surgical diseases of urethra
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
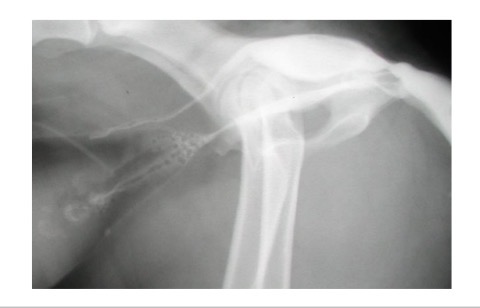
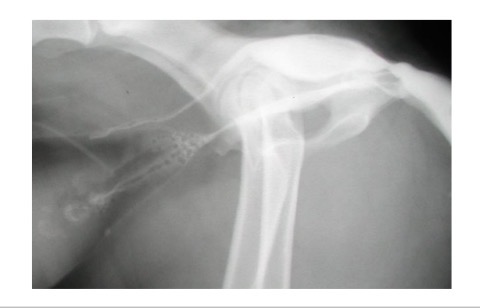
M dog urethra - sections
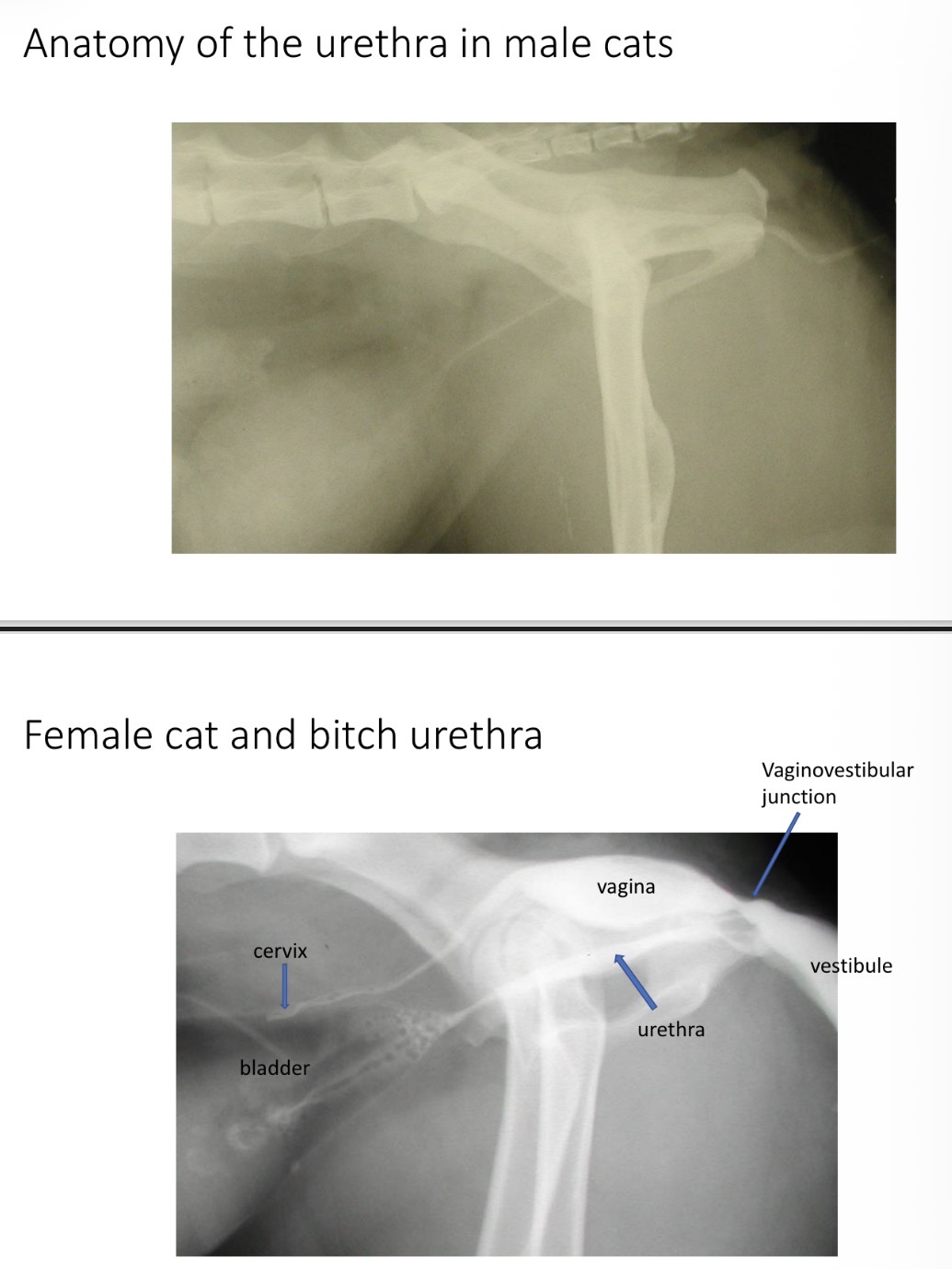
prostatic → pelvic/ membranous → penile/ cavernous
M dog urethra - location of pelvic sectioon
prostate → ischial arch
M dog urethra - location of penile section
os penis groove
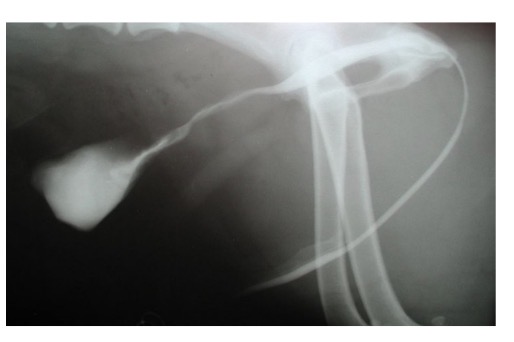
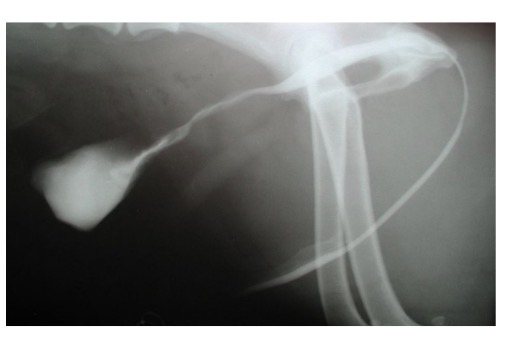
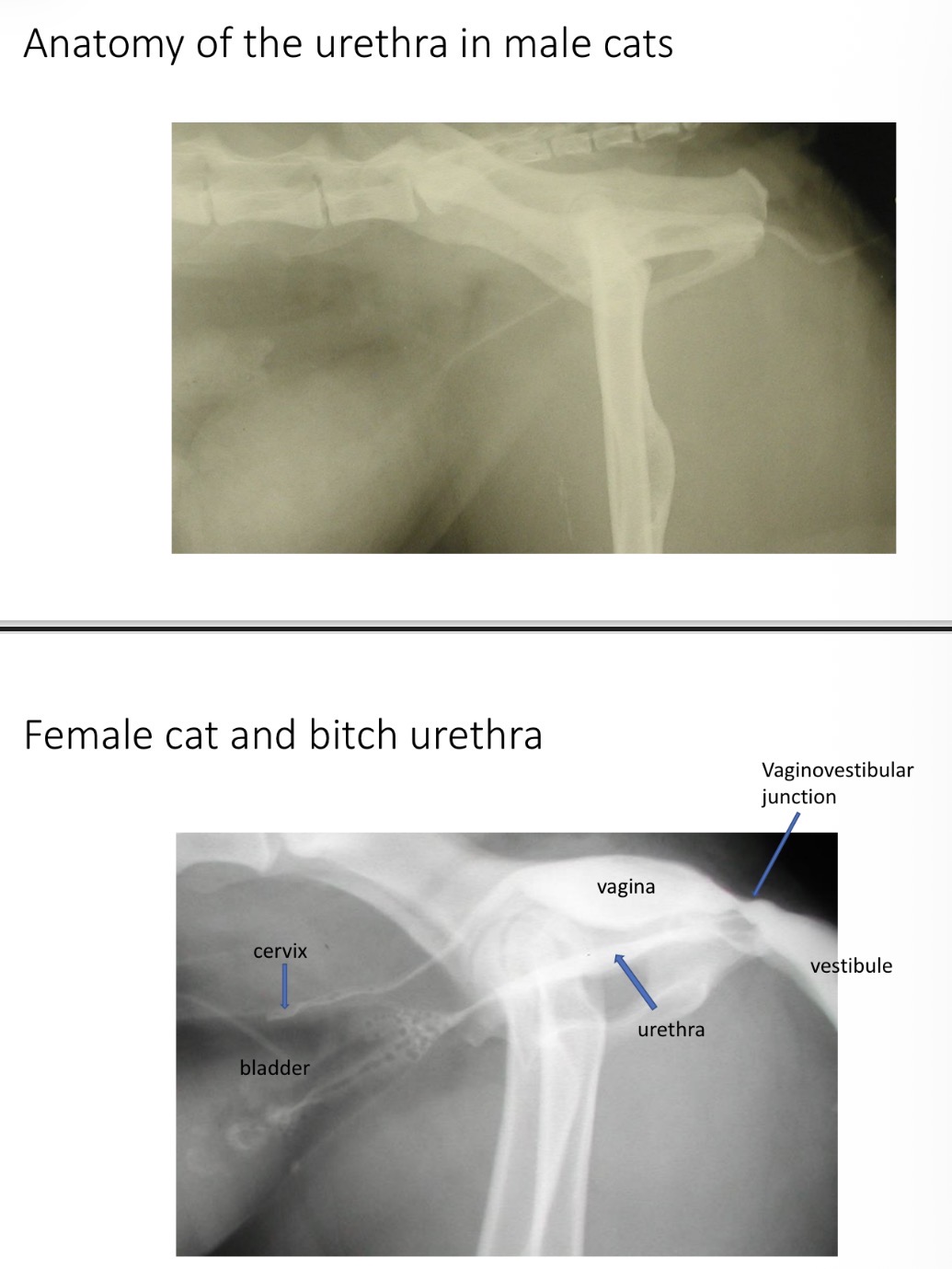
F SA urethra- where does it enter vestibule
2-5mm cd to vaginovestibular junction (dor wall close to ven vagina)
F vs M urethra - which can distend more + why
F - wider, folded mucosa, no bone
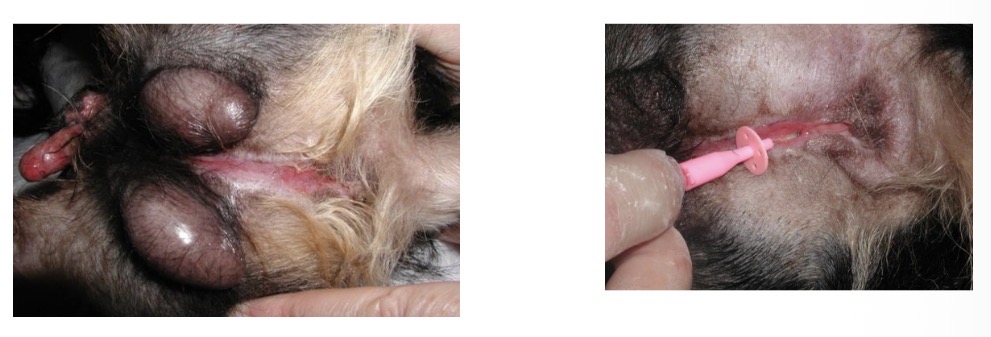
