Anatomy Lecture Exam 4
1/200
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
201 Terms
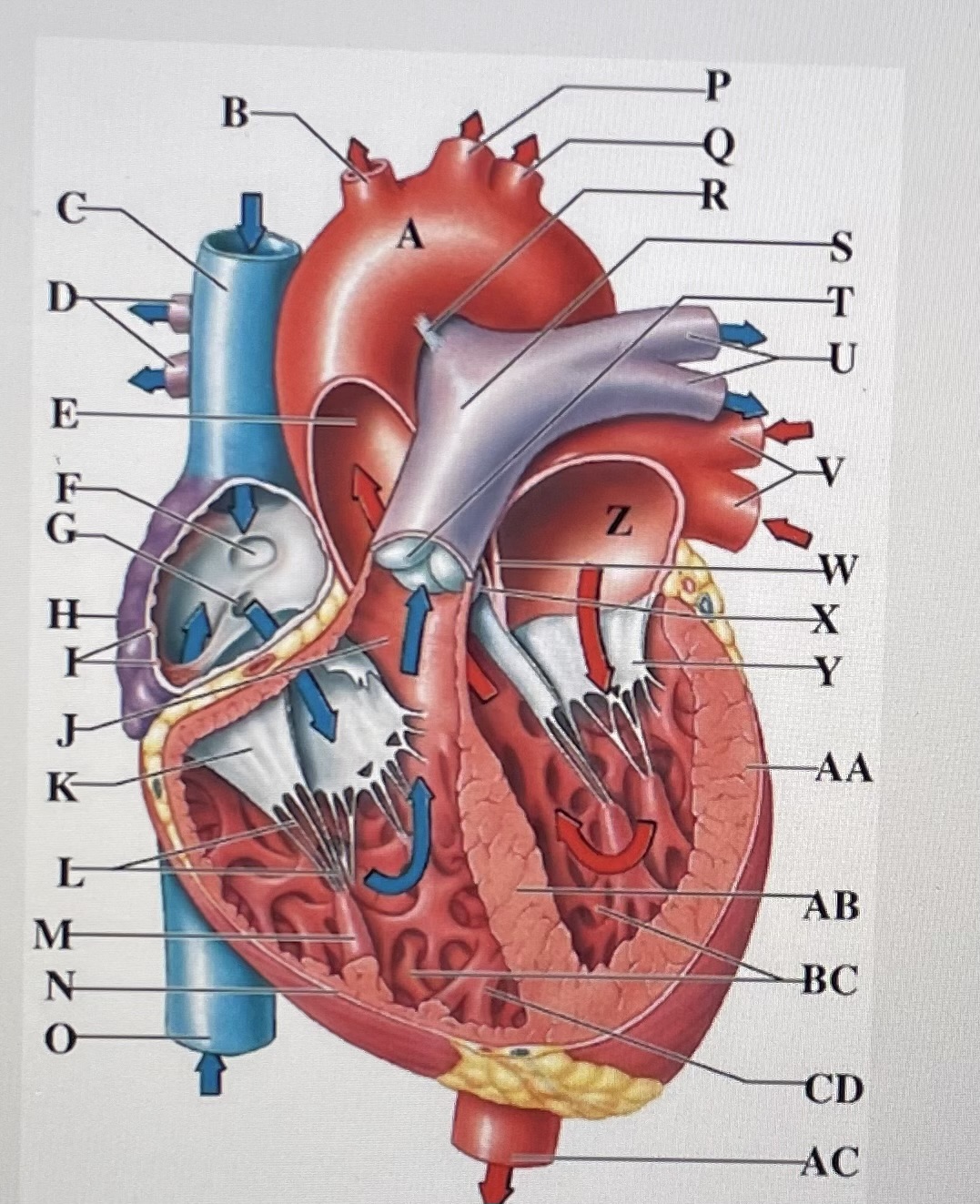
aortic arch
A
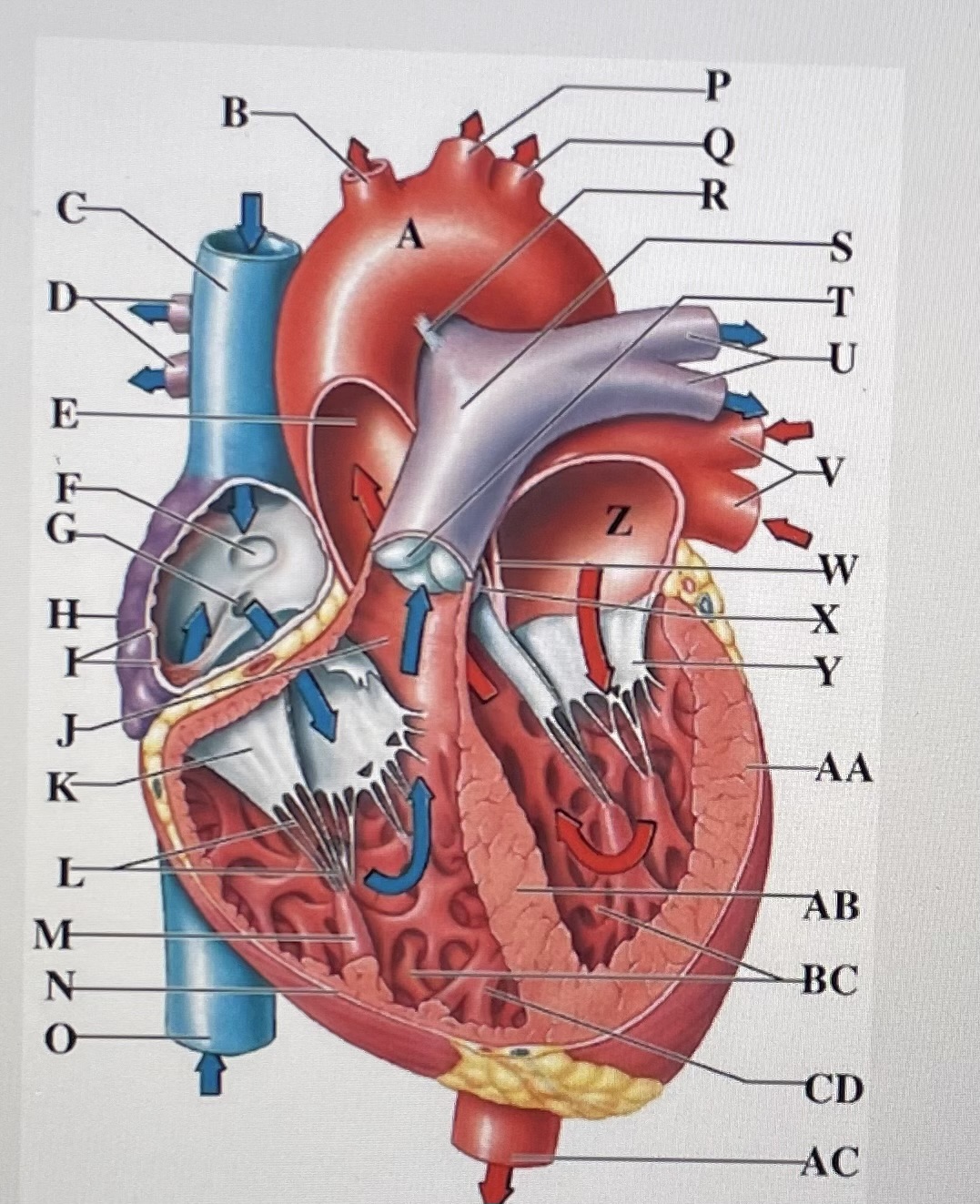
brachiocephalic trunk
B
Superior Vena Cava
C
right pulmonary arteries
D
ascending aorta
E
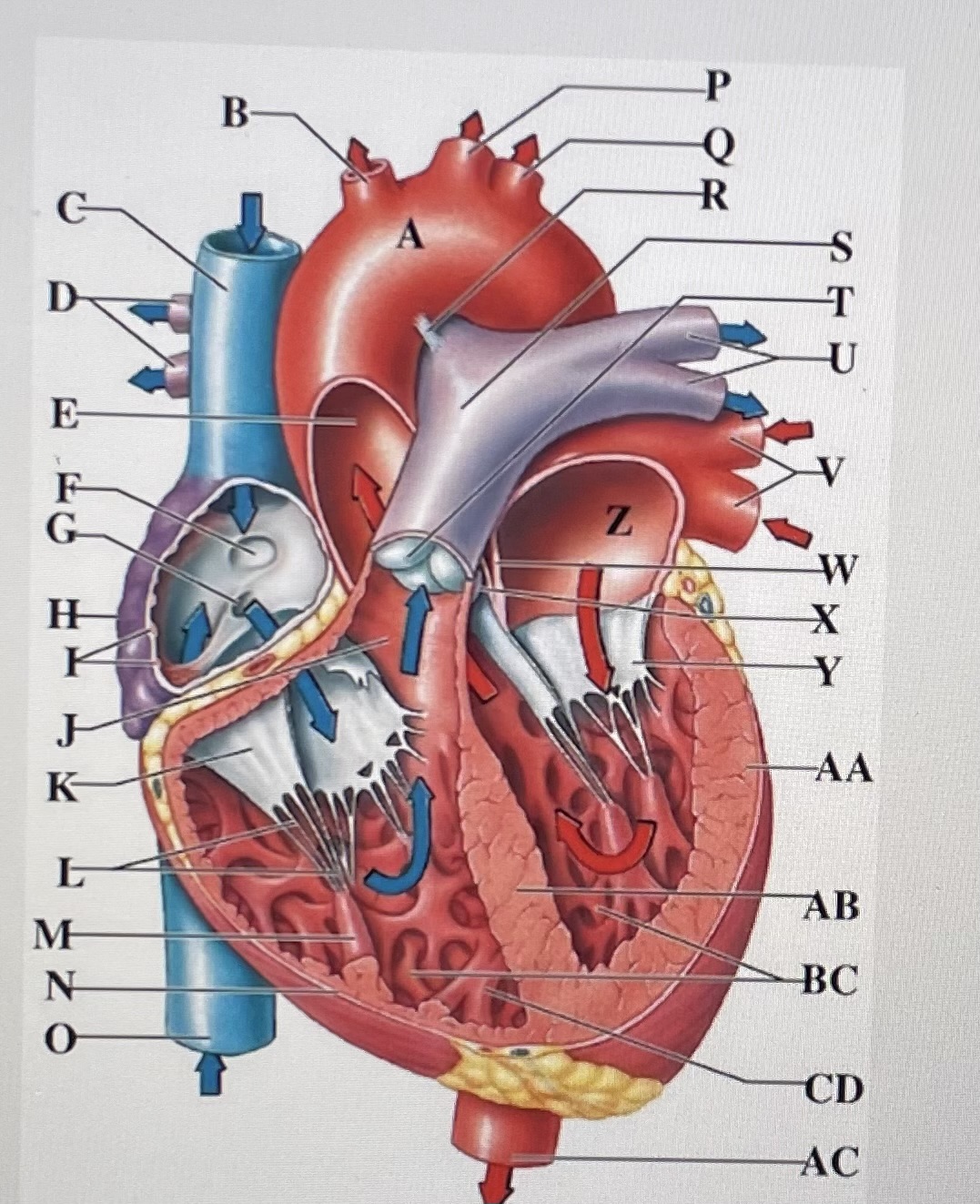
fossa ovalis
F
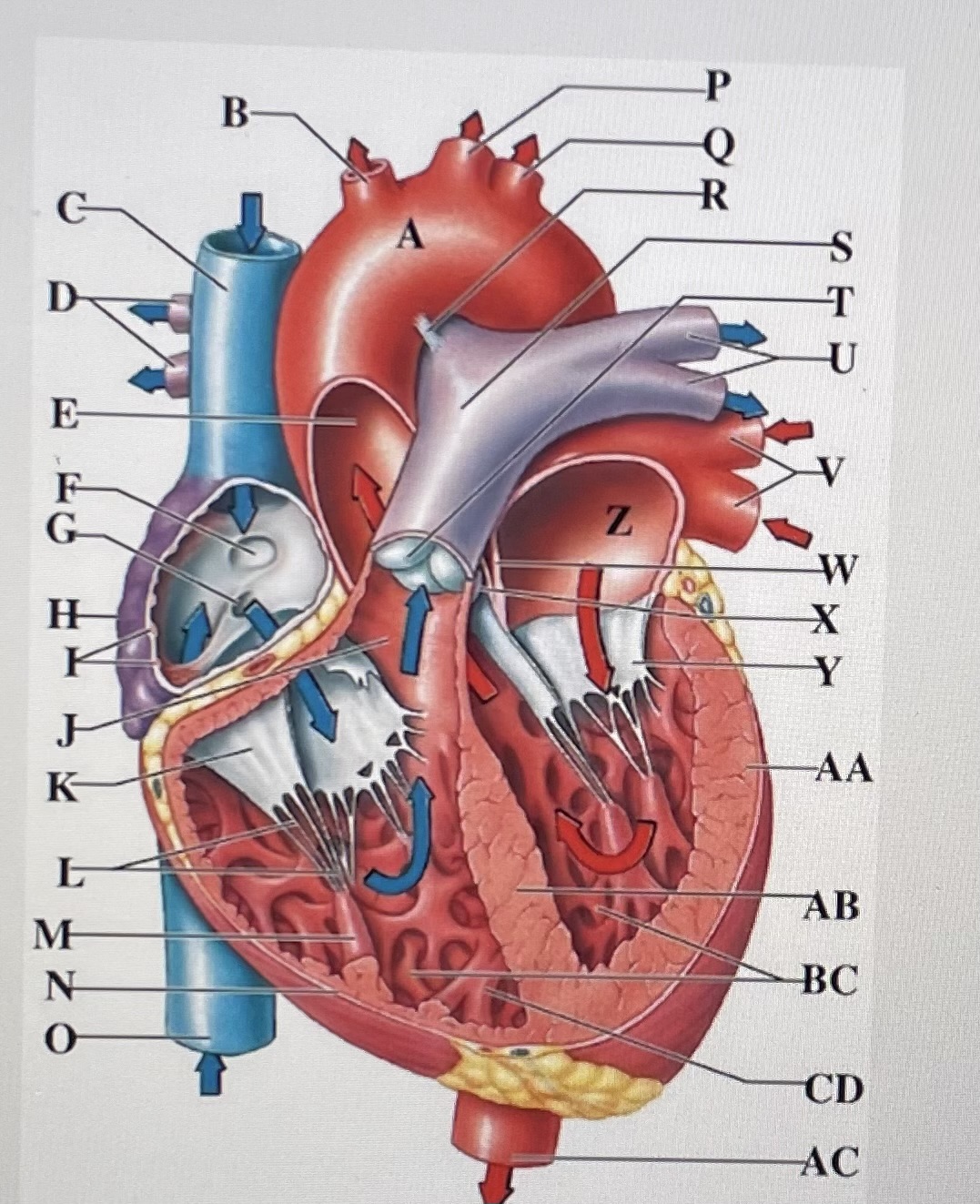
opening of coronary sinus
G
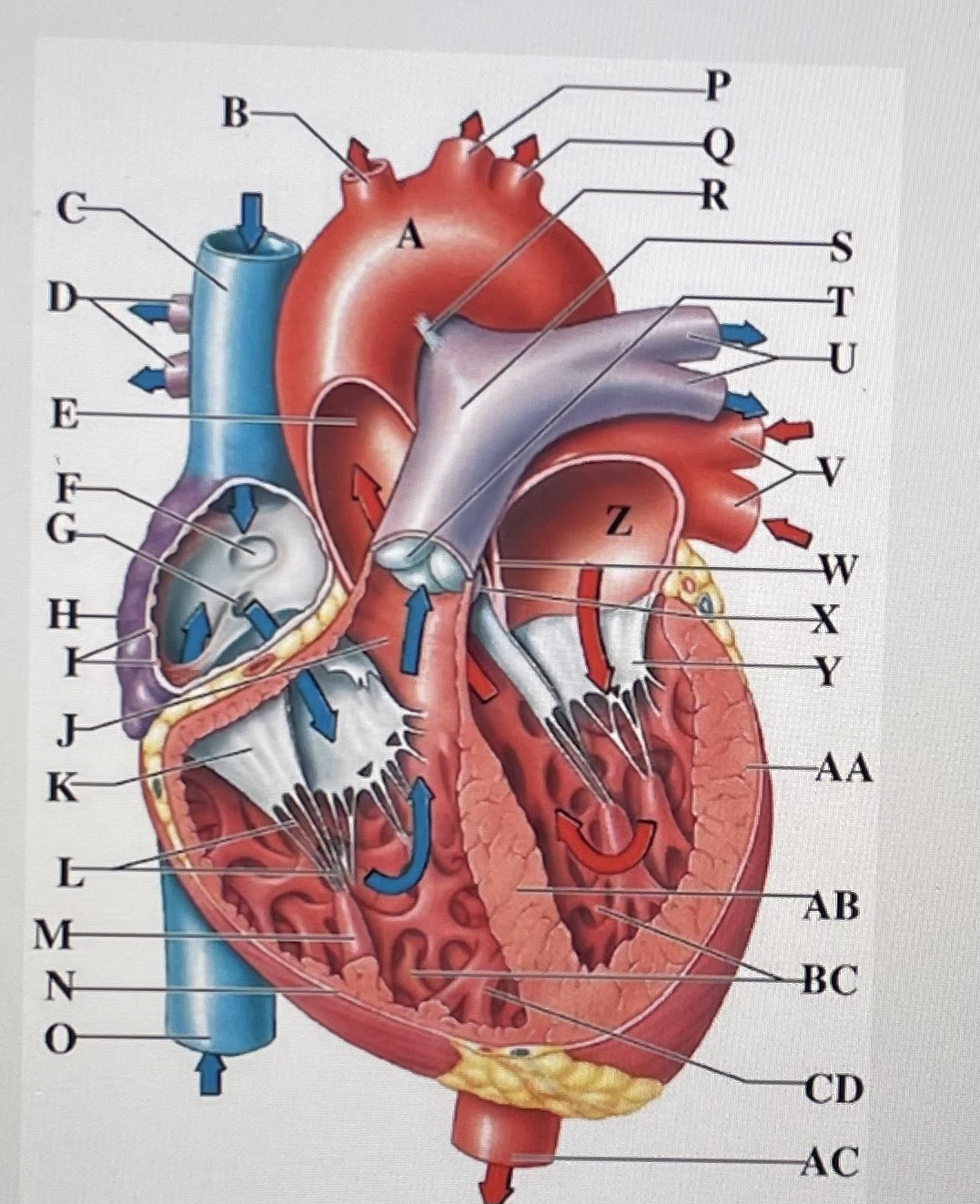
right atrium
H
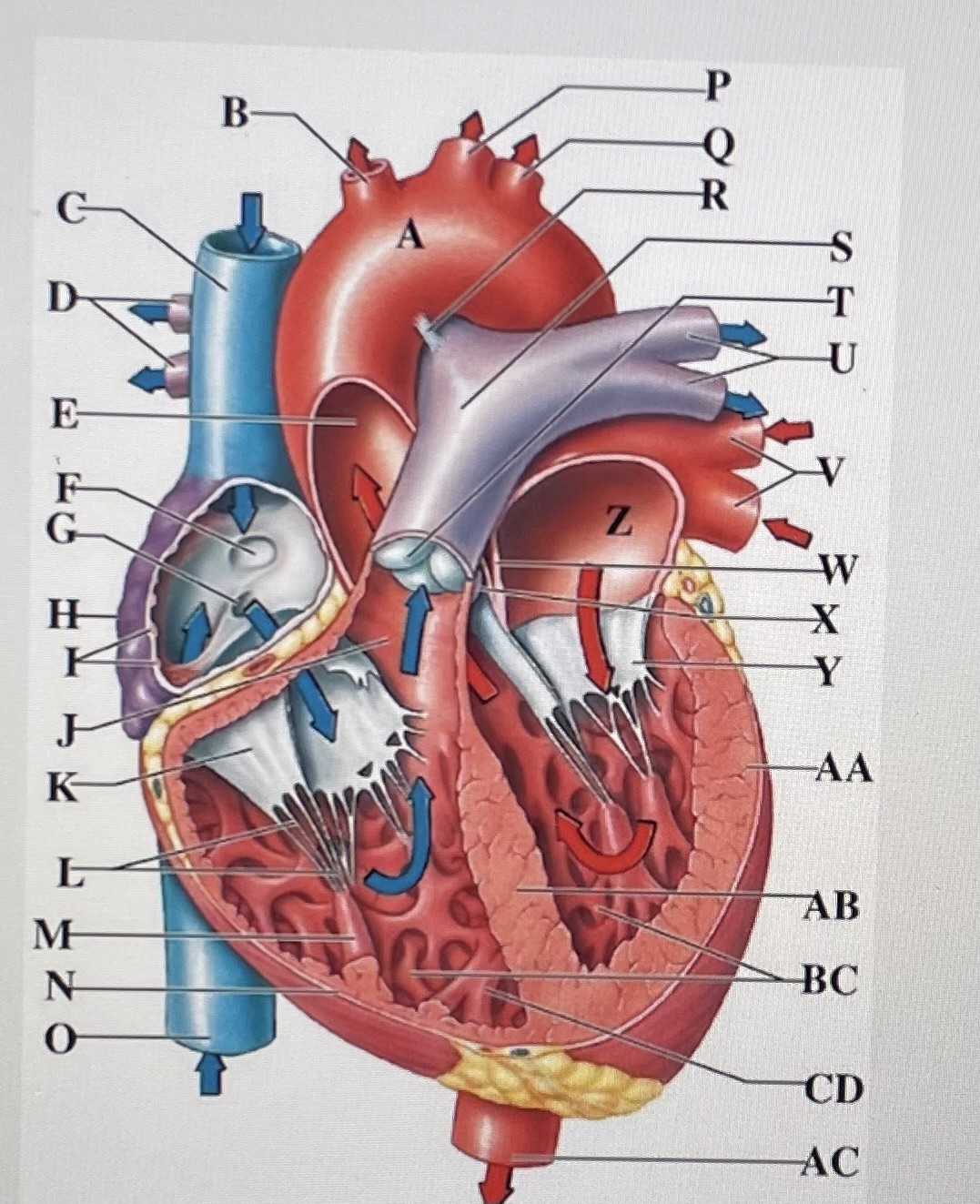
pectinate muscles
I
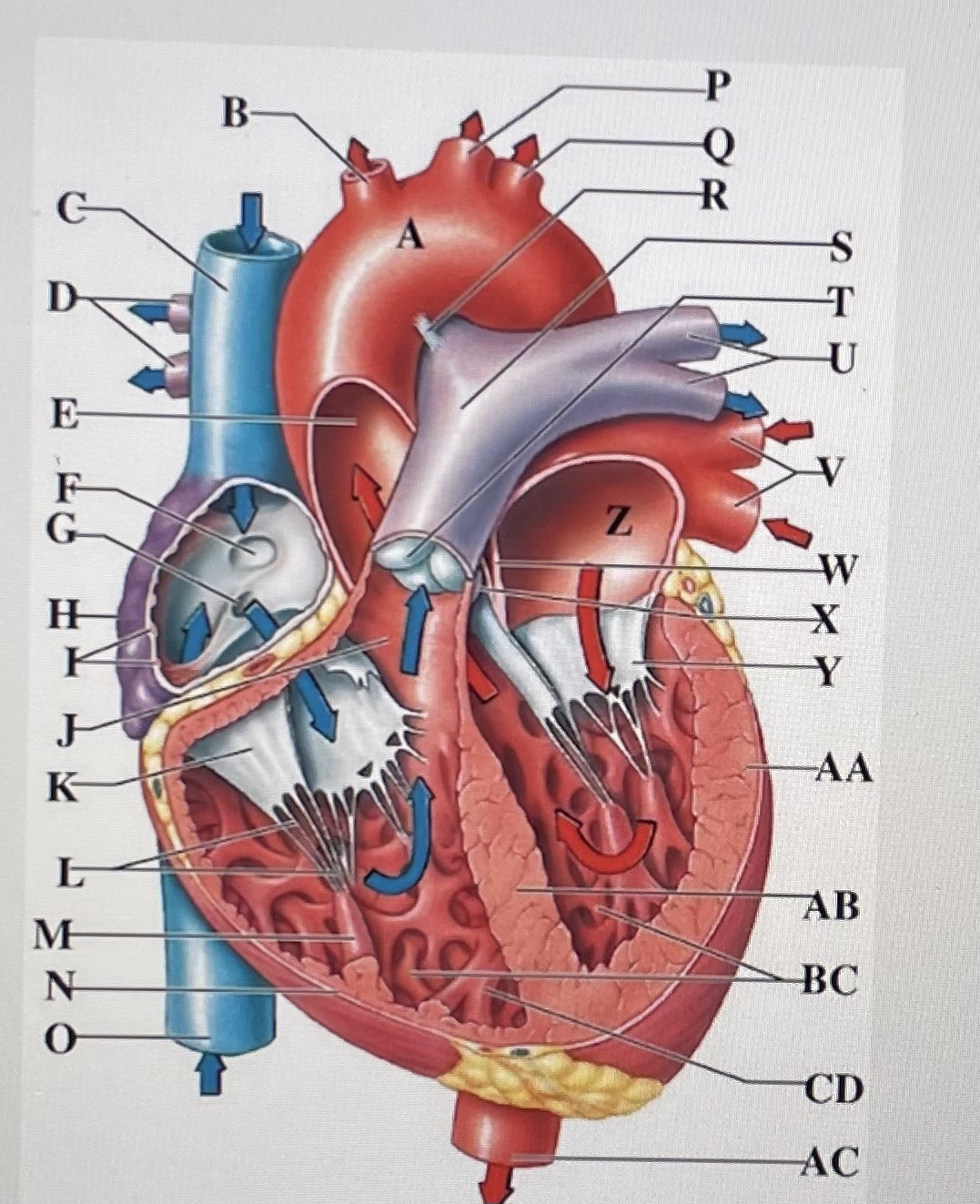
conus arteriosus
J
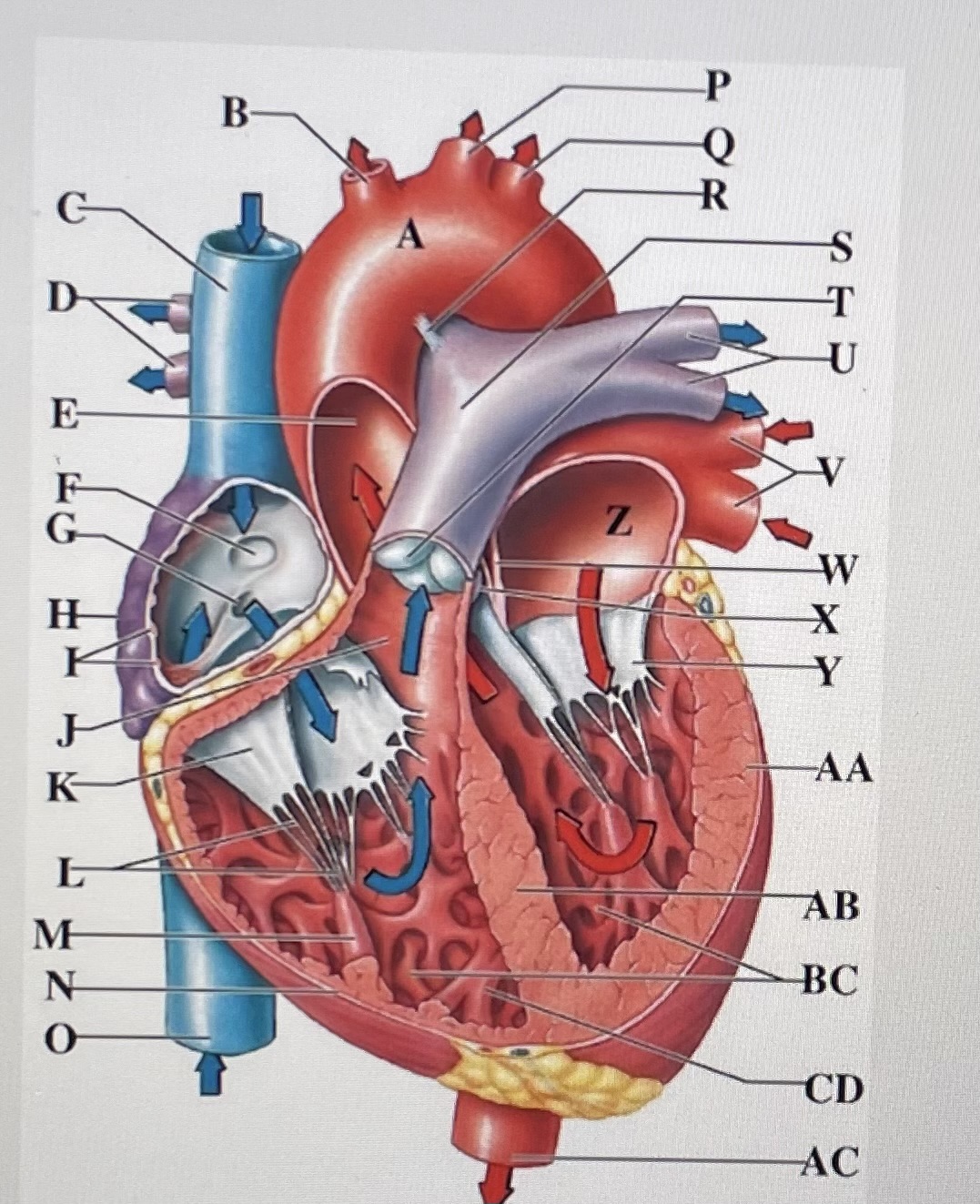
Cusp of right AV (tricuspid) valve
K
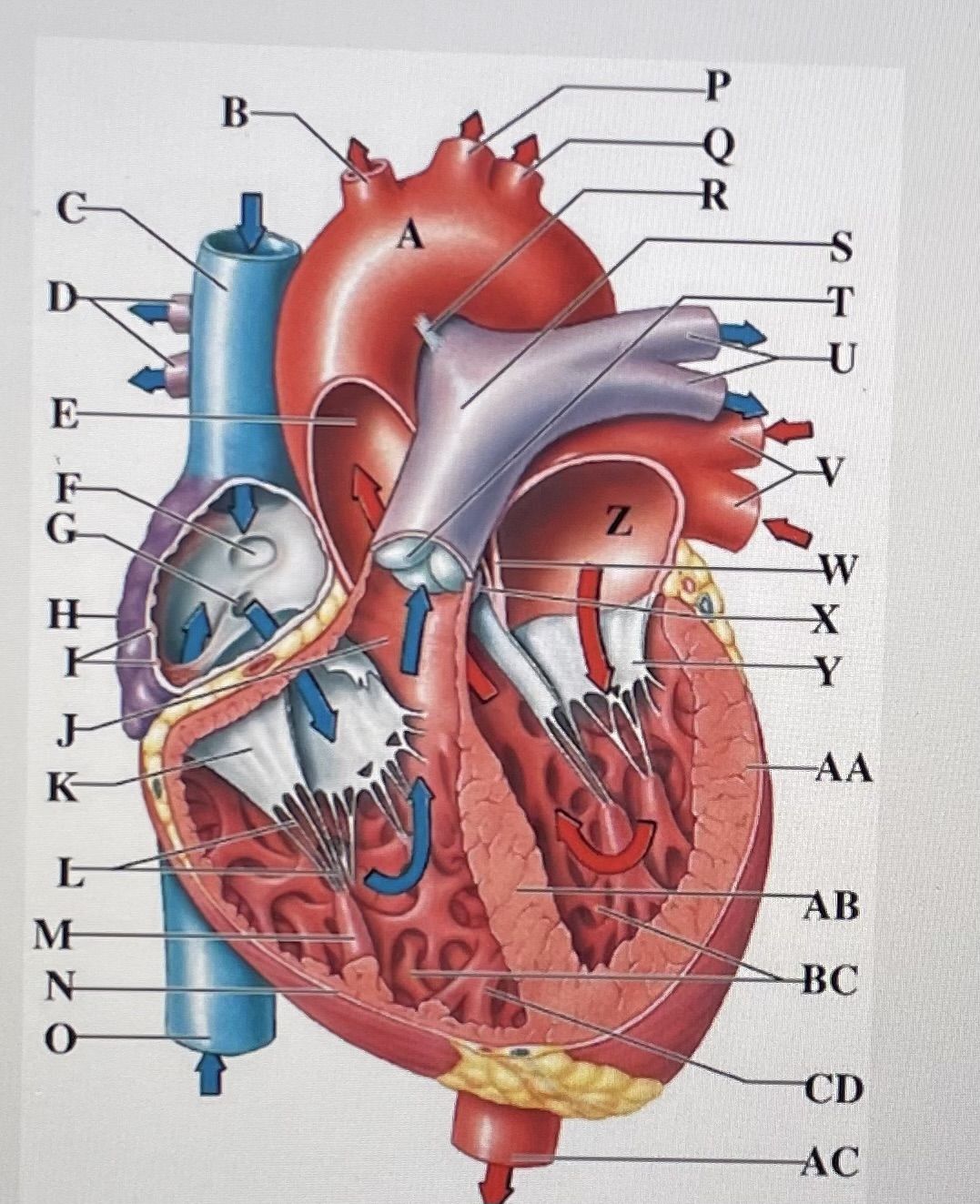
chordae tendineae
L
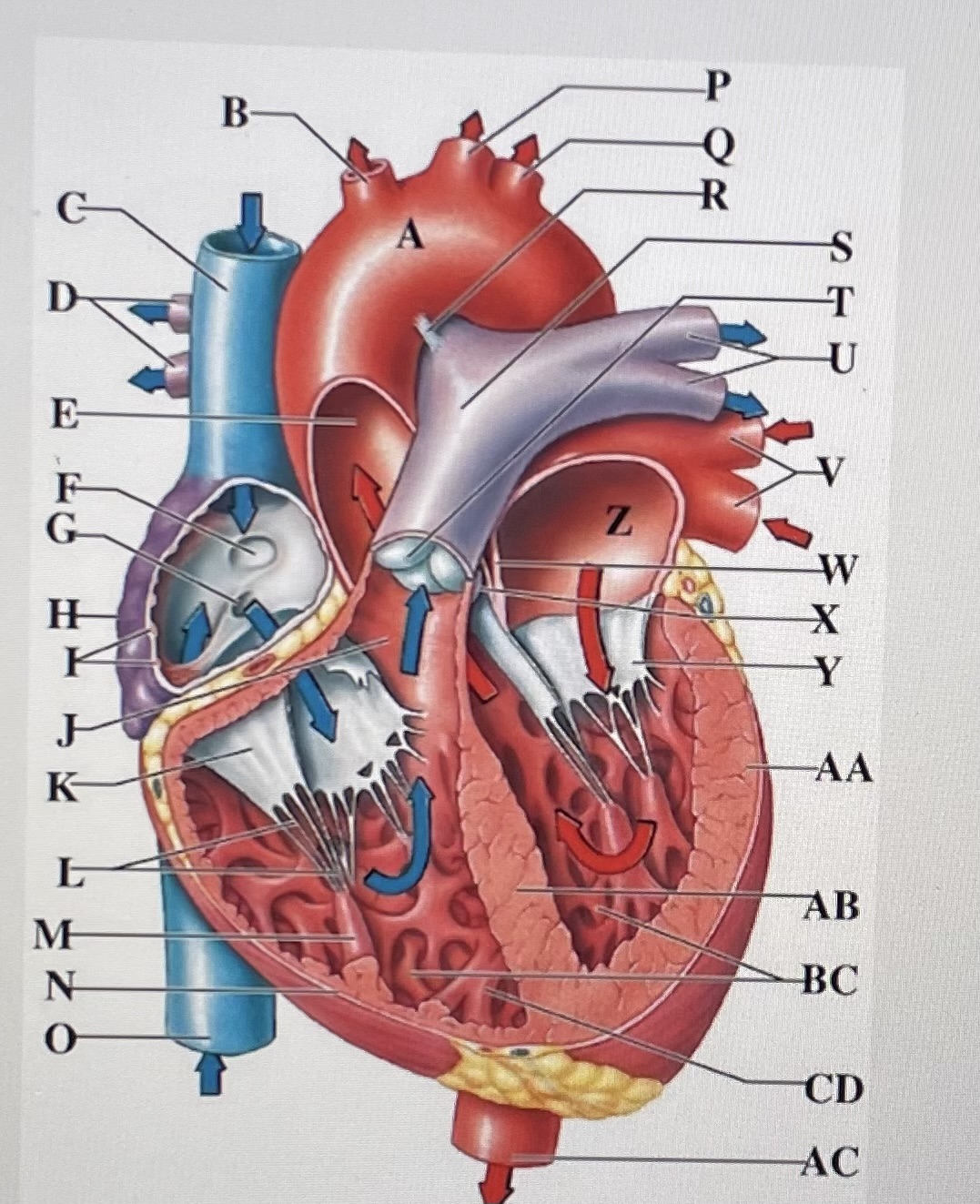
papillary muscle
M
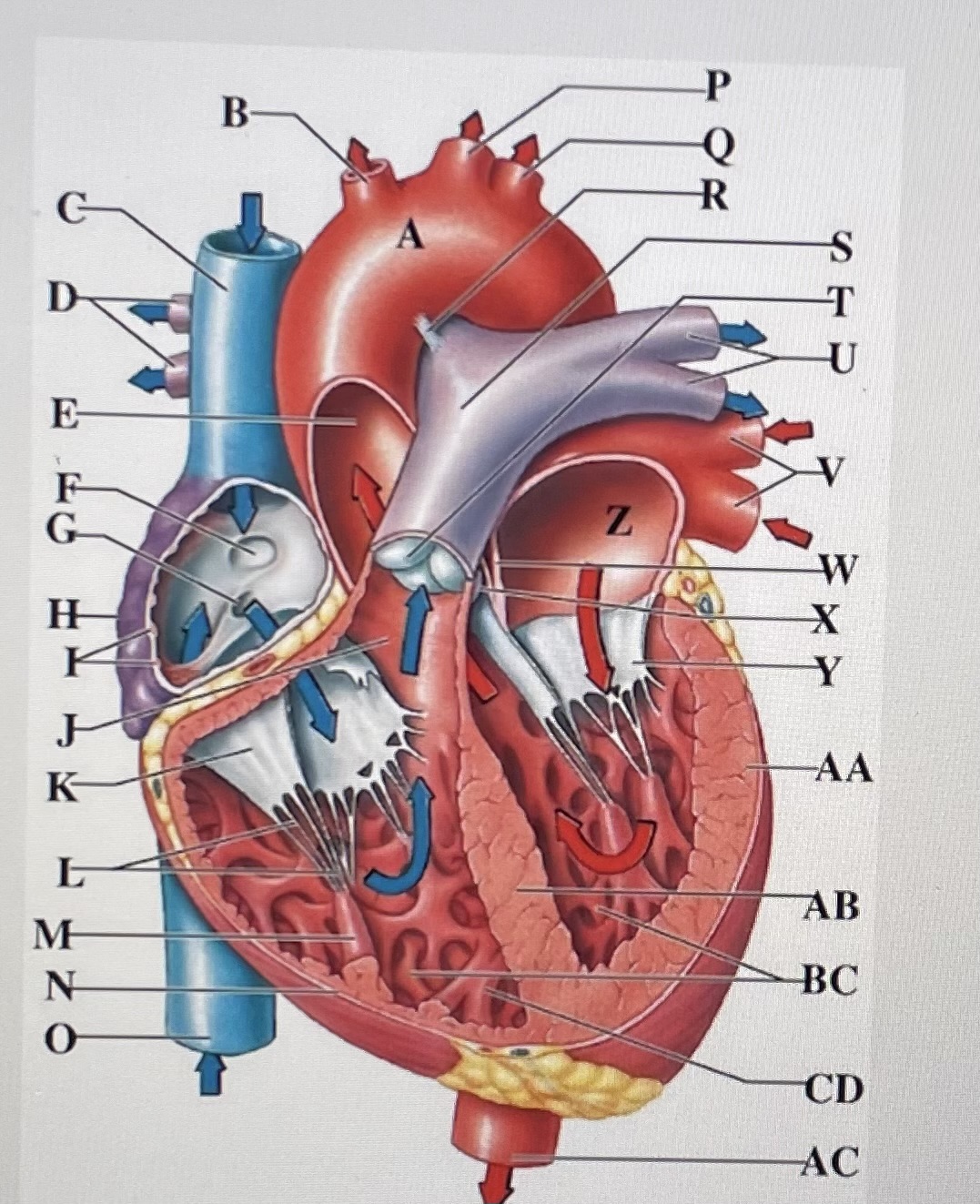
right ventricle
N
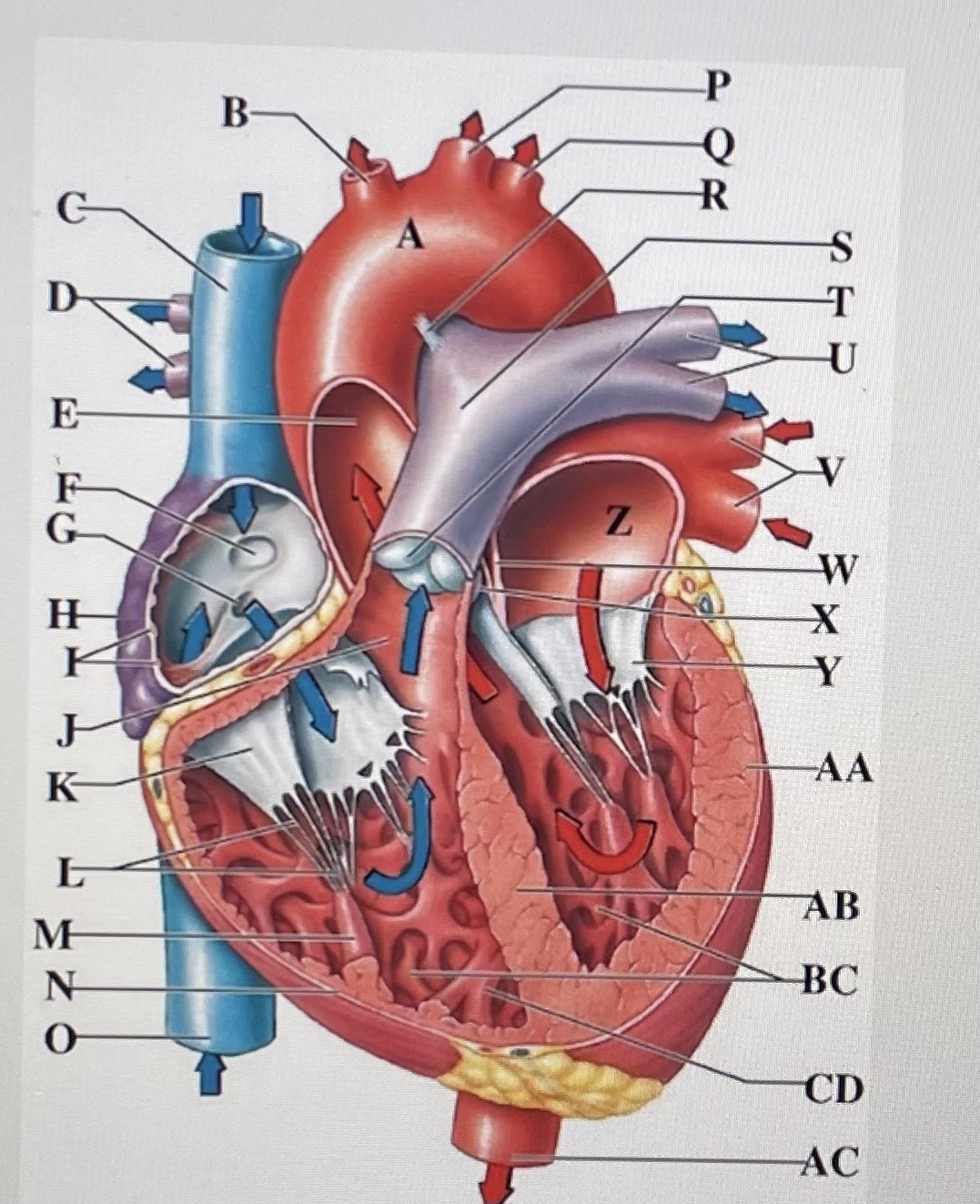
