Peripheral nervous system Lecture
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Cranial nerves
Apart of the PNS originating from brain
Numbered with roman numerals according to their position
Begin with most anteriorly located nerve
Name of nerve often related to function
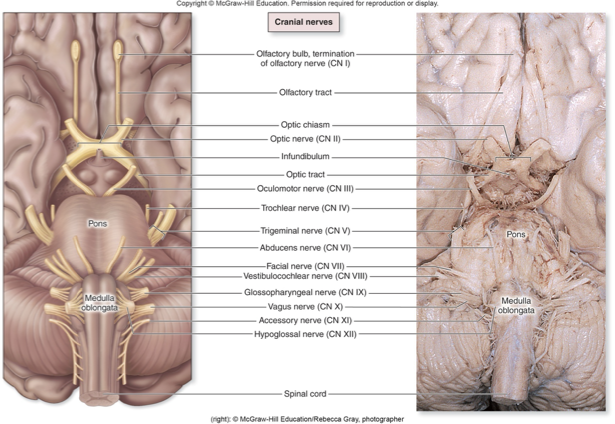
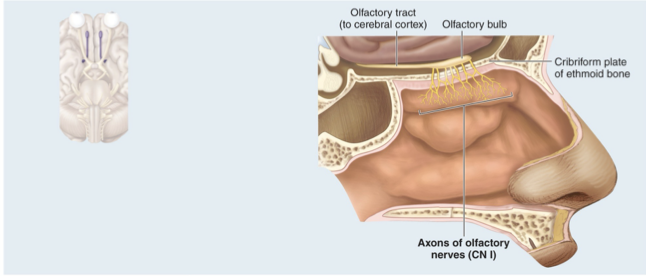
CN I olfactory Nerve
Sense of smell
Special sensory nerve within temporal lobe that conducts olfactory sensation from nose to the brain
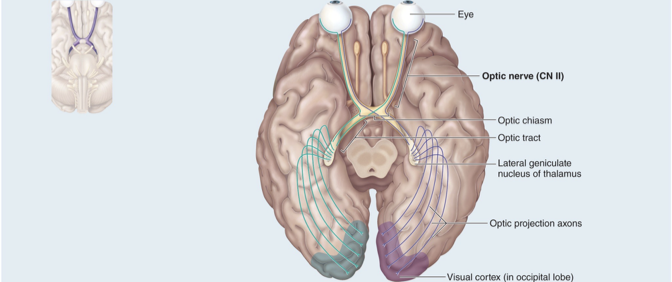
CN II Optic nerve
Sensory nerve controlling sense of vision
Crossing over occurs at optic chiasm where some nerves cross to the other side allowing for 3D vision
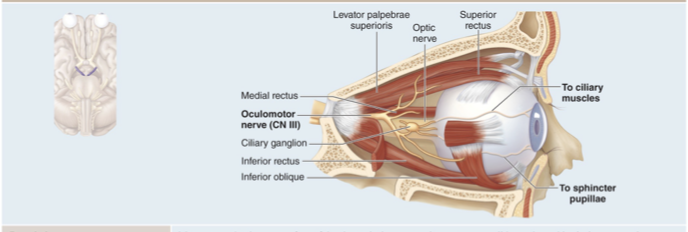
CN III Oculomotor nerve
Motor nerve that controls muscles that move eye, lift eyelid, change pupil diameter
Innervates four of the six extrinsic eye muscles
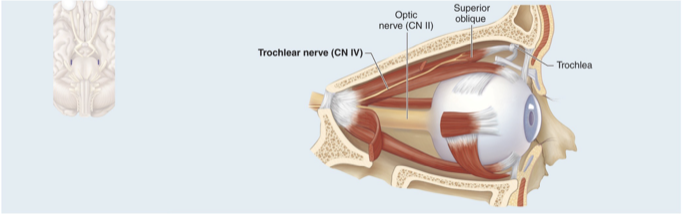
CN IV Trochlear nerve
Motor nerve that innervates one extrinsic eye muscle: superior oblique
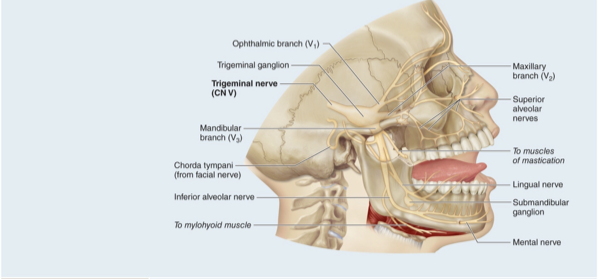
CN V Trigeminal nerve
Mixed nerve controlling somatic sensation from face, chewing movements
Three branches: ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular
Receives sensory nerve signals from face, oral cavity, nasal cavity, meninges, and anterior scalp, and innervates muscles of mastication
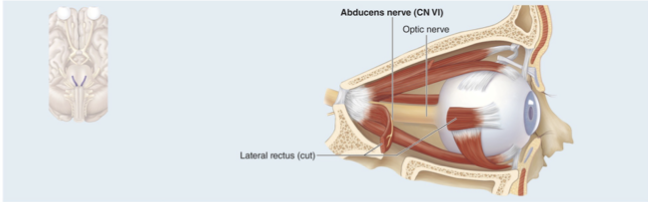
CN VI Abducens Nerve
Motor nerve that controls one eye muscle: lateral rectus muscle to abduct eye away from the center
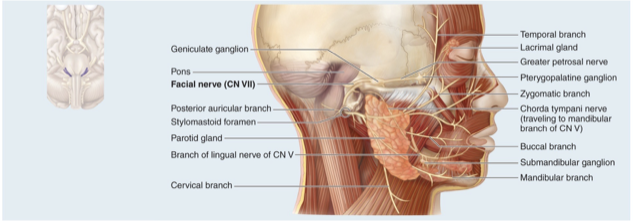
