L13 Diseases and Disorders of the Ovaries (HR)
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
What are the characteristics of ovaries during the premenarchal stage?
Non-palpable
What are the characteristics of ovaries during the reproductive stage?
Palpable about 50% of the time
How does OCP usage affect ovaries?
causes smaller, symmetrical, less palpable ovaries
What are the characteristics of ovaries during the perimenopausal stage?
functional cysts
What are the characteristics of ovaries during the postmenopausal stage?
normal = non-palpable; palpable enlargement needs evaluation
What is the primary imaging of choice for the evaluation of ovaries?
Pelvic ultrasound
simple, unilocular cysts <10cm. benign or malignant?
Almost universally benign
What is the role of Cancer antigen 125 (CA-125) in ovarian cancer?
used for monitoring response to therapy in patients with known ovarian cancer
What is the most used biomarker for the evaluation of adnexal masses for cancer?
Cancer antigen 125 (CA-125), although it is not approved for this indication
What is a limitation of CA-125 regarding early-stage ovarian cancer?
Low sensitivity
What is a limitation of CA-125 in premenopausal patients?
Low specificity
What are functional ovarian cysts NOT?
NOT neoplasms
During which life stage are functional ovarian cysts most common?
Reproductive years
What symptoms may functional ovarian cysts have until they rupture?
May be asymptomatic
What complications can occur with functional ovarian cysts?
Rupture, torsion, or hemorrhage
What is the typical size of functional ovarian cysts?
Usually less than 10 cm
three types of functional cysts
follicular, corpus luteum cysts, theca lutein cyst
What is the most common type of functional ovarian cyst?
Follicular cysts
During which phase do follicular cysts typically occur?
follicular phase.
What is the second most common type of functional ovarian cyst?
Corpus luteum cysts
During which phase do corpus luteum cysts typically occur?
luteal phase.
What is a rare type of functional ovarian cyst that has a risk for torsion or rupture?
Theca lutein
What occurs when an ovarian follicle fails to rupture during follicular maturation?
Follicular cyst
What happens to ovulation when a follicular cyst develops?
Ovulation doesn't occur
What effect does a follicular cyst have on the follicular phase of the cycle?
Causes lengthening of the follicular phase
What can result from a follicular cyst?
(transient) secondary amenorrhea
Follicular cysts lined by __________ cells
- Fluid rich in estrogen or progesterone?
- cells persist and enlarge through luteal phase
granulosa
estrogen
when are follicular cysts clinically significant?
when large enough to cause pain or last longer than one cycle
-Transient secondary amenorrhea
-lower abdominal/pelvic pain
-Irregular bleeding
-Failed ovulation
-Endometrium overstimulated
what type of cyst is this?
follicular cyst
signs of a follicular cyst on physical exam
-Unilateral tenderness
-Palpable, mobile and cystic mass
diagnostic study of choice for a follicular cyst
Pelvic Ultrasound
what does the cyst look like on a pelvic US?
smooth, thin walled, unilocular
if a pt has a follicular cyst, what must be ruled out before any further steps are taken?
rule out pregnancy with HCG!
*r/o preg with almost every condition
follicular cyst treatment/when to f/u?
-Most resolve spontaneously within 6 weeks
-f/u with pelvic exam in 6wks
if a cyst persists after 6 weeks, further evaluation with _______ and _______ are needed
imaging, surgery
acute pelvic pain occurs when the cyst does what?
ruptures
what oral medication can help suppresses development of new cysts?
OCPs
*does not shrink the existing cyst
Type of functional ovarian cyst that fails to degenerate after ovulation
Corpus Luteum Cyst
the Corpus Luteum Cyst is termed cyst once corpus luteum diameter exceeds > cm
-Related to postovulatory phase of menstrual cycle (follicular or luteal phase?)
-__________-dominant cyst
Corpus luteum fails to regress
3cm
luteal
Progesterone
What does a slightly enlarged corpus luteum produce?
It produces progesterone longer than usual (for more than 14 days), delaying menstruation from days to several weeks.
