Chapter 14 SG
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
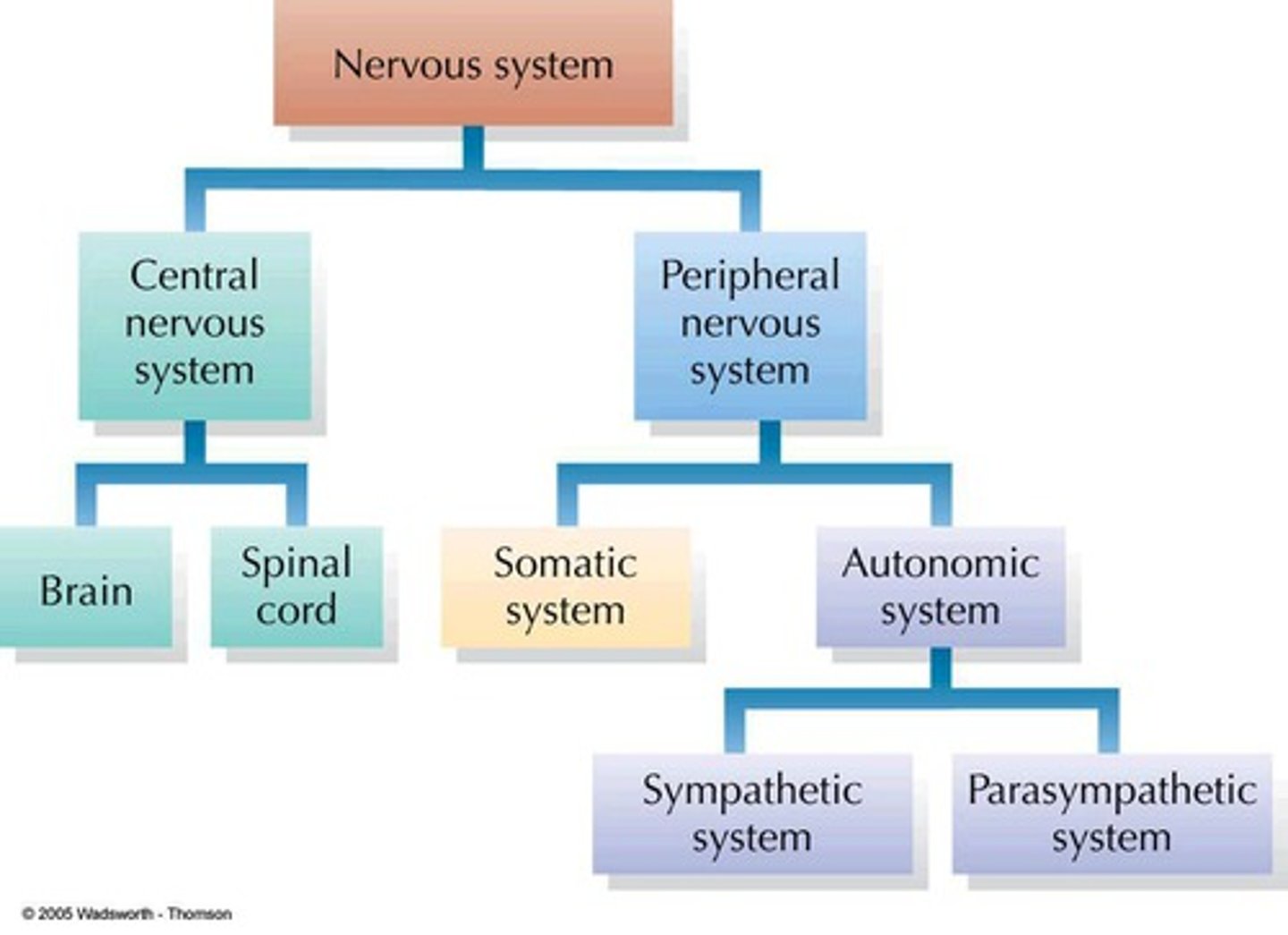
Central nervous system (CNS)
includes brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
includes central nerves, spinal nerves, ganglia
Three functions of Nervous system
1. Collect information
2. Process and evaluate information
3. Initiate response
Organization of nervous system (CNS) & (PNS)
Two organizations of PNS:
1. Sensory (afferent) neurons: receives info then sends to CNS
2. Motor (efferent) neurons: Sends impulses from CNS to muscles and glands
** Both have parts in somatic and autonomic systems
Sensory (afferent) neurons subdivided in two:
1. Somatic sensory: conscious (general senses)- Somatic
2. Visceral sensory: not conscious (impulse of blood and viscera)- autonomic
Motor (efferent) neurons subdivided in two:
1. Somatic motor (SNS): voluntary (contraction of skeletal muscles) - somatic
2. Autonomic motor (ANS): involuntary (regulates smooth M, cardiac M, glands) - autonomic
Classifications of Neurons
-Excitable
-Conductive
-Secretory
-Long-Lived
-Amitotic
-Highly Metabolic
Structure of Neurons
-Cell body
-Dendrites
-Axon- axon hillock, synaptic knob
Three functional classes of neurons:
1. Sensory (afferent) neurons
2. Interneurons (in between communication)
3. Motor (efferent) neurons
Four types of Glial cells in (CNS):
1. Astrocytes
2. Obligodendrocytes
3. Microglial
4. Ependymal
Astrocytes characteristics
-Most abundant in CNS
-Helps form BBB-perivascular feet
Ependymal characteristics
-Ciliated cuboidal epi. cells that line ventricles of brain, central central canal of spinal cord
-Helps produce CFS (CNS)
