30 - Sexually Transmitted Diseases (Dr. Griffiths)
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
Historically, how have the rates of STDs changed in the US?
Huge historic increase

Treponema pallidum causes what STD?
syphilis

syphilis is cause by what bacterium?
Treponema pallidum

Highest incidence of syphilis is seen in
20-30 year old, sexually active adults

the contraction of syphilis is also commonly associated with the contraction of _____
HIV
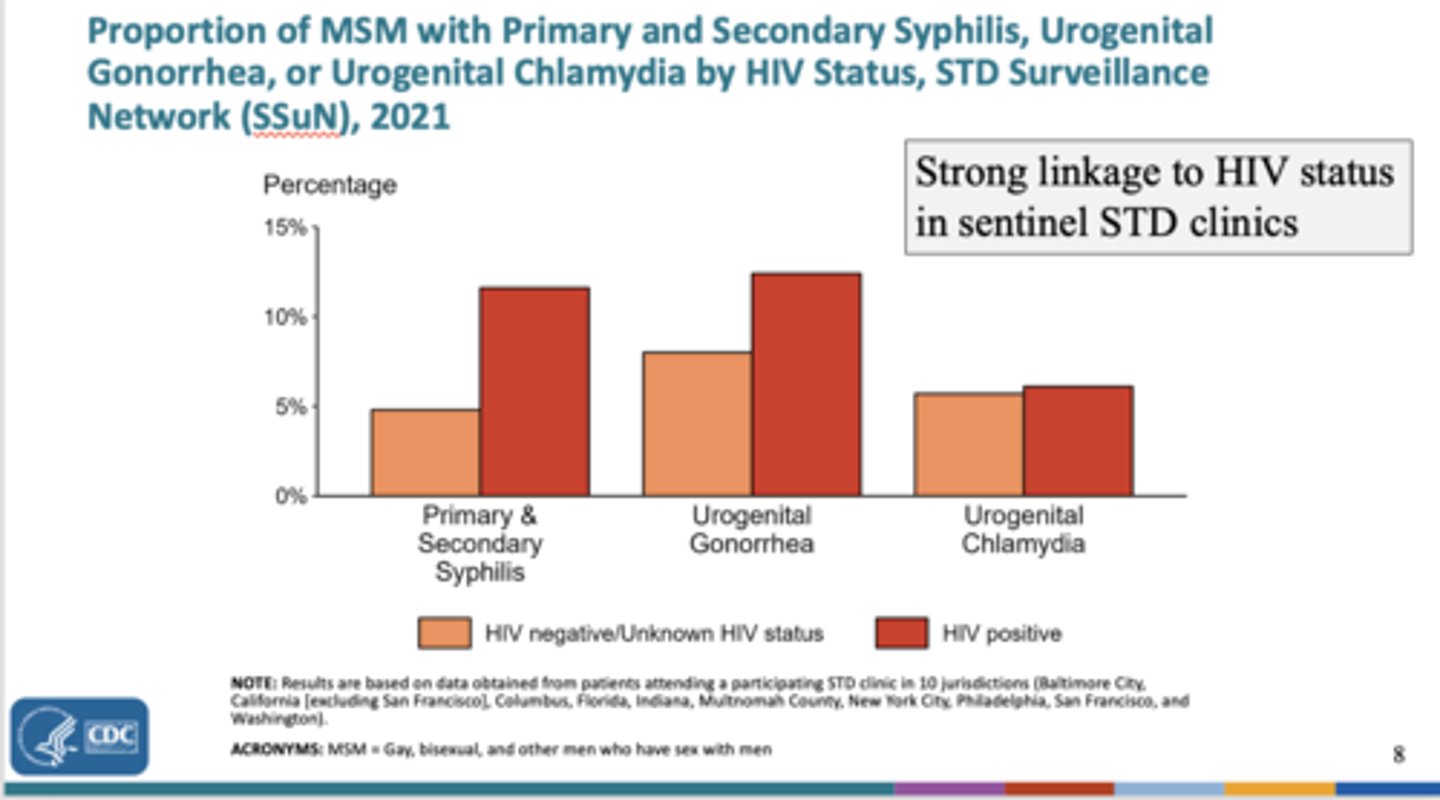
cases of primary and secondary syphilis are higher in what patient population?
men that have sex with men (MSM)
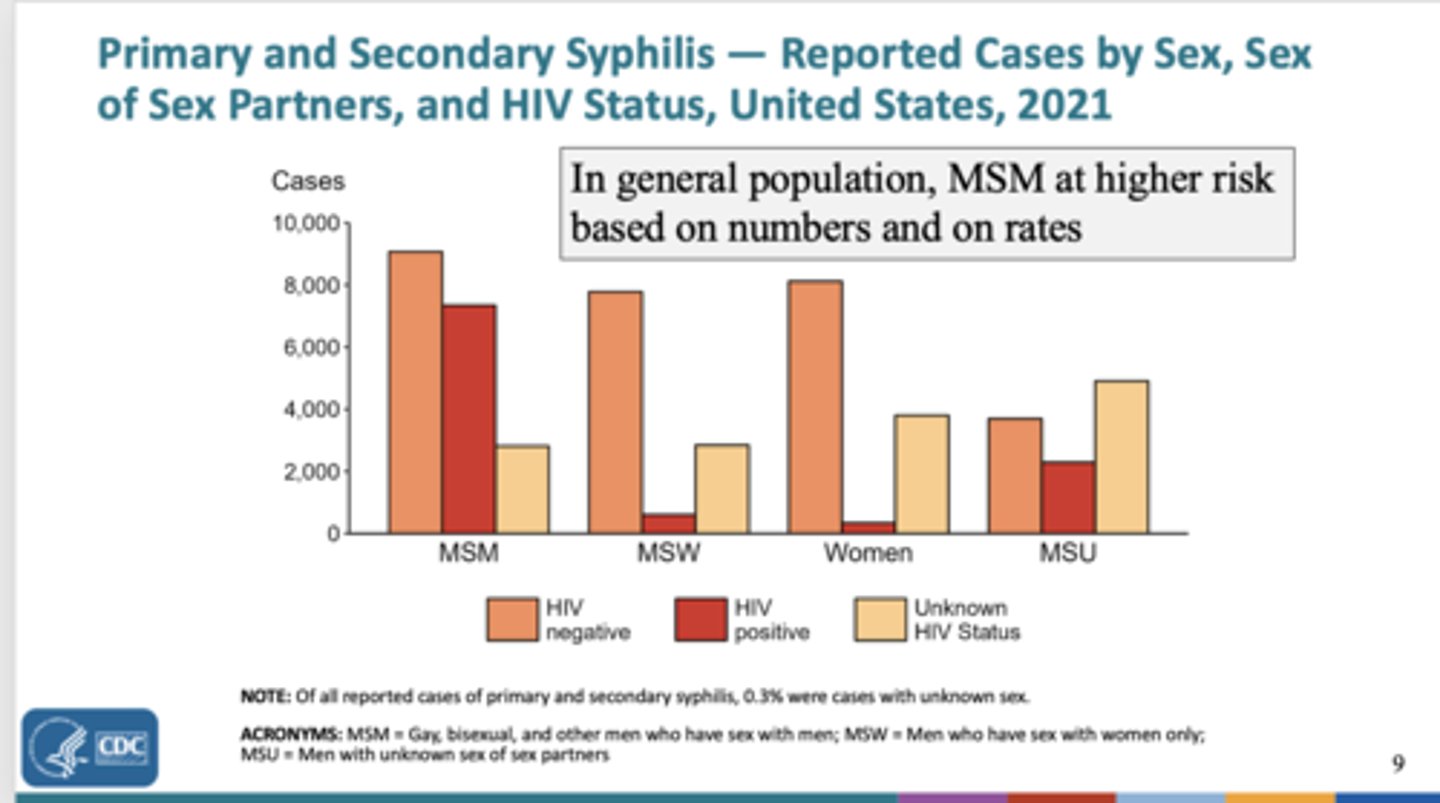
How have the syphilis rates in women changed since 1990?
Increased
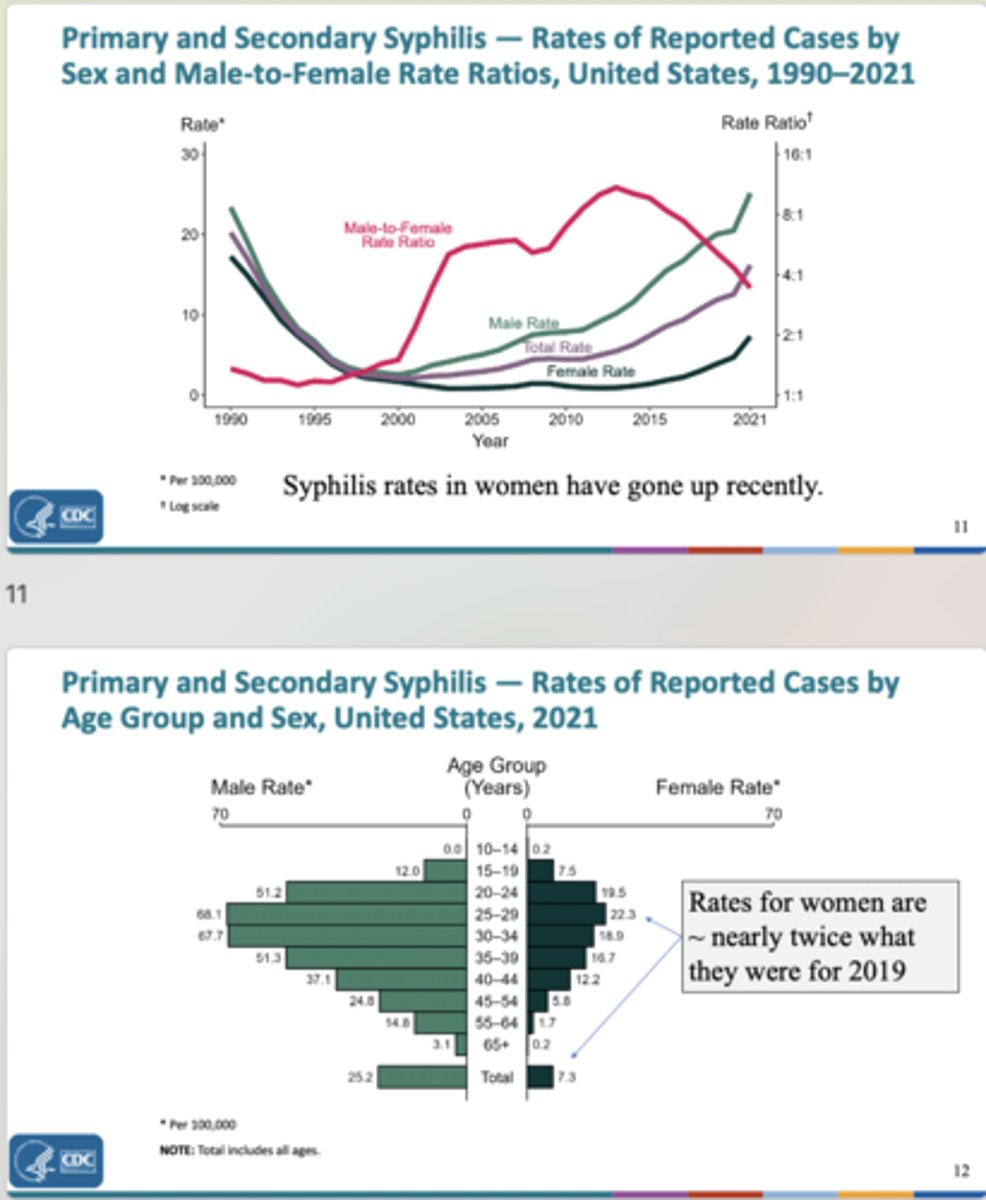
syphilis infection that is localized to an area is most likely what type of syphilis?
primary syphilis