CN VII Facial nerve
Controls muscles of facial expression and provides signals for taste from tongue
Mixed nerve that conducts taste sensations from anterior two-thirds of the tongue, relays motor output to muscles of facial expression; lacrimal (tear) gland and most salivary glands
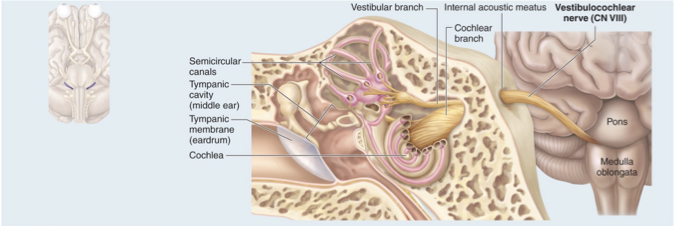
CN VIII Vestibulocochlear nerve
Sensory nerve controlling sense of hearing and equilibrium
Sensory nerve with two branches that conducts equilibrium and auditory (hearing) sensations from the inner ear to the brain
Has three fluid filled canals
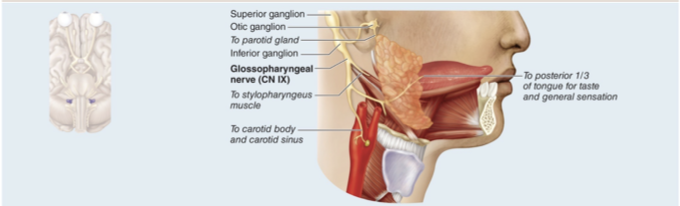
CN IX Glossopharyngeal nerve
Mixed nerve that controls taste and touch from tongue; control of pharynx muscle
Receives taste and touch sensations from posterior one-third of the tongue, innervates one pharynx muscle and the parotid salivary gland
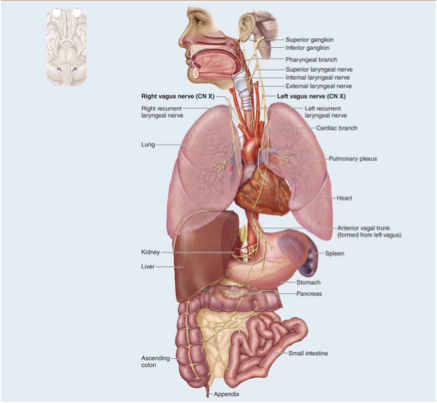
CN X Vagus nerve
Mixed nerve, visceral sensation; parasympathetic nerve to many organs of the body with lots of branches
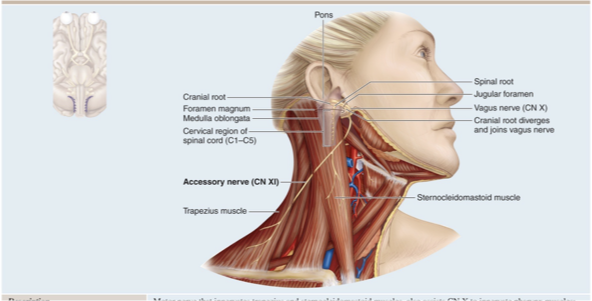
CN XI Accessory nerve
Controls muscles of neck, pharynx
Motor nerve that innervates trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles, also assists CN X to innervate pharynx muscles, formerly called the spinal accessory nerve
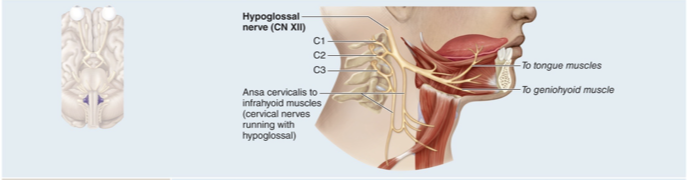
CN XII Hypoglossal nerve
Motor nerve that innervates both intrinsic and extrinsic tongue muscles “under tongue”
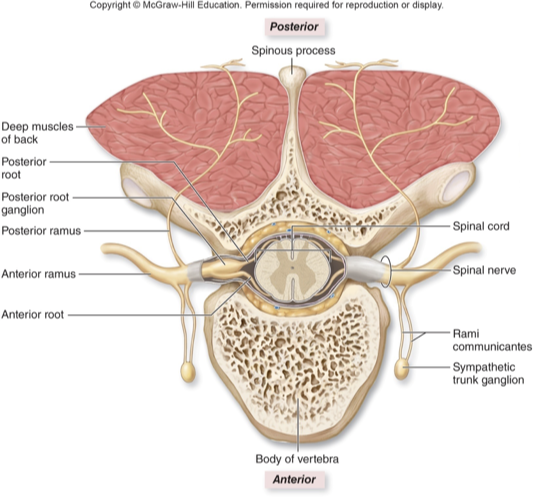
Spinal nerve characteristics
31 pairs
Each nerve formed from merger of anterior root and posterior root