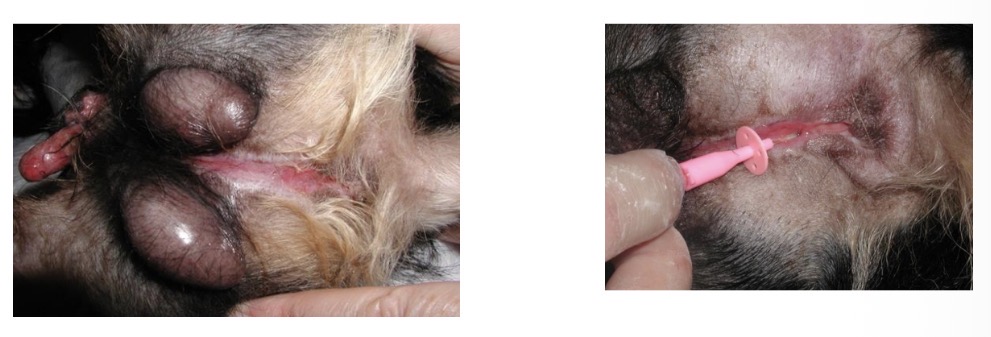
congenital urethral abnormalities - (Hypospadias, epispadias) what happens + how to treat
incomlete formation of urethra, cleft scrotum, incomplete prepuce formation, hypoplastic penis
resect hypoplastic penis
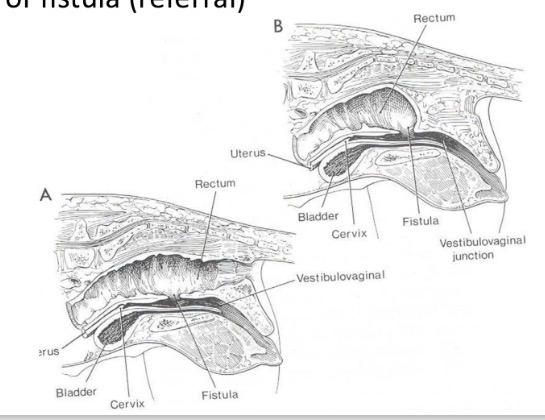
congenital urethral abnormalities - (urethrorectal fistula) what happens + how to treat
communication between urethra + rectum persits (foetal cloaca) → urine passed from anus + vulva/penis
resect fistula
acquired urethral lesions
urethritis
urethral prolapse
urethral obstruction
neoplasia
stricture
urethritis - associated with what
urogenital infl (cystitis, prostatitis, vaginitis)
urethral calculi, iatrogenic, neoplasia
urethritis - leads to
stricture, urethral prolapse
urethritis - CS + treatment
