L15 - Anomalous Secondary growth
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ADD CLICKERS (SEE RECORDING)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Fascicular Cambium comes from
residual Procambium
Interfascicular Cambium is formed by
de-differentiation of cortical parenchyma cells
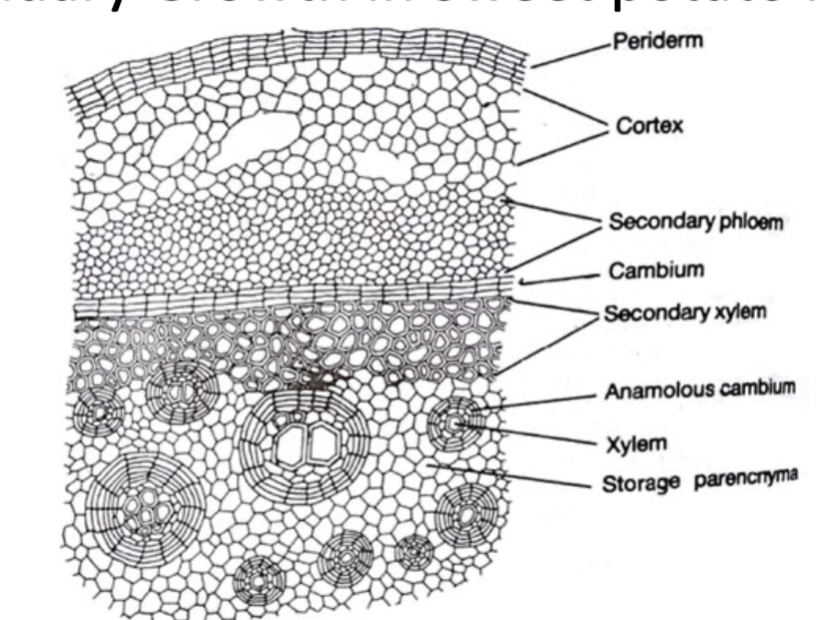
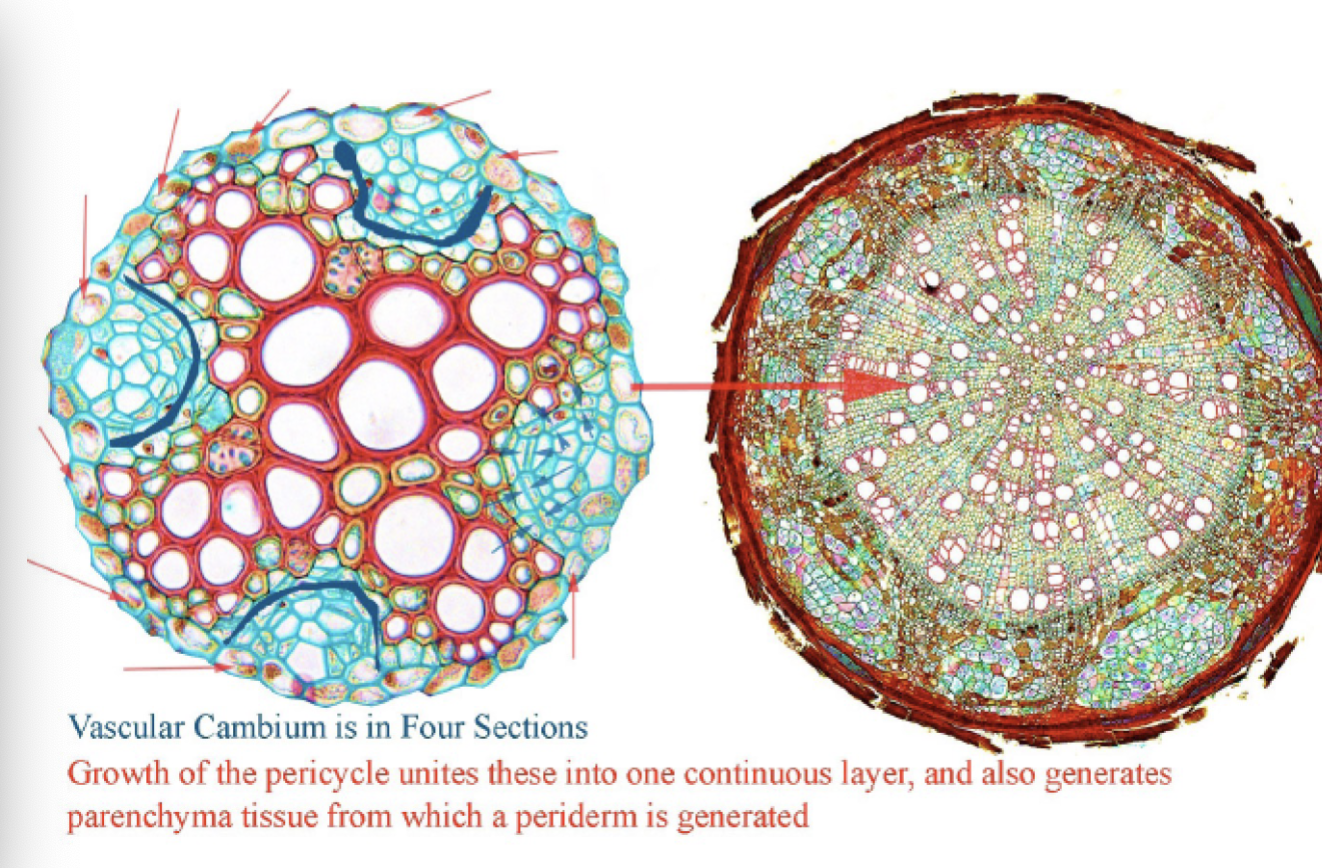
A complete ring of vascular cambium around the stem leads to a _________________ in the stem
a cylinder of secondary growth in the stem
What two things are common in normal secondary growth
1. The secondary xylem and phloem form complete rings
2. The cambium separates the secondary xylem from secondary phloem
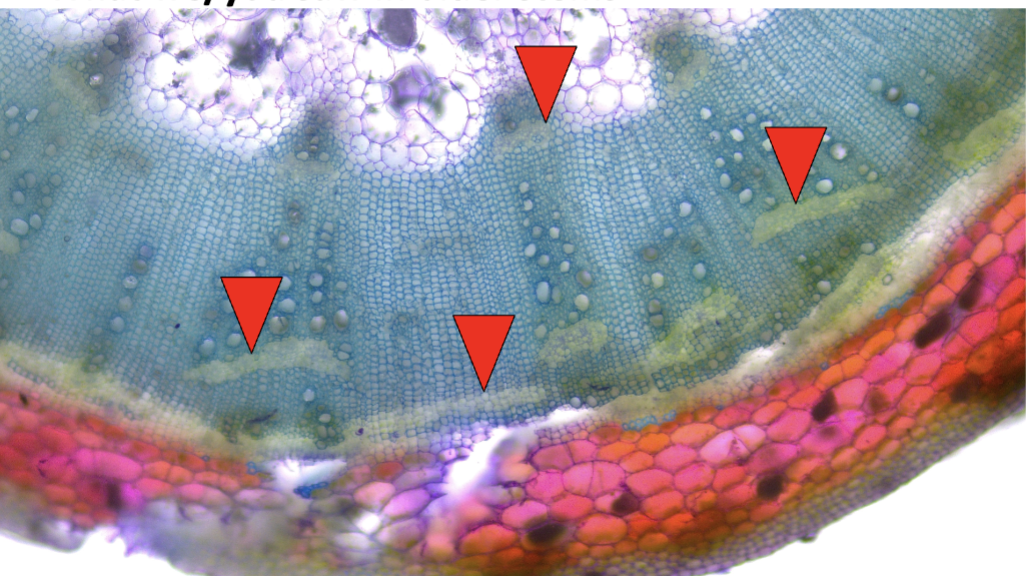
abnormal secondary phloem