inferior vena cava
O
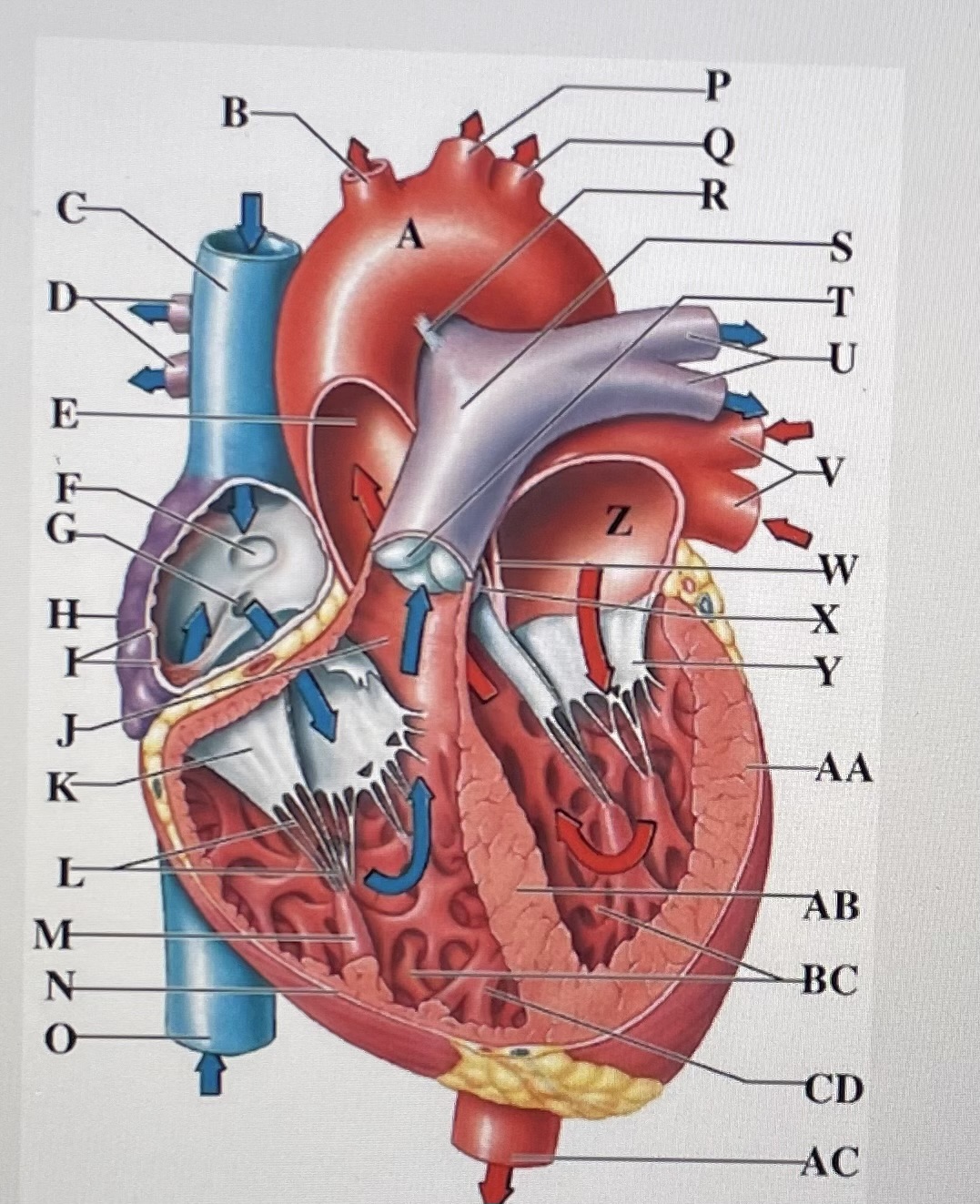
left common carotid artery
P
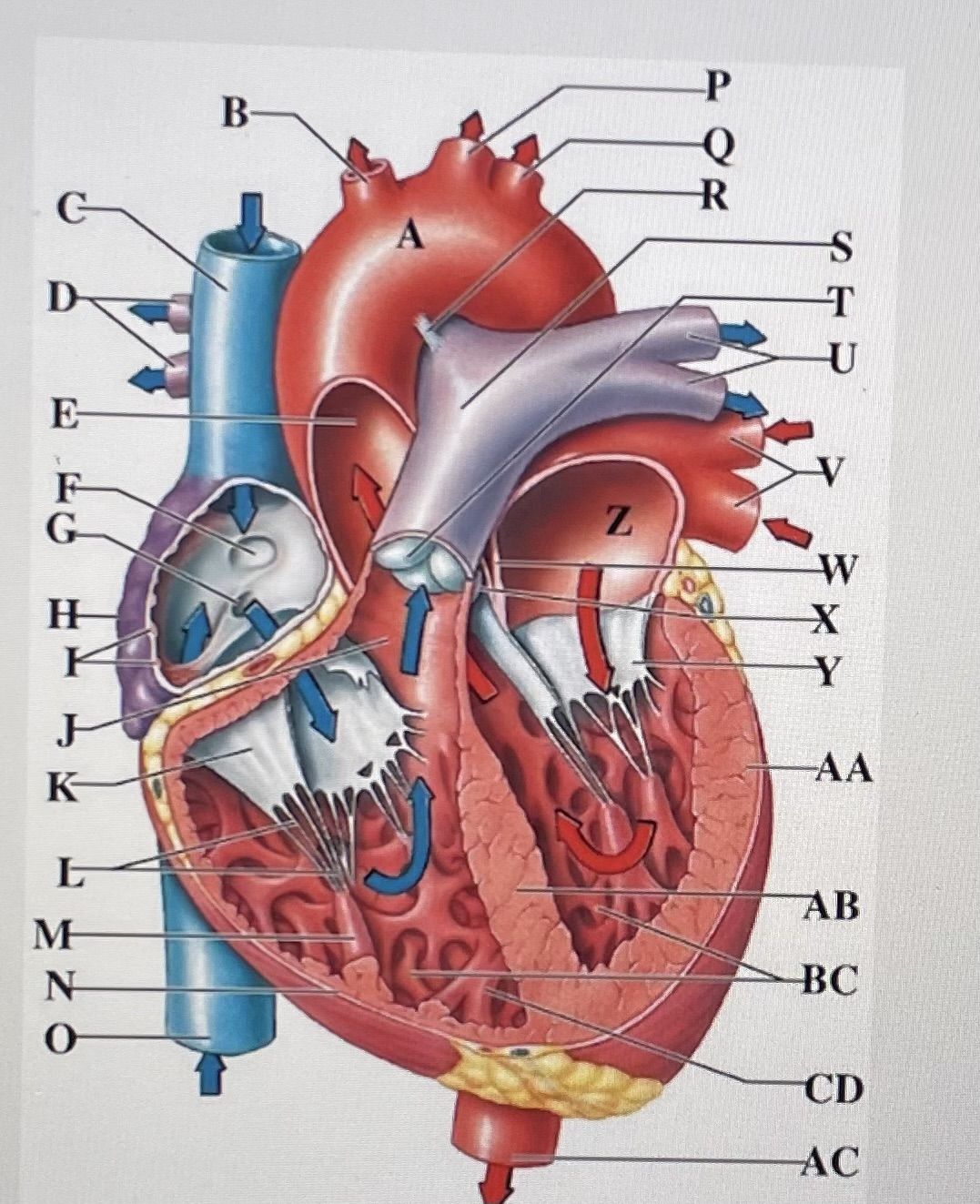
left subclavian artery
Q
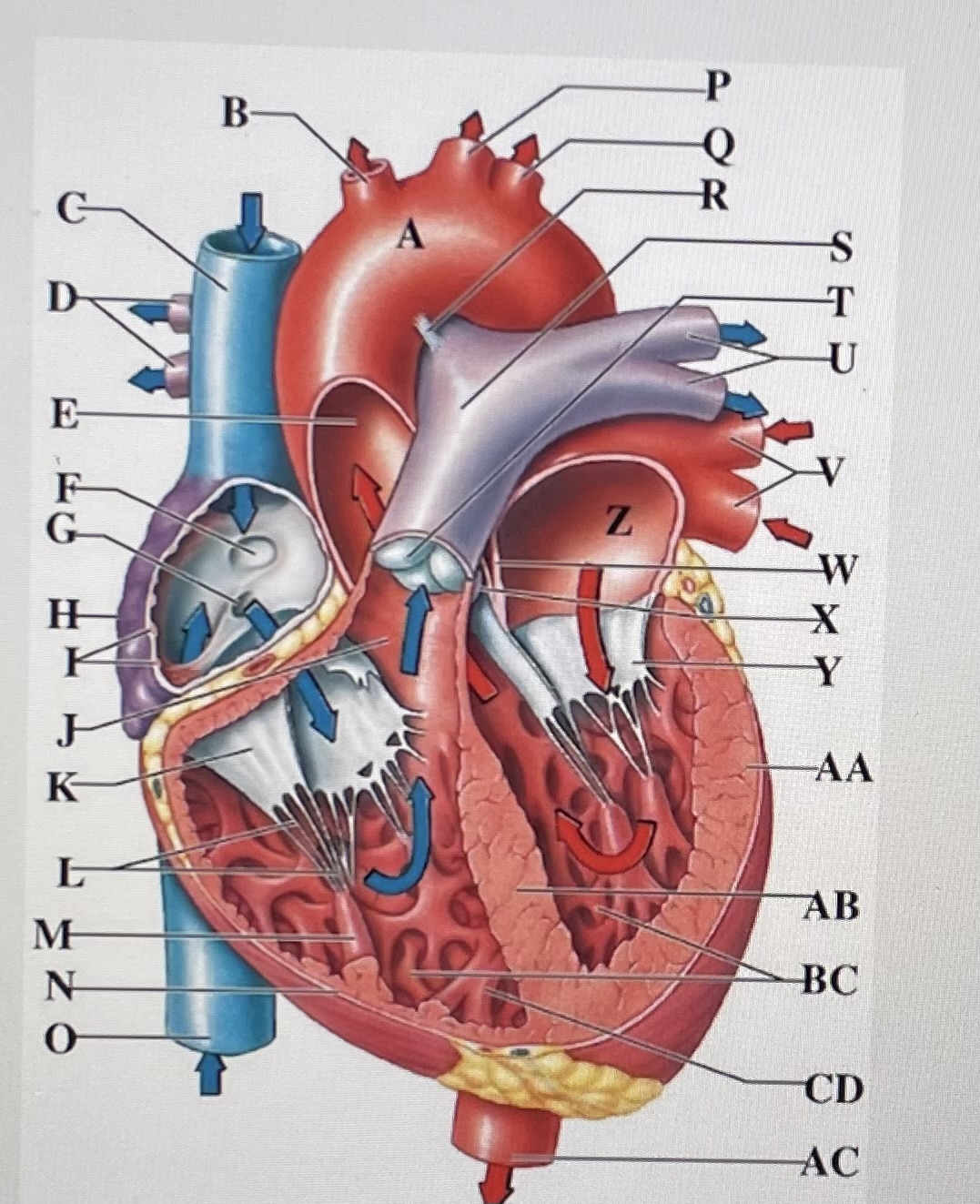
ligamentum arteriosum
R
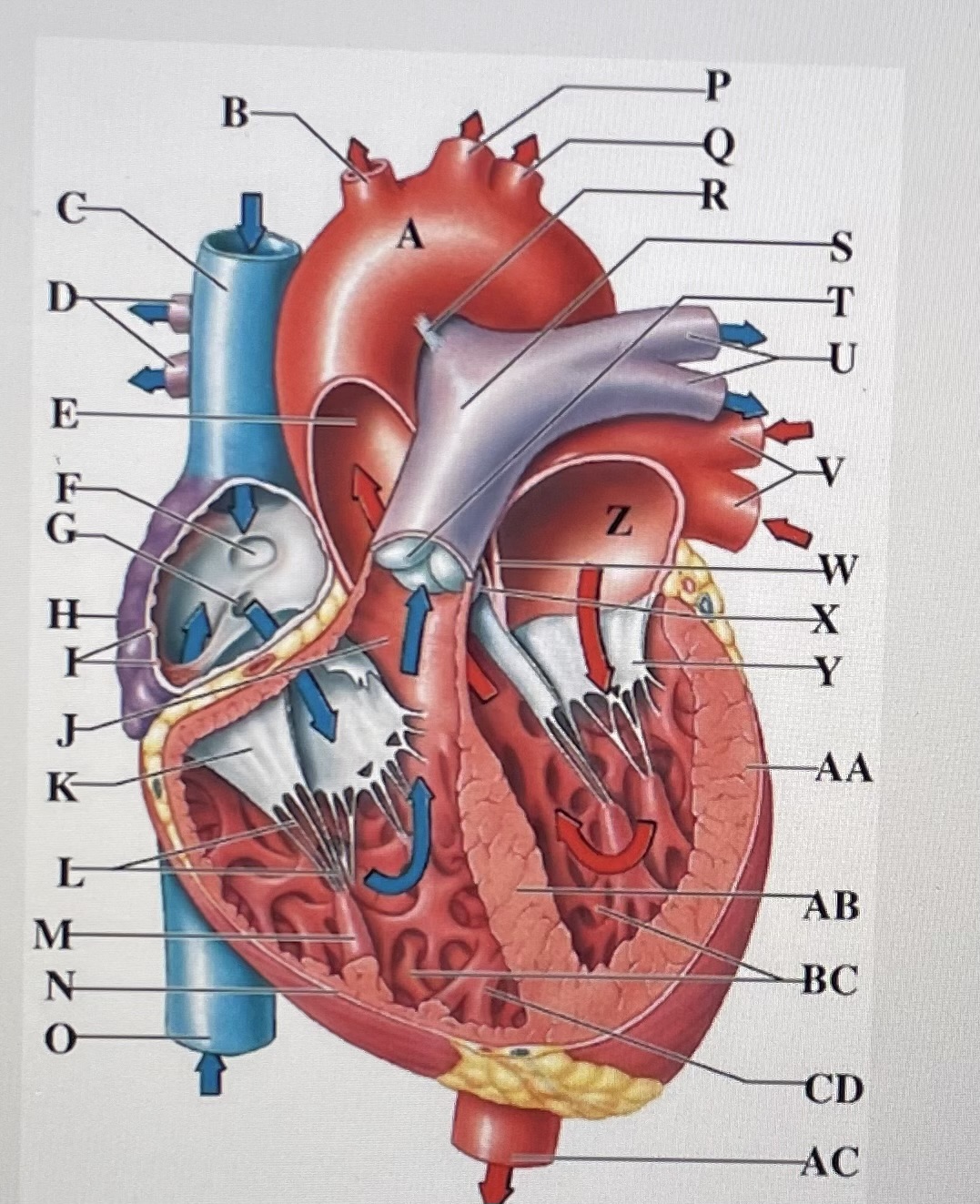
pulmonary trunk
S
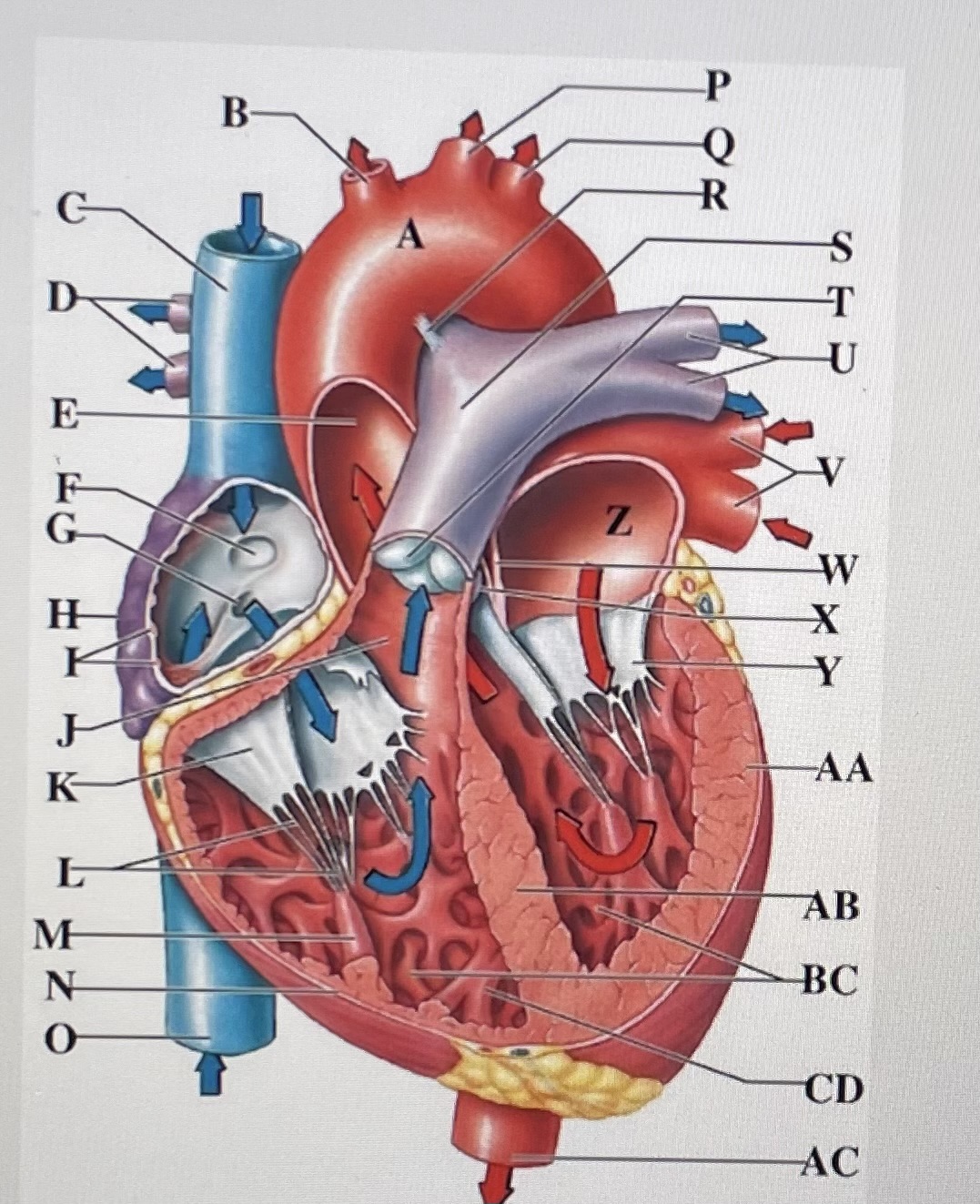
pulmonary valve
T
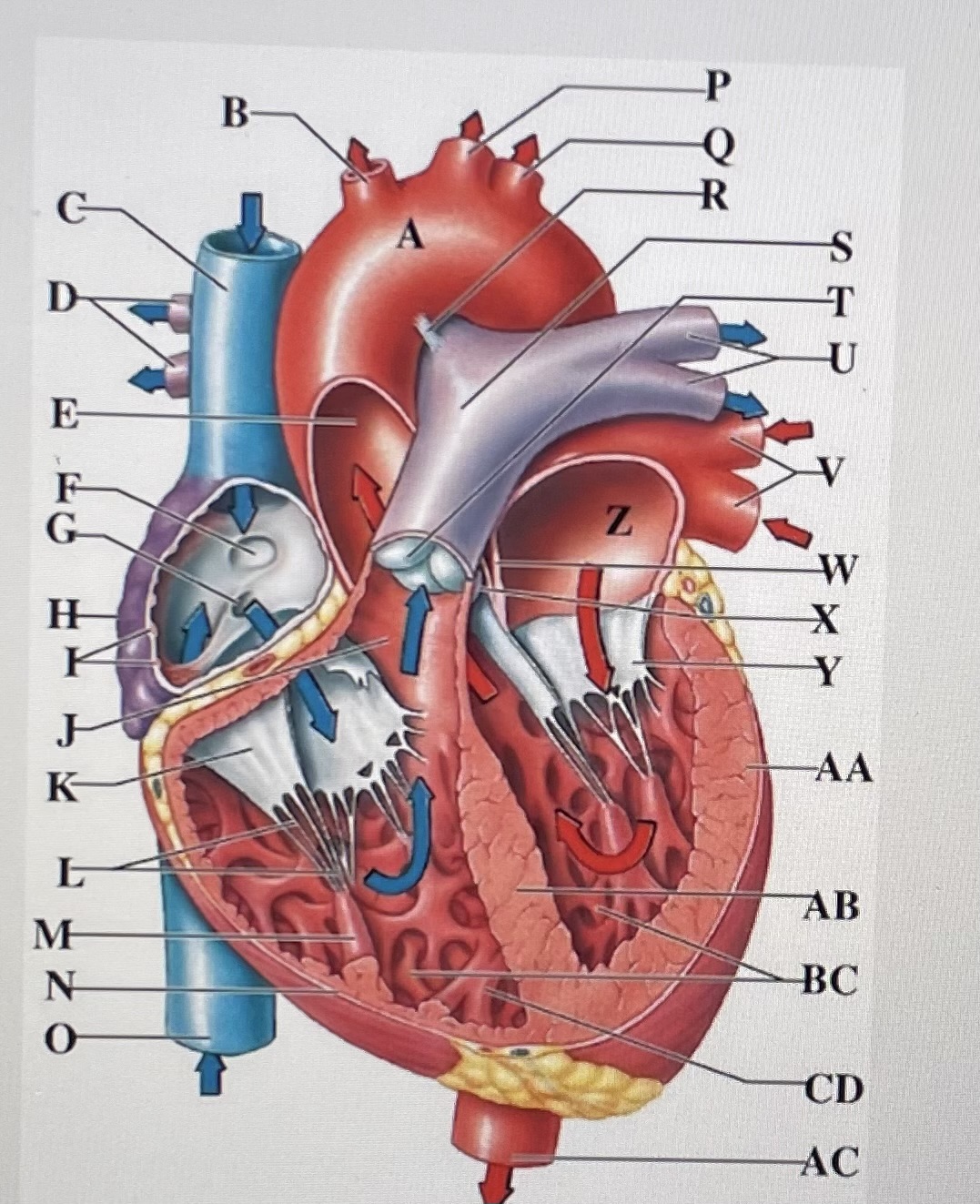
left pulmonary arteries
U
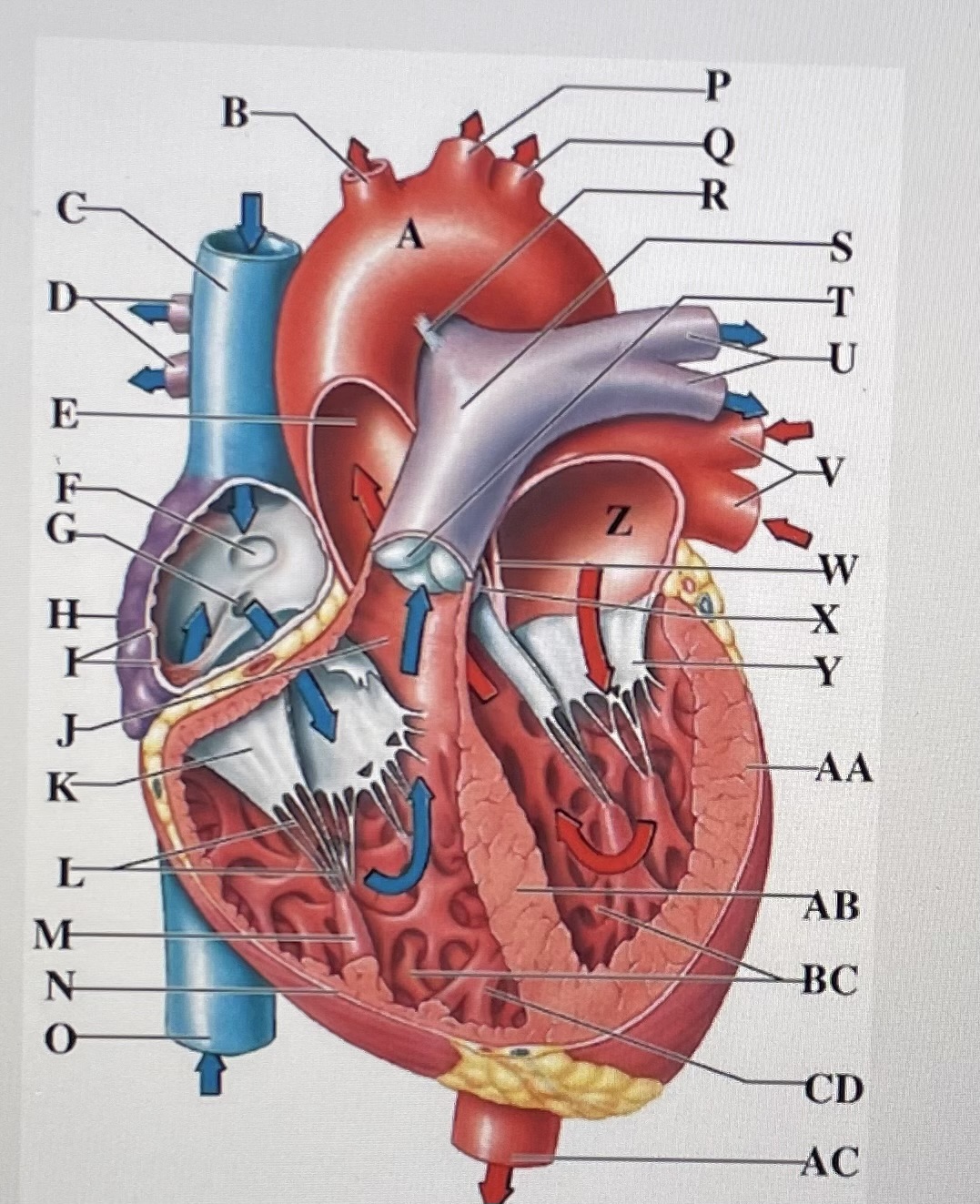
left pulmonary veins
V
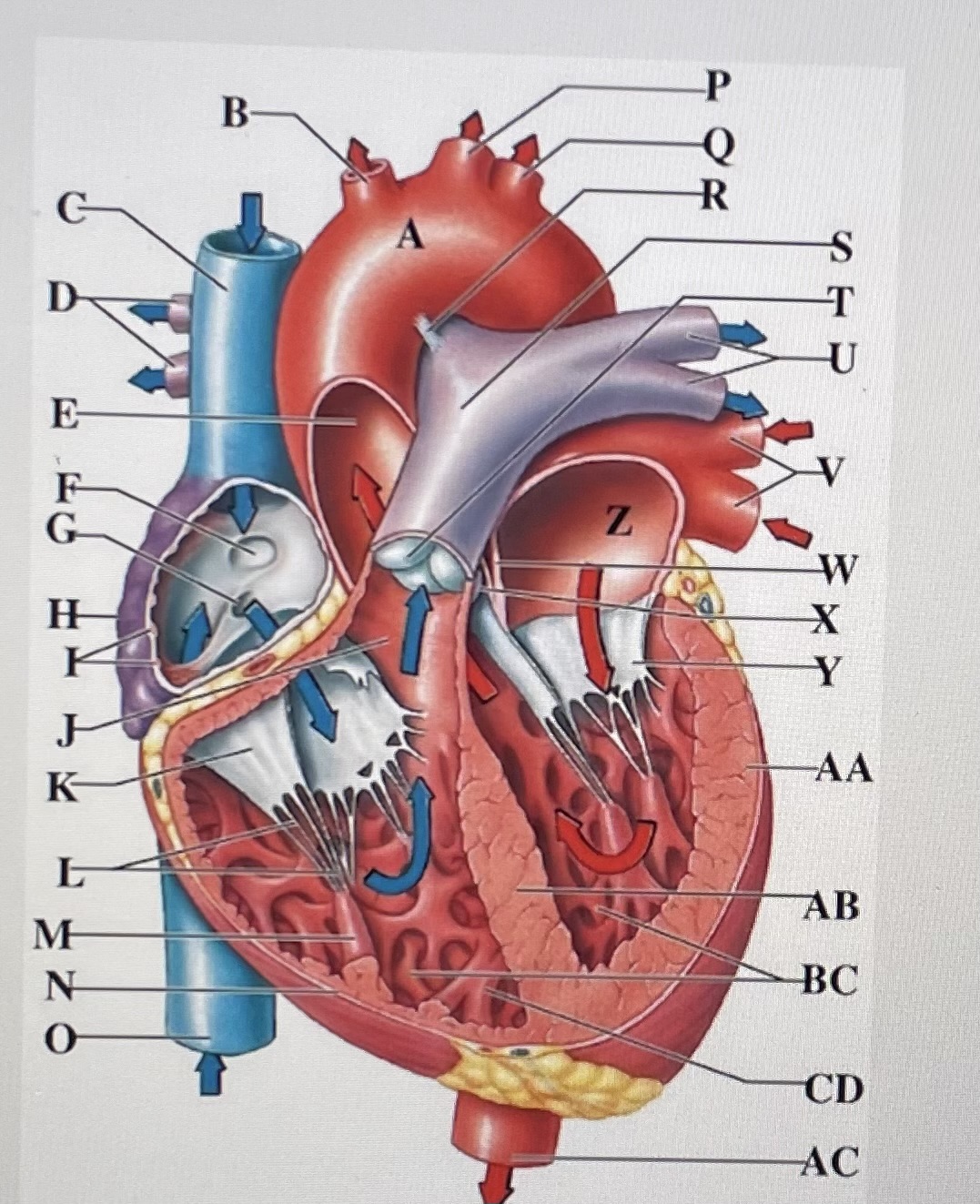
interatrial septum
W
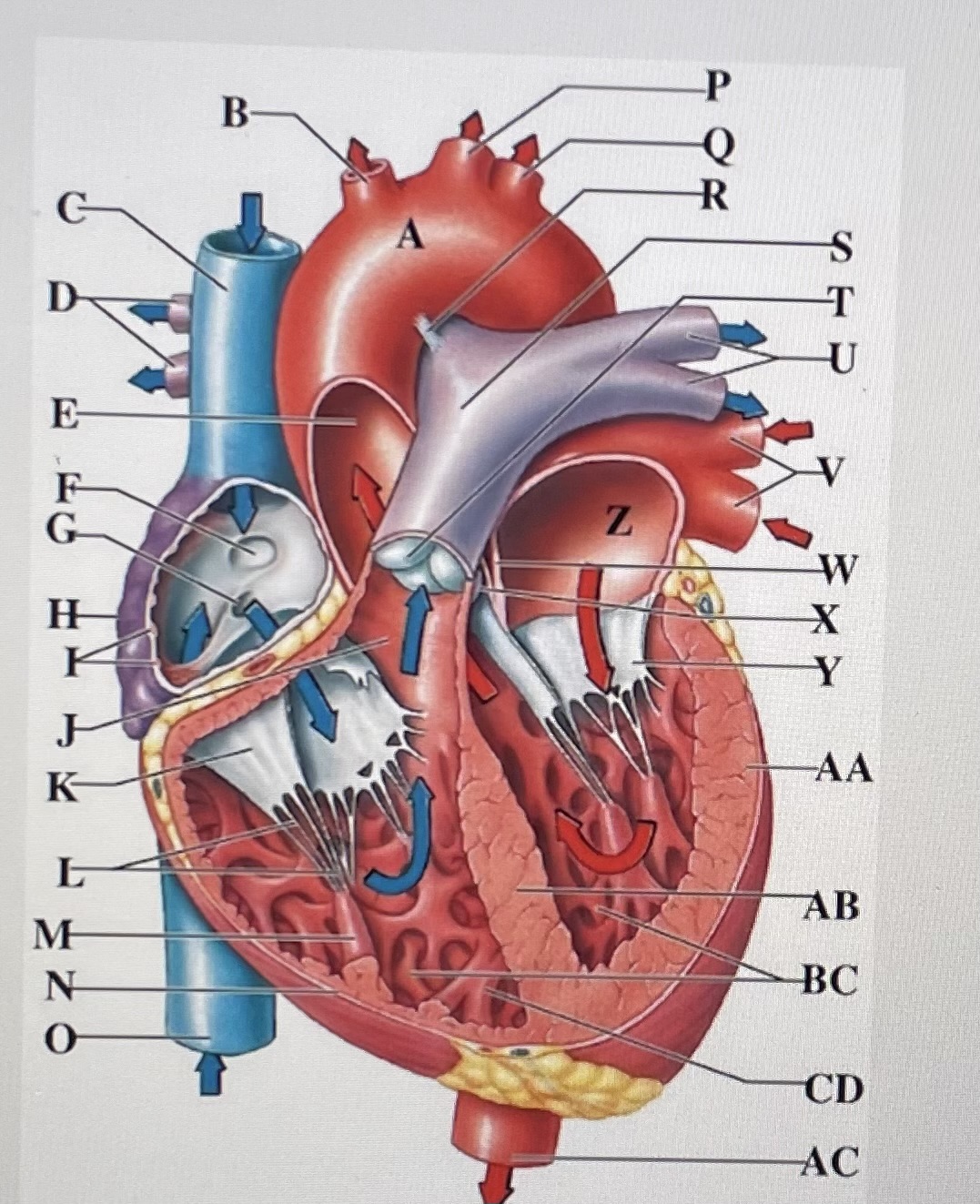
aortic valve
X
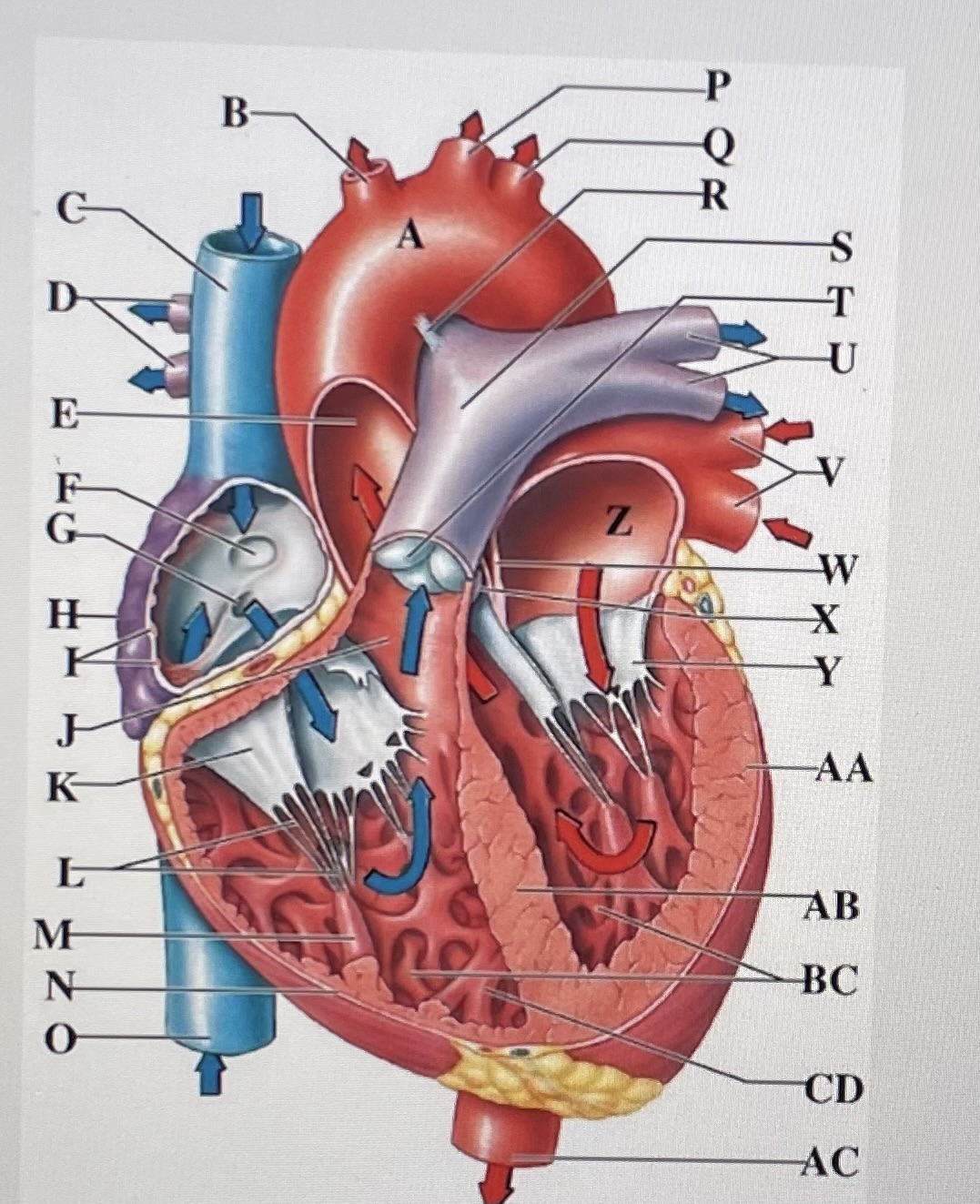
cusp of left AV (mitral) valve
Y
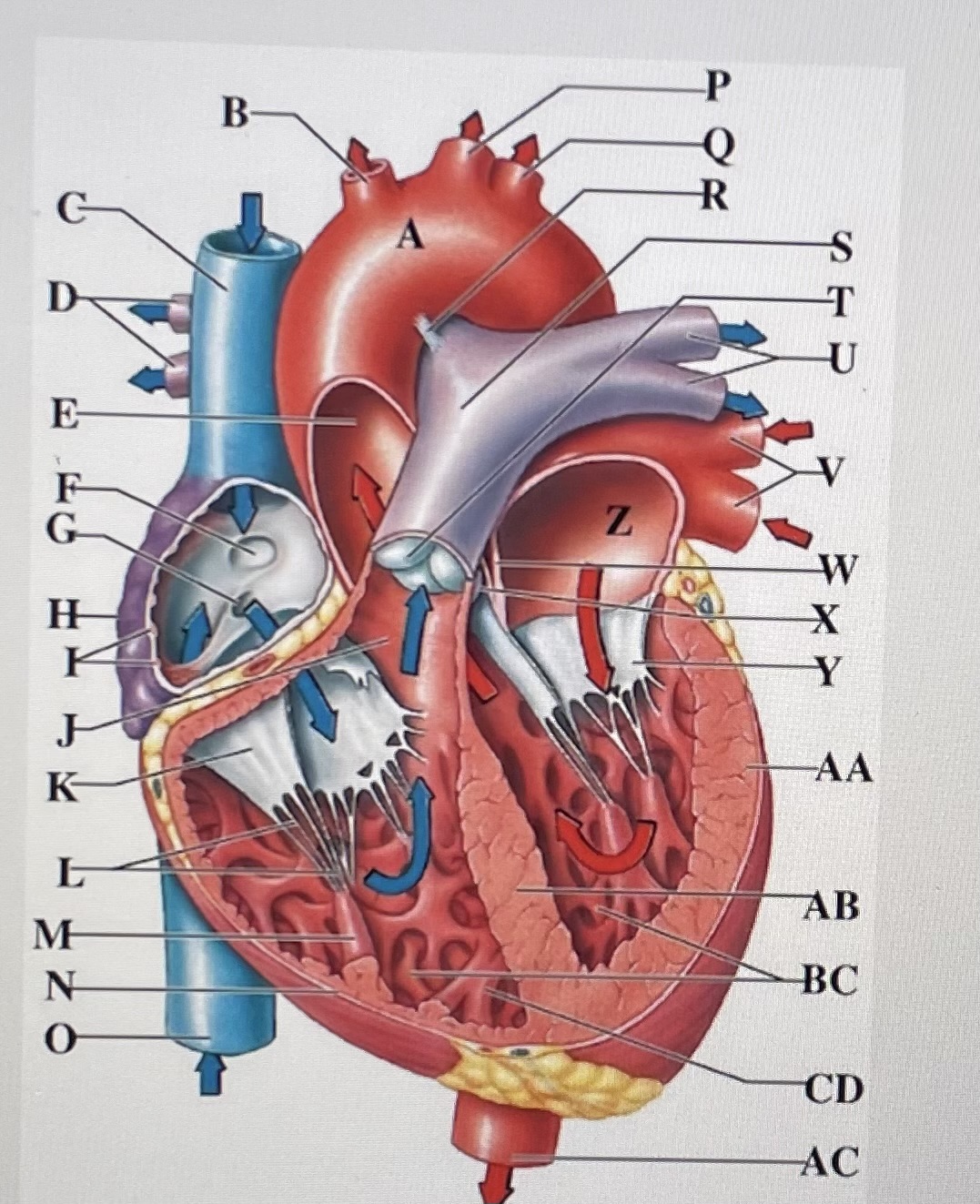
left atria
Z
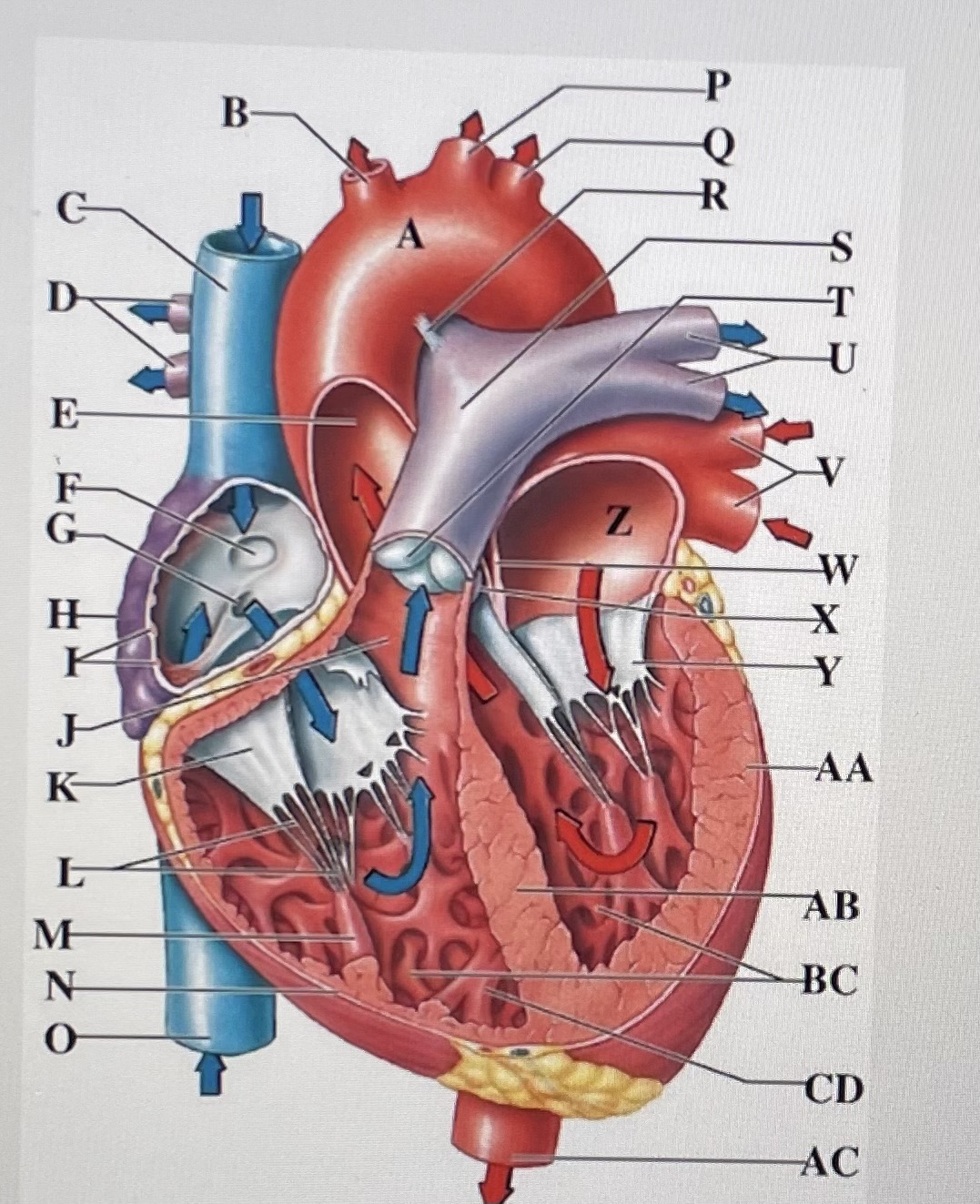
left ventricle
AA
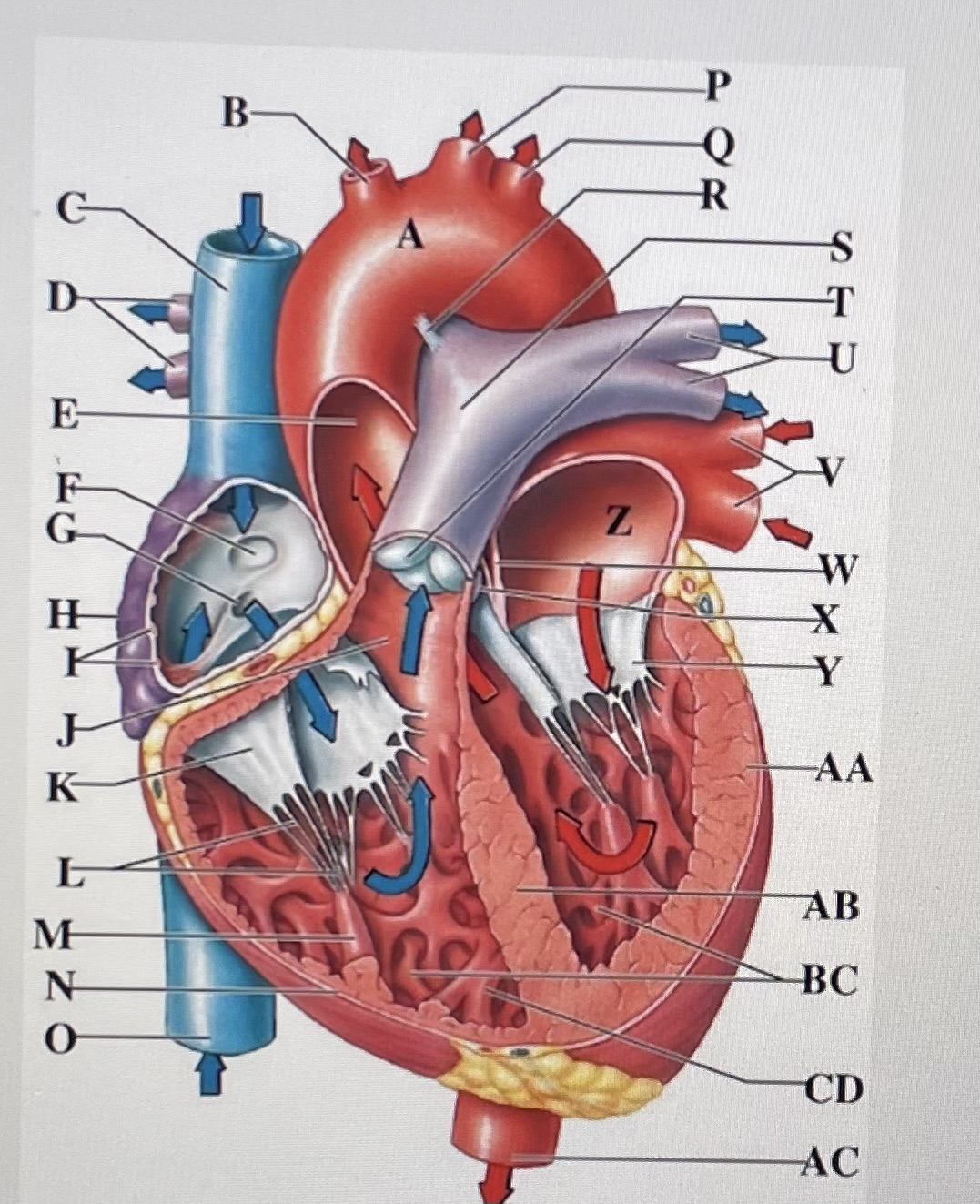
interventricular septum
AB