Microglial characteristics
- Removes debris and dead or damage tissue (CNS)
Oligodendrocytes characteristics
-ONLY in CNS
-Is myelin sheets around axons (short portions)
Two type of glial cells in (PNS):
-Satellite
- Neurolemmocytes (Schwann cells)
Satellite characteristics
-Regulate fluid around neuron cell body in (PNS)
Neurolemmocytes (schwann) characteristics
-Helps with axon regeneration
-Is myelin sheets around axon in (PNS) (outside layer-Neurilemma)
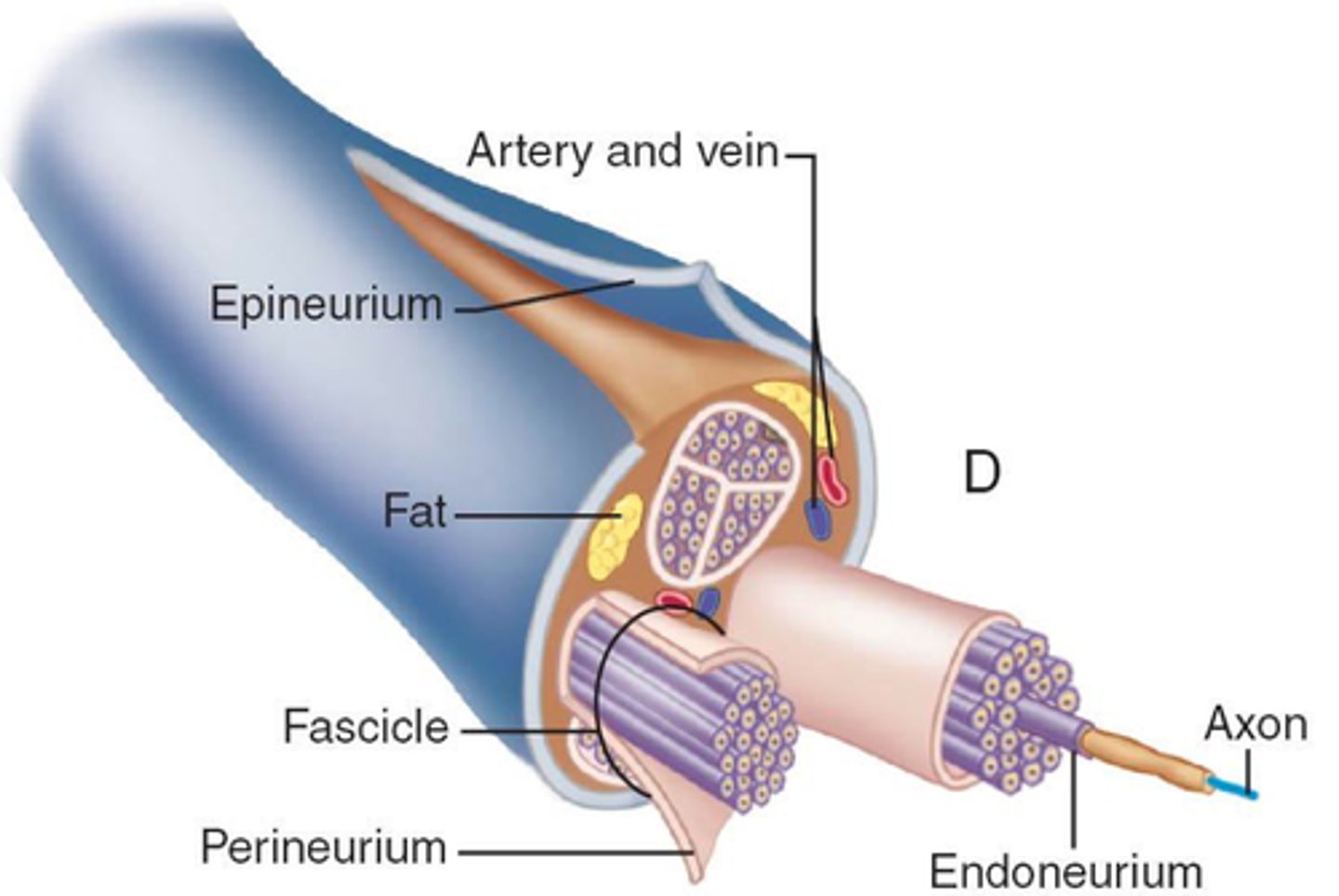
Nerves connective tissue wrapping (three types)
1. Endoneurium- areolar around each axon
2. Perineurium- dense irregular around each fascicle
3. Epineurium- dense irregular around entire nerve
What is a Synapses?
Is a junction between two neurons, between a neuron and muscle or gland
Characteristic of a synaptic between two neurons
-Presynaptic neuron: has synaptic knobs
-Synaptic cleft: that narrow space
-Postsynaptic neuron: receives signals
Synpatic Communication (two)
1. Electrical Synapses: involves gap junctions, rapid ion flow, rare in nervous system
2. Chemical synapses: involves release of neurotransmitter like (Acetylcholine), (review system w/ synaptic knob)
Neural Circuites (grouped neurons)
-Converging
-Diverging
-Reverberating
-Parallel after discharge
Converging (Grouped neurons)
Impulses come together to a single postsynaptic neuron
Diverging (Grouped neurons)
Impulses spread from one presynaptic neuron to many postsynaptic neurons
Reverberating (Grouped neurons)
Cyclical stimulation of the circuit
Parallel after discharge (Grouped neurons)
Several neurons process the information simultaneously (in parallel)