syphilis infection that becomes systemic is most likely what type of syphilis?
secondary syphilis

syphilis infection that causes long term inflammation of the CNS is most likely what type of syphilis?
tertiary syphilis

syphilis infection that causes systemic and chronic inflammation is most likely what type of syphilis?
Congenital syphilis

how is syphilis contracted?
direct contact with infected human

patient presents with a large chancre ulcer on the glans penis. Patient denies pain. Patient has regional adenopathy in the groin. Patient's serological test comes back negative for syphilis. What is the diagnosis?
primary syphilis
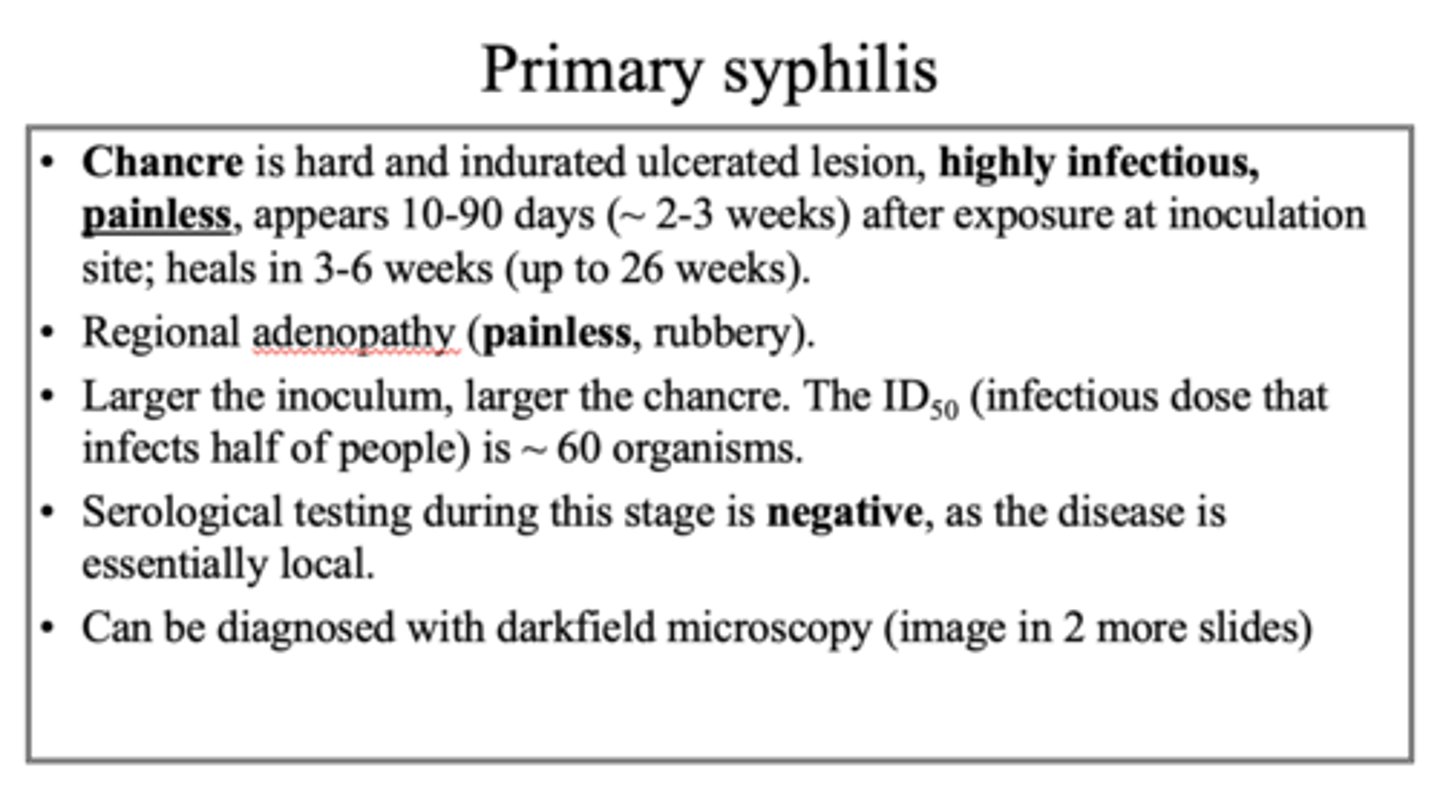
hard and indurated ulcerated lesion
chancre (appears anywhere with contact)
what diagnostic method can you use to diagnose a suspected syphilis ulceration?
darkfield microscopy