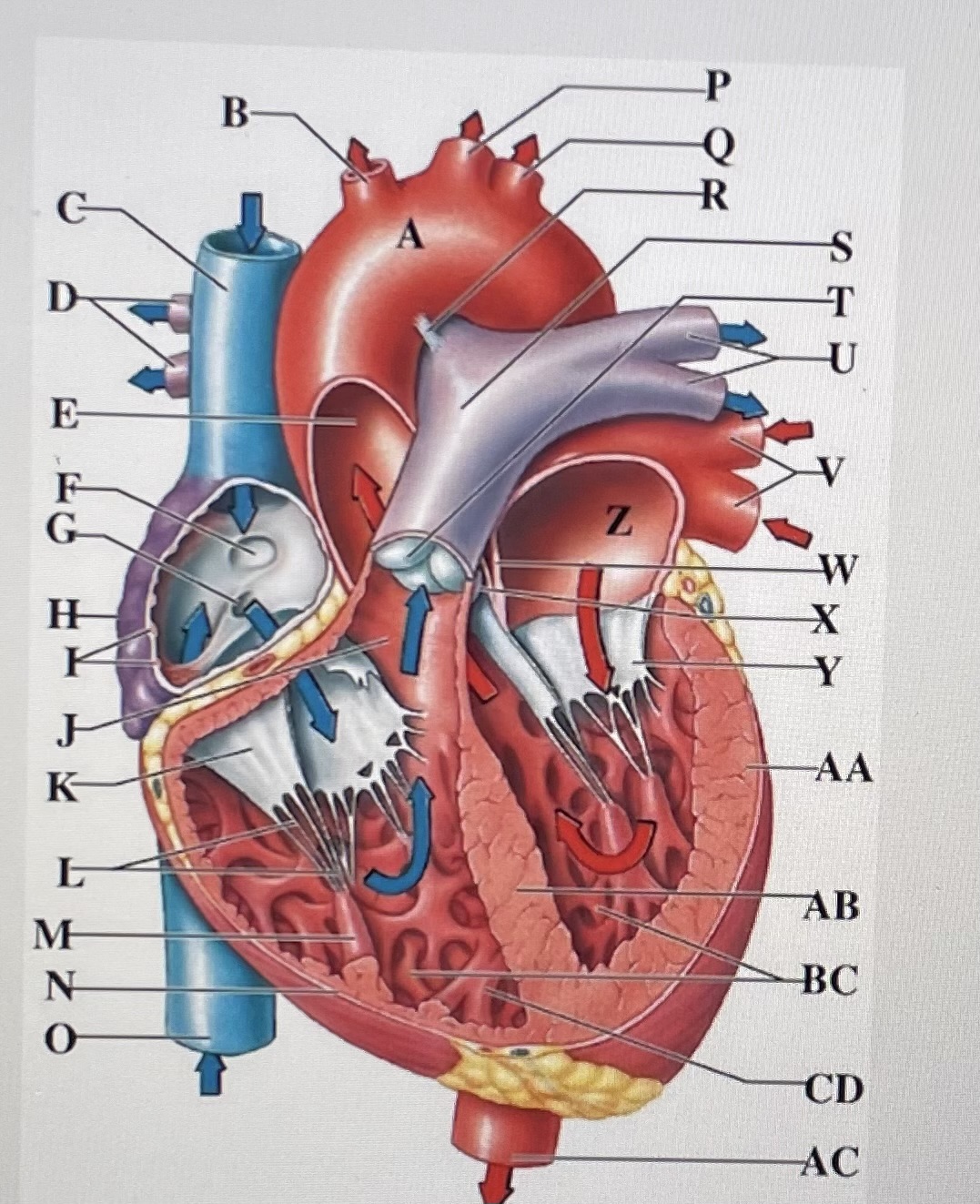
trabeculae carneae
B.C
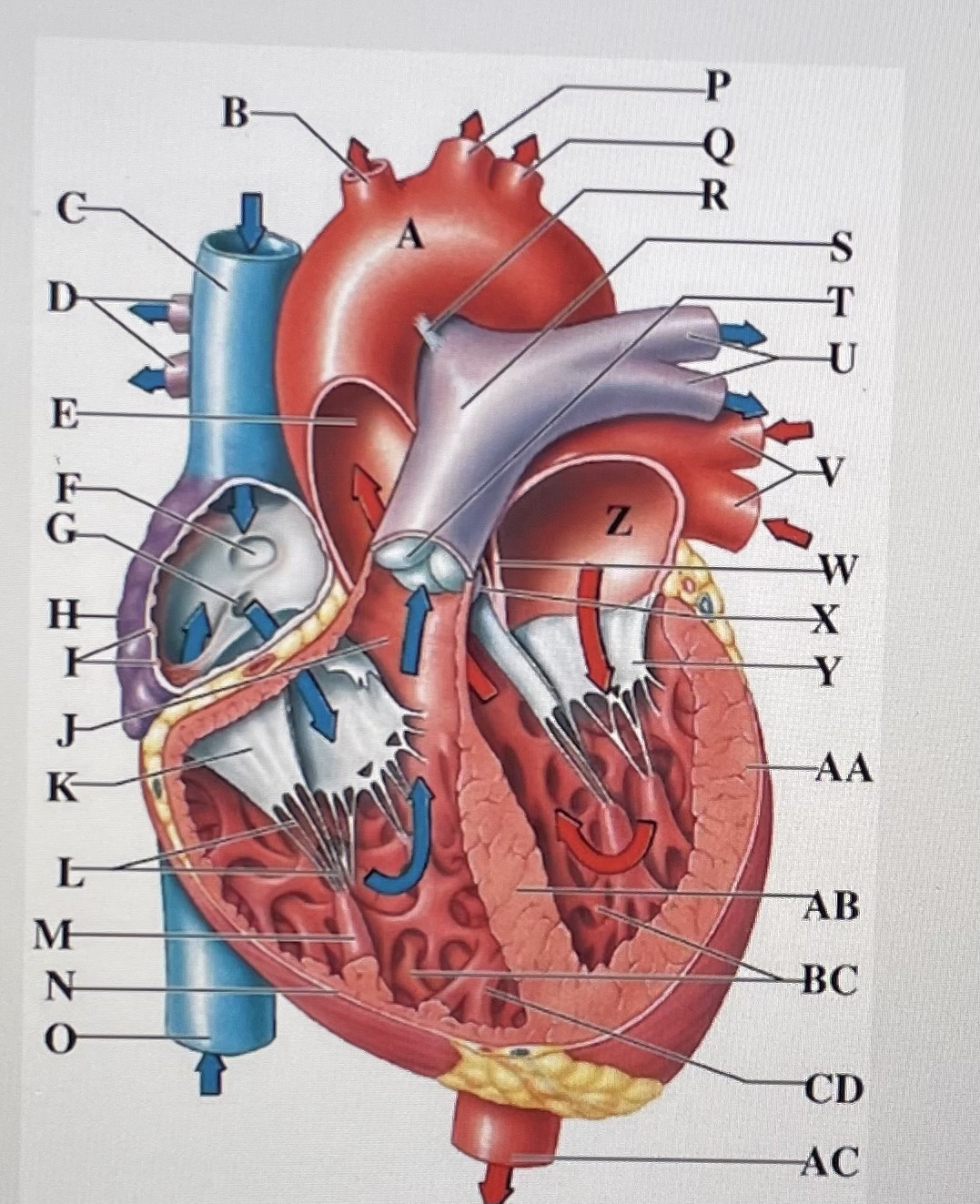
moderator band
CD
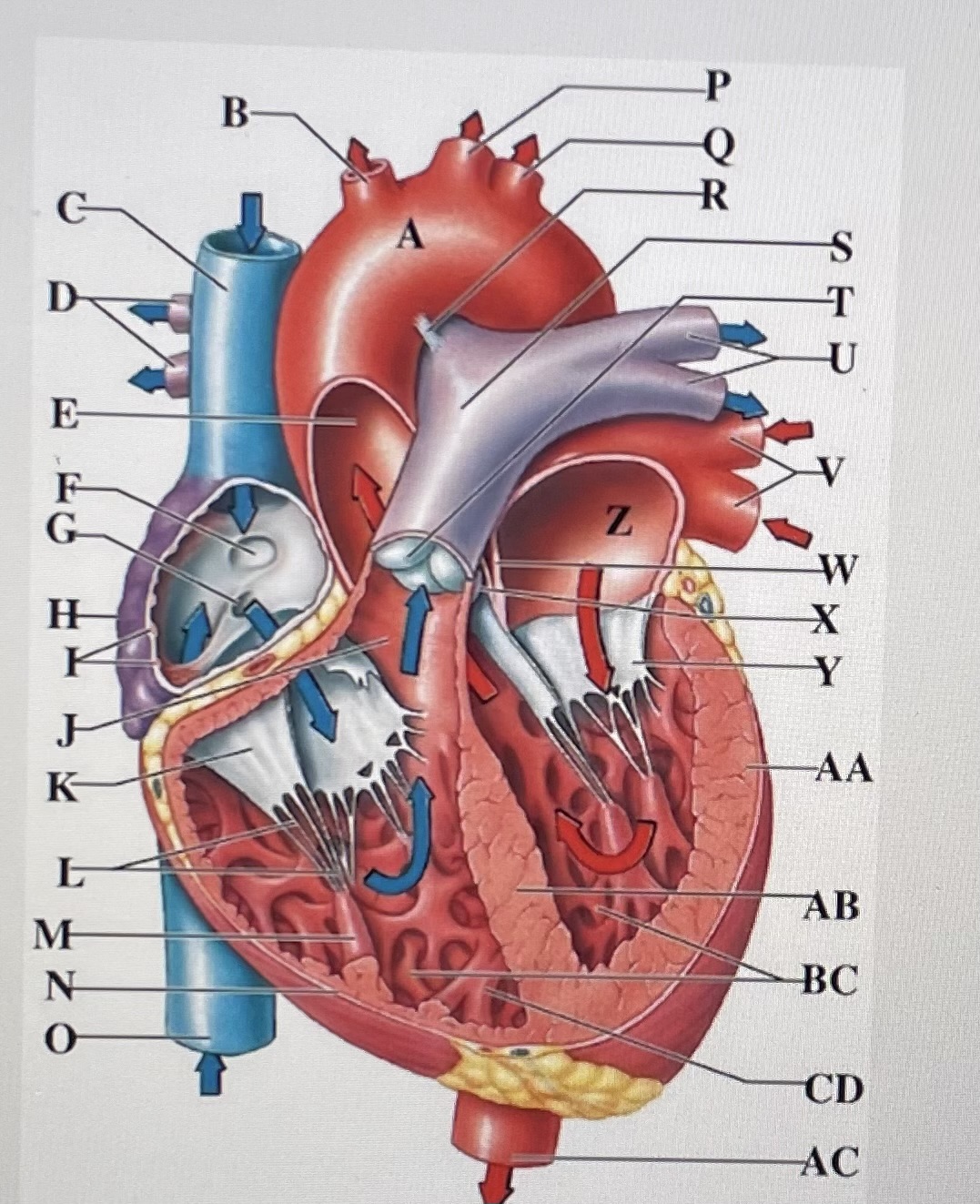
descending aorta
AC
intracellular fluid
in cells (largest component of water)
extracellular fluid
outside of cells
interstitial fluid
between cells; not in blood
plasma
fluid portion of blood
plasma
higher O2
lower CO2
higher dissolved proteins
interstitial fluid
lower O2
higher CO2
lower dissolved proteins
plasma proteins
albumins (60%)
globulins (35%)
fibrinogen (4%)
regulatory proteins ( < 1%)
albumins
major contributors to osmotic pressure of plasma; transport lipids, steroid hormones and thyroid hormones
help keep blood inside blood vessels by regulating osmotic pressure / factors
largest component
globulins
plasma proteins that transport ions, hormones, lipids; immune functions
transport globulins
