OTS Mod 3
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
List the 5 USAF core functions
1. Air superiority
2. (ISR) Intelligence, Reconnaissance, and Surveillance
3. Rapid Global Mobility
4. Global Strike
5. Command and Control (C2)
CIGAR
List the 5 USSF Core competencies
1. Space Security
2. Combat power projection
3. Space mobility and logistics
4. Information mobility
5. Space domain awareness
CISSS
Describe Air Superiority
Freedom from attack and freedom to attack
Describe Intelligence, Reconnaissance, and Surveillance (ISR)
1. Eyes and ears
2. Situational awareness for command elements
Describe Global Strike
Any target, anytime
Describe Command and Control (C2)
1. Total flexibility in operations . . . right info to the right people at the right time
2. Reliable communication and information networks
Describe Space Security
1. Mission presence: establishes conditions for safe and secure access to space for civil, commercial, Intelligence Community (IC), and multinational partners
Describe Combat Power Projection
1. Goal: freedom of action
2. Defensive operations: ensuring U.S. freedom of action in space
3. Offensive operations: deny adversary's freedom of action
Describe Space Mobility and Logistics
1. Movement and support of military equipment and personnel into, through and back from the space domain
2. Ability to launch military equipment into the proper orbit in a safe, secure, & reliable manner
Describe Information Mobility
1. Timely, rapid, reliable collection and transportation of data even in remote areas
Describe Space Domain Awareness
1. Effective identification, characterization, and understanding of any factor associated with the space domain that could affect operations
2. Physical, network, and cognitive dimensions of space
Identify the purpose and 3 principles of AFFORGEN
1. Enables operational preparedness and readiness recovery while ensuring a predictable and sustainable force offering.
2. Readiness, predictability, and sustainability
Cite the 4 rotational phases of readiness in the AFFORGEN cycle
1. Reset
2. Prepare
3. Ready
4. Available
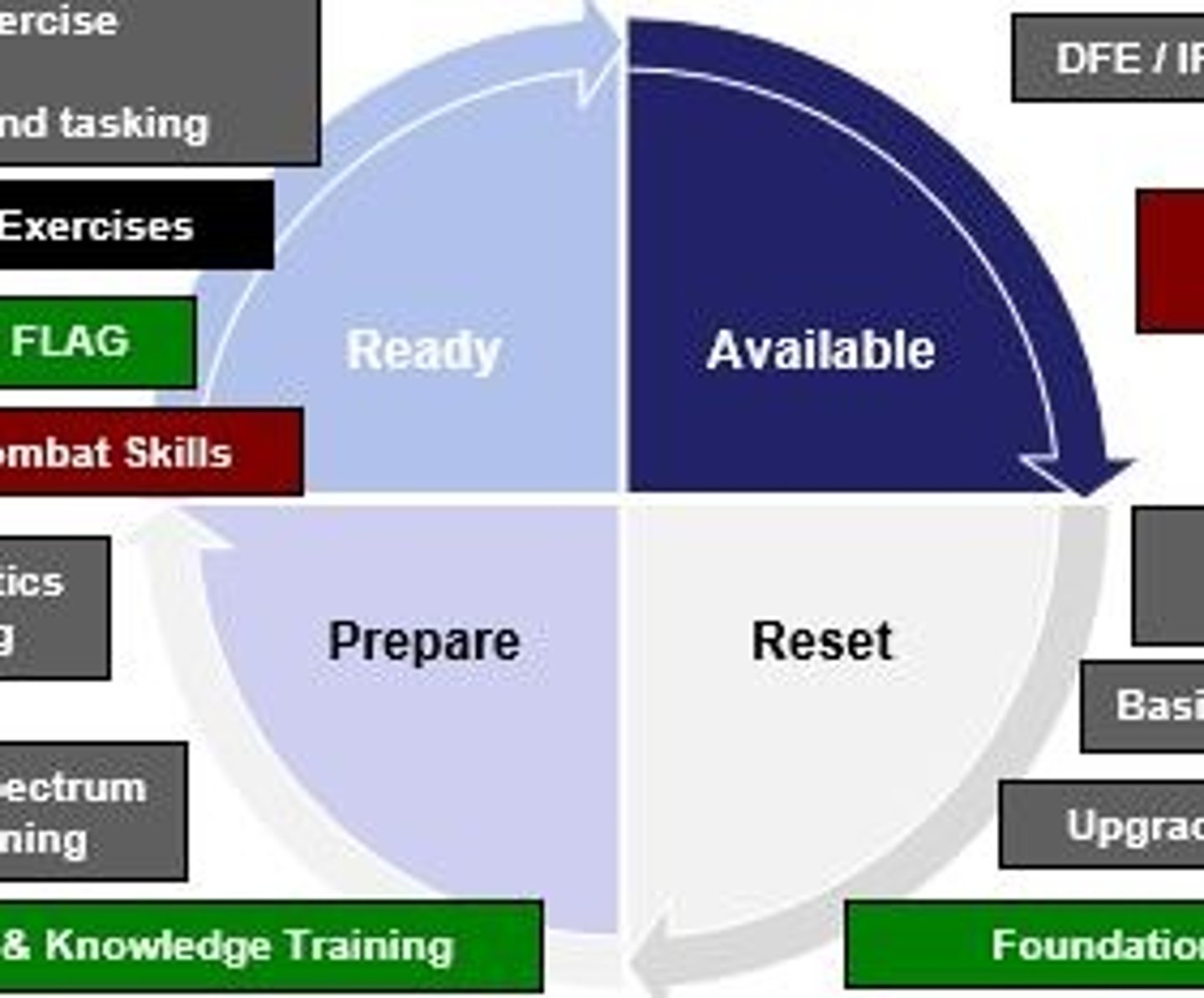
Recall the importance of readiness on mission accomplishment
Ability to fulfill requirements of the mission
Describe the Laissez-faire style of leadership
· Near-avoidance or absence of leadership
· Avoids making decisions
· Abdicates responsibility
· Avoids taking a stand on issues
· Does not develop followers
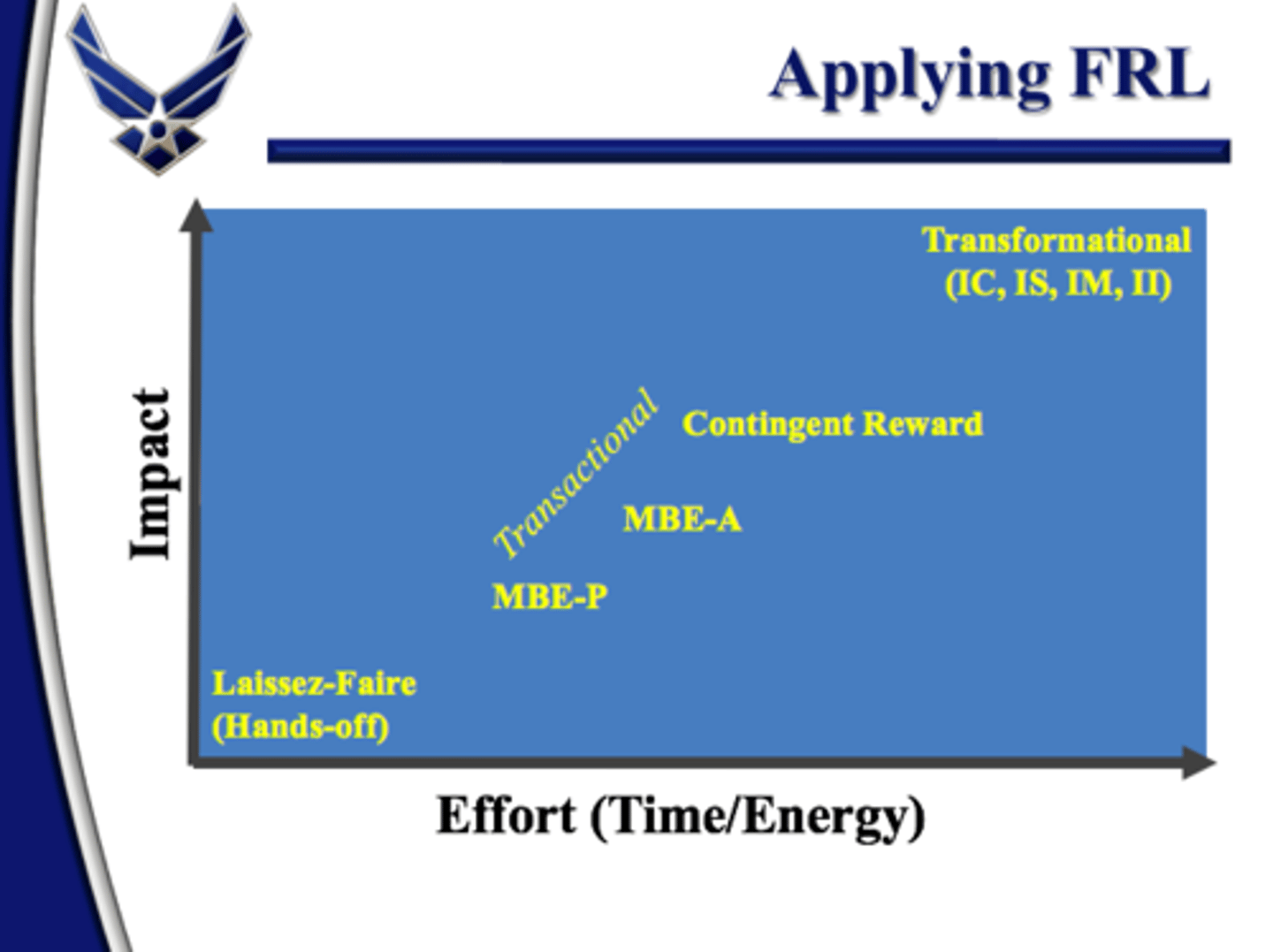
What are the three types of transactional leadership?
· Contingent reward (CR): reward for performance (carrot and the stick)
· Management by Exception (MBE)
§ MBE-A (active): Responds to deviations in standards as soon as possible necessary
§ MBE-P (passive): Responds to deviations in standards only when they are not met
Describe the contingent reward style of transactional leadership
Reward for performance (carrot and the stick)
Describe the MBE-A and MBE-P styles of transactional leadership
§ MBE-A (active): Responds to deviations in standards as soon as possible necessary
§ MBE-P (passive): Responds to deviations in standards only when they are not met
What are the four types of transformational leadership?
1. Idealized influence
2. Inspirational motivation
3. Intellectual stimulation
4. Individual consideration
Describe idealized influence
Role model respected/ admired, high ethical standards
Describe inspirational motivation
Motivates, inspires, articulates a vision
Describe intellectual stimulation
Thinks 'outside the box', reframes old problems, innovates
Describe individual consideration
Coaching, mentoring, active listener, values diversity
Describe how to apply Full-Range Leadership
•NOT a continuum from "bad" to "good"
•Different circumstances require different behaviors
•May utilize several behaviors in one day or at the same time
•Blending and emphasizing behaviors is critical
•Laissez-faire is the absence of leadership: avoid it!