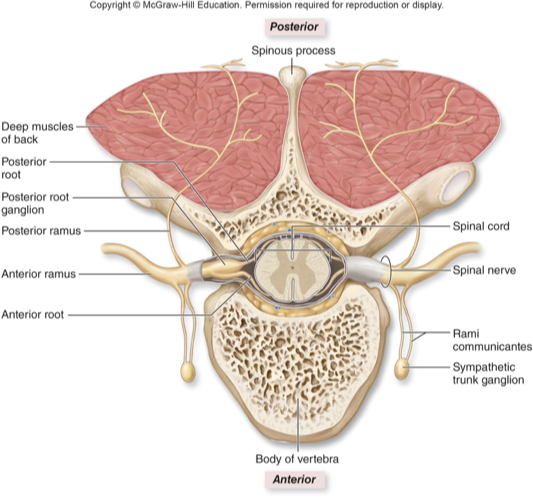
Anterior root
Many axons of motor neurons whose cell bodies are in anterior and lateral horns (motor output)
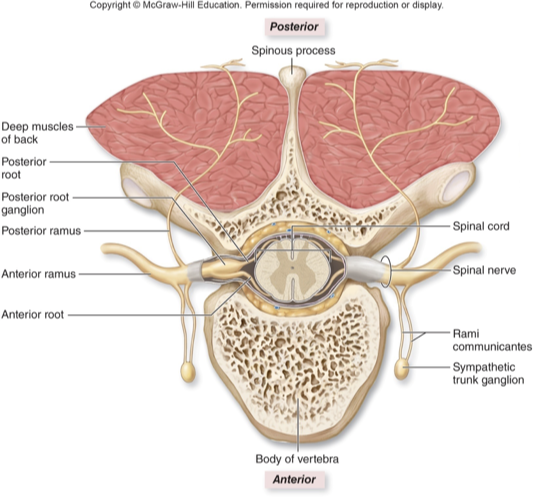
Posterior root
Many axons of sensory neurons whose cell bodies are in posterior root ganglion (sensory input)
Naming of spinal nerves
Each is named for part of spinal cord it comes from and a number
Intervertebral foramina
This is place that cervical nerves exit superior to the vertebra of the same number (C2 nerve exits between C2 and C1 vertebrae)
Exception is nerve C8 which exits below the C7 vertebra
Below C8, nerves exit inferior to the vertebra of the same number (T2 nerve exits between T2 and T3 vertebrae)
Lumbar, sacral and coccygeal spinal nerves have long rootlets that extend inferiorly before exiting vertebrae
Rootlets form cauda equina
Somatic nervous system (SNS)
Consciously perceived or controlled sensory and motor processes
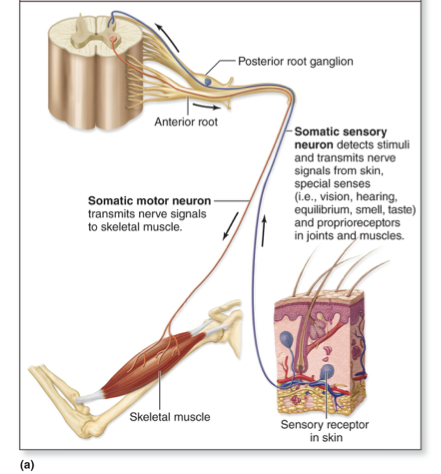
Somatic sensory
Portion detects signals from special senses (vision, hearing, equilibrium, smell taste) and from skin and proprioceptors that we are consciously aware of
Somatic motor
Portion sends signals from CNS to skeletal muscles
Voluntary movements involve cerebrum
Reflexive movements involve brainstem and spinal cord
Sensory nervous system
Detects stimuli and transmits information from receptors to the CNS
Somatic and visceral sensory
Visceral sensory
Sensory input that is not consciously perceived from receptors of blood vessels and internals organs. It provokes autonomic motor output