Causes of anomalous secondary growth (5)
1) The ACTIVITY of cambium is abnormal, despite normal appearance
2) The SHAPE of cambium is abnormal, despite normal fxn
3) Formation of secondary tissues by the accessory cambium
4) Formation of INTER-XYLARY phloem (AKA included phloem)
5) Formation of INTRA-XYLARY phloem
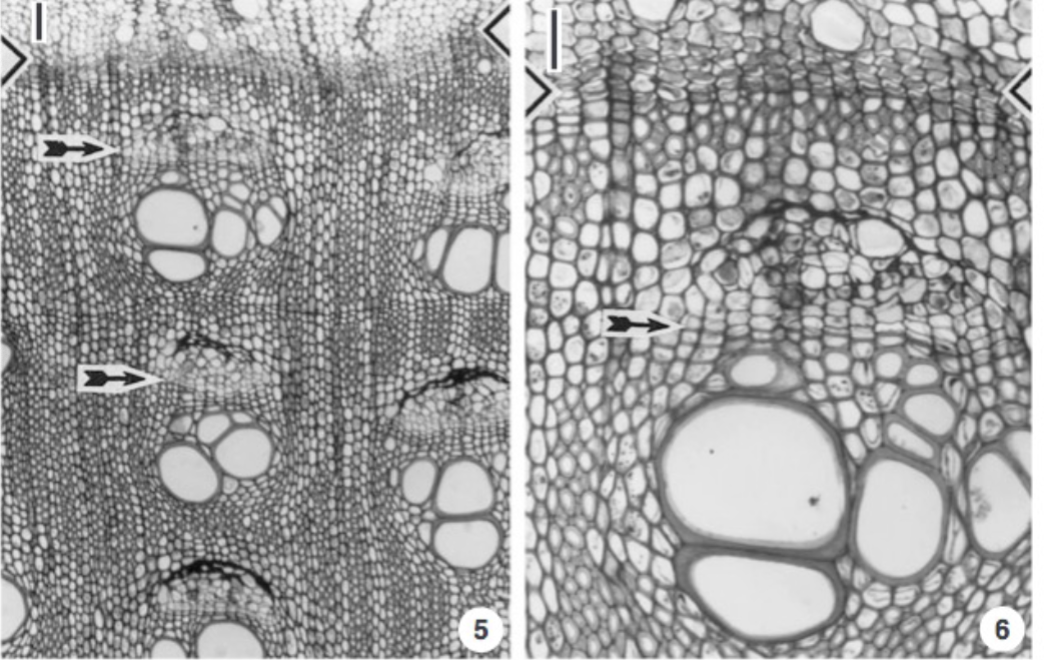
Wedge Parenchyma is an example of
normal cambium is normal, but abnormal activity
describe wedge parenchyma
The interfascicular sections of the cambium contribute wide rays or
spokes of parenchyma cells
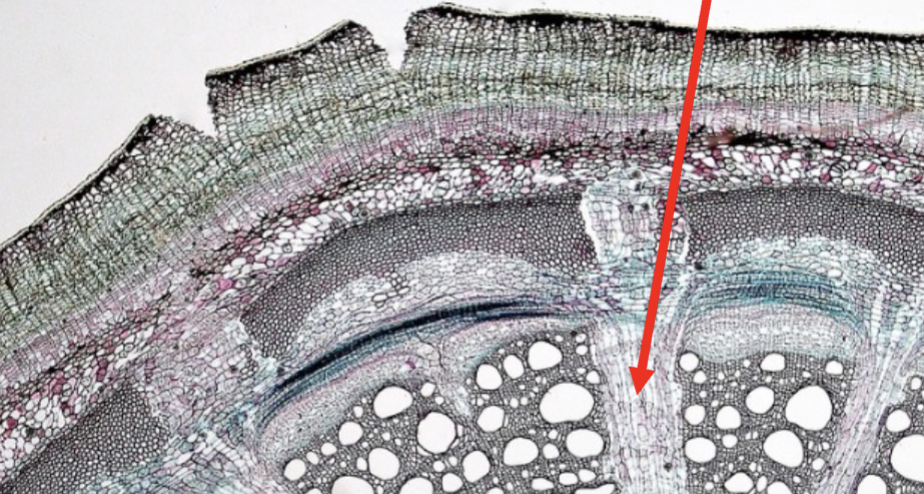
Wedge Parenchyma or connective tissues
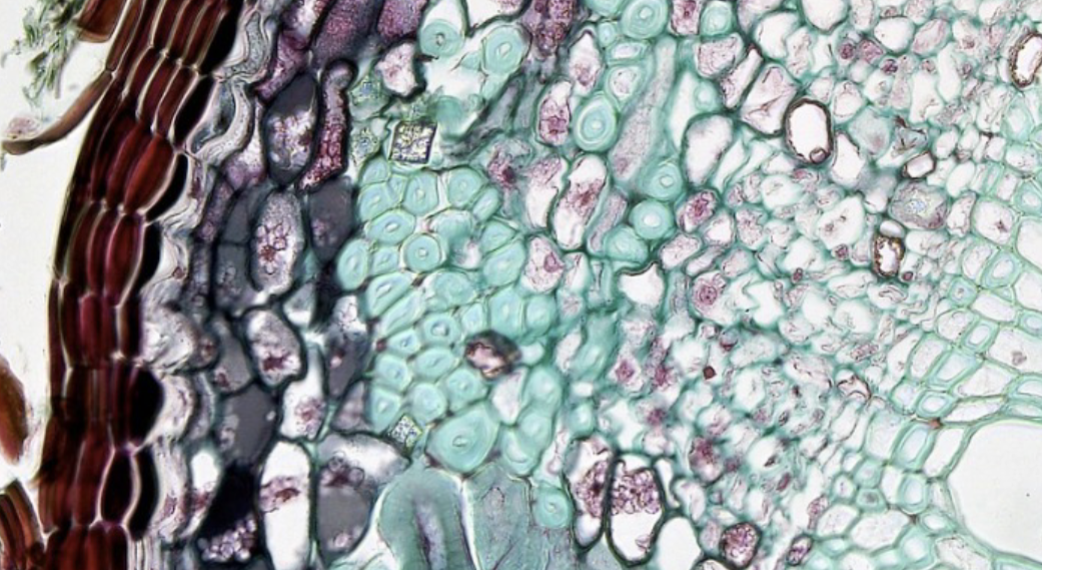
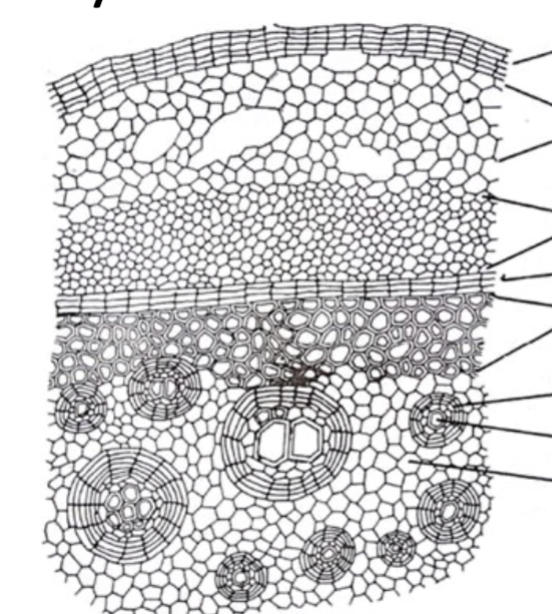
Green Arrow - Fascicular Cambium