What is a luteal phase cyst also known as?
Corpus hemorrhagicum
What are the characteristics of a luteal phase cyst?
It is less common, rapidly enlarges, can cause spontaneous hemorrhage, and may rupture late in the luteal phase.
What is the typical patient luteal phase cystt (is or is not) on oral contraceptive pills, has regular cycles, and experiences _________.
Not on
acute pain late in the luteal phase
Clinical presentation and ultrasound findings for a Corpus Luteum Cyst
-Delayed or missed menstrual period
-Ipsilateral pelvic pain (dull lower quadrant)
US:
-Enlarged, tender, cystic or solid adnexal mass
-Unilocular
-Internal debris (hemorrhage)
-Thicker-walled
-Peripheral vascularity
-“ring of fire” with hemorrhagic cyst
if a pt has a corpus luteum cyst, why do you order a Beta-hCG?
RULE OUT ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
Corpus Luteum Cyst treatment for a Slightly Enlarged Corpus Luteum (what to do if recurrent?)
-Mild analgesia & reassurance (supportive)
-If recurrent: cyclic contraceptive therapy
-Repeat u/s after 6wks
how to tx if a corpus luteum cyst is >8cm/persistent or in postmenopausal pt?
surgery
Corpus Luteum Cyst treatment for a Corpus Hemorrhagicum : initial tx, if hemoperitoneum and hypovolemia, and if Recurrent hemorrhagic cysts
-initial = self limiting despite pain and blood loss
-hemoperitoneum and hypovolemia = surgical resection of cyst
-Recurrent hemorrhagic cysts (Consider anticoagulant medications or inherited bleeding disorder as cause!)
-Luteinized follicle cysts that form as a result of overstimulation from high human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels or extreme sensitivity to hCG.
-Generally seen in molar pregnancy, multiple gestation, fertility tx
Usually asymptomatic
Theca Lutein Cyst
what other sxs of a theca lutein cyst can occur?
-Sometimes maternal virilization, hyperemesis gravidarum, preeclampsia, or thyroid dysfunction may occur
what is seen on imaging for a theca lutein cyst?
Bilateral, multilocular, large ovarian cysts- “spoke wheel”
theca lutein cyst tx. what if a torsion occurs?
gradually resolves weeks to months after the source of hCG is eliminated
Surgery if torsion
BENIGN Ovarian Neoplasms are mostly in reproductive age women and are what type of cyst?
functional cyst
*risk of transformation increases with age
we worry about ovarian masses that do not respond to therapy in what age woman?
older women and in reproductive age
tx for malignancy or torsion
surgery
Benign Ovarian Neoplasms signs/symptoms
sxs:
-Asymptomatic
-Bloating
-abdominal, pelvic or back pain
-Urinary symptoms
-Pain during intercourse
-GI complaints
-Cramping, heartburn, constipation
S:
-Palpable ovarian mass
-Unilateral > bilateral
-Torsion presentation
-Pain on palpation of abdomen
Benign Ovarian Neoplasms: Management IF pt is
-Pre-menopausal
-Asymptomatic
-has a mobile mass
-Unilateral simple cystic mass < 7.5cm
then...
-Observe for 4-6 weeks. Most will resolve spontaneously
-If larger or unchanged on repeat exam = surgical evaluation needed
Benign Ovarian Neoplasms are categorized by cell type of origin: 3 types
1. Benign epithelial cell tumors
2. Germ cell tumors
3. Sex-cord stromal cell tumors
What is the largest class of ovarian neoplasm?
Benign Epithelial Cell Tumors
What fraction of all ovarian tumors do benign epithelial cell tumors represent?
2/3
What is the typical age of women who develop benign epithelial cell tumors?
> 30 years of age
What type of cells do benign epithelial cell tumors consist of?
Typical glandular epithelial cells
Is the source for the development of benign epithelial cell tumors clear?
No, it is unclear
Benign Epithelial Cell Tumors: Serous Cystadenoma aka serous tumors is the MC ________ cell tumor and is bilateral or unilateral?
epithelial
bilat
how to treat serous cystadenoma
Surgical removal because of high rate of malignancy!
