CHEM EXAM 2
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
HCL
hydrochloric acid, strong acid
is hydrochloric acid strong or weak?
strong
HCL products when reacting with water
Cl- + H3O+
HBr
hydrobromic acid, strong acid
Is hydrobromic acid strong or weak?
strong
HBr products when reacting with water
Br- + H3O+
HI
hydroiodic acid, strong acid
is hydroiodic acid strong or weak
strong
HI products when reacting with water
I- + H3O+
HNO3
nitric acid (strong acid)
is nitric acid strong or weak
strong
HNO3 products when reacting with water
NO3- + H3O+
H2SO4
sulfuric acid, strong acid
is sulfuric acid strong or weak
strong
H2SO4 products when reacting with water
HSO4- + H3O+
HClO3
chloric acid, strong acid
is chloric acid strong or weak
strong
HClO3 products when reacting with water
ClO3- + H3O+
HClO4
perchloric acid, strong acid
is perchloric acid strong or weak
strong
HClO4 products when reacting with water
ClO4- + H3O+
What do strong acids do in water?
They ionise completely - all acid particles dissociate to release positive hydrogen ions
are strong acids ionic or molecular
molecular
Are weak acids ionic or molecular
molecular
are strong bases ionic or molecular
ionic
are weak bases ionic or molecular
molecular
how do molecular compounds dissociate in water
dipole-dipole rxns, most don't dissociate
Dipole-Dipole reaction
molecules with permanent dipoles attract each other electrostatically; the positive end of one molecule attracts the negative end of another molecule, and so on, leading to an alignment of the molecules
molarity
the number of moles of solute per liter of solution
molarity equation
moles of solute/liters of solution
molecular compound
a chemical compound whose simplest units are molecules,
If water is added to an existing solution, what happens to volume and mols of solute?
mols are unchanged but volume increases
soluble compounds
able to dissolve in water
how do polyatomic ions interact?
they do not dissociate
Solvation/Hydration
dissolved particles are surrounded by water molecules; thepositive end of H2O points towards the anions and the negative end of H2Opoints towards the cations
what attractive force between ions w/in ionic compounds and ions w/ water causes a solution to dissolve
when force btw ions and water > ions in ionic compound
acids
compounds that form hydrogen ions when dissolved in water, H+ ionizes in aqueous solution
complete ionization
the condition when all donor atoms are positively charged by giving up their donor electrons and all acceptor atoms are negatively charged by accepting electrons. WEAK ATTRACTION
partial ionization
weak acid seperate only some of the ions in aqueous solution. STRON ATTRACTION
strong electrolytes
soluble ionic compounds, strong acids, strong bases. Strong conductor, many ions present, 100% ions in solution
weak electrolytes
weak acids and weak bases, weak conductor,
non electrolytes
molecular compounds, no ions present, not a conductor
precipitation rxn
(aq) + (aq) --> (s) + (aq)
acid-base rxn
A special type of double replacement rxn in which water and a salt are produced (HY + XOH --> H2O + XY)
molecular equation
a reaction equation that shows the complete chemical formulas of all reactants and products
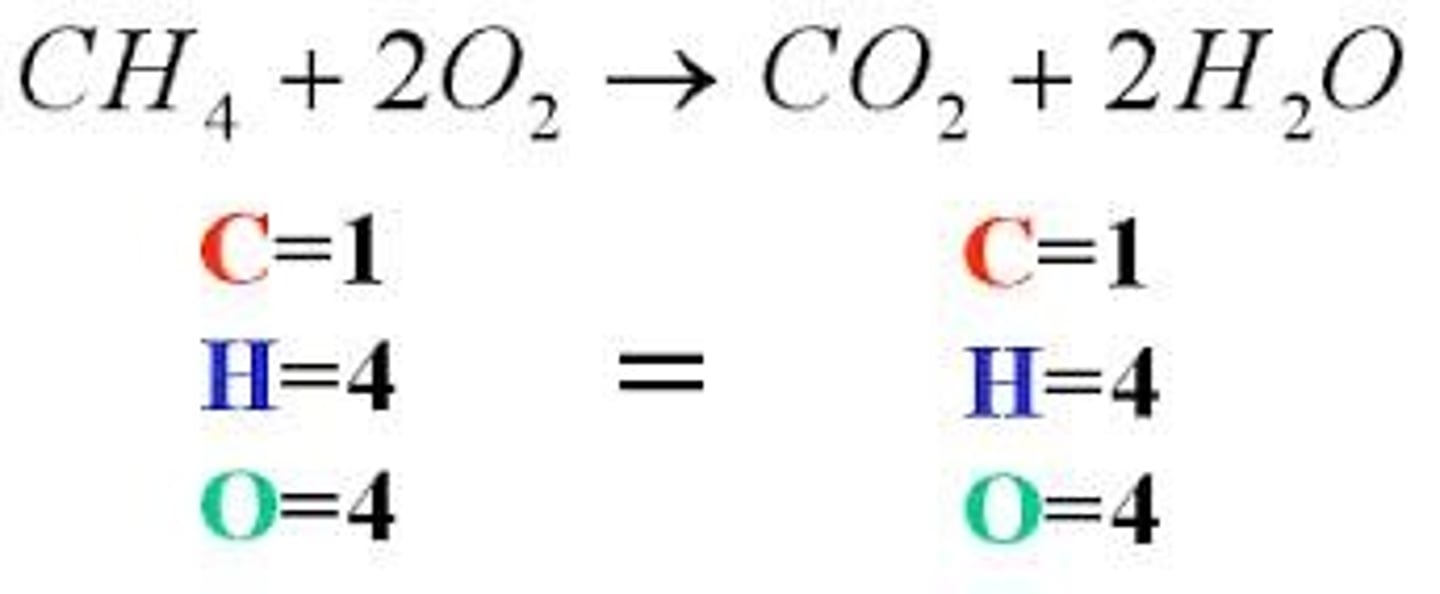
total ionic equation
an equation for an aqueous reaction that shows all the strong electrolytes dissociated into ions. Weak and non electrolytes are intact undissociated compounds

net ionic equation
an equation for a reaction in solution showing only those particles that are directly involved in the chemical change, eliminates spectator ions

spectator ions
Ions that do not take part in a chemical reaction and are found in solution both before and after the reaction
precipitation reaction
The formation of a solid from a solution during a chemical reaction. Precipitates are often formed when two aqueous solutions are mixed together. More than one solid product is possible. Forms with net removal of ions
homogenous and heterogenous solutions in ions
2 homogenous ionic mixtures (g) form a heterogenous mixture (s or l)
conversion factor for mols to entities (atoms, molecules, ions..)