Orange Bracket - Crushed Primary Phloem
Pink Arrow - Phloem Fiver
Red Arrow - Cambium Ray
Blue Arrow - Metaxylem
Yellow Arrow - Secondary Phloem
Liana are an example of
Normal cambium with abnormal activity
describe Liana cambium
why are they abnormal in activity
The cambium makes more phloem than xylem
Results in VARIENT PHLOEM WEDGES
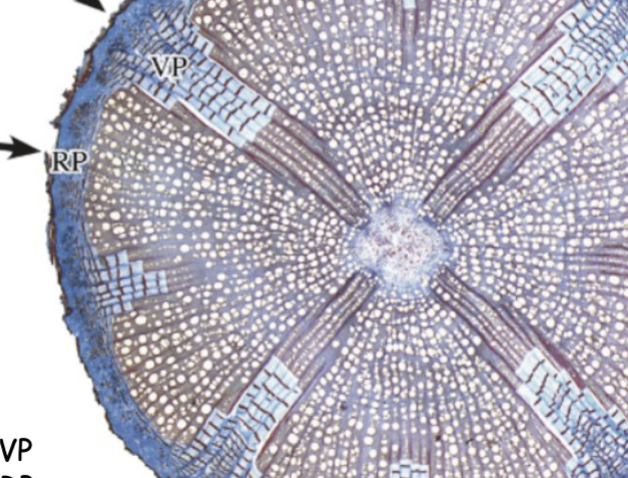
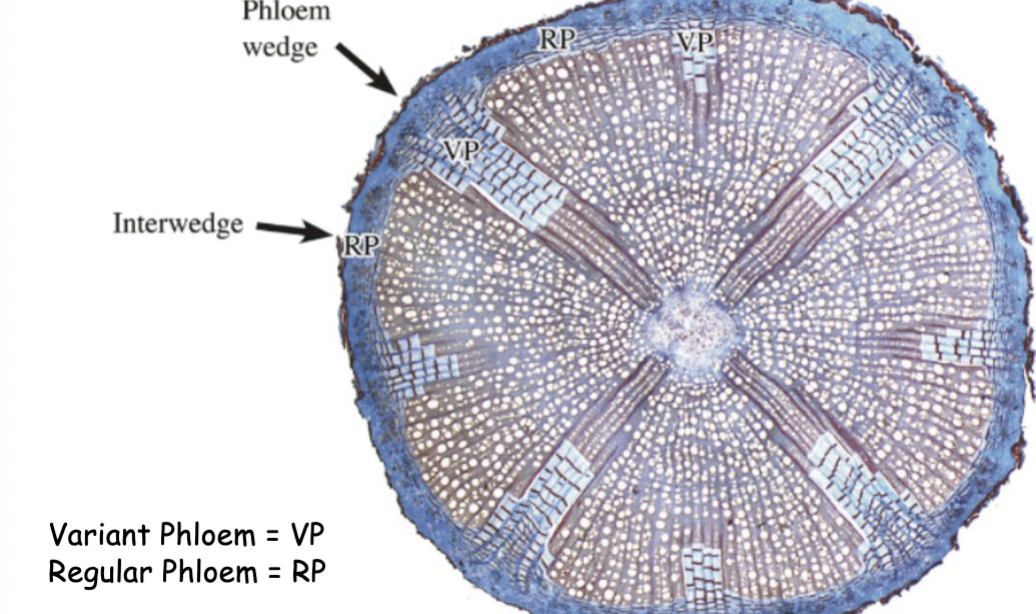
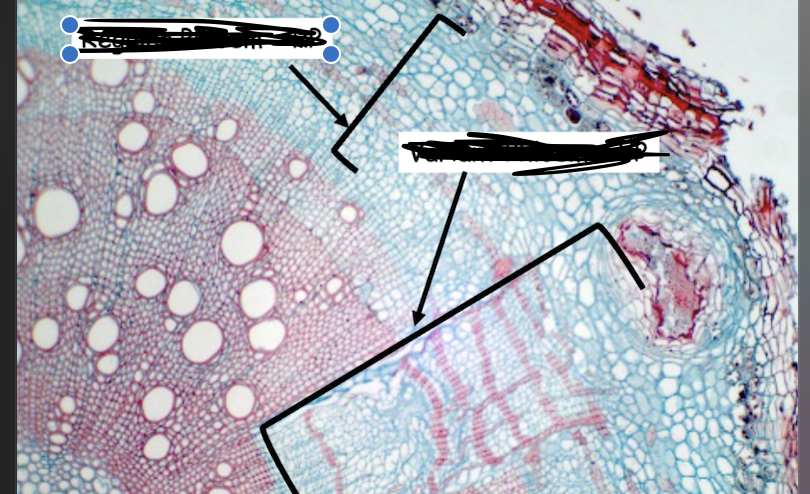
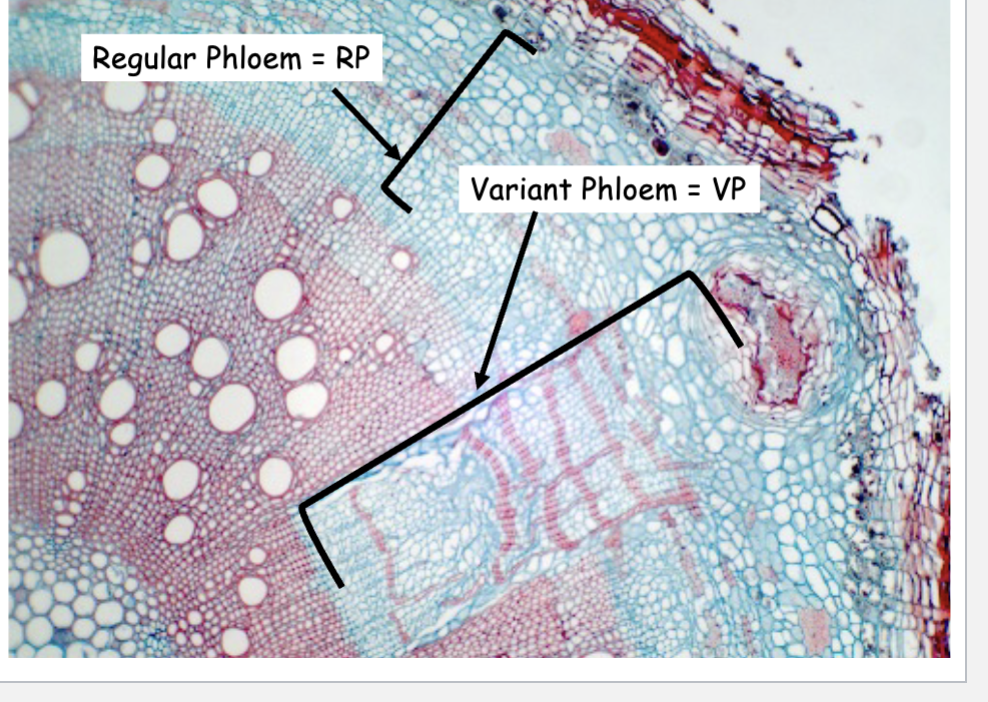
Varient phloem wedges in liana are caused by
Leaves and axillary buds
Fewer leaves in Liana, _______- wedges
fewer wedges
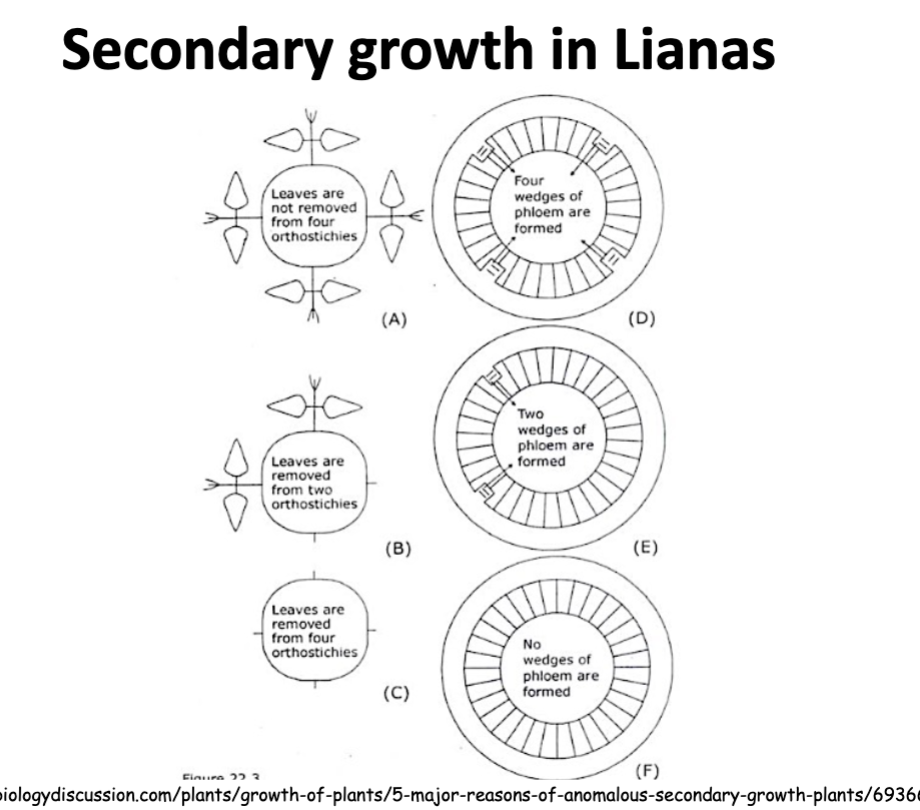
Bauhinia is an example of
Normal cambium, abnormal activity
Bauhinia have an abnormal shape due to