What are the four stages of team growth
1. Forming
2. Storming
3. Norming
4. Performing
Describe leader-follower actions that contribute to effective teams:
Forming
Team leader (DIRECTOR) should be directive, helping team focus on:
• Getting to know one another
• Identifying member's roles
Clearly understanding team's mission/tasks
Describe leader-follower actions that contribute to effective teams:
Storming
Team leader (COACH) who can control the chaos by:
• Creating climate of open discussion
• Listening to member's concerns
• Obtaining members' inputs on how to achieve goals
• Being encouraging and supportive
Facilitating conflict resolution
Describe leader-follower actions that contribute to effective teams:
Norming
Team leader (COLLABORATOR) as a facilitator, focusing on maximizing members' contributions by:
• Delegating responsibilities
• Building members' confidence
Maximizing members' strengths
Describe leader-follower actions that contribute to effective teams:
Performing
Team leader (VISIONARY) efforts should be on maintaining success and shifting teams' perspective from inward to outward focus by:
• Planning for the future
• Cultivating leadership talent with team
• Fostering new ideas from team members
Ensuring solid mechanisms for feedback
Contrast the difference between organizational climate and culture
a. Organizational Culture: Soldiers wearing reflective belts for visibility in a camouflage uniform (established tradition)
· Ideologies, values, norms
· Long-term, ingrained
· Foundational beliefs
· Established traditions
b. Organizational Climate: How soldiers currently and collectively feel about wearing reflective belts (moods & feelings)
· Attitudes & perceptions
· Short-term, adjustable
· Moods & feelings
· Product of culture but more flexible
Discuss strategies to build a positive organizational climate (3)
1. Respect Diversity (forbid discrimination, embrace diverse perspectives and talents)
2. Safe & secure (physical safety, emotional safety)
3. High standards (challenged to reach new heights, establishing expectations)
Describe how to positively change an organizational climate
1. Address your unit (results of DEOCS, list +/- trends, describe mission impact, strategies or research for problem resolutions, follow-up resources)
2. Inspire action (communicate mission, vision, enable action, reinforce actions)
3. Focus on the Little Things (Everything a leader does influences organizational climate)
What are the four types of diversity and their sub-components
a. Demographic
· Age, race/ethnicity, religion, gender, socioeconomic status, family status, disability, geographic origin
b. Cognitive/behavioral
· styles of work, thinking, learning, and personality
c. Organization/structural
· background characteristics such as prior experience in a particular organization/institution that could affect team interactions
d. Global
· language(s) spoken, citizenship/naturalization status
Discuss the importance of managing organizational diversity and inclusion
Foundational Competency: Developing Others
Teamwork, Develops People, Service Mindset, Leadership, FOSTERING INCLUSION
Discuss the importance of managing organizational diversity and inclusion
Organizational Culture and Climate
· Eradicating stereotypes, "micro-aggressions," and FOSTERING CREATIVITY AND POTENTIAL
Discuss the importance of managing organizational diversity and inclusion
Respect Individuality and Leverage Diversity
· Multitude of motivations, interests, strengths, weaknesses
· Improves TEAM PRODUCTIVITY
Discuss the importance of managing organizational diversity and inclusion
Establish Common Ground
· Vision, goals, rules, regulations, processes for mission accomplishment
What are the four competencies of managing organizational diversity and inclusion
1. Foundation competency: Developing others
2. Organizational Culture and Climate
3. Respect Individuality and Leverage Diversity
4. Establish common ground
Mnemonic: FORE
Summarize the 3-step process for countering bias
a. Acknowledge
· Accept or admit the existence of our own bias(es)
· Understand that our bias(es) are often not reflective of reality
b. Calibrate
· Adjust our perceptions so they can be used more accurately
· Transcend binary thinking, explore with empathy
c. Transform
· Make changes to the character and form of your engagement
· Set the example
Mnemonic: ACT
What is the definition of culture
The creation, maintenance, and transformation across generations of SEMI-SHARED patterns of meaning, sense making, affiliation, action, and organization
What are the 12 cultural domains?
History & Myth (historical markers & myth)
Economics & Resources (goods & thinks that influence the culture)
Language & Communication (transmitting information)
Politics & Social Relations (cold war, space race)
Sex & Gender (biological differences and how they're treated)
Learning & Knowledge
Technology & Material (phones, cars)
Sustenance & Health (how people feed themselves, food production)
Family & Kinship (blood relative, marriage)
Aesthetics & Recreation (beauty, style, activities based on region)
Religion & Spirituality
Time & Space (information influenced by language/communication)
Mnemonic: HELPS LTS FART
Describe the relationship between human security and national security
- Human security is the foundation of national security
- Protecting individuals from violent conflicts is the cornerstone of peace-building
- Security of nation is often measured by: 'Protecting citizens from violence, hunger disease, and natural disasters.'