immunoglobulins
fibrinogen
plasma proteins that forms blood clots by converting to fibrin.
serum
anticoagulants
serum
plasma with clotting proteins removed
anticoagulants
compounds that prevent fibrin formation
cellular components
RBCs (99.9%)
WBCs ( < 0.1%)
platelets ( < 0.1%)
Red blood cells
erythrocytes
white blood cells
leukocytes
neutrophils
eosinophils
basophils
lymphocytes
monocytes
platelets
thrombocytes
hematocrit
% of blood sample volume made of erythrocytes
If low hematocrit
anemia
blood loss
micronutrient deficiency
chronic infection
if high hematocrit
dehydration
polycythemia
lung / heart disease
RBC
biconcave disc
large SA
flexible
lack most organelles
anucleated
no mitochondria
contain hemoglobin: respiratory pigment
rouleaux formations
RBCs stacked on top of each other
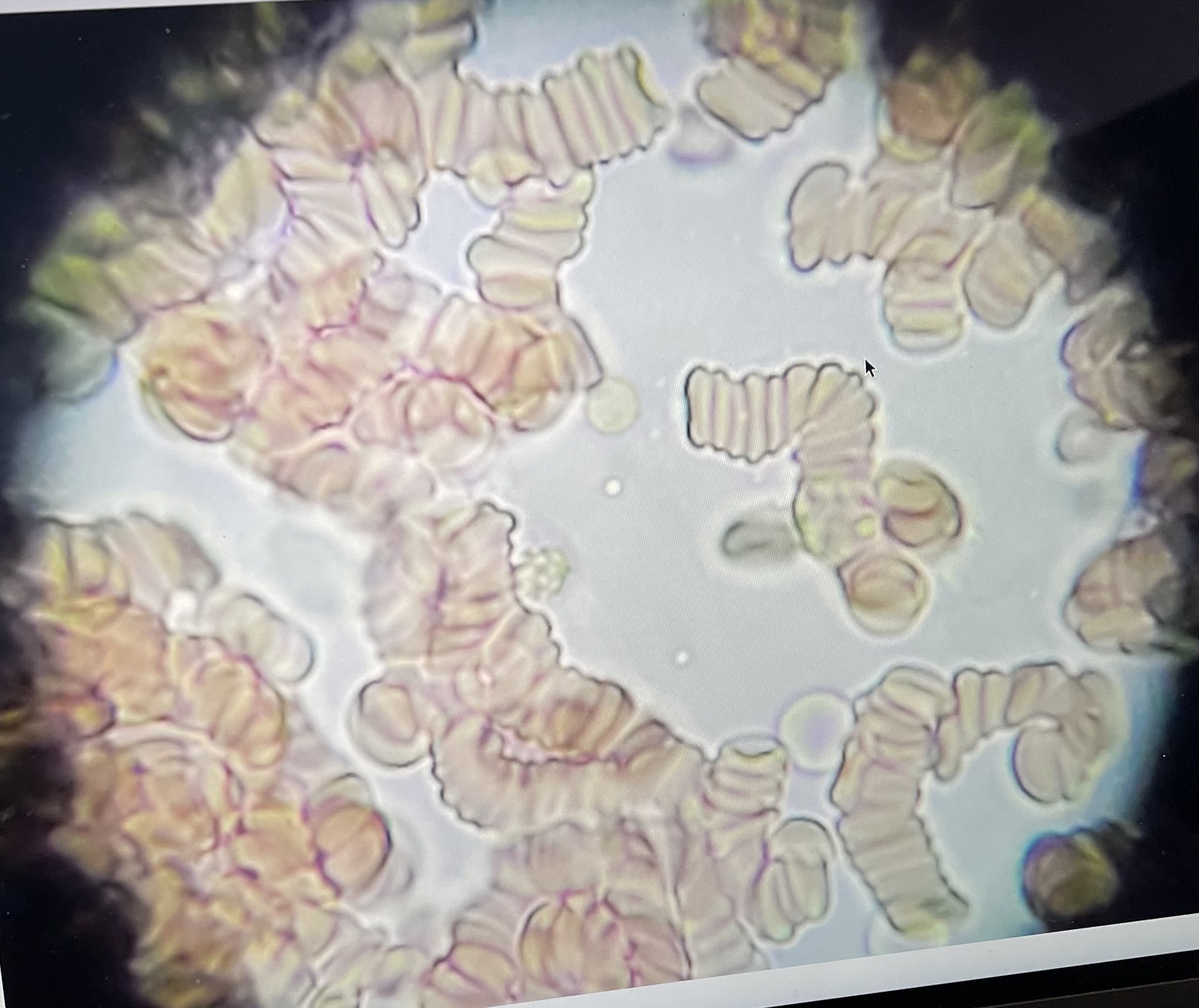
hemoglobin (Hb)
has 4 heme units
