gene which codes for insecticidal proteins
to produce large quantities of a protein of interest e.g. insulin
give 3 ways of making DNA fragments:
reverse transcriptase
restriction endonucleases/enzymes
gene machine
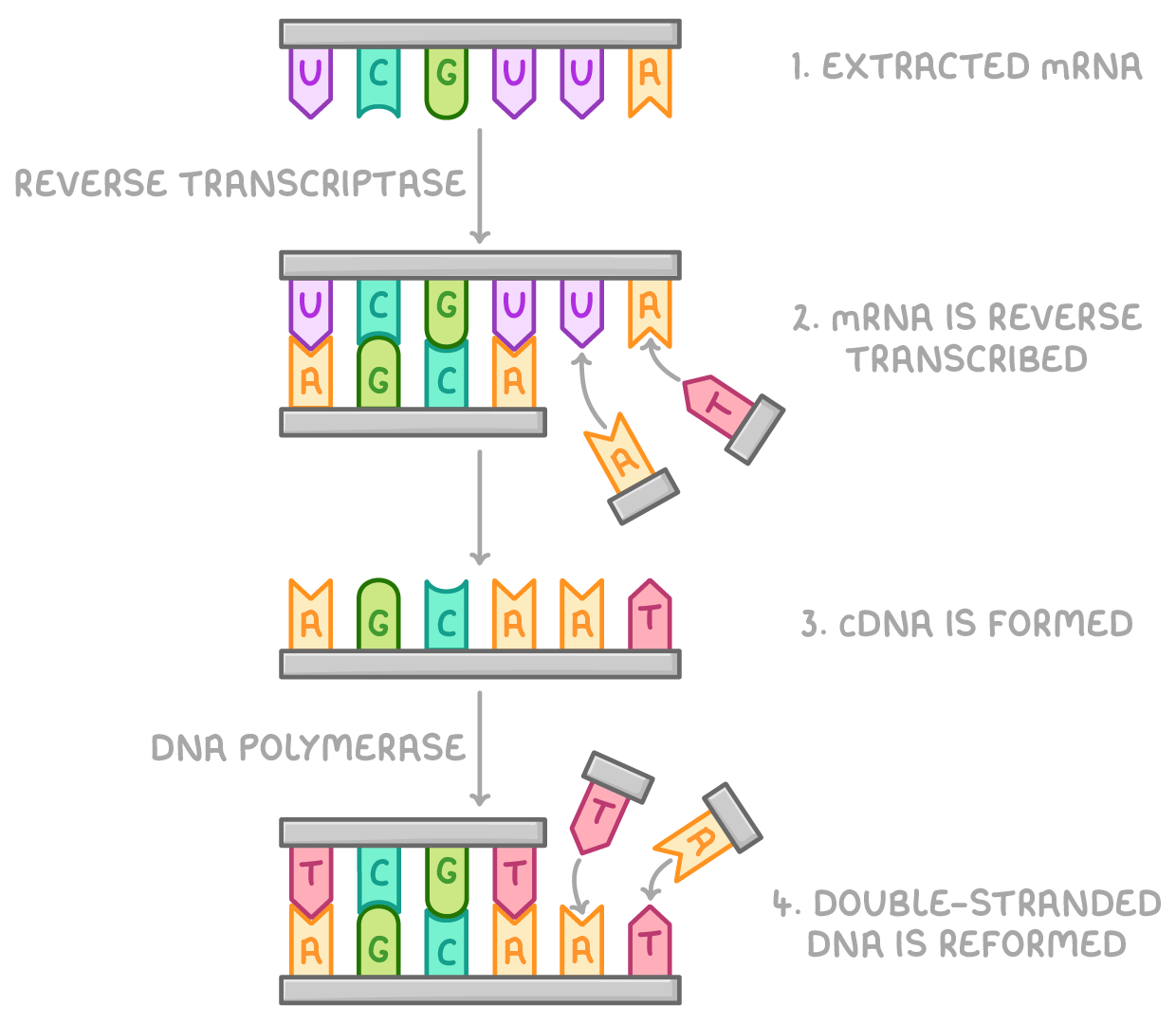
describe the process of using reverse transcriptase to form DNA fragments:
mRNA extracted from cells and used as a template
complementary DNA (cDNA) formed from DNA nucleotides using reverse transcriptase and isolated from mRNA strand
cDNA acts as template to form desired gene using DNA polymerase
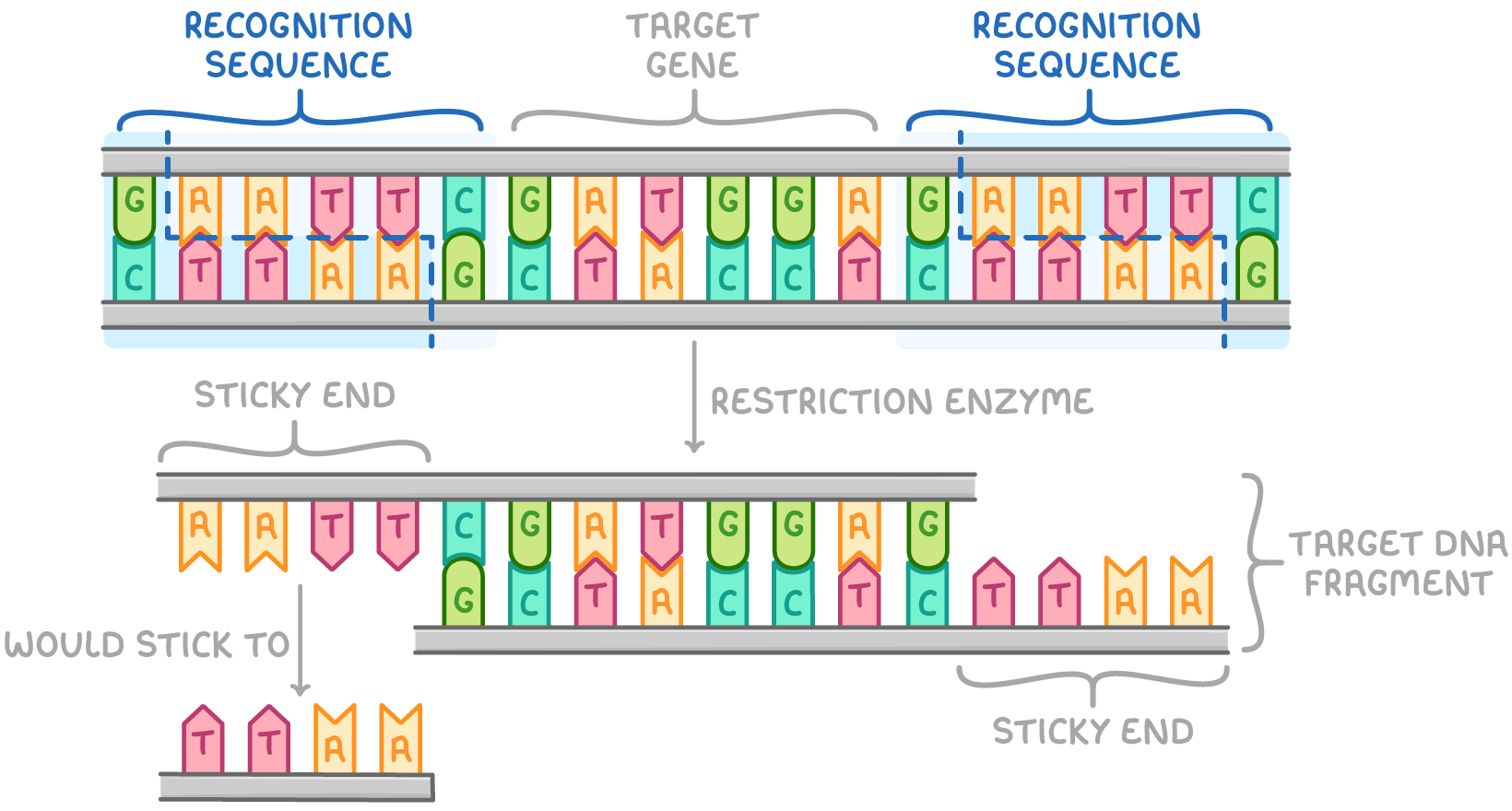
describe the process of using restriction endonuclease enzymes to form DNA fragments:
DNA incubated with chosen restriction enzyme(s)
restriction enzymes identify recognition sequences in DNA and cut dsDNA at specific base sequences, hydrolysing phosphodiester bonds if their recognition sequence is present
what is a restriction enzyme and what is its function?
bacterial enzymes which cut DNA at specific 6 base codes
lots of different types - each cut DNA at specific base sequences known as recognition sites
why do different restriction enzymes cut at different specific recognition sites?
shape of recognition sequences complementary to restriction enzyme’s active site
what are sticky ends? what can they be used for?
small tails of unpaired bases at the end of a DNA fragmenet
to anneal DNA fragment to another DNA fragment with sticky ends with complementary sequences
what is the purpose of a gene machine?
synthesises correct DNA code when programmed with the sequence of amino acids needed to make the protein
what is a oligonucleotide?
short strands of nucleotides
describe the process of using a gene machine to form DNA fragments:
amino acid sequence used to identify mRNA codons and thus complementary DNA sequence
fed into computer
computer produces oligonucleotides which can be constructed into the desired gene
the desired gene is formed without introns or non coding DNA sections
give 2 advantages of using a gene machine to synthesise a protein:
faster
more reliable