same as underlying disease
urethral prolapse - causes
urethral inf, sex
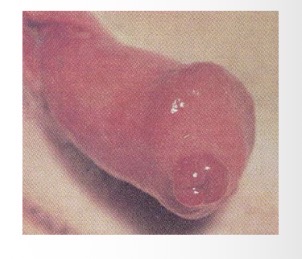
urethral prolapse - CS
excessive licking
protruding urethral mucosa
profuse intermittent bleeding
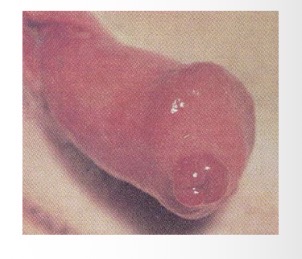
urethral prolapse - treatment
string suture around penis
resect prolapsed tissue + suture to urethra
castration
Issues due to urethral obstruction
Fail to eliminate urea + K
Hyperkalaemia → arrhythmias
Permanent renal damage
Pain
Bladder stretch
Causes of urethral obstruction
Urethral calculi
Urethral plugs
Prostatic disease
Hernia + body wall rupture → bladder displacement
Urethral neoplasia
Urethral stricture
Os penis fracture
Blood clots
Granulomatous urethritis
Urethral obstruction CS
Stranguira
Dysuria
Anuria
Haematuria