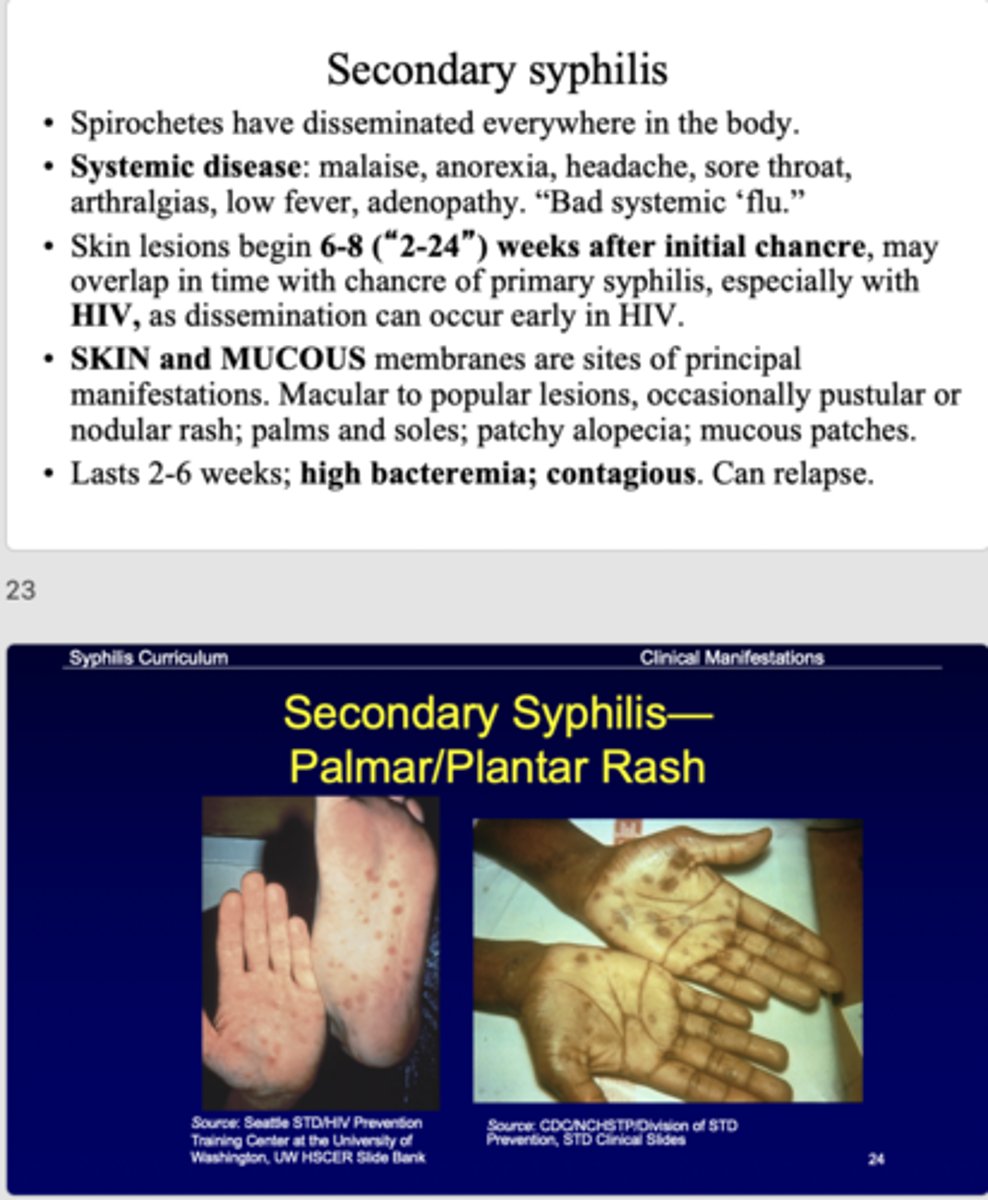
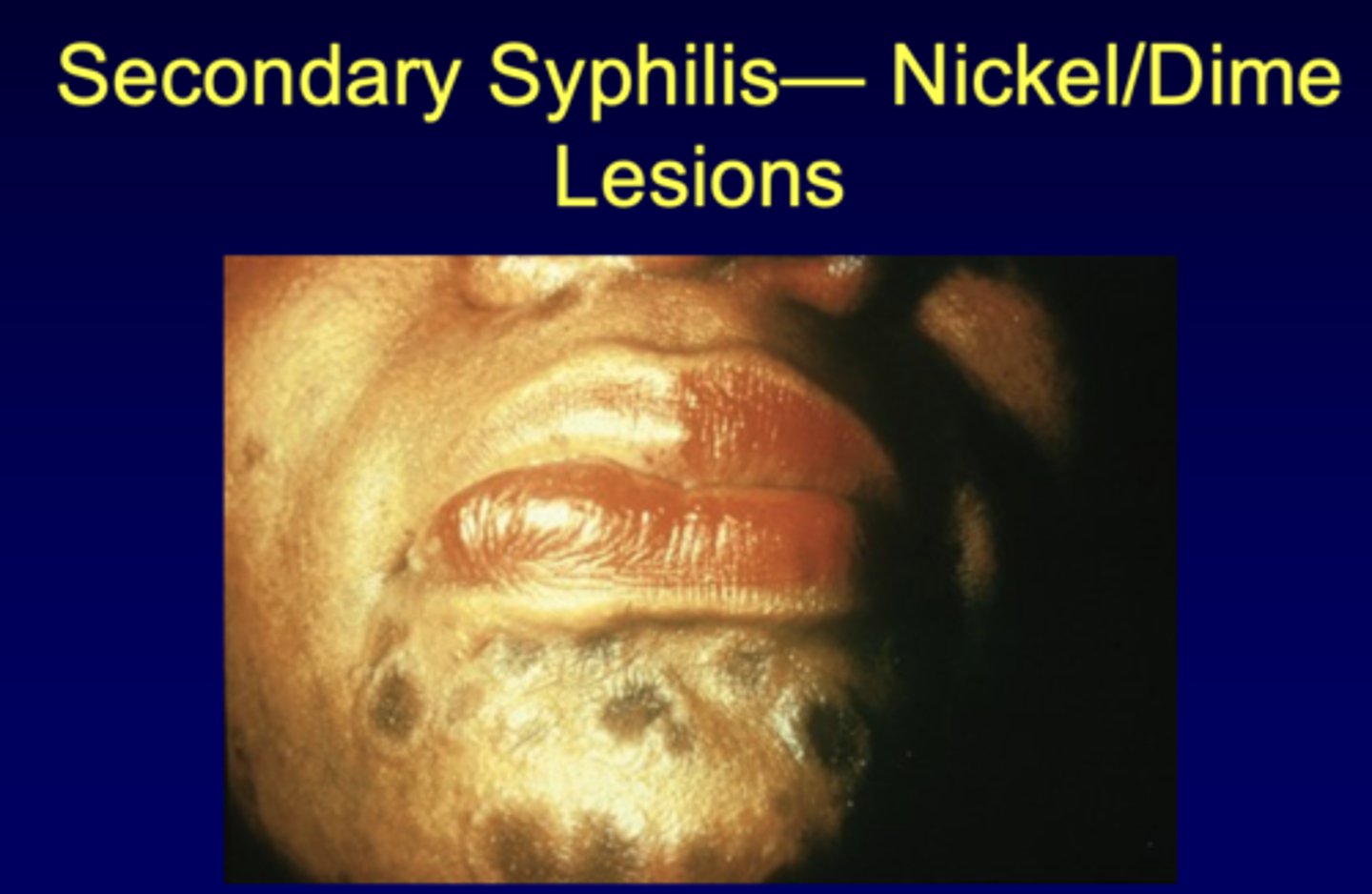
patient presents to your office complaining of flu-like symptoms. Patient exhibits malaise, headache, sore throat, arthralgias, low fever, and adenopathy. Patient exhibits nickle/dime lesions on the chin and one on the buccal mucosa. Patient also exhibits palmar and plantar rashes. Serological test comes back positive, high bacteremia for syphilis. What is the diagnosis?
secondary syphilis
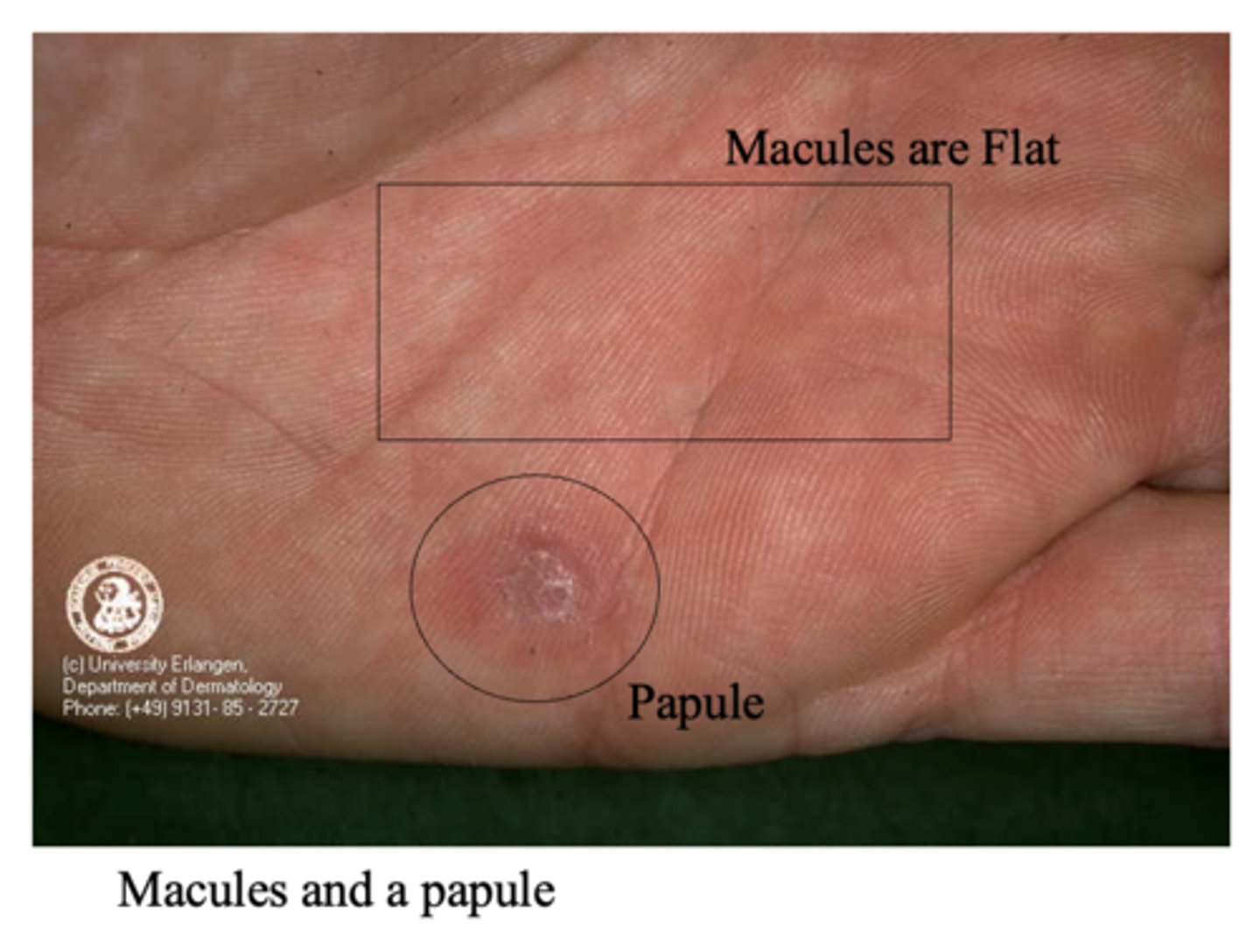
What is the difference between macules and papules in secondary syphilis?
Macules are flat
Papules are elevated
What are the lesions like of secondary syphilis?
Nickel/dime lesions
latent syphilis occurs between what stages?
secondary and tertiary syphilis
a patient that has a history of secondary syphilis presents asymptomatic, absent of any clinical disease or symptoms, however the serological test comes back positive for syphilis. What is the diagnosis?
latent syphilis
What is the hallmark of latent syphilis?
positive serological test in absence of any clinical disease/symptoms
patients with primary syphilis are _____ contagious
highly
patients with secondary syphilis are _____ contagious
highly
patients with tertiary syphilis are _____ contagious
not

What are the nodular granulomatous lesions in any organ in tertiary syphilis?
Gummas
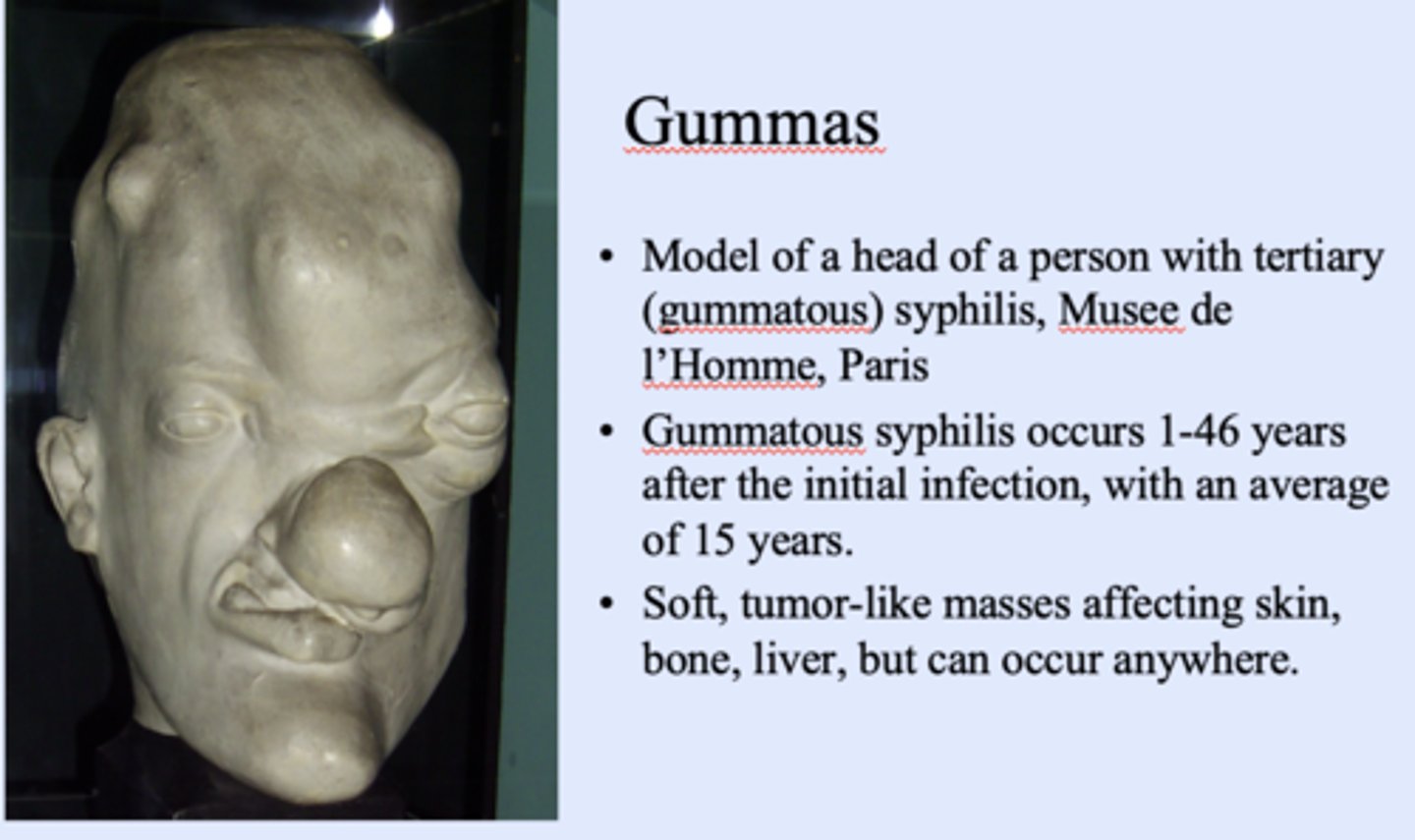
what two conditions are associated with tertiary syphilis?
cardiovascular disease
neurosyphilis

patient presents to your office complaining of symptoms consistent with arteritis/vasculitis. Patient has a long history of syphilis. Patient has gummas on multiple surfaces of skin and MRI scan had detected presence of gummas in the brain. What is the diagnosis?
tertiary syphilis

