Biotin
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Biotin
• “Egg white injury”
• Eating raw egg whites → hair loss, dermatitis, neuromuscular problems
• Szent-Gyorgyi: substance (biotin) in liver could cure and prevent “egg white injury”
Sources
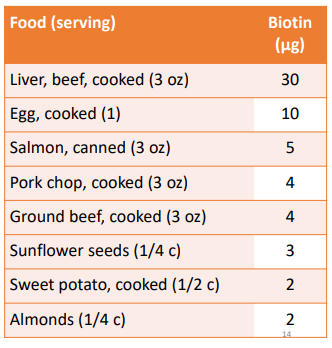
• Widely distributed in foods
• Made by bacteria in large intestine
• Commonly found free or bound to proteins
• Avidin (glycoprotein) in raw egg whites binds biotin and prevent its absorption
• Supplements: free form
• Single-nutrient: 10 mg
Biotin Digestion
• Protein-bound biotin digested by pepsin and intestinal proteases → free biotin and some biocytin (biotin bound to lysine)
• Biocytin (biotin + lysine) may be absorbed intact by a peptide carriers or hydrolyzed by biotinidase
• Biotinidase found in intestinal brush border, pancreatic and intestinal juices, in the plasma, and intracellularly
• Genetic mutation → biotinidase deficiency • Lethargy, hypotonia, seizures, ataxia, dermatitis, and alopecia
• Treatment: 5-20 mg biotin daily
Biotin Absorption
• Free biotin absorbed primarily in proximal small intestine
• Pharmacologic doses: passive diffusion
• Physiological intakes: SMVT in small intestine
• Regulated by [biotin]
• Negatively affected by alcohol
• Biotin synthesized by colonic bacteria absorbed in proximal and transverse colon (SMVT)
• Transport across the basolateral membrane is carriermediated
• 100% of oral free biotin is absorbed
Biotin Transport
• In plasma 80% is free biotin, 20% bound to proteins (albumin, globulins, and biotinidase)
• Blood [biotin]: 200 - 750 pg/mL
Biotin Uptake
• Liver and probably other tissues: SMVT and monocarboxylate transporter (MCT) 1
Biotin Storage
• Small quantities stored in muscle, liver, brain
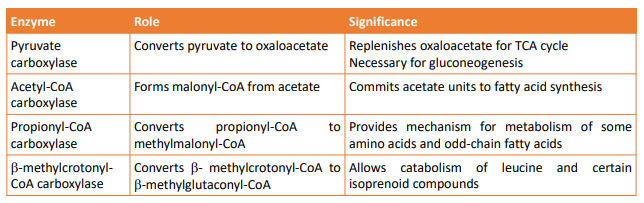
Biotin Functions & Mechanisms of Action
• Coenzyme roles: holocarboxylase
• Genetic mutation → holocarboxylase synthetase
• Vomiting, lethargy, hypotonia, acidosis, and seizures
• Treatment: 10 - 200 mg oral biotin daily
• Non-coenzyme roles • Biotinylation
• Histones and nonhistone proteins
• Biotinylation of histones allow transcription factors to affect gene expression
Biotin Metabolism & Excretion
• Small amounts of biotin and biocytin found in urine
• Biocytin degraded to lysine & biotin (biotinidase)
• Biotin is usually further degraded
• Metabolites excreted in urine
• Biotin that was synthesized by colonic bacteria, but not absorbed, is excreted in feces
Biotin Adequate Intake
• Adults: 30 µg/day
• Pregnancy: 30 µg/day
• Lactation: 35 µg/day
Biotin Deficiency (Rare but serious)
• Excessive consumption of raw egg whites
• Lethargy, paresthesia, hypotonia, depression, hallucinations, dermatitis (red, dry, scaly), anorexia, nausea, brittle nails, alopecia, and muscle pain
• 10 mg daily
Biotin At Risk for Deficiency
• Those consuming excess raw egg whites
• Those with GI disorders
• Pregnant and lactating women
• People who consume excess alcohol
• Those on anticonvulsant drug therapies
Biotin Toxicity
• None reported, no UL
• Up to 200 mg without side effects (inherited disorders of biotin metabolism)
Biotin Assessment of Nutriture
• Blood concentrations do not accurately reflect intake or status
• Decreased urinary biotin excretion (< 6 μg/day) is a sensitive and early indicator of biotin deficiency
• A diet devoid of biotin can decrease [biotin] in plasma and urine in ~2-4 weeks