Motor nervous system
Initiates and transmits information from CNS to effectors
Somatic and autonomic motor
Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
Motor output that is not consciously controlled; transmits signals from CNS to effectors which are heart, cardiac muscle, smooth muscle and glands
Also called autonomic motor or visceral motor
Responds to visceral sensory inputs (from blood vessels)
Functions to maintain homeostasis to keep body conditions within optimal range
Parasympathetic division (of autonomic motor nervous system)
Preganglionic neurons located in brainstem nuclei and S2-S4 segments of spinal cord (caniosacral)
Functions to bring body to homestasis in conditions of rest and digest and conserves energy and replenishes nutrient stores
Slows down heart rate
Airways constrict
Caniosacral division
Myelinated long preganglionic axon
Short unmyelinated postganglionic axon
Autonomic ganglion is close to or within effector organ wall
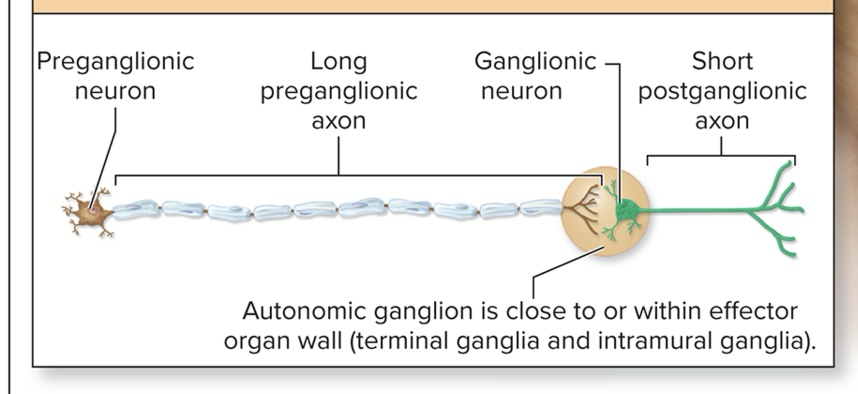
Sympathetic division (of autonomic motor nervous system)
Preganglionic neurons located in lateral horns of T1-L2 segments of spinal cord (thoracolumbar)
Functions to bring body to homeostasis in conditions of fight or flight
Increases alertness and metabolic activity
Thoracolumbar division
Short branching myelinated preganglionic axon
Long unmyelinated postganglionic axon
Autonomic ganglion is close to the vertebral column
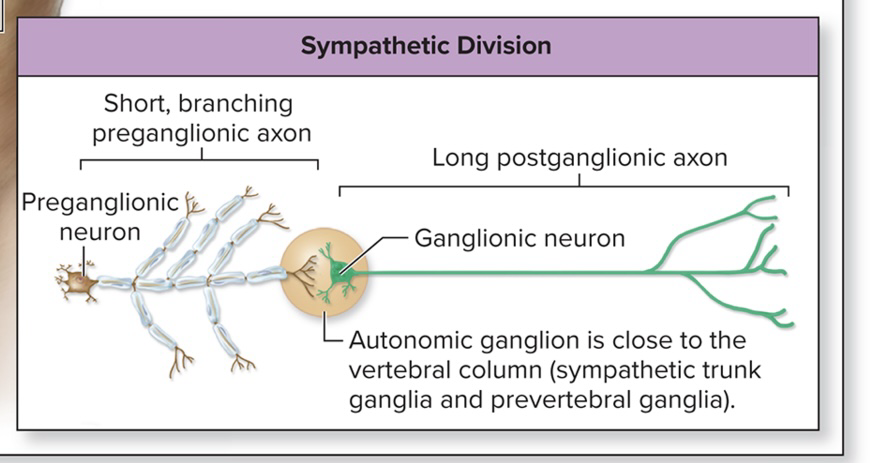
Sympathetic division function
Emergency, excitement, exercise