Excessive licking
Incontinence
Inappetance, lethargy, V
Abd distension, pain
Collapse
Urethral obstruction diagnosis
History
Abd palp - large, firm bladder
Serum biochem - urea, creatinine, K
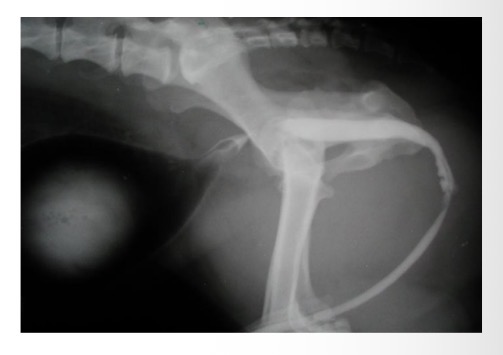
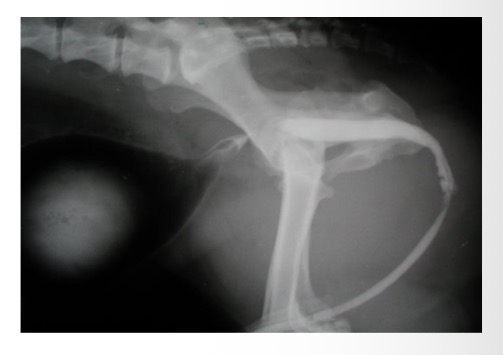
Radiography - plain, positive contrast urethrography
US
What can positive contrast radiography detect in urethral obstruction
Displaced bladder, radiolucent calculi, soft tissue lesions
Urethral obstruction management
Empty bladder, IVFT, electrolyte balance, pain relief
Investigate cause
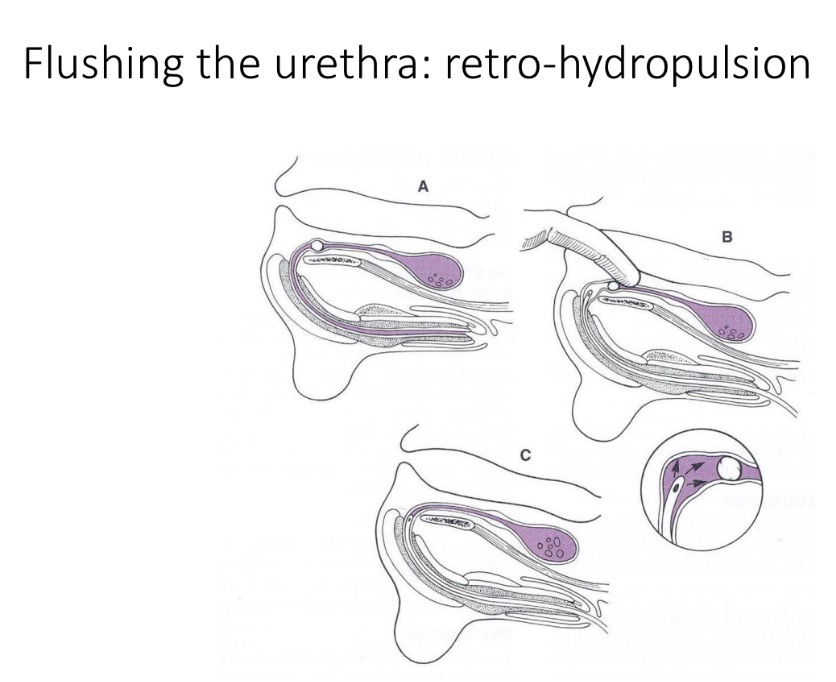
Urethral obstruction management- from calculi
1- empty bladder (cystocentesis)
2- IVFT
3- urethral catheter - GA, saline flush
4- empty bladder
5- retrograde urethrogram to confirm patency