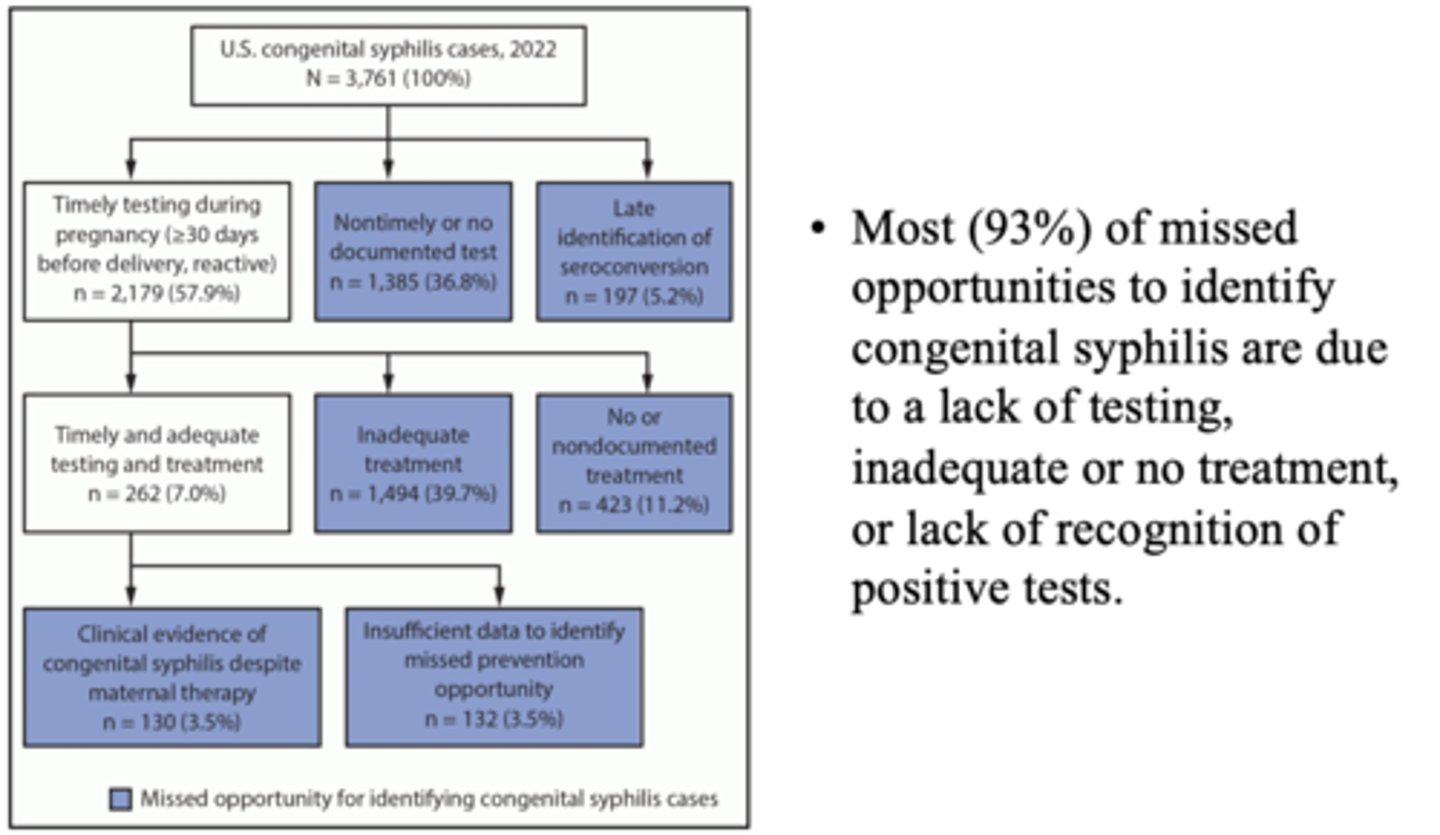
Most (93%) of missed opportunities to identify congenital syphilis are due to...
A lack of testing, inadequate or no treatment, or lack of recognition of positive tests
mother gives birth to infant that is suffering from rhinitis and has cutaneous rashes. The infant has developed osteochondritis, hepatosplenomegaly and adenopathy. The mother explained that she was initially carrying twins but the second infant was stillborn. What is the diagnosis for the child?
congenital syphilis

Which of the following will be present in a child with congenital syphilis?
a. rhinitis, snuffles followed by skin lesions
b. osteochondritis
c. hepatosplenomegaly/adenopathy
d. immune complex glomerulonephritis
e. all of the above
e. all of the above

12 year old patient presents to dental office. Patient is deaf and has been diagnosed with symmetric hydrarthorisis. Patient presents with saddle noses, saber shins and rhagades. Upon oral examination you notice the anterior teeth have a screwdriver shaped appearance "hutchinson's teeth" and the 12 year molars take on a mulberry appearance. What is the diagnosis?
congenital syphilis

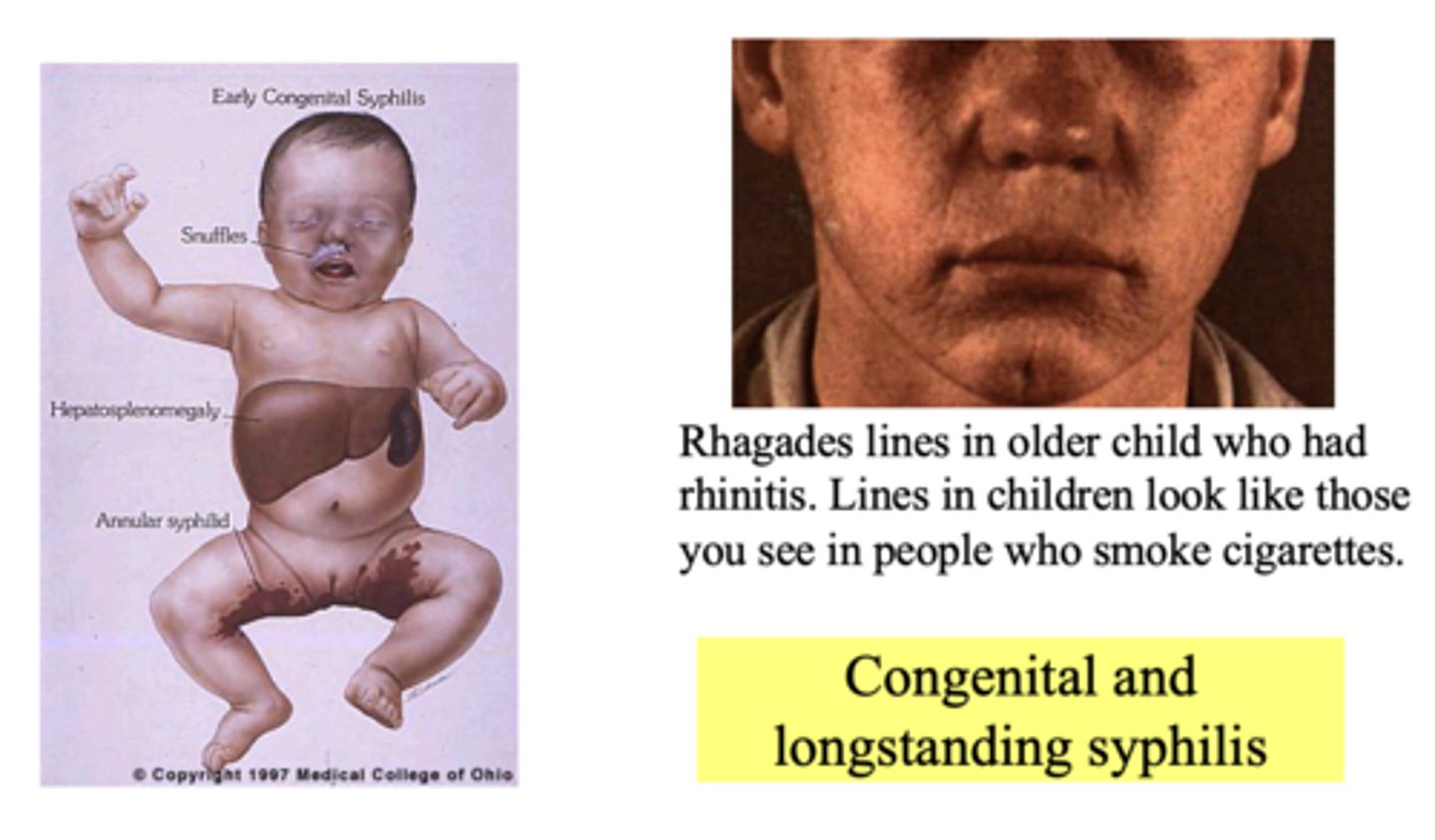
Rhagades lines in older child who had rhinitis. Lines in children look like those you see in people who smoke cigarettes. What is the diagnosis?
Congenital and longstanding syphilis
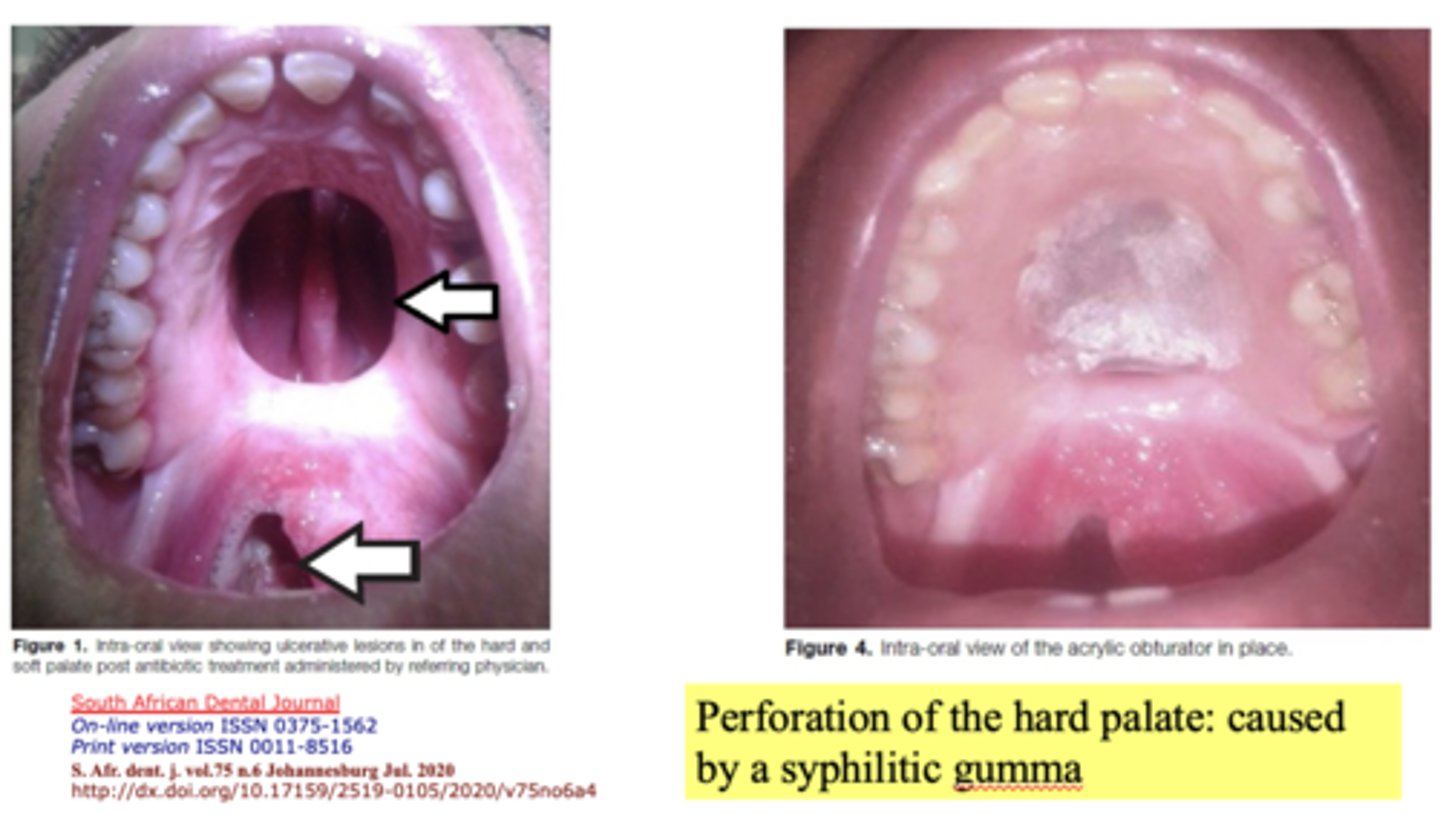
What can a perforation of the hard palate be caused by?
Syphilitic gumma
t/f: Congenital Syphilis causes death in first 2 years with pulmonary hemorrhages, bacterial infections, hepatitis.
true
t/f: 60% of 2-year survivors of congenital syphilis suffer from subclinical infection. Remainder develop lesions similar to secondary syphilis
false, develop symptoms similar to tertiary syphilis