stem shape
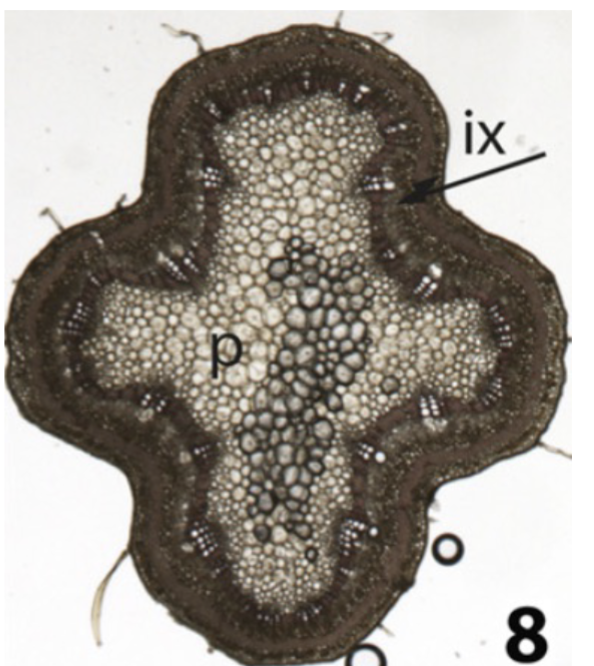
After secondary growth, what happens to Bauhinia
inner cylinder stays same, but the cambium ONLY makes outer xylem in 2 rings with many gelatinous fibers
Bauhinia gelatinous fibers do what
offer flexibility for the wood
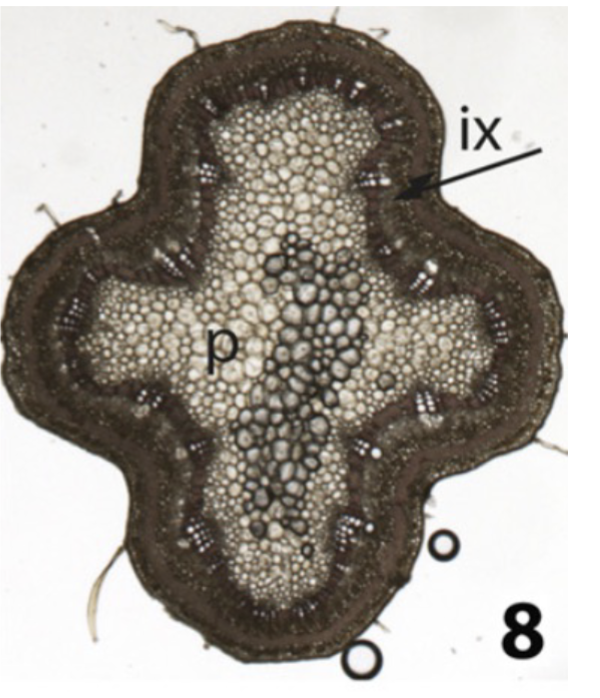
what happens here with secondary growth
Outer xylem has gelatinous fiber
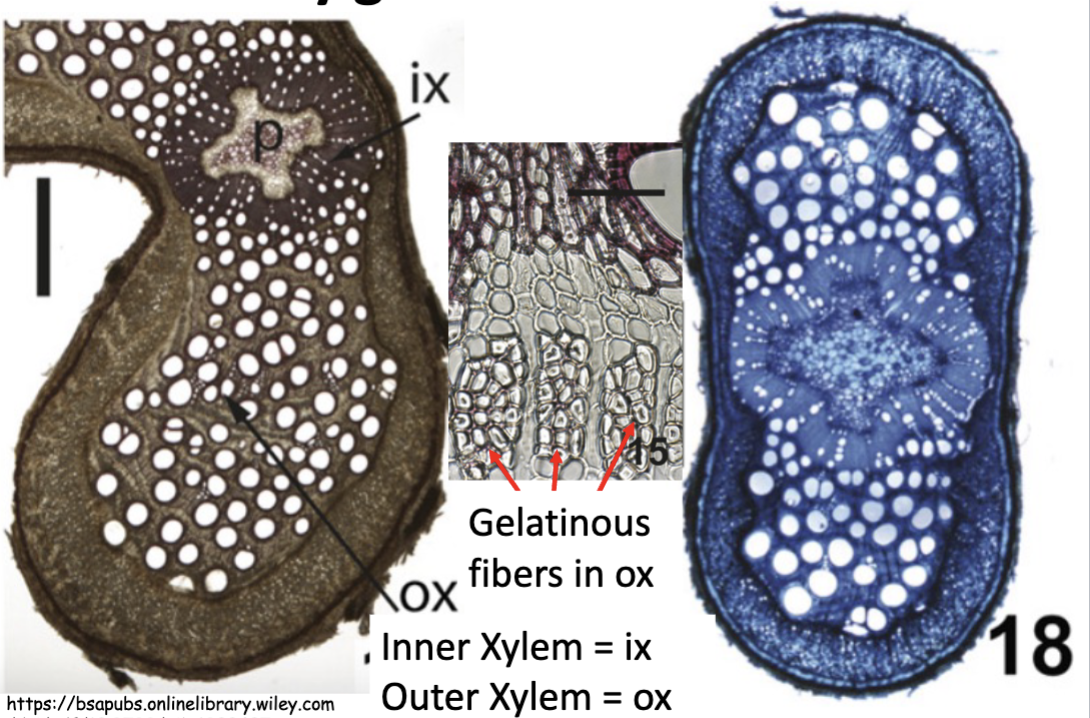
Secondary growth through unequal or asymmetrical cambial activity
( Asymmetric stems ) result from the activity of ___________ starting with a regular, ________ stem, and later becoming ___________ stem
of a single cambium
Round stem
an asymmetrical stem
Secondary growth through unequal or asymmetrical cambial activity is an example of