6- cystotomy to retrieve calculi
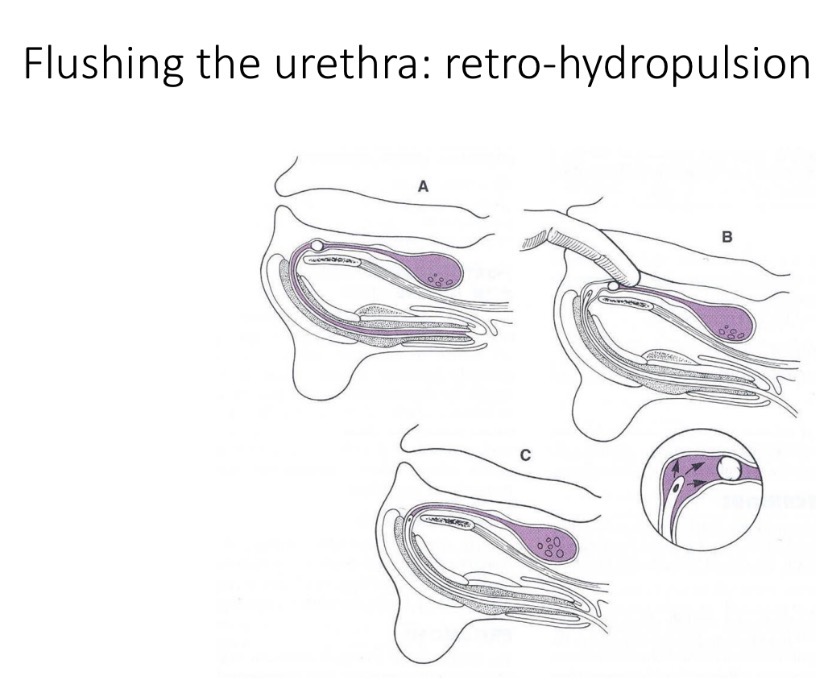
Urethrotomy in M dog steps - urethra incision for surgical exploration
1- Catheter to obstruction
2- ven long midline incision cd to os penis
3- reflect retractor penis
4- longitudinal incision through urethra over calculus
5- remove + analyse calculus
6- advance catheter
7- suture shut
8- remove catheter
Urethrotomy - suture pattern to close
1.5 G monofilament absorbable suture
Simple interrupted/ continuous
Complications of urethrotomy
Haemorrhage
Corpus spongiosum haemorrhage if off midline cut
Urine into sc tissues
Stricture formation
Urethrostomy def
Create permanent urethral opening
When to do urethrostomy
Failure of retrograde flush for urethral calculi
Recurrent urolithiasis
Urethral stricture