heme units
where O2 and Co2 will bind to Hb
bohr effect
pH will impact binding affinity of O2 to Hb
changes in Hb O2 affinity due to pH changes
decreased pH Hb release O2
increased pH Hb take up O2
respiratory acidosis
too much CO2
respiratory alkalosis
too little CO2
metabolic acidosis
low pH and HCO3-
metabolic alkalosis
high pH and HCO3-
blood types
genetically determined
based on RBC surface antigens
antibodies produced against non-self antigens
donor/recipient compatibility
Rh groups
Rh+
Rh-
anti Rh antibodies only produces when Rh- individuals are exposed to Rh antigens
Rh+
RBC have Rh surface antigens
Rh-
RBC lack Rh surface antigens
O-
universal donor
AB+
universal recipient
Rh antibodies produced if Rh- person is exposed to Rh+ via:
pregnancy: Rh- mother; Rh+ fetus
blood transfusion
cross-reaction
when antibody meets specific antigen
agglutination
clumping of RBCs and antibodies
hemolysis
rupturing of RBCs
donor/recipient compatibility
cross-reaction
agglutination
hemolysis
diapedesis
leukocytes squeeze between endothelial cells to leave capillaries
chemotaxis
chemical signals that attract leukocytes to infections
agranulocytes
lack cytoplasmic granules
monocytes
lymphocytes
monocytes
large cells; kidney-shaped nucleus
use chemotaxis
attract fibroblasts to encase pathogen in collagen
produce scar tissue
lymphocytes
round nucleus; responsible for specific immunity
primary cells of lymphatic system
can differentiate in into: T, B and NK cells
T cells
enter tissues to directly attack pathogens
B cells
produce plasma cells that secrete antibodies
NK cells
attack abnormal cells; immune surveillance
granulocytes
have cytoplasmic granules
neutrophils
eosinophils
basophils
neutrophils