Thoracolumbar anatomical origin
Ganglia are close to CNS but anatomical pathways are complex because of branching
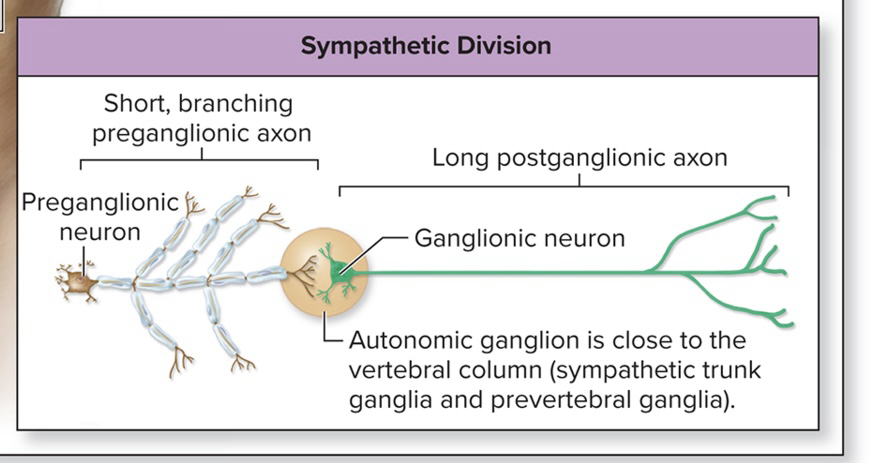
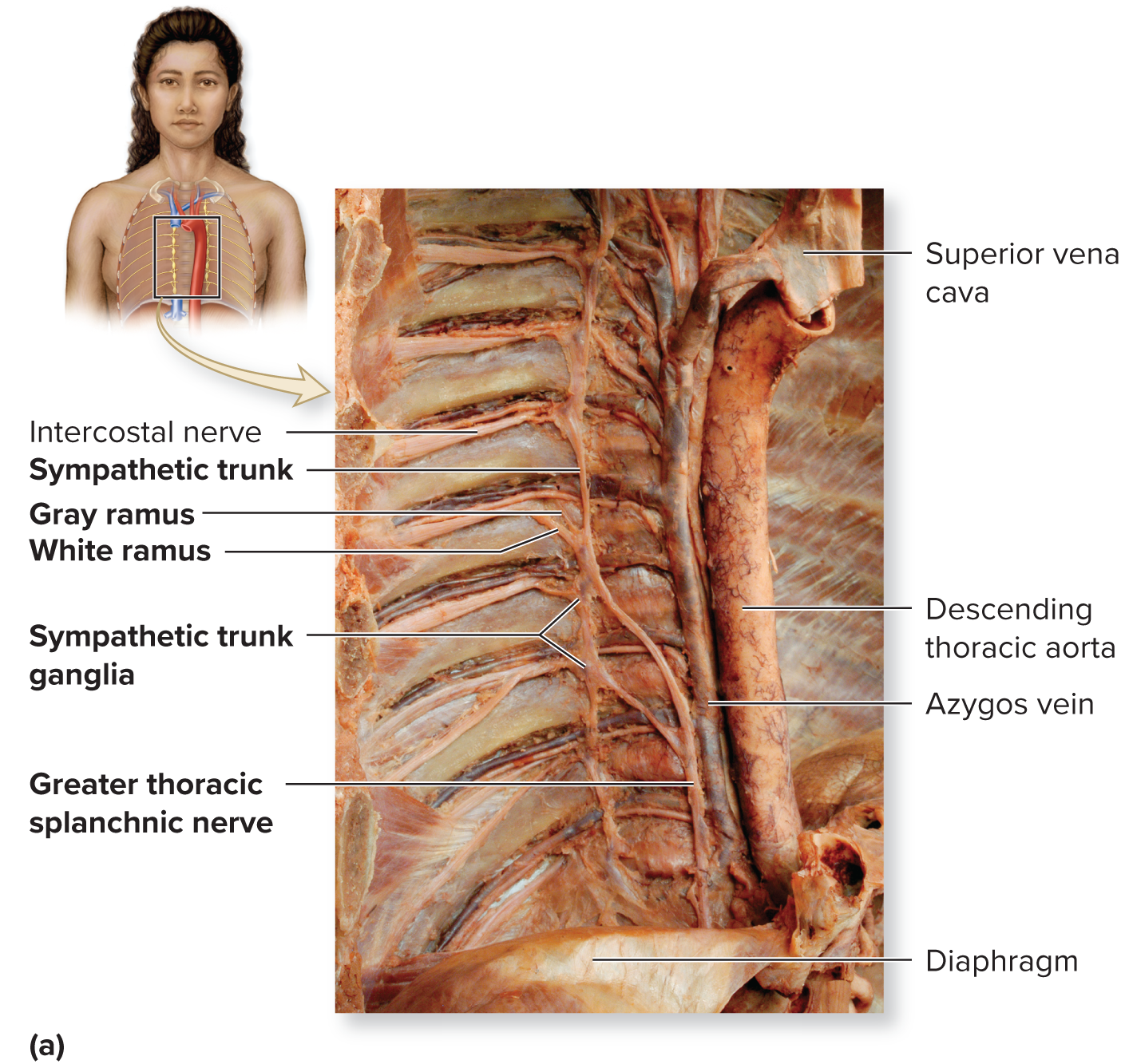
Sympathetic trunks and ganglia
Left and right trunks just lateral to the vertebral column
Trunk resembles a string of pearls
“string” composed of axons
“pearls” composed of sympathetic trunk ganglia housing cell bodies
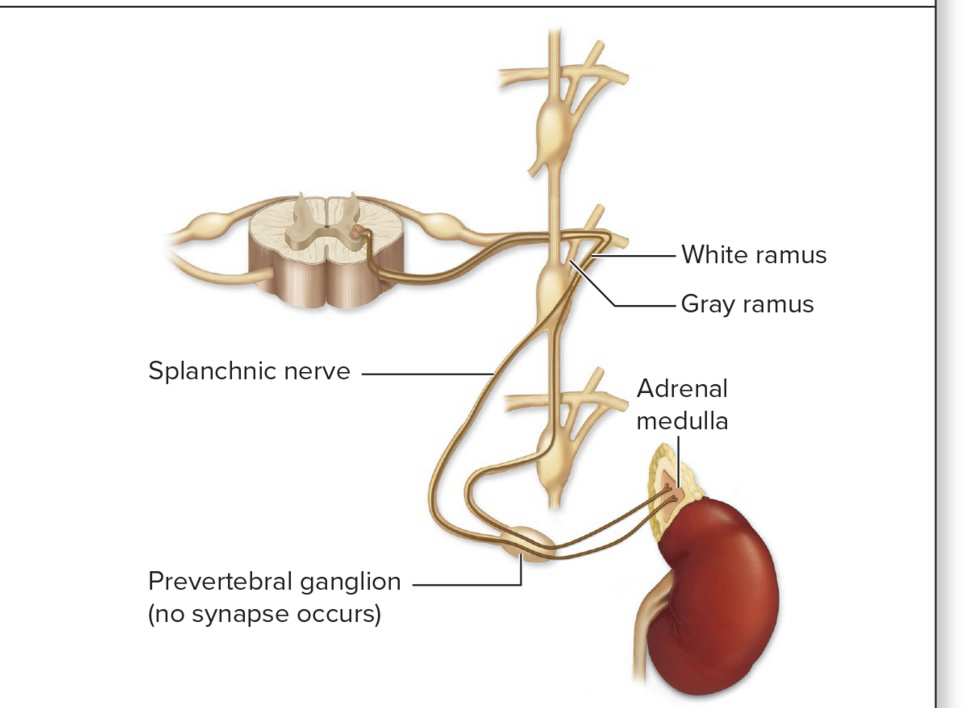
Adrenal medulla pathway
Innervates cells in medulla, only one neuron
For central region of adrenal gland (its medulla)
Preganglionic sympathetic axons extend through sympathetic trunk and pre vertebral ganglia without synapsing in either
Preganglionic cells stimulate adrenal medulla cells to release epinephrine and norepinephrine into the blood
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
Hormones that prolong the “fight or flight” response
ANS neurotransmitters
Acetylcholine (ACh) and norepinephrine (NE)
Either transmission can cause stimulation or inhibition, depending on the postsynaptic receptor (excitatory or inhibitory)
Cells that release ACh are cholinergic neurons
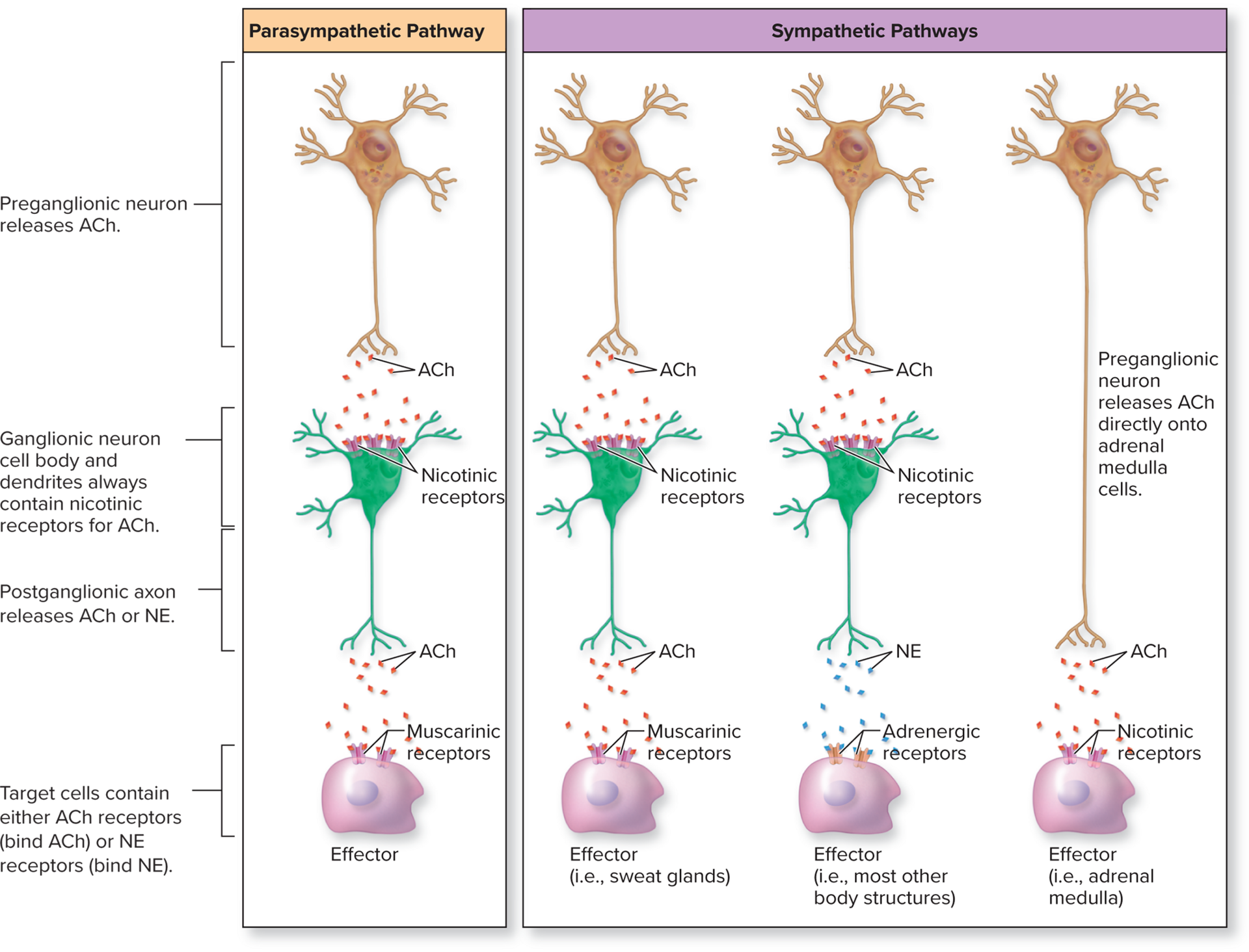
Cholinergic neurons
Release ACh
All ANS preganglionic neurons
All parasympathetic ganglionic neurons
Sympathetic ganglionic neurons innervating sweat glands and blood vessels in skeletal muscle
Target cells in ANS that release ACh
Have cholinergic receptors
Adrenergic neurons
Cells that release norepinephrine (NE)
Target cells in ANS that release norepinephrine
