Marine Science Semester 2 Final Exam Study Guide 2025
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Dorsal Side
Top of animal
Ventral Side
bottom of an organism, often referring to the belly or underside.
Anterior Side
The front side of an organism, typically where the head or face is located.
Posterior Side
Opposite of anterior; the back side of an organism.
Radial symmetry
A type of body symmetry in which body parts are arranged around a central axis, allowing for multiple planes of symmetry.
Bilateral symmetry
A type of body symmetry in which the body can be divided into two identical halves along a single plane, typically resulting in distinct left and right sides.
Kingdom
A major taxonomic rank that classifies living organisms into groups based on shared characteristics, encompassing multiple phyla.
Phylum
A rank in the biological classification system that groups together related classes based on similar characteristics and evolutionary history.
Class
A taxonomic rank below phylum and above order that groups together organisms sharing common attributes.
Order
A taxonomic rank below class and above family that categorizes organisms based on further shared characteristics and evolutionary traits.
Family
A taxonomic rank below order and above genus, used to group organisms that are closely related and share a set of characteristics.
Genus
A taxonomic rank below family and above species, which includes one or more species that are closely related.
Species
A taxonomic rank below genus, which identifies individual organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
Porifera
sponge
Cnidarian
a phylum that includes aquatic animals like jellyfish and sea anemones, characterized by their stinging cells called cnidocytes.
jellyfish
sea anemone
Echinodermata
a phylum of marine animals that include starfish, sea urchins, and sea cucumbers, known for their radial symmetry and a water vascular system.
sea star
sea urchin
sea cucumber
Mollusca
a diverse phylum of invertebrate animals that includes snails, clams, and octopuses, characterized by their soft bodies, often protected by a hard shell
octopus
clam
snails
kiten
Arthropoda
a phylum that includes invertebrate animals like insects, arachnids, and crustaceans, characterized by their exoskeleton, segmented bodies, and jointed appendages
crab
shrimp
crustacean
insect
spider
centipede
Chordata
a phylum of animals that have a notochord at some stage of development, including vertebrates like mammals, birds, and fish, as well as some invertebrates
dolphin
shark
Order of taxonomic terms
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Binomial Nomenclature
two word - name
Rules for writing proper scientific names
underlined/italicized
genus name starts with capital letter
species name in all lowercase
Pelagic
Open water
Benthic
Sea floor
3 S’s of sand
sorted
shape
size
Sediment size from largest to smallest
coarse sand → medium sand → fine sand → silt → clay
Summer Beach
low tide allows for berm to build up
smaller & well sorted sand
Winter Beach
high tide erodes berm
deposit larger sediment
Spherical Sediment Grains
high energy environments
particles are transported over long distances
Angular Sediment Grains
