1.1 vocab: structure of water and hydrogen bonding
1/20
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
matter
anything that takes up space and has mass
atomic mass
number of protons plus neutrons averaged over all isotopes
covalent bonds
when two or more atoms share electrons (usually between two nonmetals)
adhesion
the attraction to other molecules that are polar or have charge (H2O to other molecules)
solution
homogenous mix of two or more substances
element
a substance that CANNOT be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions
octet rule
elements will gain, lose, or share electrons to complete their valence shell and become stable (like noble gases)
nonpolar covalent bonds
electrons are shared equally between two atoms
EX: O2
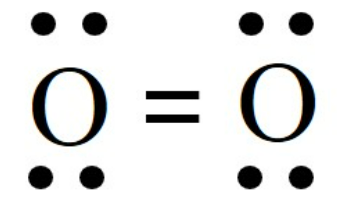
cohesion
attraction of molecules for other molecules of the same kind (H2O to H2O)
capillary action
the upward movement of water due to the forces of cohesion, adhesion, and surface tension
electronegativity
the measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons to itself
chemical bonds
an attraction between two atoms, resulting from the sharing or transferring of valence electrons
polar covalent bonds
bond where electrons are NOT shared equally between two atoms
pH
measure of how acidic or basic (alkaline) a solution is
acid
substance that releases hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water
base
a substance that accepts H+ OR releases hydroxide ions (OH-)
atomic number
number of protons
compound
a substance consisting of 2 or more different elements combined in a fix ratio
EX: H2O or NaCl
ionic bonds
attraction between oppositely charged atoms (ions); usually between a metal and nonmetal
solvent
dissolving agent in a solution
buffer
solution that changes in pH when an acid or base is added