Have adrenergic receptors
Types of cholinergic receptors
Nicotinic and muscarinic
Nicotinic receptors
Type of cholinergic receptor found in all ganglionic neurons and adrenal medulla cells
When ACh binds to receptor it opens cation channels to allow (+) cations to move through (stimulatory effect)
More Na+ moves into the cell then K+ leaving so it becomes more positive
Cell depolarizes: excitatory postsynaptic potential is produced (always excitatory)
Muscarinic receptors
Type of cholinergic receptor found in all target organs of parasympathetic division and a few of sympathetic division
Sympathetic effectors with these receptors include sweat glands and blood vessels in skeletal muscle
Different subtypes
ACh binds to receptors of smooth muscle in GI it is stimulated to contract more
When ACh binds to receptors on cardiac muscle the heart rate decreases
Have stimulating and inhibitory effects
Types of adrenergic receptors
Alpha (a) and beta (B) receptors
Can be stimulatory or inhibitory
Cells with alpha receptors are typically stimulated by NE
Cells with beta receptors are typically stimulated or inhibited by NE
Dual innervation
Organ receives input from both the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
Two divisions may have antagonistic or cooperative effects
Antagonistic effects
The parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions oppose each other
Parasympathetic activity slows heart rate; sympathetic activity increases heart rate
Cardiac cells have both cholinergic and adrenergic receptors
Cooperative effects