Normal cambium, abnormal activity
What does the cambium do in plants
The cambium is a layer of plant cells responsible for growth, particularly secondary growth, which increases the plant's girth by producing new wood (xylem) and inner bark (phloem)
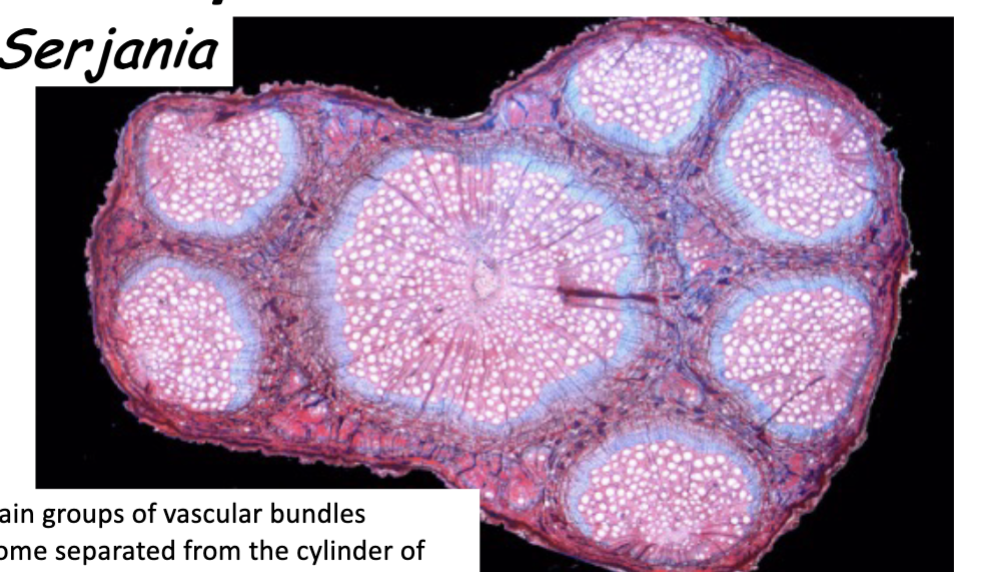
Liana VASCULAR BUNDLES are an example of
abnormal cambium, normal activity
What makes Liana cambium abnormal
Certain parts of the vascular cylender seoerate out, but cambium differentiation continues until each forms its own cambium
What do the multiple bundles of a Liana do
helps offer support for the woody vine
Bougainvillea is another climbing vine,
It makes ________ by making __________
it makes secondary tissue by making accessory cambium