multilobed nucleus
granules are vacuoles w/lysosomal enzymes and bactericidal compounds
phagocytotic
short-lived- will secrete chemotaxic chemicals upon death
eosinophils
bilobed nucleus
attack objects marked with antibodies
involved w/ allergies and/or parasites
secrete compounds that reduce inflammation
basophils
very high density of granules
histamine
heparin
histamine
dilate blood vessels to enable diapedesis
heparin
prevents blood clots
thrombocytes (platelets)
derived from megakaryocytes
hemostasis
clump together to form a platelet plus using fibrin
contain actin and myosin that function to contract clot
megakaryocytes
fragment forming bits & pieces of membrane-encolsed packets of chemicals
hemostasis
blood clotting
hemopoiesis
general process of blood cell formation; red marrow; yellow marrow can be converted to red
lymphatic stem cells
NK cells
T cells
B cells
myeloid stem cells
neutrophils
basophils
eosinophil
macrophages
megakaryocyte
platelets
erythrocytes
erythropoiesis
erythrocytes formation
in red marrow
requires Vitamin B12, amino cards, and Fe
Erythropoietin
erythropoietin
glycoprotein hormone by kidney and liver in response to low O2; hypoxia
stimulates erythroblast and stem cell division rates
speeds up Hb formation
leukopoiesis
differentiation of myeloid cells into leukocytes
colony-stimulating factors
colony-stimulating factors (CSFs)
hormones that stimulate leukocytes production
lymphopoiesis
differentiation of lymphoid cells into lymphocytes
lymphoid stem cells will also travel to peripheral lymphatic tissue
thymus
spleen
lymph nodes
atria
receive blood
ventricles
send blood out
left side of heart
oxygen rich blood
right side of heart
oxygen poor blood
pulmonary circuit
send blood to lungs