Severe penile trauma
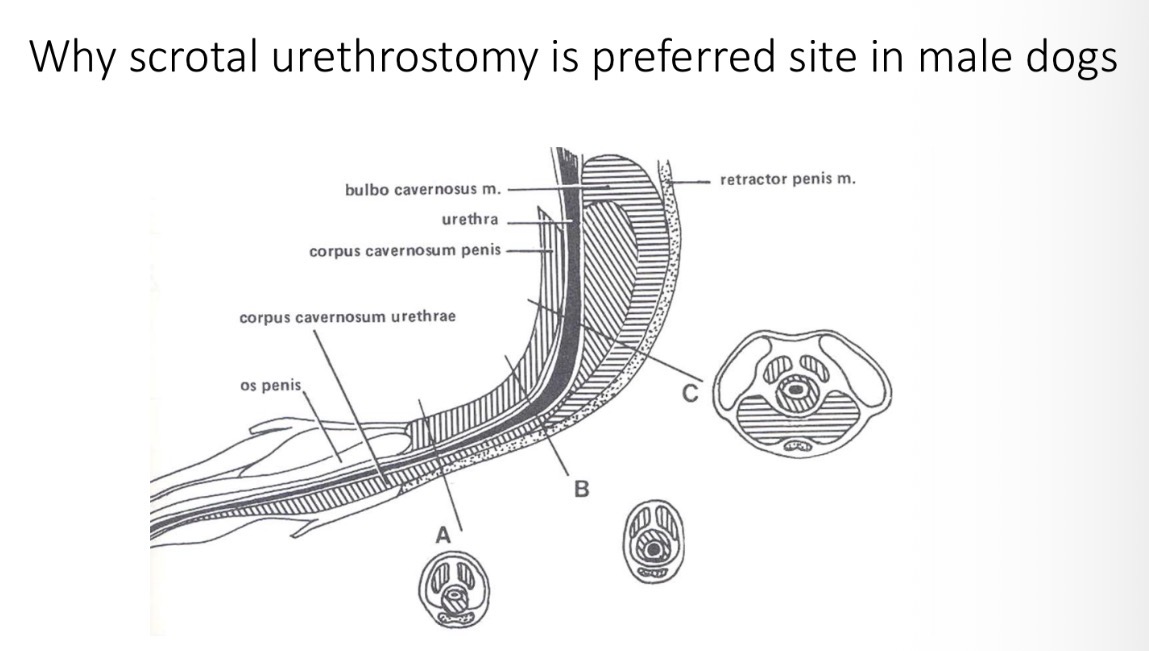
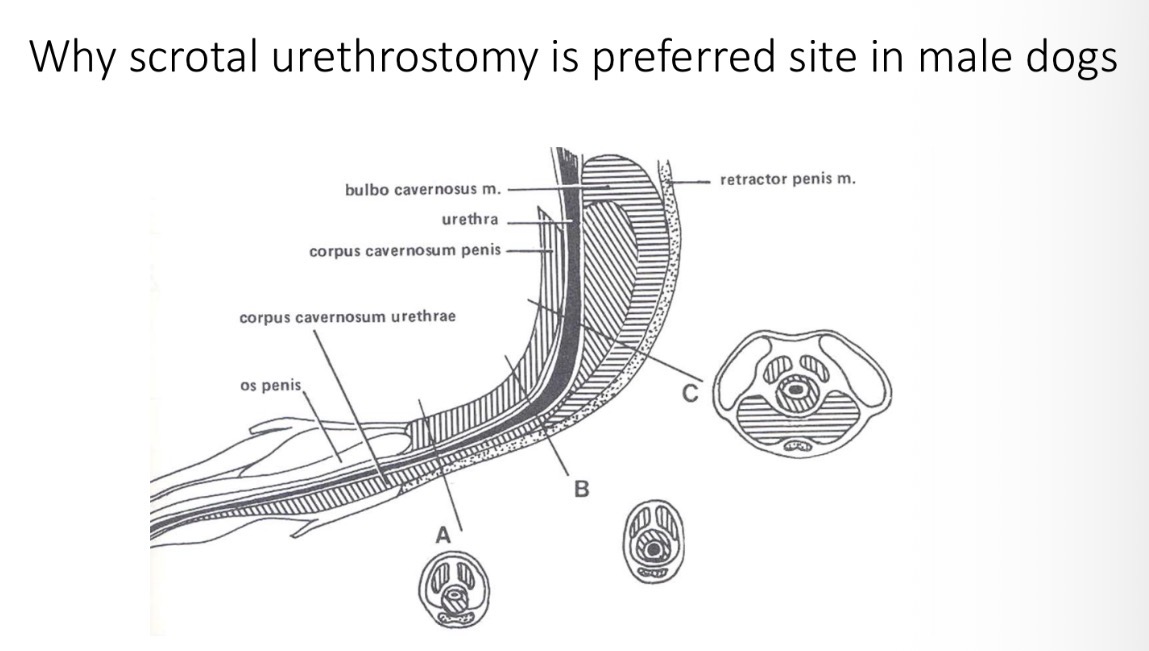
Urethrostomy - sites + species
Scrotal - dogs, less cavernous tissue
Pre scrotal - dogs
Perineal - cats
Pre pubic - intrapelvic urethral rupture in cats + dogs
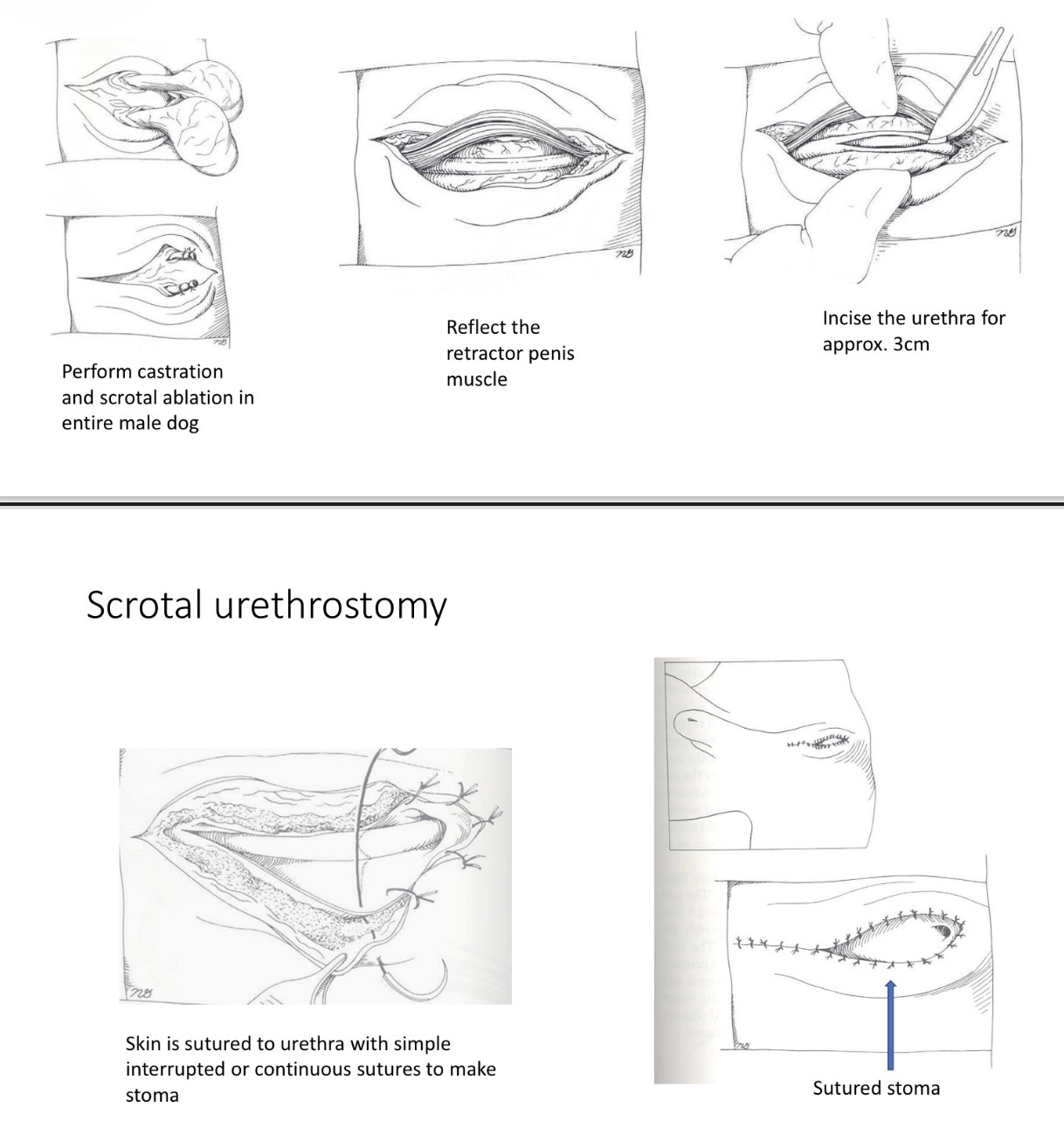
Scrotal Urethrostomy - steps if not castrated
1- castrate
2- scrotal ablation
3- midline incision 3-4cm long
4- reflect retractor penis
5- 3-4cm incision along urethra
6- suture urethra to skin
7- close skin + sc tissue cd +cr to stoma
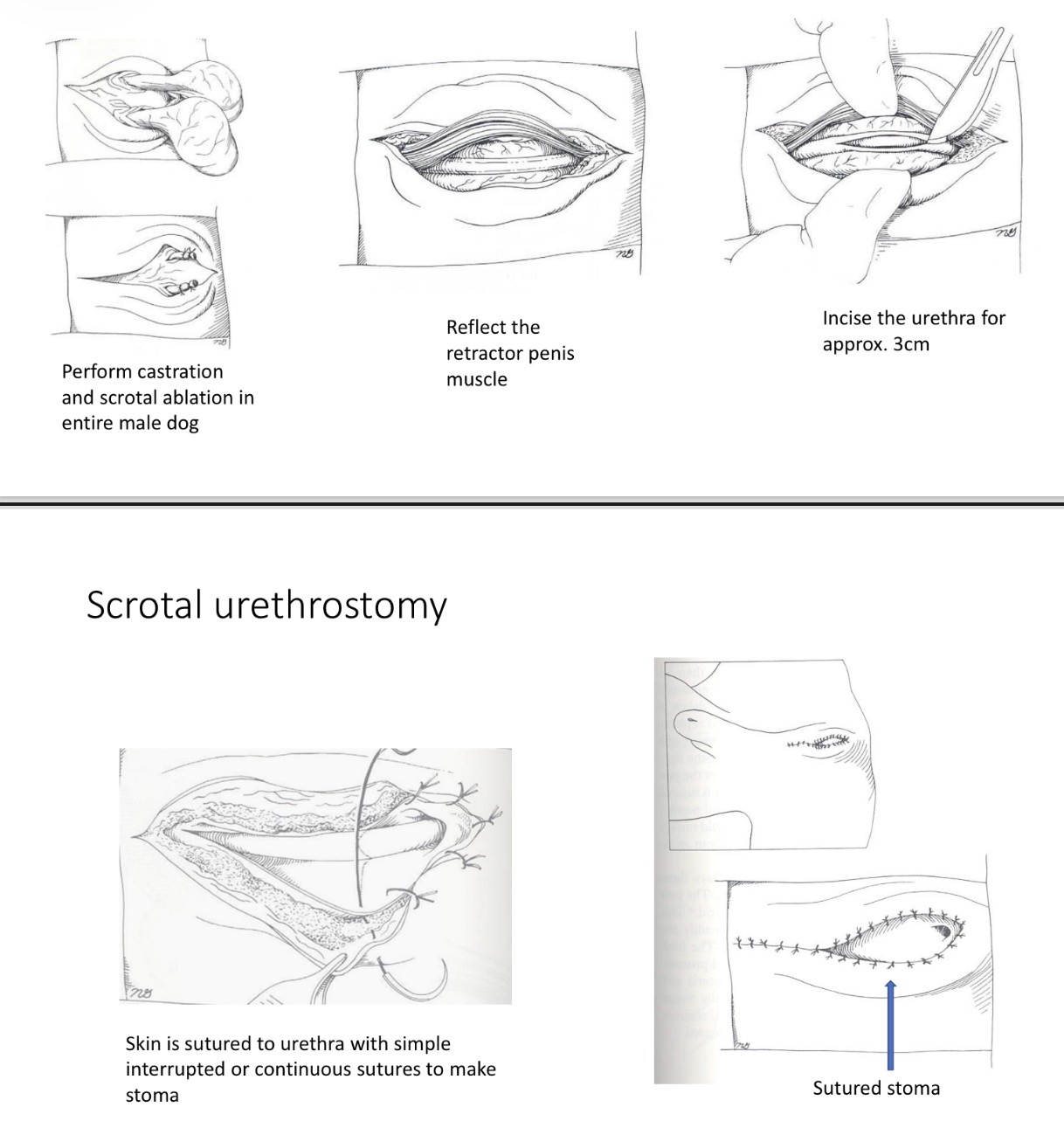
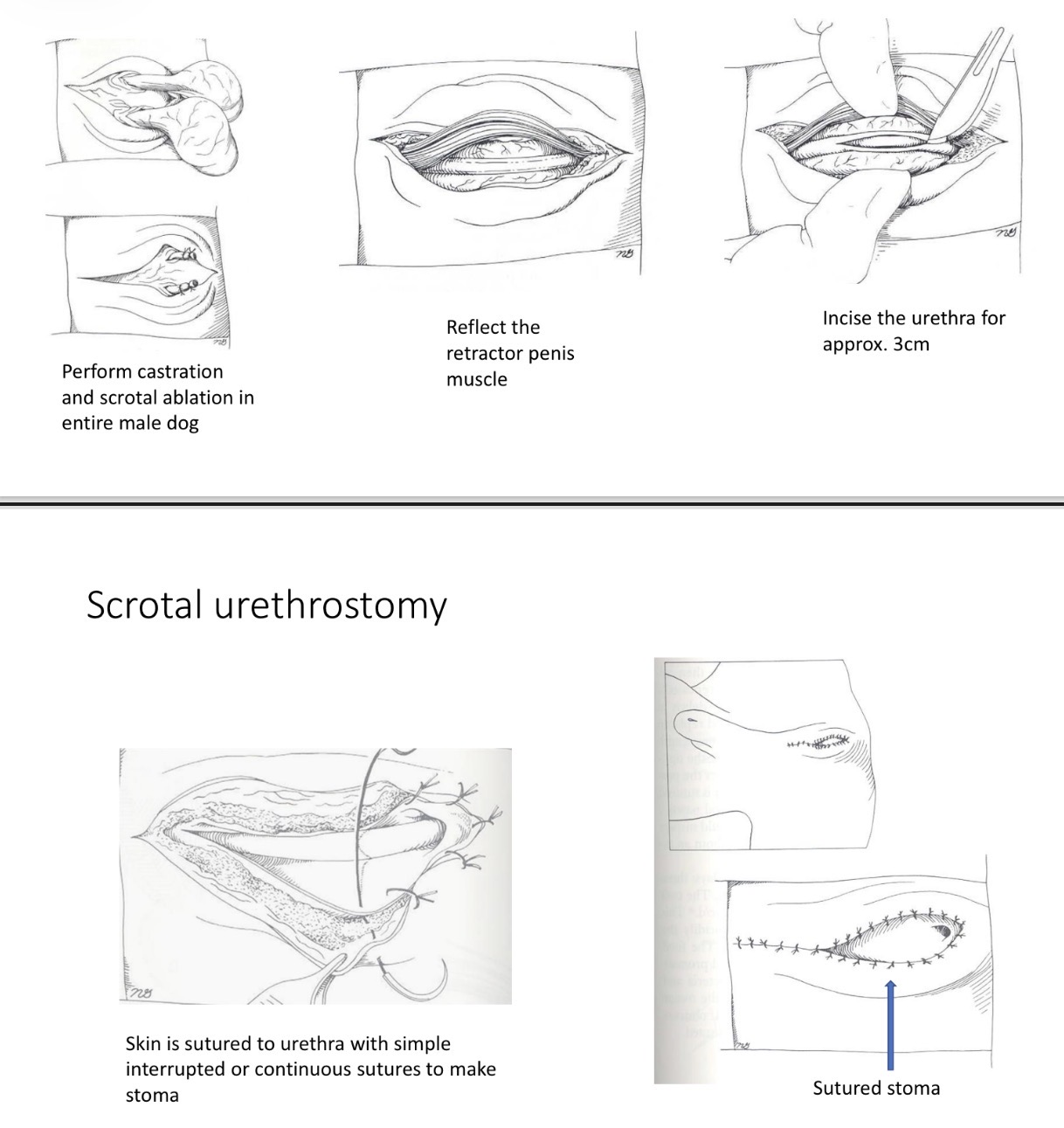
Scrotal Urethrostomy - Steps if castrated
1- midline incision 3-4cm long
2- reflect retractor penis
3- 3-4cm incision along urethra
4- suture urethra to skin