Hutchinson teeth are considered to be pathognomonic of:
congenital syphilis
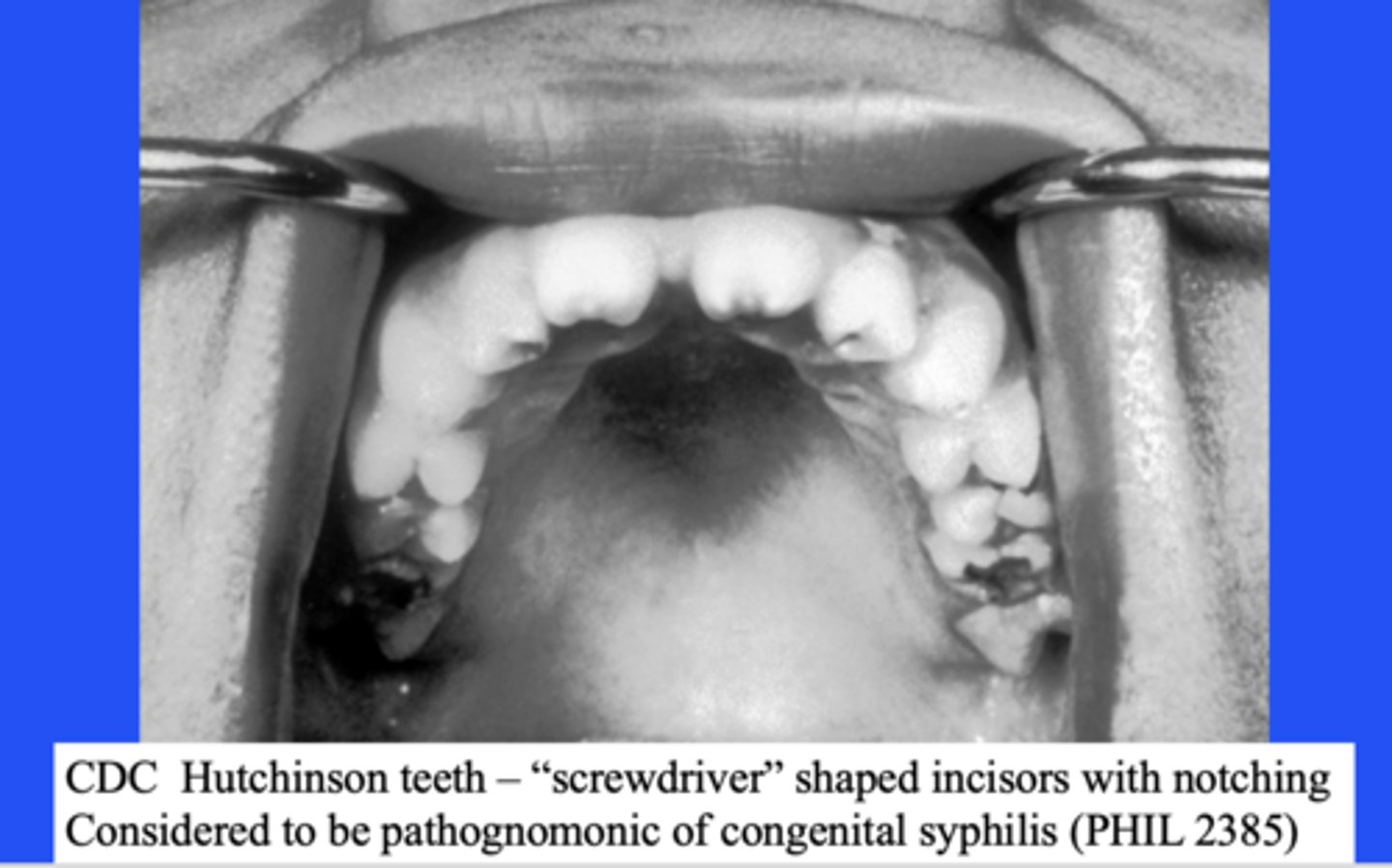
Define the following:
Notched, narrow edged permanent incisors
Hutchinson's teeth (screwdriver shaped incisors)
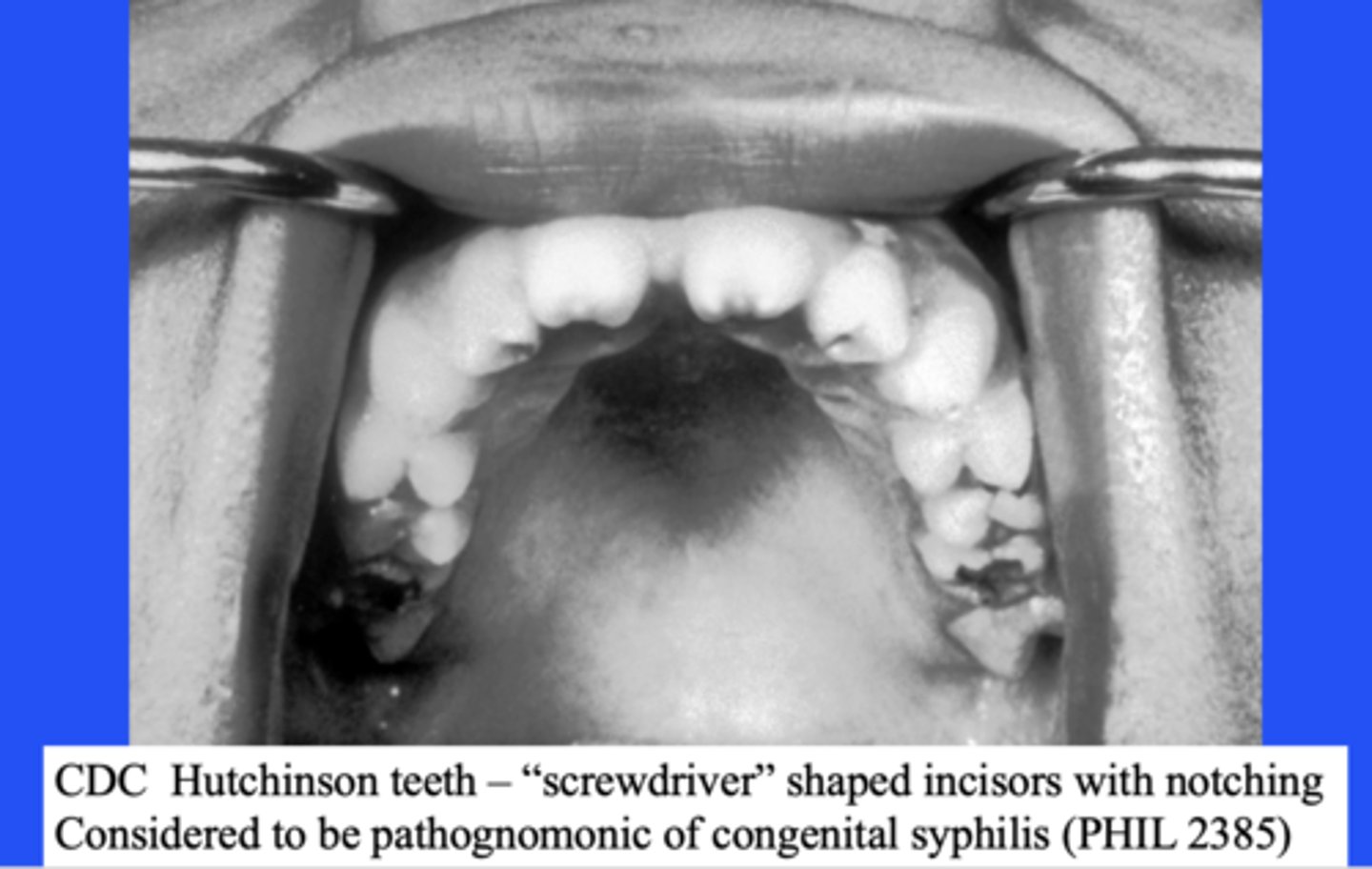
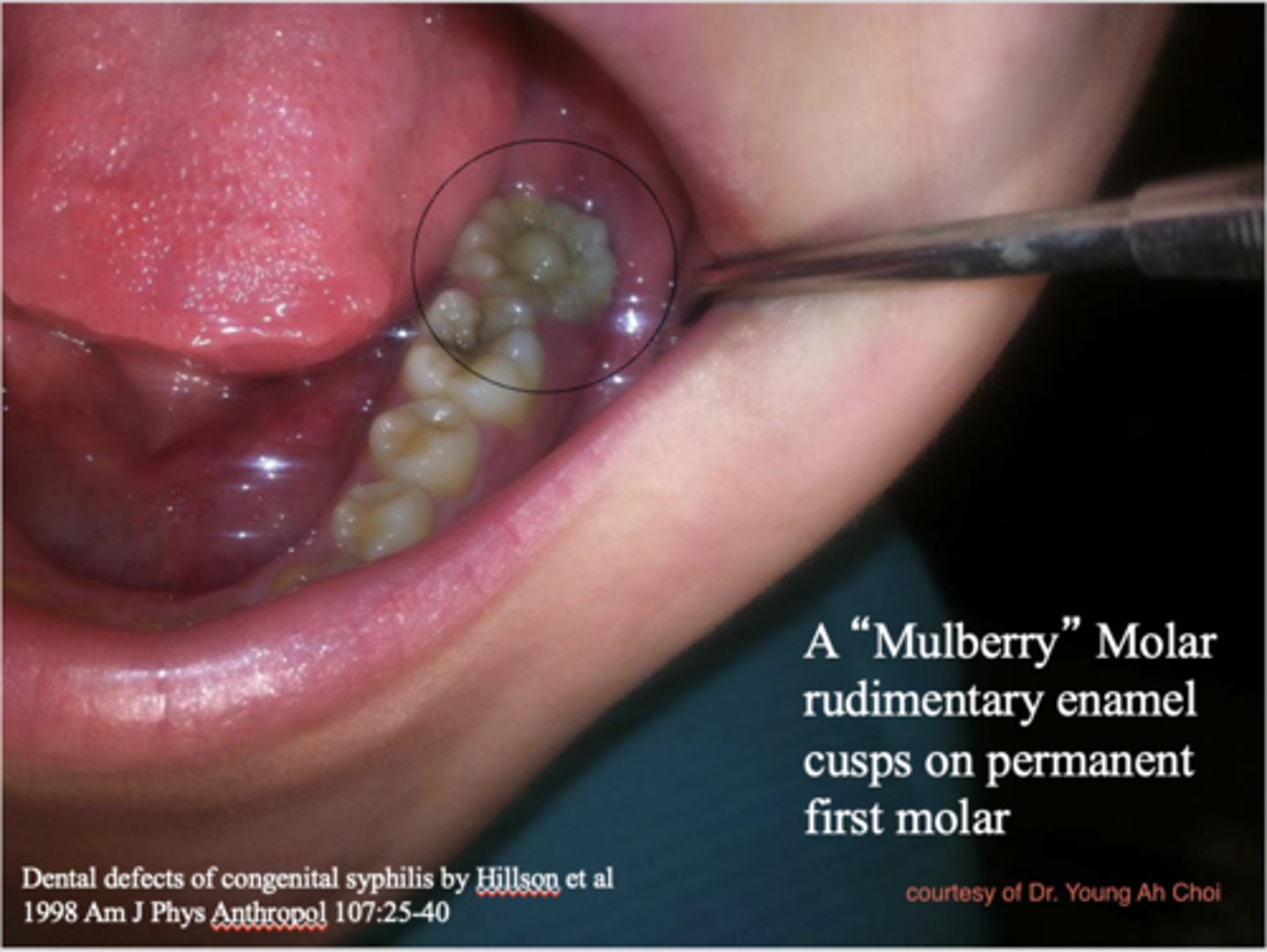
Mulberry molars are considered to be pathognomonic of:
congenital syphilis
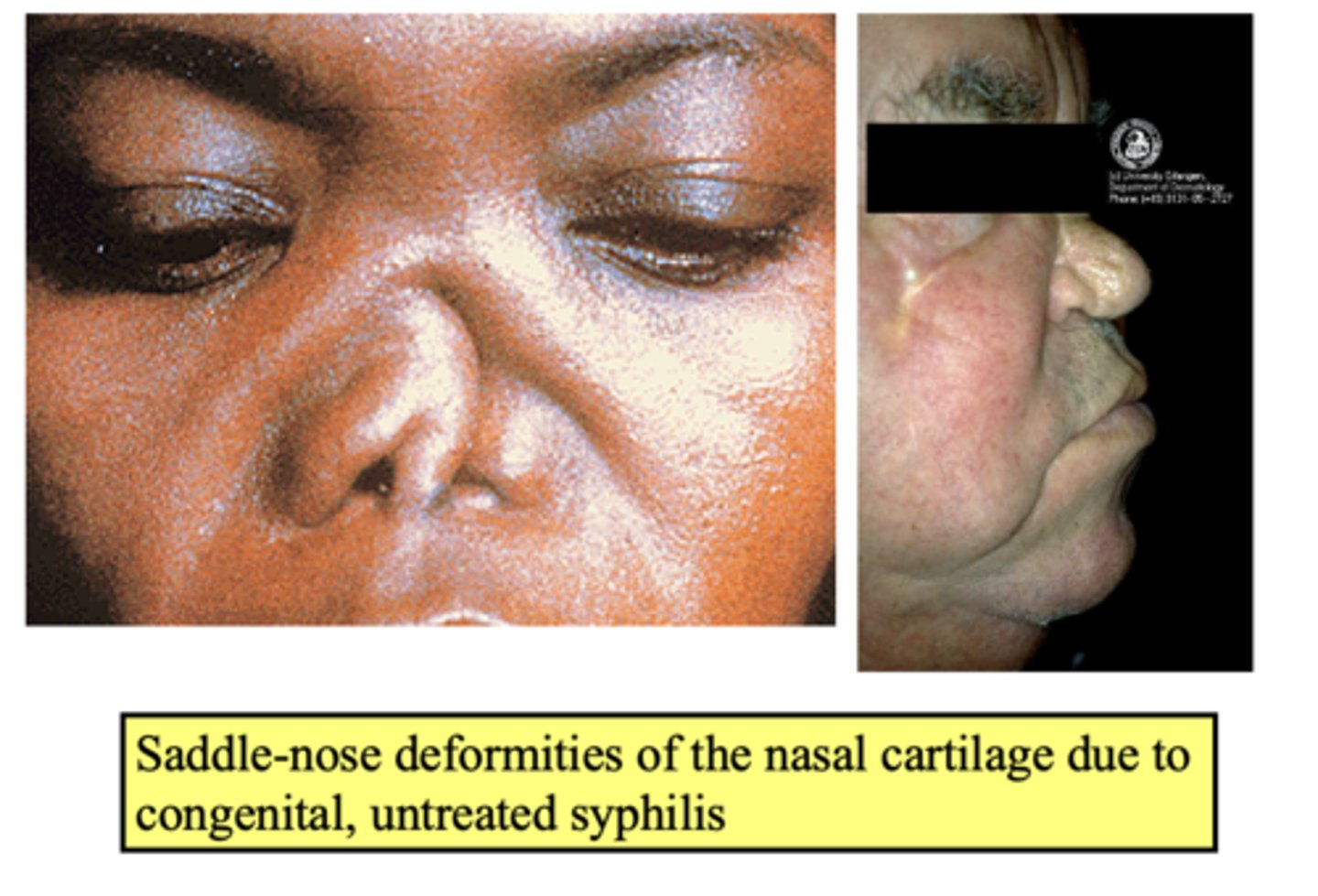
Saddle-nose deformities of the nasal cartilage are due to untreated:
congenital syphilis
How can you diagnose primary syphilis?
Presenting signs and symptoms