What are accessory cambium
Accessory cambium refers to a type of secondary meristematic tissue that forms after the primary vascular cambium and results in anomalous secondary growth, thickening the stem in unusual ways
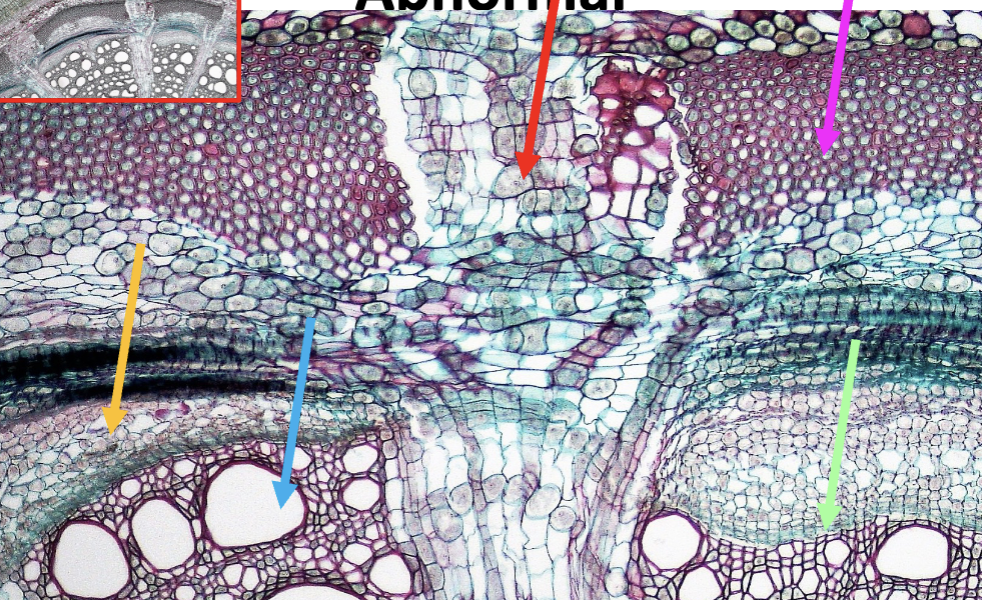
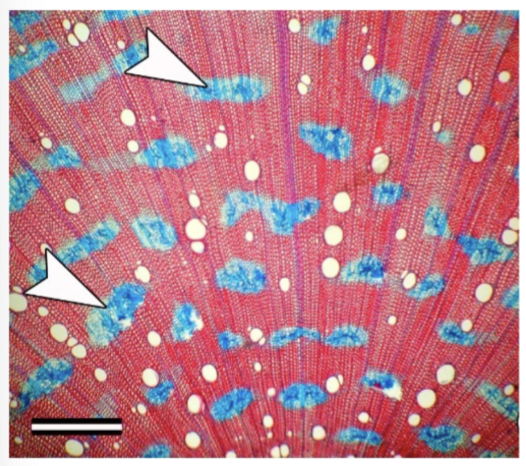
Accessory Cambium and crushed Phloem arches are an example of
abnormal cambium, normal activity
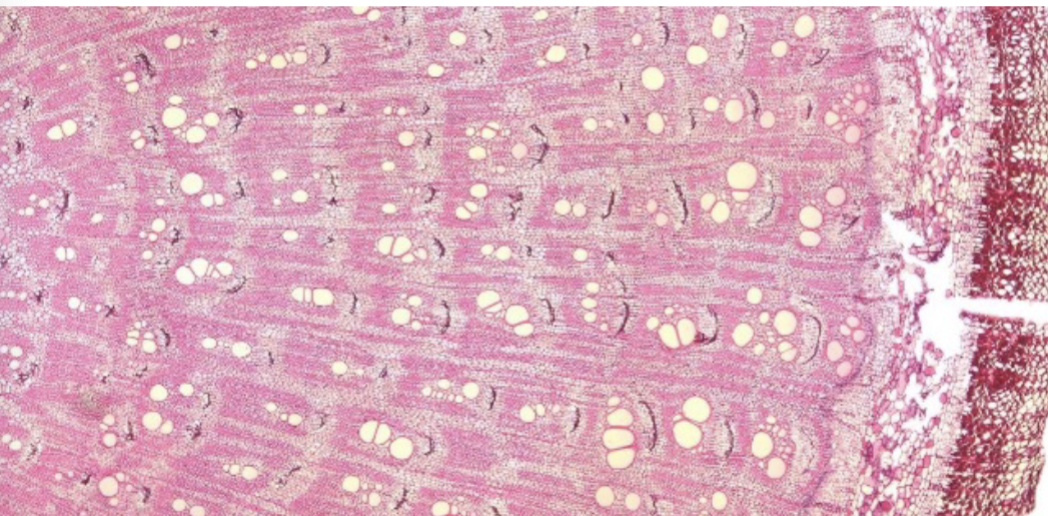
Whats this
crushed phloem rings frm accessory cambium
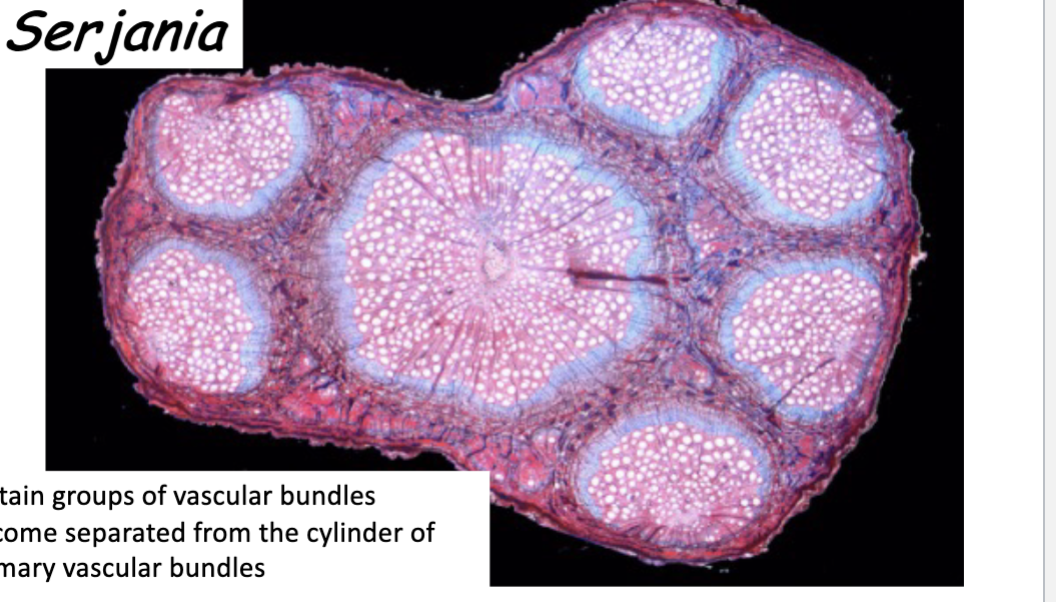
Whats this
Liana cambium bundles
In Bougainvillea secondary growth, how are the crushed phloem made
Patches of accessory cambium form, each having its own vascular bundles, which each has its own ‘secondary growth’, resulting in smaller patches of crushed phloem arches