Avogadro's #
conversion factor for mols to volume
molarity of solution (# mols/volume in L)
6 strong acids:
HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, H2SO4, HClO4
strong bases
group 1 hydroxides
Ca(OH)2
Sr(OH)2
Ba(OH)2
Strong acid/electrolyte + strong base/electrolyte equation
molec: all products and reactants as if not dissociated
total ionic: all strong electrolytes dissociate into ions (strong bases, strong acids, soluble ionic compounds)
weak acid/electrolyte + strong base/electrolyte
Weak acids don't dissociate!
titration
A solution of known concentration is used to determine the concentration of another solution.
titrant
the standard solution added to the sample in a titration: KNOWN CONC
buret
dispensing and transferring known volumes of fluids
Indicator
a compound that can reversibly change color depending on conditions such as pH
equivalence point
the point at which the two solutions used in a titration are present in chemically equivalent amounts
end point
the point in a titration at which an indicator changes color
Gas
A state of matter with no definite shape or volume
- particles far apart
- particles fill shape of container
- compressible
liquid
A state of matter that has no definite shape but has a definite volume.
- particles close together
- not compressible
solid
A form of matter that has a definite shape and volume
- particles tightly packed
- not compressible
particle mobility of gas
- high mobility and velocity
- constant motion
particle mobility of liquid
less freedom of motion than gas
particle mobility of solid
immobile
attractive forces between gas particles
little to no attraction
attractive forces between liquid particles
moderate attraction
attractive forces between solid particles
strong attraction
Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
a model used to explain the behavior of gases
- tiny with large spaces in btwn
- constant random straight line motion until collision, which is elastic
- assumed to exert no force on each other, no attraction or repulsion
- avg kinetic energy of a collection of gas particles is directly proportional to temp of gas in K
Kinetic molecular theory equation and explanation
Kinetic energy= 1/2(mass)(velocity)^2
molecules of different gases at the sametemperature always have the same average kinetic energy. Average kinetic energydepends only on the temperature.
pressure=
force/area
Atmospheric pressure arises from
the force exerted by atmospheric gases on the earth's surface
what natural force can decrease atmospheric pressure
increasing of altitude
common value of pascal (Pa)
1.01325 (10^5)
common value of kilopascal (kPa)
101.325
common value of atmosphere (atm)
1
common value of millimeters of mercury (mmHg)
760
common values of torr
760
common unit of lbs per square inch (lb/in^2)(psi)
14.7
common unit of bar
1.01325
1 atm=
760 mmHg= 760 torr
Gas Laws
the laws that state the mathematical relationships between the volume, temperature, pressure, and quantity of a gas
ideal gas
a hypothetical gas that perfectly fits all the assumptions of the kinetic-molecular theory, does not exist but most simple gases behave almost ideal @ normal temp and pressure
Boyle's Law
A principle that describes the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature
P1V1=P2V2
Boyle's Law Equation
P1V1=P2V2
Charles's Law
the law that states that for a fixed amount of gas at a constant pressure, the volume of the gas increases as the temperature of the gas increases and the volume of the gas decreases as the temperature of the gas decreases. V AND T DIRECTLY PROPOERTIONAL
Charles's Law Equation
V1/T1 = V2/T2
Absolute zero
The coldest temperature, 0 Kelvin / -273.15 C, that can be reached. It is the hypothetical temperature at which all molecular motion stops.
Amonton's Law
if the volume of a gas is held constant, increasing the temperature of the gas increases its pressure. P AND T ARE DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL
Amonton's Law equation
P1/T1=P2/T2
Avogadro's Law
equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules
Avogadro's Law equation
V1/n1=V2/n2
n= # mols
standard temp in C
0
STP
standard temperature and pressure
Ideal Gas Law
the relationship PV=nRT, which describes the behavior of an ideal gas
direct proportionality
one value increases as another increases
indirect proportionality
one factor goes up, the other goes down