5- close skin + sc tissue cd +cr to stoma
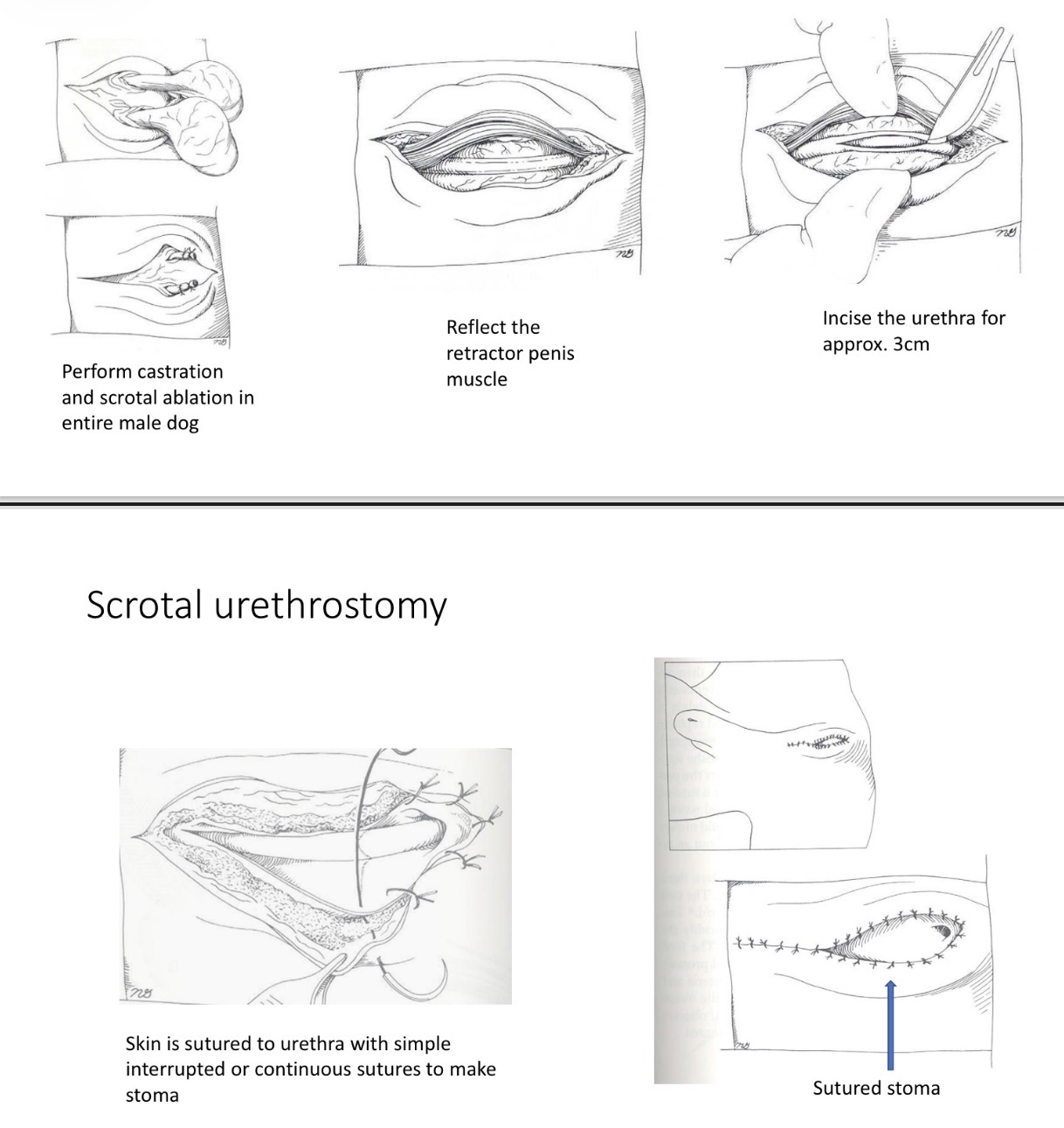
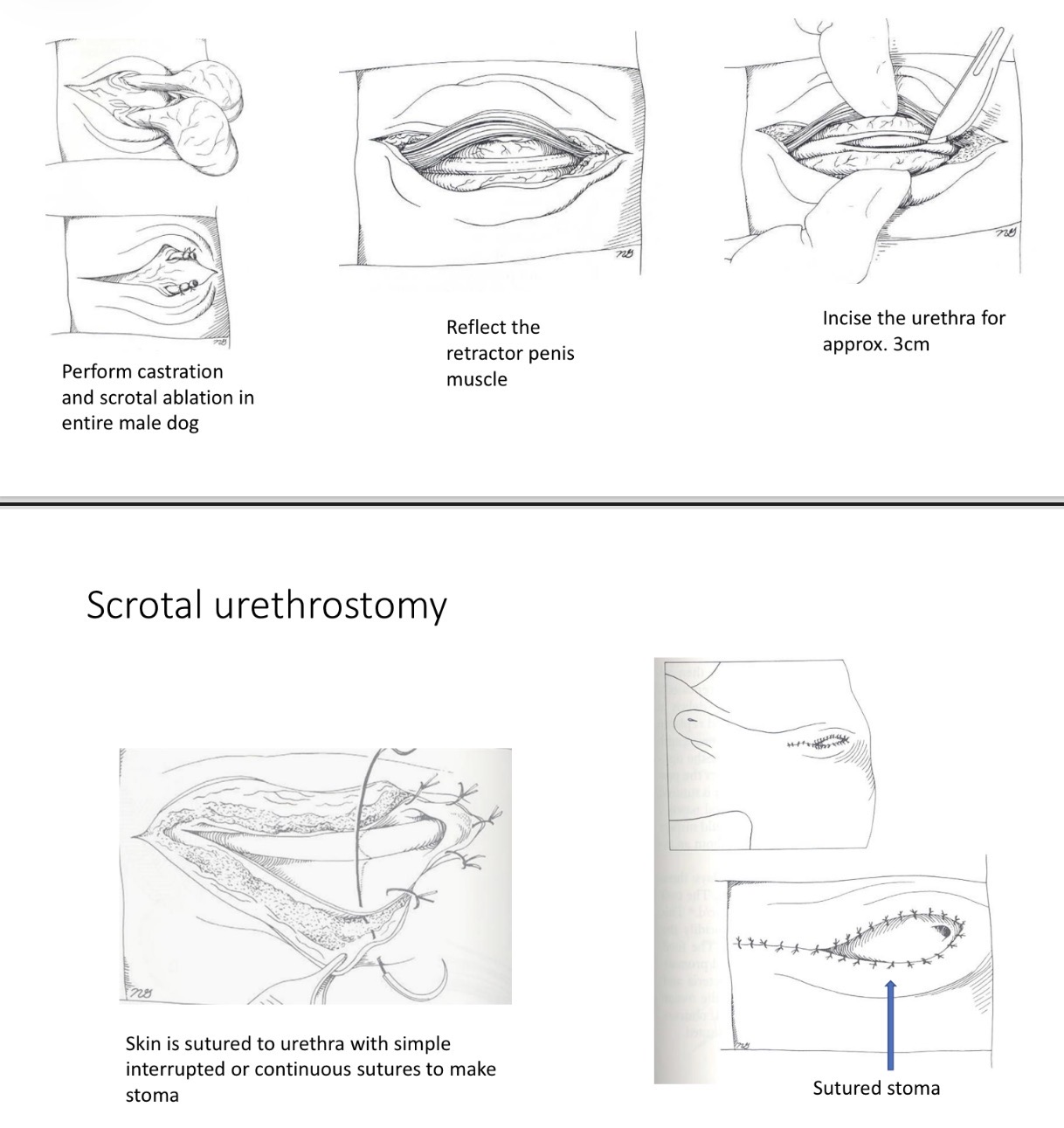
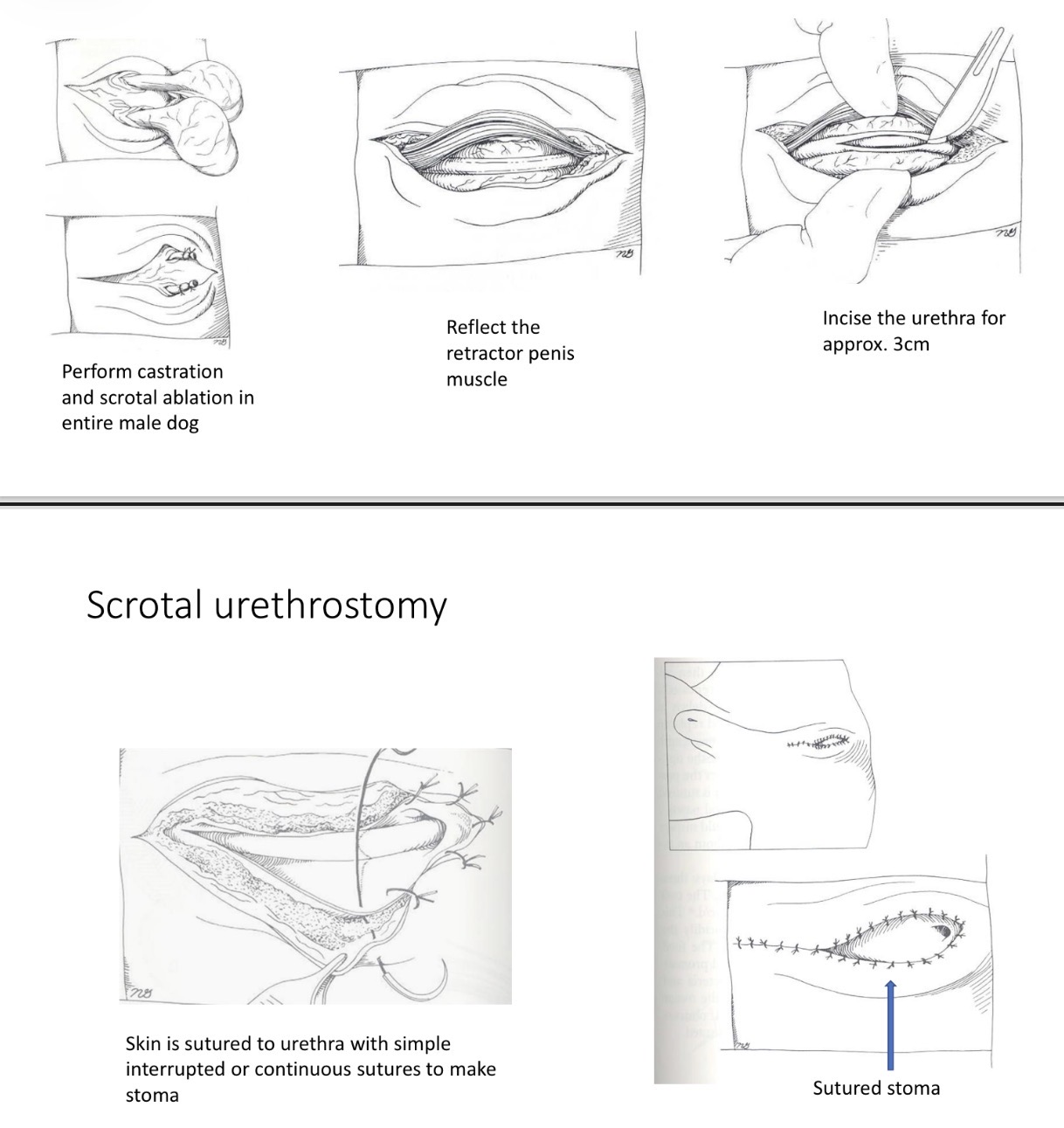
Scrotal Urethrostomy - Closure
1.5 G monofilament suture in simple interrupted/ continuous
Scrotal Urethrostomy - What to do if non absorbable suture
Sedate in 14d for removal
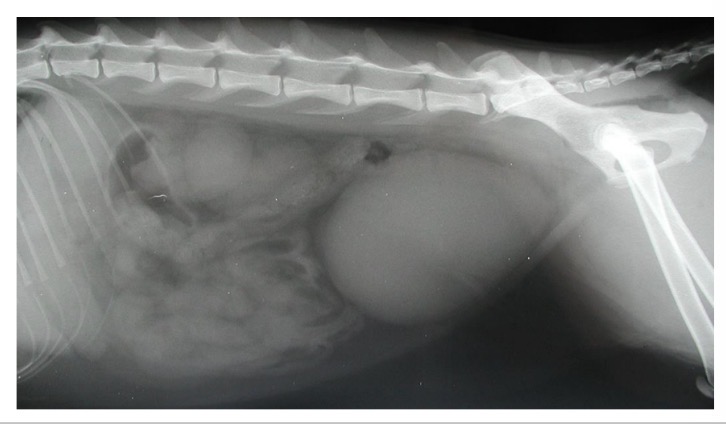
Urethral obstruction in M cats - main location
Dist penile urethra - narrows
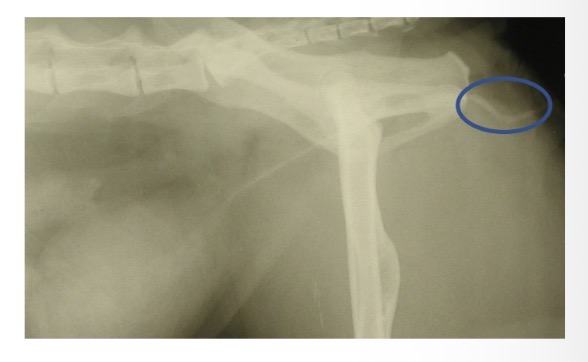
Perineal urethrostomy in M cats - when to do
Fail to relieve urethral obstruction by retrograde flushing
Recurrent / chronic urethral obstruction
Penile urethral stricture
Severe penile urethral trauma
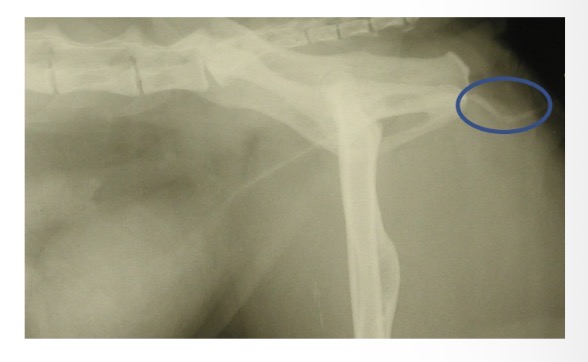
Perineal urethrostomy in M cats - Complications from surgery