How can you diagnose secondary syphilis?
1. Send T pallidum specific test
2. If positive – get antibody titre test

if you treat primary syphilis with penicillin, what is the prognosis?
cured (1 dose)
if you treat secondary syphilis with penicillin, what is the prognosis?
cured (1 dose usually)

if you treat tertiary syphilis with penicillin, what is the prognosis?
gummas resolved, other damage remains

How many doses are Late latent, tertiary, or neurosyphilis treated with?
3

for women that are pregnant and contract syphilis, before what week should they get treatment in order to prevent lesions of congenital syphilis?
16

what is the treatment for syphilis?
benzathine penicillin (or Ceftriaxone)

What % of persons with secondary syphilis have relapses?
25%
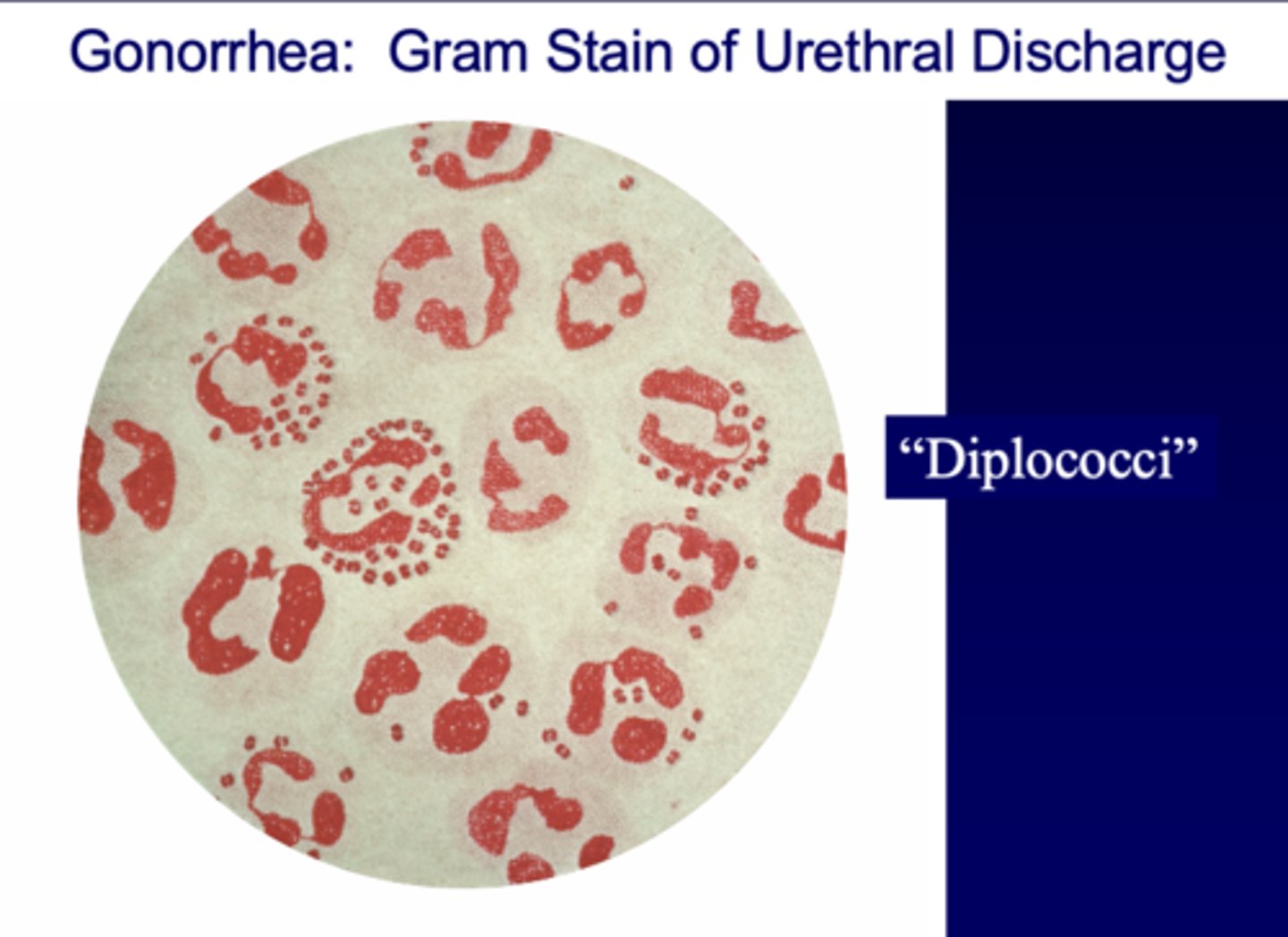
Neisseria gonorrhoeae causes what STD?
gonorrhea

gonorrhea is caused by what bacterium?
Neisseria gonorrhoeae

Gram-negative diplococcus on Gram stain which infects mucus-secreting epithelial cells:
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Neisseria gonorrhoeae evades host immune system through alteration of:
cell surface and pili