Parasympathetic and sympathetic stimulation have different effects that are part of an overall response
E.g., male sexual function
Penis erection due to parasympathetic activity
Ejaculation due to sympathetic activity
Sensory receptors
Provide information about external and internal environments
Respond to stimuli
Each type of receptor responds best to a type of stimulus
Light energy for eye receptors, sound energy for ear receptors
Modality
Nature of stimulus (light, sound, touch, pressure)
Transducers
Convert stimulus energy into electrical energy
Receptors have resting membrane potential
Receptor membranes have modality gated channels that respond to their type of stimulus
Action potentials are conveyed to CNS for interpretation
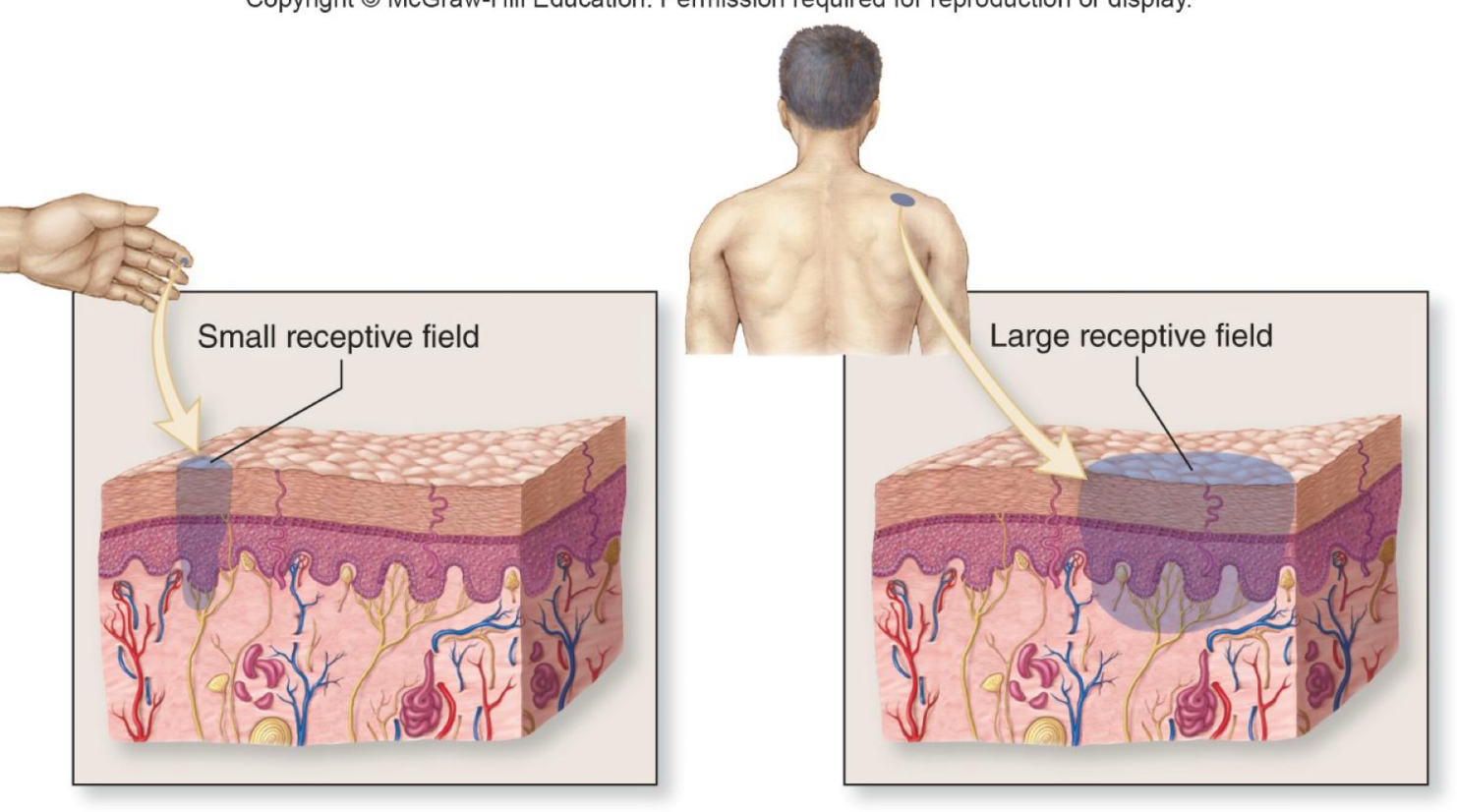
Receptive field
The distribution area of the endings of a sensory neuron
Smaller receptive fields allow more precise stimulus localization where larger receptive fields are less precise
Sensory receptor classification
Categorized by distribution, stimulus origin, and stimulus modality
Receptor distribution
General vs special
General sense receptors
Simple structures distributed throughout the body
Somatic sensory receptors
Tactile receptors of skin and mucous membranes, proprioceptors of joints, muscles, tendons
Visceral sensory receptors
Found in walls of internal organs, they monitor stretch, chemical environment, temperature, pain
Special sense receptors
Specialized receptors in complex sense organs of the head
5 senses: olfaction, gustation, vision, audition, equilibrium
Stimulus origin categories