Wound breakdown
Cellulitis
Stricture formation
Recurrent UTI
Perineal hernia
Urethral trauma - causes
Abd Trauma, pelvic fracture, iatrogenic (catheter)
Urethral trauma - CS
Haematuria, dysuria, anuria
Pain
Abd distension
Inappetence, lethargy, V
Collapse
Skin discolouring, cellulitis of perineum+thigh+cd abd
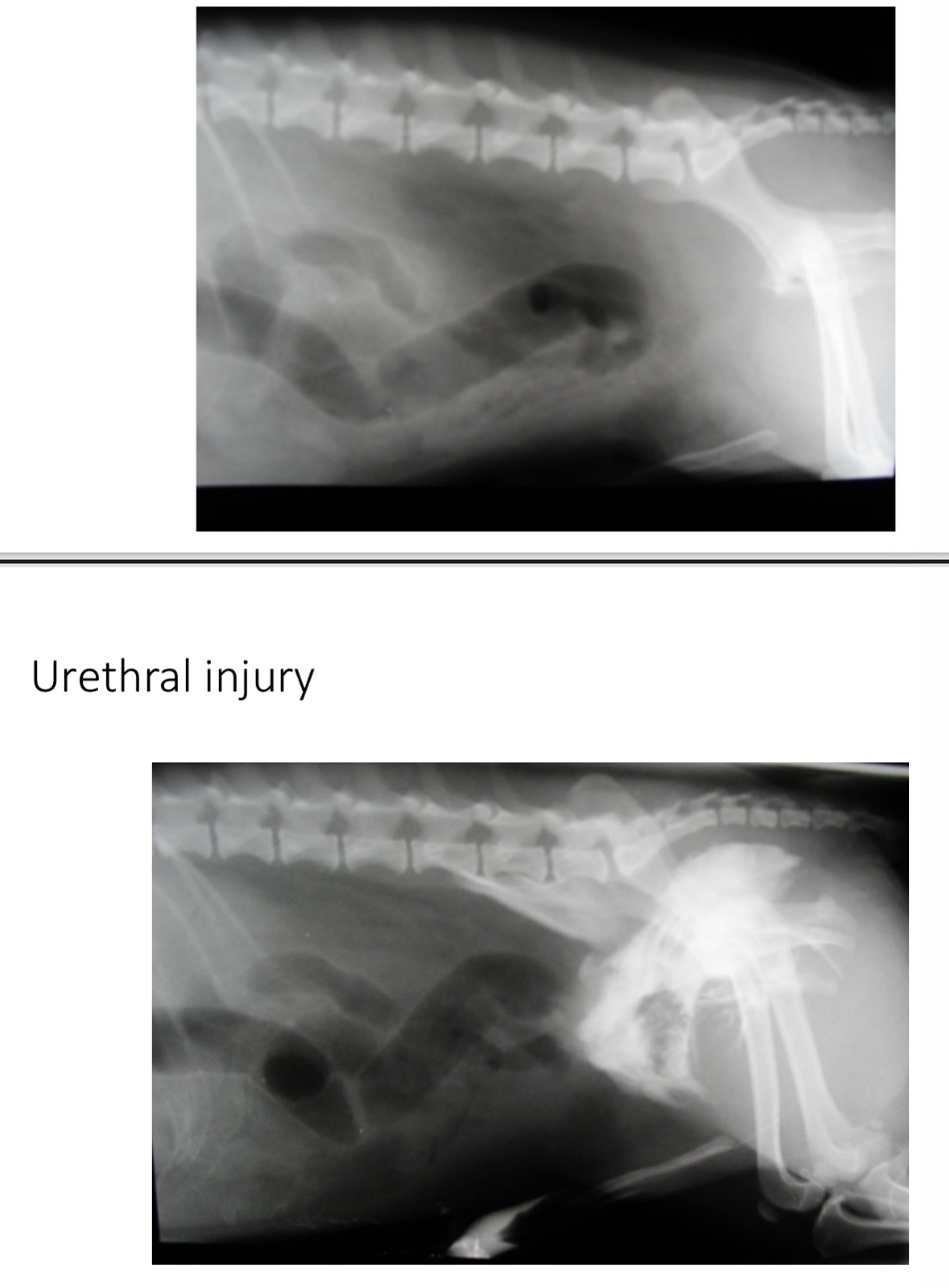
Urethral trauma - Diagnosis
History
Radiography (Plain, retrograde urethrogram)
Serum biochem - inc urea, creatinine, K
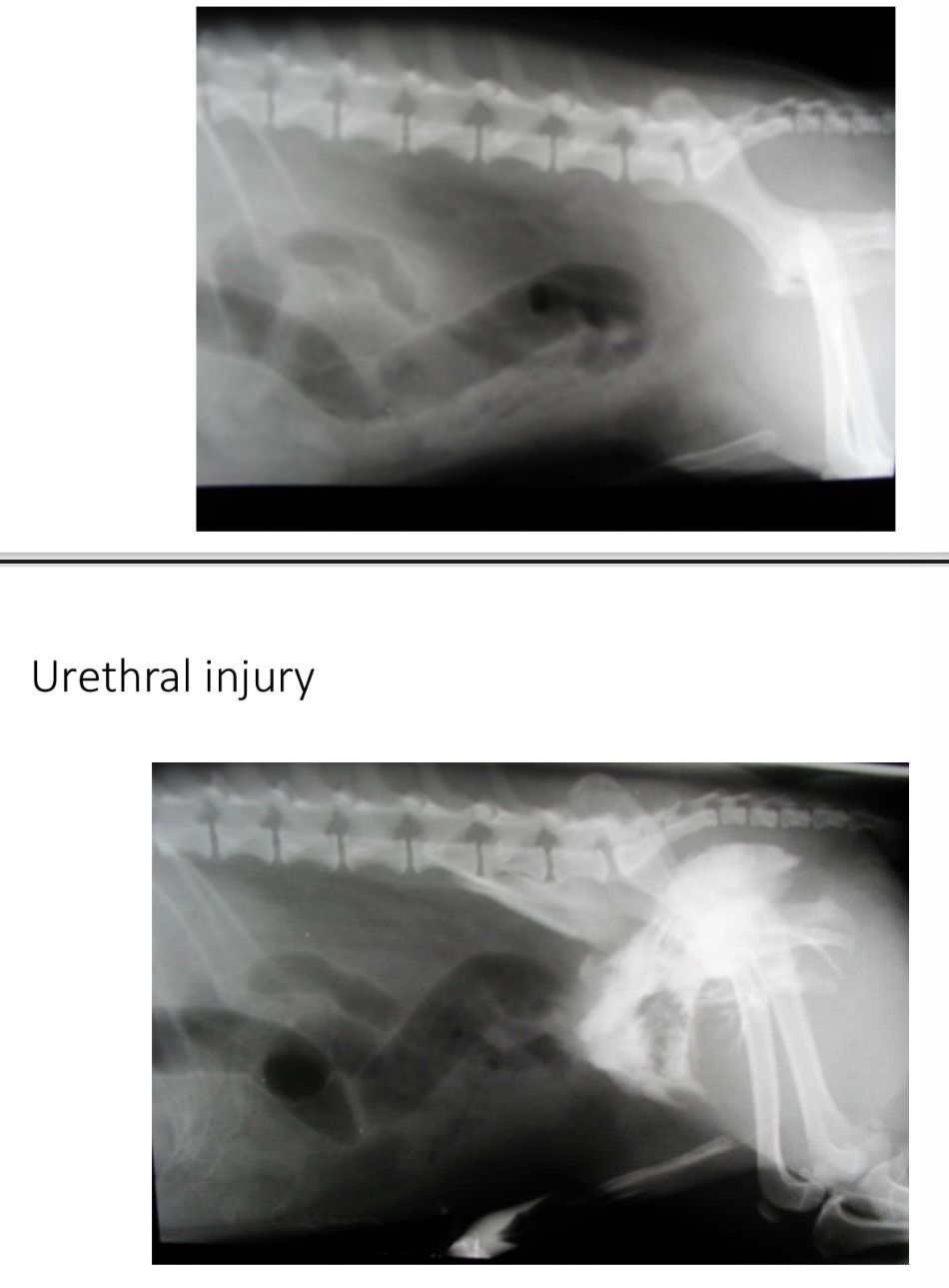
Urethral trauma - Treatment
Establish patency with catheter
Stabilise patient
Conservative treatment - in dwelling catheter
Surgery
Prepubic urethrostomy - steps
Salvage procedure for intrapelvic injury if not enough length
Create new opening on ven cd abd