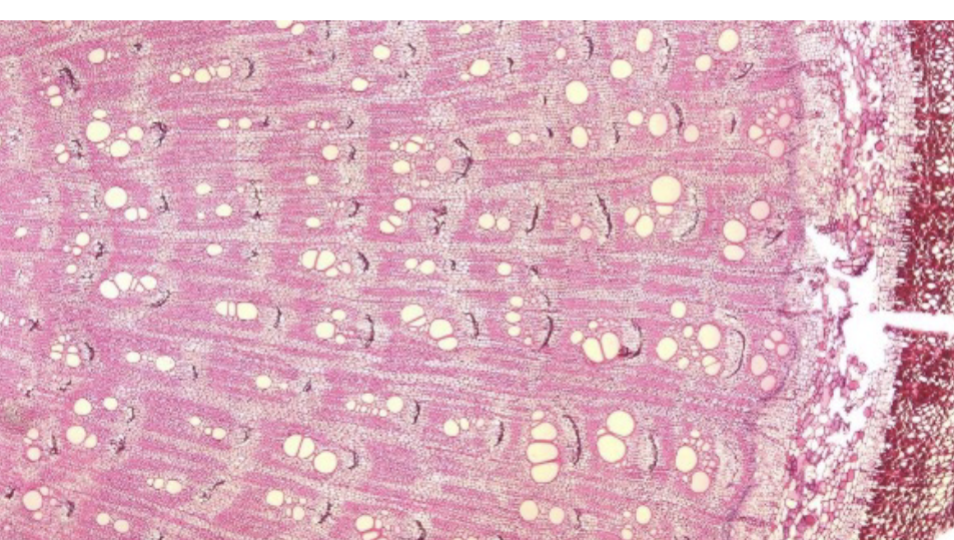
whats this
crushed phloem arches caused by accessory cambium rings
What is the difference of accessory cambium rings and arches
HELP - ADD (rewatch)
Thunbergia is an example of
formation of inter-xylary phloem
explain the formation of inter-xylary phloem
Vascular cambium makes secondary phloem instead of xylem, but goes back to making the xylem later on
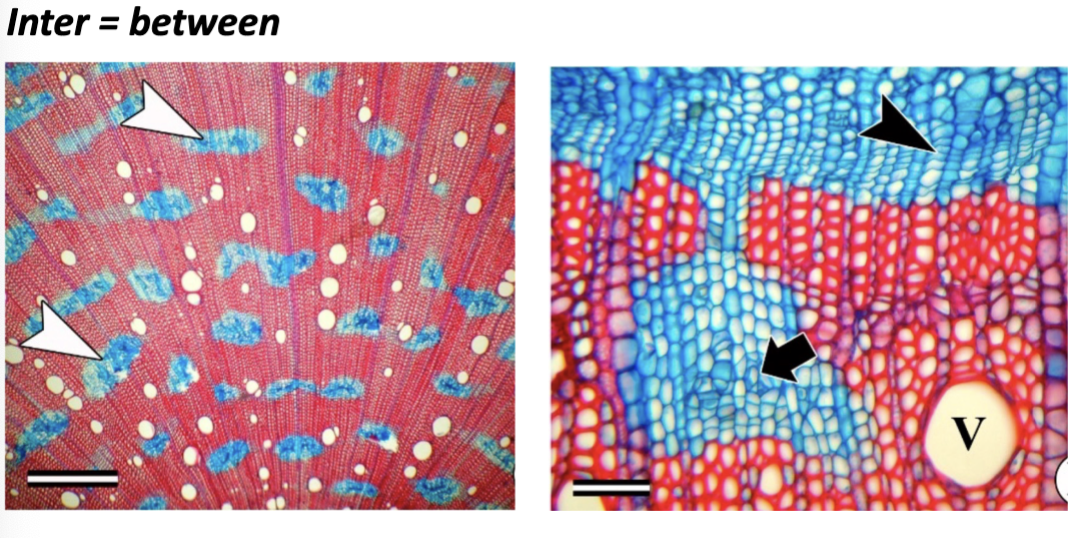
whats this
Inter-Xylary Phloem
what does Inter-Xylary Phloem do // what is it like
it is a mixture of hard and soft cells intertwined, offering support and flexibility
Intra-xylary Phloem is most common in _________
Monocots
We learned that monocots often have closed collateral bundles.