Exteroceptors
Interoceptors
Proprioceptors
Exteroceptors
Detect stimulus from external environment
Skin, mucous membranes, special sense receptors
Interoceptors
Detect stimuli from internal organs
Visceral sensory receptors monitoring internal environment
Proprioceptors
Detect body and limb movements
Somatosensory receptors of muscles, tendons, joints
Modality of stimulus categories
chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors, photoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, nociceptors
Chemoreceptors
Detect chemicals dissolved in fluid
Include receptors for external environment (smell of food) or internal environment (oxygen levels in blood)
Thermoreceptors
Detect changes in temperature
Include receptors in skin, hypothalamus
Photoreceptors
Detect changes in light intensity, color, movement
In retina of the eye
Mechanoreceptors
Detect distortion of cell membrane
Include touch, pressure, vibration, and stretch receptors
Function as baroreceptors, proprioceptors, tactile receptors and specialized receptors in inner ear
Nociceptors
Detect painful stimulus
Somatic nociceptors, visceral nociceptors
Somatic nociceptors
Detect chemical, heat or mechanical damage to the body surface or skeletal muscles (Skin, muscle, bone etc.)
Visceral nociceptors
Detect internal organ damage
Classifying a receptor
Classification based on receptor distribution, stimulus origin, modality
Eyes
Special sense, exteroceptors, photoreceptors
Receptors for blood vessel stretch
General sense, interoceptors, mechanoreceptors (baroreceptors)