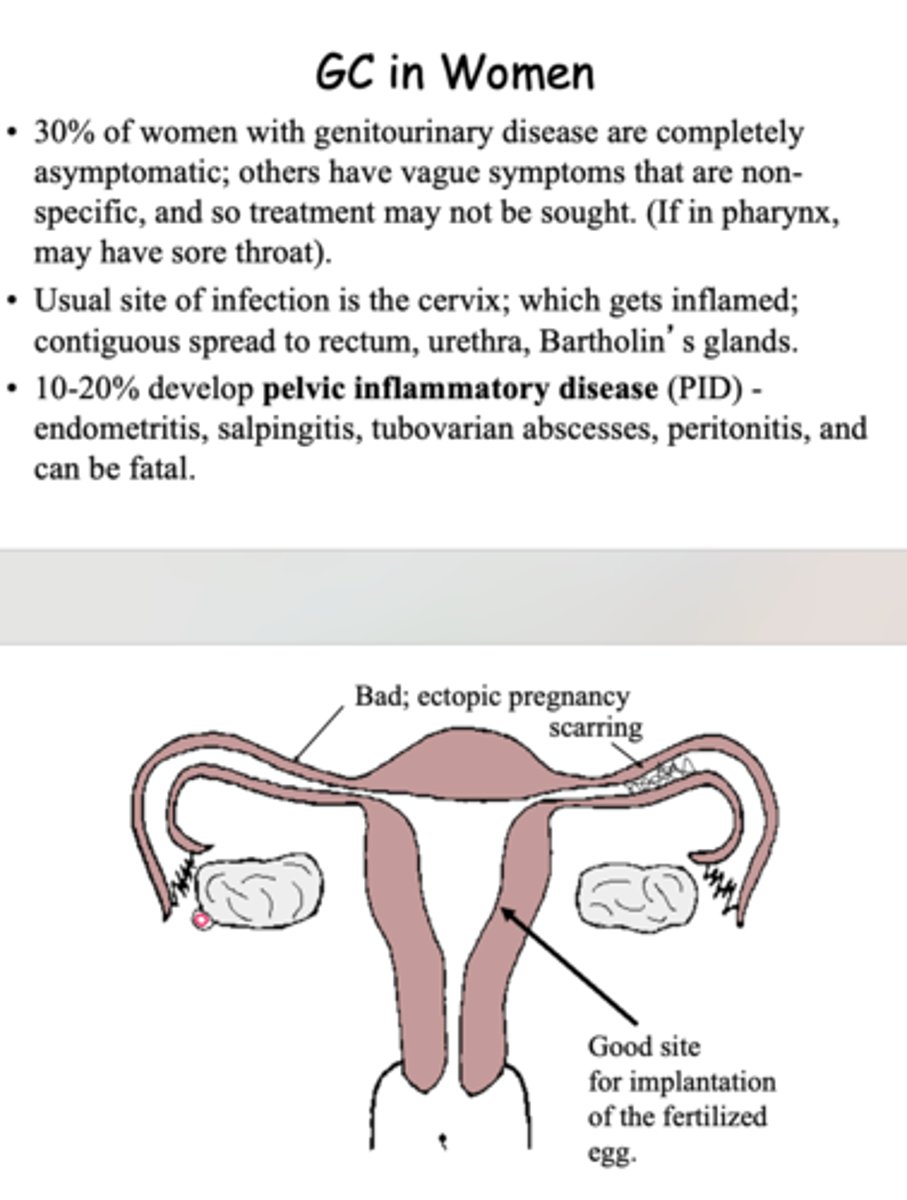
cause of pelvic inflammatory disease in women?
gonorrhea

complications of gonorrhea for women (3)
pelvic inflammatory disease
ectopic pregnancy
sterility

How does gonorrhea present in men?
Urethral scaring

gonorrhea is normally _______ in women
asymptomatic

gonorrhea is normally _______ in men
symptomatic

Neisseria gonorrhoeae infect what type of cells?
mucus-secreting epithelial cells

in Neisseria gonorrhoeae, these proteins bind receptors on immune cells and prevent the generation of an immune response
Opa protein

t/f: it is not possible to get a repeated gonorrhea infection
false, re-infection prossible

N gonorrhoeae can grow inside _____________
Phagocytes
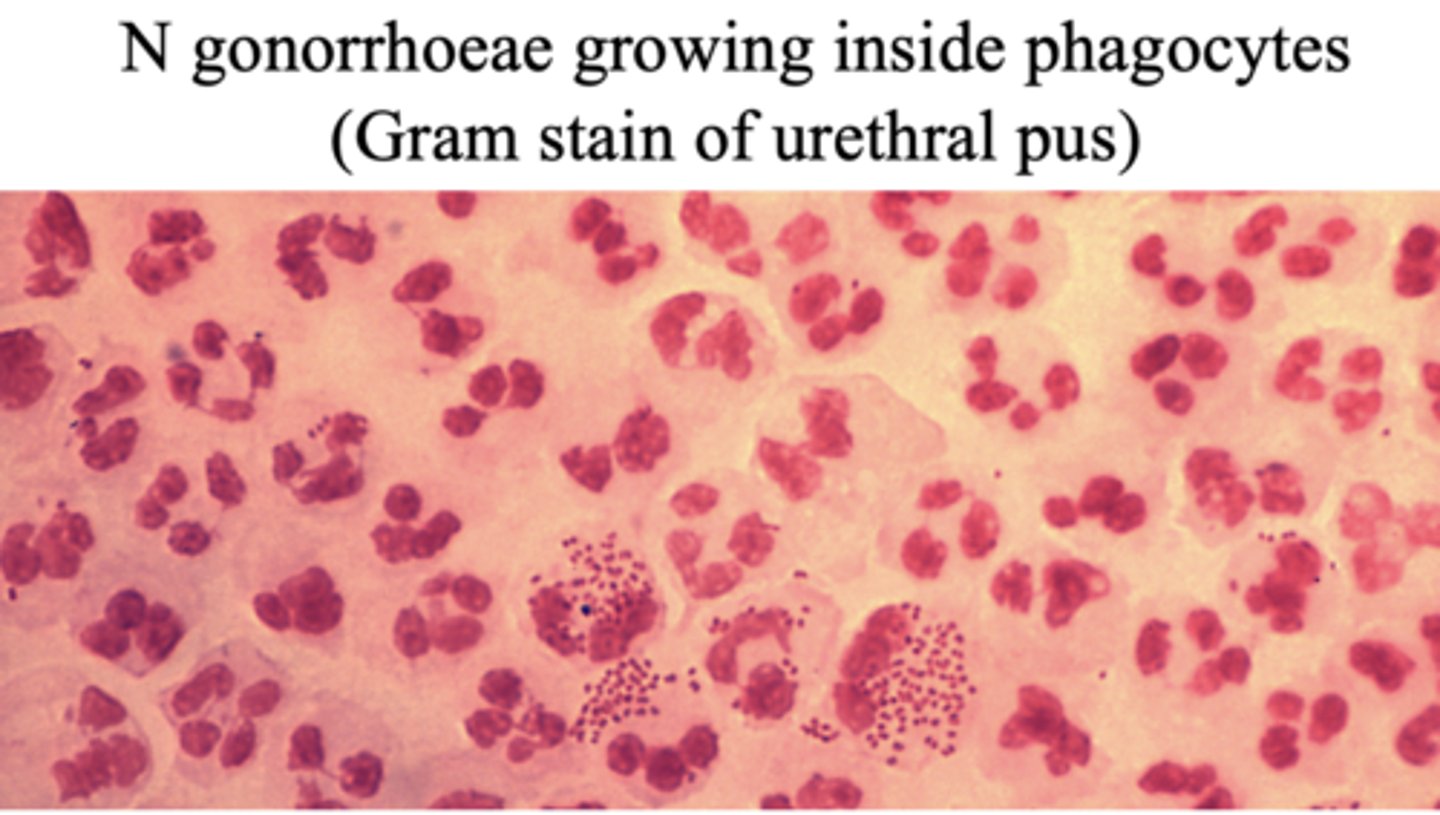
Neisseria gonorrhoeae need what nutrient to survive?
CO2

t/f: protease cleaves IgA1 and IgA2
false, IgA1 only

what STD can cause Epididymitis?
gonorrhea
t/f: regarding N gonorrhoeae, MSM incidence rate is x42 that of MSW in US
true

_______________ infection with GC (N. gonorrhoeae) common cause of sore throat - pharyngitis, tonsillitis, gingivitis - in MSM and is principal origin of gonococcemia.
Pharyngeal

Gonococcal Ophthalmia Neonatorum is acquired in infants born while their mother has what STD?
gonorrhea
what is the 2nd most common cause of sore throat?
gonorrhea