low energy environments
minimal transport
retaining sharp edges
Abiogenic sand
Formed from non-living sources; minerals, rocks
Biogenetic sand
From living organisms, coral fragments, shells, calcium carbonate
Open Circulatory System
Blood isn’t always enclosed in vessels
Blood flows through the body
Closed Circulatory System
Blood is always contained in vessels
Blood flows through arteries, veins
Marine chemical that makes up shells of mollusks
Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3)
Bivalve
clams
mussels
scallops
Gastropod
abalone
nudibranch
limpets
Cephalopod
squids
octopus
cuttlefish
Polyplacophora
Chiton
Foot
used for movement, burrowing, or attachment to surfaces
Mantle
Secretes shell and lines the mantle cavity
Mantle Cavity
Houses gills/lungs; for excretion, respiration
Visceral Mass
Most of the internal organs
Endoskeleton
Internal support structure, protects internal organs, attachment for muscles
Exoskeleton
External protective covering, support and protects body
Exoskeletons of bivalves are made of
Calcium carbonate
Exoskeletons of crustaceans are made of
Chitin
Suspension feeders
Filter tiny particles (plankton, organic matter) from water using gills or siphons
Grazers
Scrape surface using radula, algae and biofilm on rocks
Defense mechanisms of cephalopods
ink release
jet propulsion
camouflage
tentacles and beak
Sessile
satin one place; immobile
clams, mussels, scallops
Motile
Adapt to almost every marine environment in the world
snails, slugs, octopus, squid
Ectotherm
Rely on external sources of heat to regulate body temperature (cold blooded)
Endotherm
Generate their own body heat internally; maintain relative constant body temperature
Holothuroidea
Eat: debris in benthic zone
Example: sea cucumber
Unique features: Thick leathery skin, toxins to prevent them from getting eaten
Asteriudea
Eats: Bivalves and barnacles
Example: Sea star
Unique features: Benthic community, keystone species
Echinoidea
Eats: herbivores, algae
Example: sea urchins and sand dollars
Unique Features: ocean acidification threats, found on sandy beaches
Keystone Species
Organisms that play a crucial role in the ecosystem, if sea stars are removed everything could fall apart
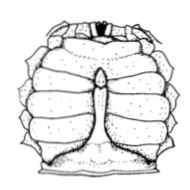
Male (jimmy) Crab
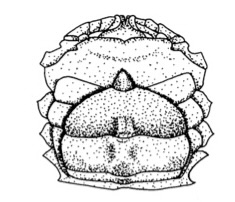
Female (sook) Crab
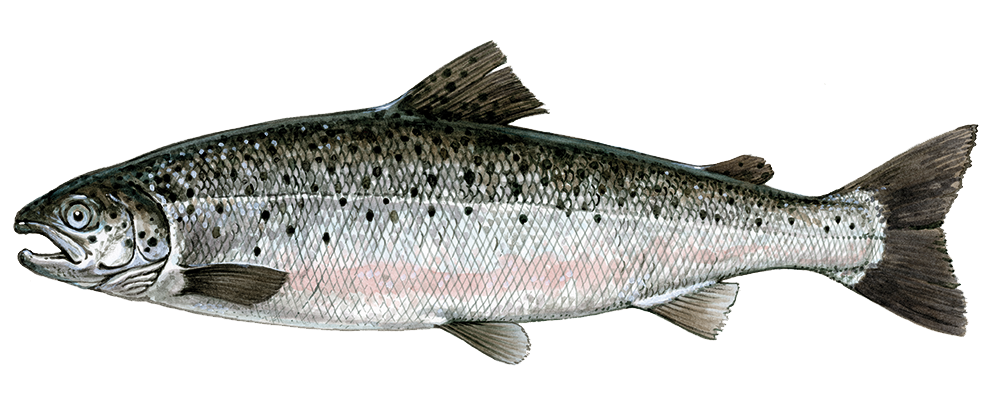
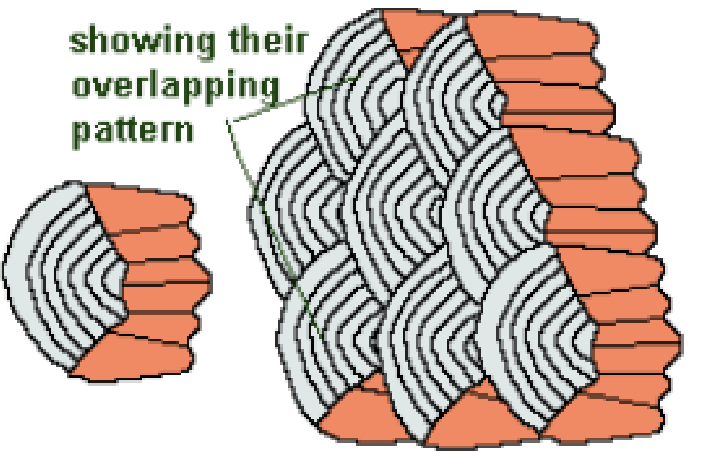
Cycloid scale
smooth edges
overlapping pattern
salmon
carp
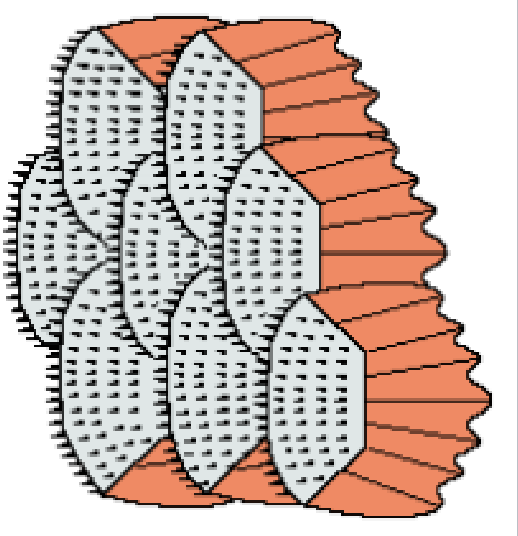
Ctnoid Scale
tiny spines along border
perch
Ganoid Scale
Diamond shaped
sturgeon
garfish
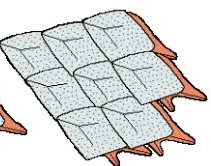
Placoid Scales
tiny tooth like structures
same material as teeth
Sharks
Rays
Skates
Bony fish
Have a gill cover; operculum; protects and regulates water flow
Cartilaginous fish
Have exposed gill slits
Bony fish buoyancy
Through their swim bladder, can adjust position in water by regulating amount of gas inside
Cartilaginous fish buoyancy
Fish lack swim bladders; relying on oil-rich liver and skeleton to help with buoyancy
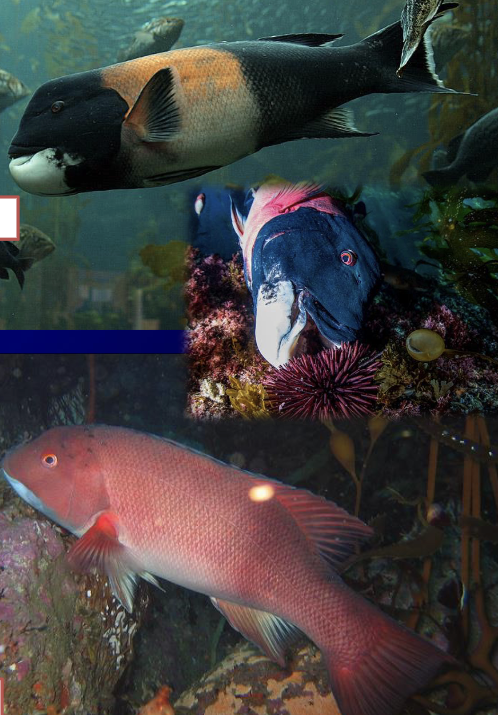
Calico Bass

Garibaldi

Yellowtail/Yellowfin

Dolphinfish/Dorado

Sculpin

California Sheephead

Salmon