Imaging of a serous cystadenoma shows what?
thin-walled, unilocular, often bilateral mass
What is the treatment for serous cystadenoma in older patients or those done with childbearing?
Bilateral salpingoo-ophorectomy (BSO)
Why is BSO performed in patients with serous cystadenoma?
To avoid future malignancy
What is the risk associated with serous cystadenoma in the contralateral ovary?
Risk of occurrence in contralateral ovary
What is the recommended treatment for small serous cystadenomas in young patients?
Ovarian cystectomy to preserve ovarian tissue
What is the treatment approach for larger serous cystadenomas in younger patients?
Unilateral oophorectomy while trying to maintain fertility
Benign Epithelial Cell Tumors: Mucinous Cystadenoma is the ___________ and is characterized by _________. Less likely to have bilateral involvement
-2nd MC epithelial cell tumor
large size
Benign Mucinous Cystadenoma, US will show what? how do you treat?
-multilocular septations, filled with mucin
-Surgery is treatment of cure!
benign Endometrioid Tumor may take the form of what?
endometrioma
* cyst-lined by well differentiated, endometrial like glandular tissue
-Endometrioid Tumor can coexist with __________ carcinoma
-Most endometrioid tumors are benign or malignant*
primary endometrial
malignant
Brenner Cell Tumors are uncommon, begin, and are ________ tumors. Occasional with _______ tumors
Solid
mucinous
What do benign germ cell neoplasms arise from?
Primary germ cells
In which age group are benign germ cell neoplasms most common?
Young females aged 10-30 years
What are common clinical presentations of benign germ cell neoplasms?
Asymptomatic or abdominal enlargement/pain, precocious puberty, symptoms of pregnancy
What tumor markers can be assessed in benign germ cell neoplasms?
hCG, AFP, LDH
How is the diagnosis of benign germ cell neoplasms confirmed?
Histology at the time of surgical excision
What is a mature cystic teratoma also known as?
Dermoid cyst
What is the most common ovarian tumor in females in their 20s-30s?
Mature cystic teratoma
What can a mature cystic teratoma contain?
Hair or bone
mature cystic teratoma may contain tissue from all three embryonic germ layers, including 1. Ectoderm 2. Mesoderm and
3. Endoderm. what layer is the MC in teratomas?
Ectoderm
if expectant management is chosen for teratoma/dermoid cysts treatment , close f/u needed with _________ to monitor for increase in size or characteristics associated with malignancy
serial ultrasounds
-Uncommon variant of germ cell tumor
-Teratoma that is predominantly functioning thyroid tissue
-Thyroid scan may show uptake in pelvis if hormonally active!
Struma Ovarii (benign)
struma ovarii sxs
-hyperthyroidism
-Right adnexa more frequently affected
-associated with dermoid cyst
-Most cases benign
Derived from specialized sex cord stroma of the developed gonad
Benign stromal cell tumors (sex-cord stromal tumors - SCSTs)
Some produce ______________ ex: pt may present with signs of virilization or estrogen excess
androgens/estrogen
1. Granulose Theca cell tumors (produce estrogen, causes _______)
2. Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors (produce androgens, causes ________)
AUB
virilization
IF adnexal mass + endocrine effects, suspect a __________
SCST
what labs do you order for SCST?