How is gonorrhea diagnosed in men vs women?
Men: Symptoms
Women: Screening
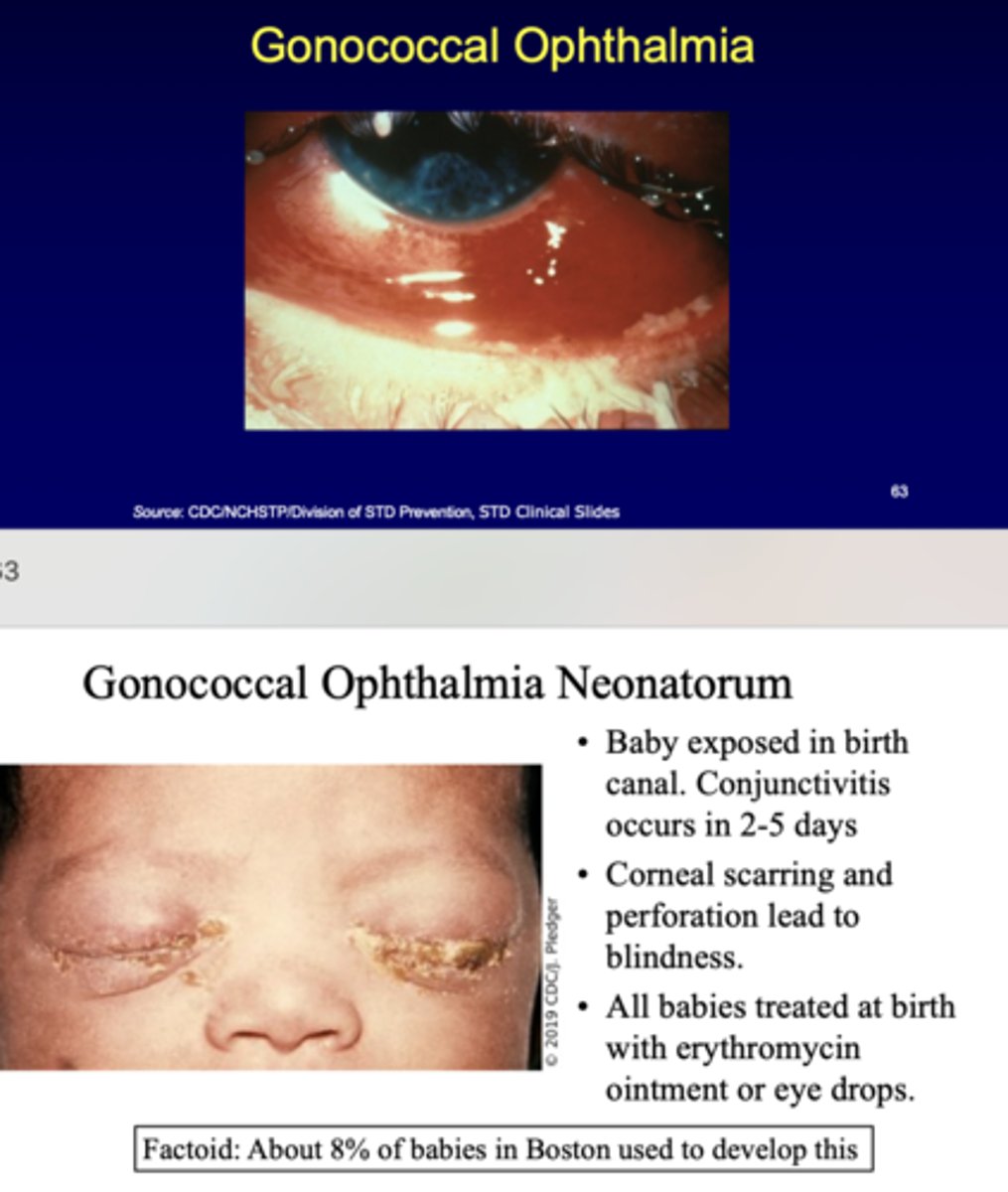
-baby exposed in birth canal. conjuctivitis occurs in 2-5 days
-corneal scarring/perforation lead to blindness
-all babies treated at birth with erythromycin or eye drops
gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum
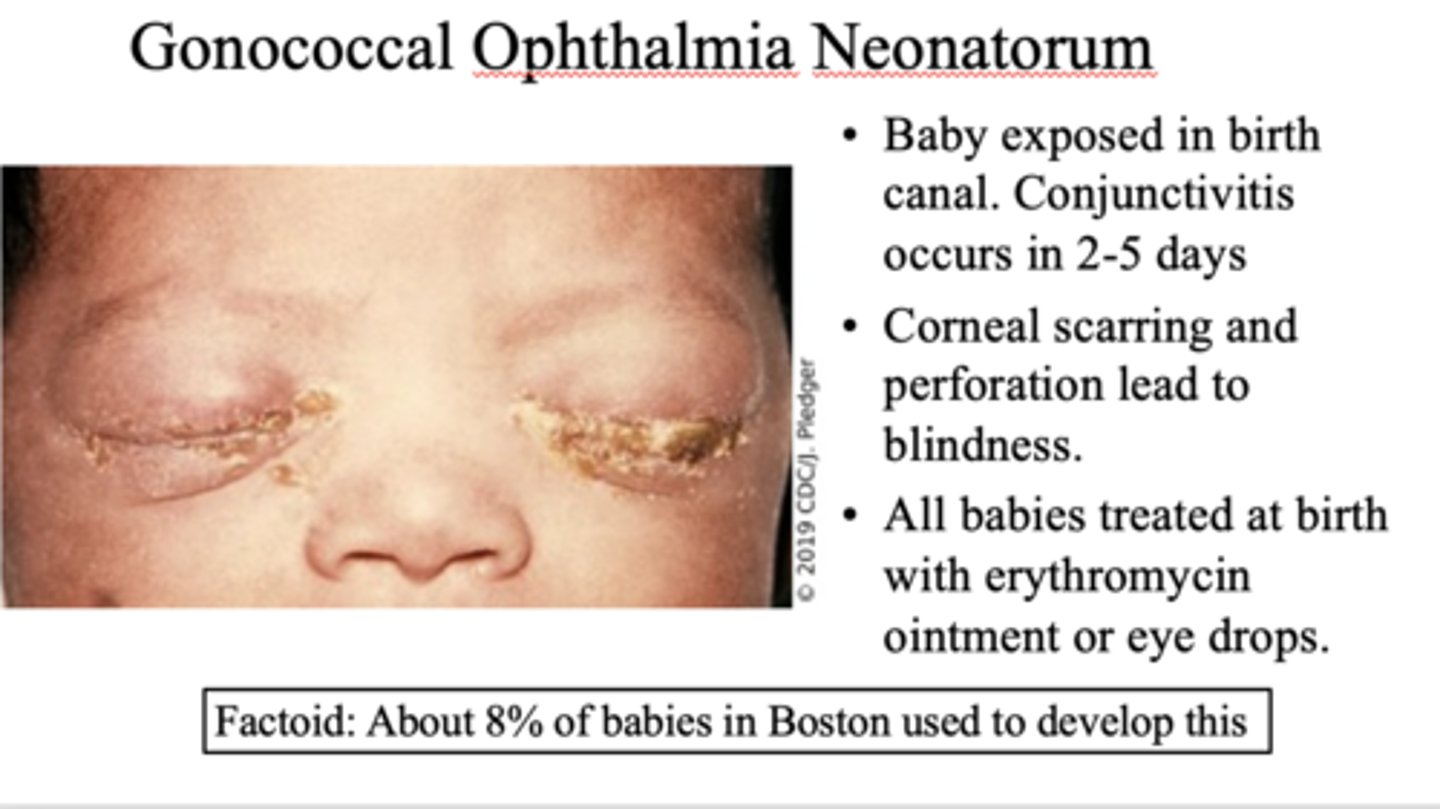
What percent of babies in Boston used to develop gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum?
8%
What percent of gonorrhea in women develop pelvic inflammatory disease?
10-20%
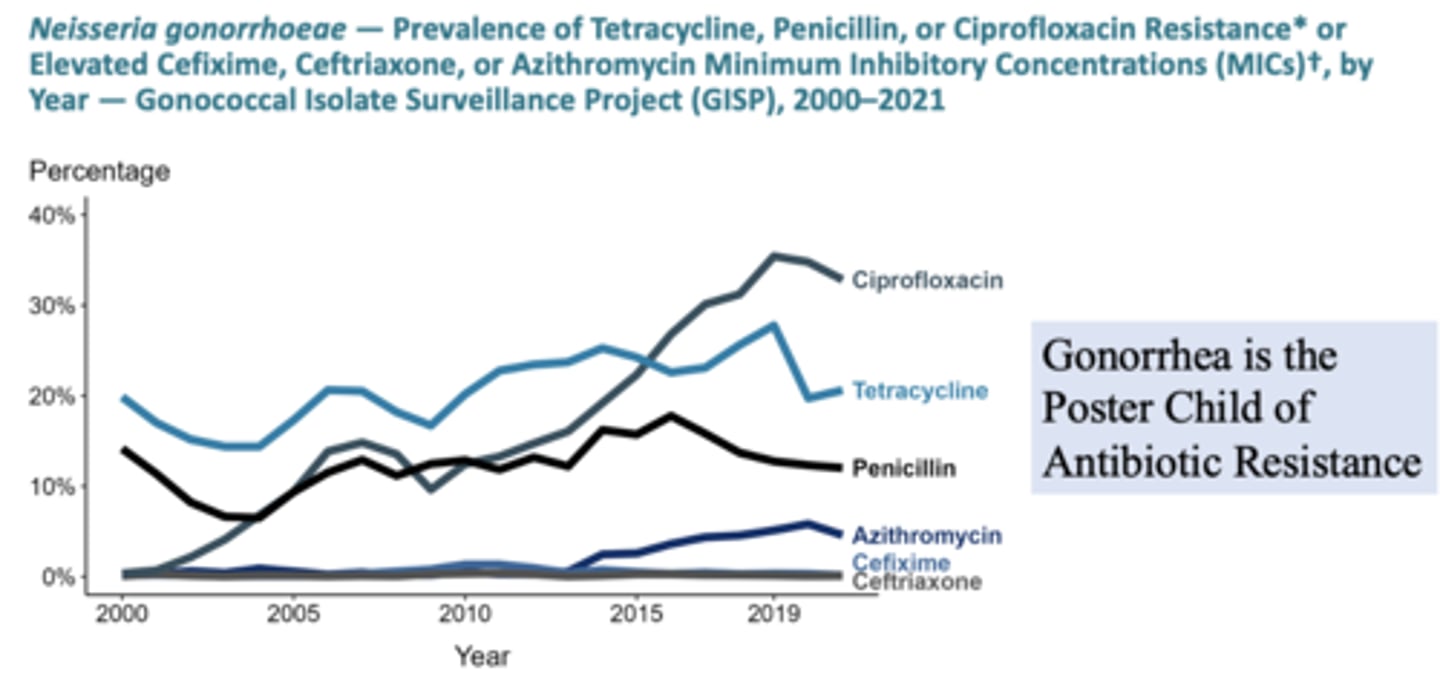
Gonorrhea is the Poster Child of _____________ Resistance
Antibiotic
what is the treatment for gonorrhea?
Ceftriaxone 500mg

C. trachomatis causes what STD?
chlamydiae

Chlamydiae is caused by what bacteria, known as one of the major human pathogens?
C. trachomatis

What are the two unique stages of chlamydiae?
Reticulate body
Elementary body

chlamydiae can cause what three diseases?
cervicitis
urethritis
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)

What disease can only replicate as a parasite within an host cell?
Chlamydia

C. trachomatis has two major STD syndromes. What are they?
Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV)
urethritis (more common - looks similar to GC)

Define the following:
Abscesses of the inguinal lymph nodes and painful genital lesions
Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV)

what STD is the cause of 1/3rd all urethritis?
gonorrhea

Strict intracellular bacteria (no media), genome small; cannot generate ATP; has no oxidative enzymes, flavoproteins or cytochromes; can make own proteins:
C. trachomatis

the reticulate body stage of chlamydiae does what?
active metabolism

antibiotics against chlamydiae are only affective against what stage?
reticular body stage

the elementary body stage of chlamydiae does what?
transit form that goes from one cell to another

what STD is the most common cause of urethritis in men?
chlamydiae

what STD is the most common cause of cervicitis in women?
chlamydiae

C. psittaci causes pneumonia in..
human and birds
This bacteria commonly causes upper and lower respiratory tract infections in humans
C. pneumoniae

what STD increases the risk of HIV acquisition x5?
chlamydiae

what is the most common STD in the US and UK?
chlamydiae

t/f: about 50% of women with undiagnosed chlymadiae will develop PID
true

Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV) are associated with what STD?
chlamydiae

-primary sore small, painless
-swelling of groin 1-4 weeks later
-lymph nodes may ulcerate
-scarring in rectum, abscesses in perineum
Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV)

how is chlamydiae diagnosed?
nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT)

what is the treatment for chlamydiae?
Doxycycline or azithromycin
Erythromycin for pregnant women/children
(Chlamydia urethritis/cervicitis - twice-daily doxycycline 100 mg for a week)

T/F: You should treat chlamydia pregnant patients with amoxicillin
No don't do it (Dr. Griffiths does not know why it is an alternative option)

which HVP strains causes cancer?
HPV 16 and 18

which HVP causes genital warts & respiratory papillomatosis?
HPV 6 and 11