Describe the importance of applying a gender perspective (4 parts)
a. Examines how the treatment of men, women, and children in a society shapes a person's needs, interests, control of resources, and security
b. How are different individuals treated in different nations
c. Tells us things about tactical, operational, and strategic situation that may be missed if gender lens/perspective is not applied during mission planning and execution
d. Allows mission planners to use knowledge about a culture's gender roles to inform and influence the activities of the mission during mission planning and execution
Recognize the barriers to cultural and gender competence (5)
1. Misrepresentation (just a 'western' or 'far left' push)
2. Faulty assumptions (biases)
3. Defense (viewing culture awareness/gender perspective as a THREAT or ANNOYANCE)
4. Stereotypes (a set idea about what someone or something is like)
5. Ethnocentrism (viewing one's culture as the best and judging other cultures)
Define OPSEC
An information-related capability that preserves friendly essential secrecy by using a process to identify, control, and protect critical information and indicators
Define Adversary
Any entity with goals counter to your own
Define Threats
Adversary with the capability and intent to undertake action detrimental to mission success
Define Vulnerabilties
Exists when the adversary can collect critical information and/or indicators, correctly analyzing them, and acting quickly enough to impact friendly objectives
Define Critical Information
a. Specific facts about friendly activities, intentions, capabilities, or limitations an adversary seeks to gain a military, diplomatic, economic, or technological advantage. Each military unit should have a published "For Official Use Only" critical information list
Define the five-step OPSEC Process
1. Identify critical information
2. Analyze threats
3. Analyze vulnerabilities
4. Assess Risks
5. Apply OPSEC countermeasures
Define the five-step OPSEC Process substep: Critical Information
· Critical information is information the organization has determined is valuable to an adversary.
· This information will vary based on the organization's role.
· It is best identified by the personnel responsible for planning and executing the organization's mission
Define the five-step OPSEC Process substep: Analyze Threats
· Threat information is necessary to develop appropriate countermeasures.
· The threat analysis includes identifying potential adversaries and their associated capabilities and intentions to collect, analyze, and exploit critical information and indicators.
Define the five-step OPSEC Process substep: Analyze Vulnerabilities
· An OPSEC vulnerability exists when the adversary is capable of collecting critical information to exploit our vulnerabilities.
Define the five-step OPSEC Process substep: Assess Risks
· Assessing the adversary's ability to exploit vulnerabilities that would lead to the exposure of critical information and the potential impact it would have on the mission.
Define the five-step OPSEC Process substep: Apply OPSEC countermeasures
· Countermeasures are implemented after a risk assessment is conducted and the amount of risk is deemed unacceptable. These countermeasures should mitigate the risk or reduce the risk to an acceptable level.
· AFI-10-701 defines countermeasures as anything which negates or reduces an adversary's ability to exploit DAF vulnerabilities.
Which branch of government establishes military authority?
The executive branch
What are the provisions embodied in the US Constitution?
1. Federalism: Distributes powers, states are governments, townships & counties are basic units of government
2. Enumerated Powers: The constitution limits federal government powers
3. Separation of Powers/Checks and Balances: 3 equal branches which limits power
What does the FIRST amendment restrict military officers from considering when making decisions?
· Gender
· Religious affiliation
· Race
· Political Associations
What does the 2nd amendment restrict military officers from doing?
From TAKING weapons from the public
What does the 3rd amendment restrict military officers from doing?
Prohibits the military from forcing the public to house them
What does the 4th amendment restrict military officers from doing?
Prohibits the military from searching the public or other military members without a warrant or probable cause. Military Commanders do control military installations and are allowed to search most areas under their control.
What does the 5th amendment restrict military officers from doing?
Protects members against double jeopardy & ensures protections for people accused of crimes
What does the 5th, 6th, and 7th Amendments restrict military officers from doing? What is the EXCEPTION?
Prohibits the military officer from punishing members for crimes without a trial.
a. Article 15s are the exception, but even still, the accused has the right to refuse the Article 15 and demand a Court Martial.
What does the 9th amendment state?
States that just because a right was not mentioned in these Amendments, it doesn't mean that the government can use this as an excuse to deny these other rights.
What does the 10th amendment state?
Was adopted to reassure people that the national government would not swallow up the states. It states:
"The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people."