-testosterone, estradiol, tumor markers
diagnosis of SCST is a ________ diagnosis and occur equally in ________ age groups
histologic
all (including peds)
Complete or partial rotation of the ovary on its ligamentous support
Ovarian Torsion
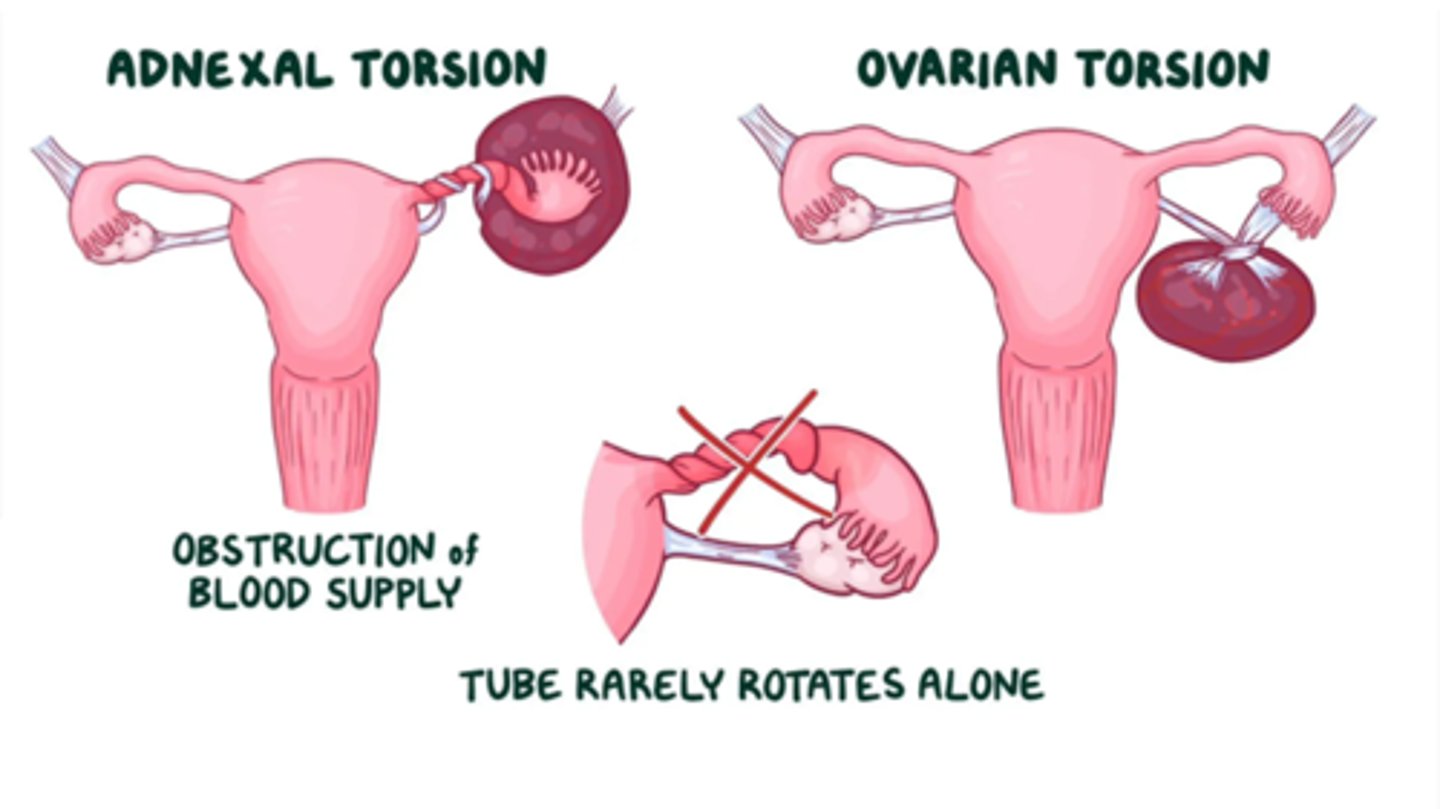
ovarian torsion results in _________
partial or complete obstruction of its blood supply
what is the MC gynecologic surgical emergency and may affect females of all ages (MC in reproductive age)
ovarian torsion
If the fallopian tube often twists along with ovary = referred to as "___________"
adnexal torsion
primary risk factor for ovarian torsion is ovarian _________!
mass, > 5cm diameter
*torsion may also occur with an ovary of any size and without an underlying cyst or mass, particularly in the pediatric population
ovarian torsion clinical pres
acute onset pelvic pain, often with nausea and vomiting
hx of recent vigorous activities or a sudden increase in abdominal pressure may be an inciting event