Does this mean that MONOCOTs NEVER undergo secondary growth
FALSE
Most do not, but exceptions exist
Explain intra-xylary phloem formation
the cambial derives outside the atactostele
atactostele is in center outside, there is further cambial activity known as monocot cambium
(look for blurry ring)
monocot cambium makes bundles unlike the standard
P surrounds X
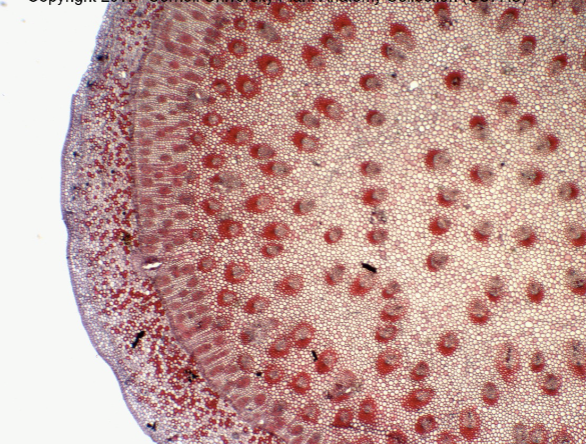
what is monocot cambium
cambium formed outside atactstele
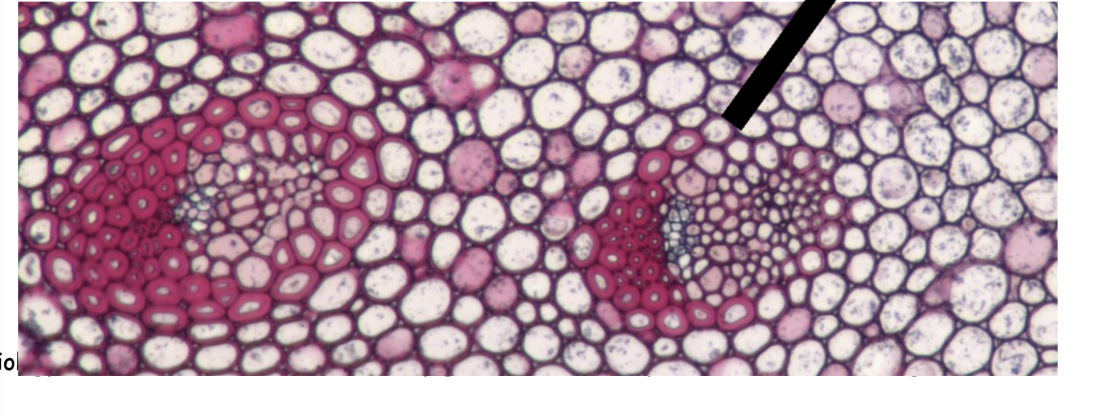
Atactostele on the RIGHT
INTRA Xy phloem on the LEFT
intra xylary phloem
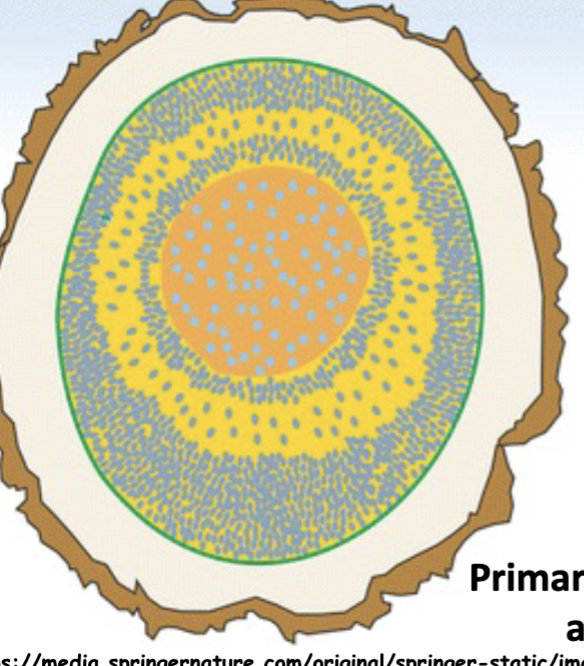
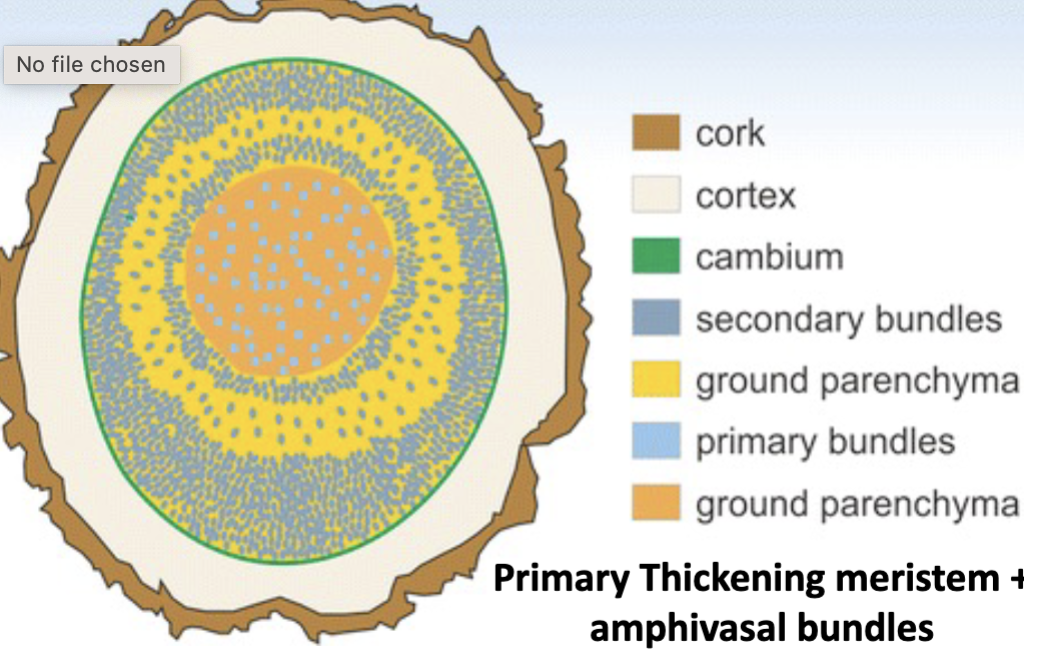
Describe secondary growth in dracena
intra-xylary phloem
Describe the formation secondary growth of palms
do not have growth rings
→ instead have overlapping leaf bases creating pseudobark
→ pseudobark is highly sclerified
→ palms lack a lt of secondary tissue
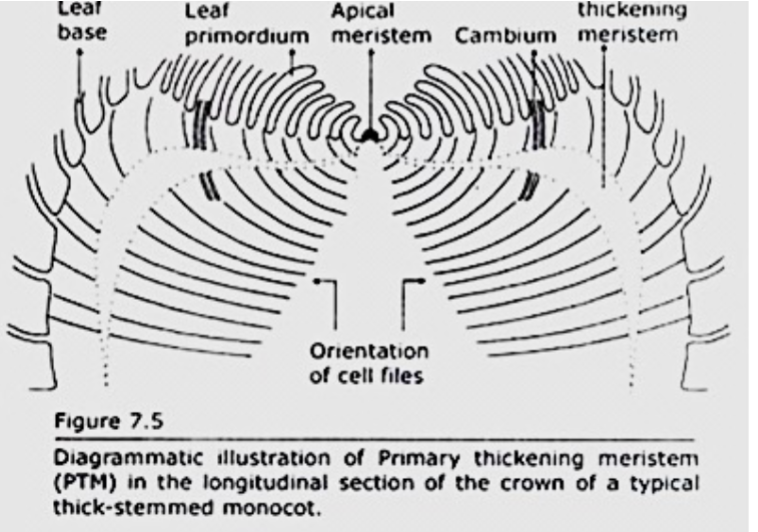
Have secondary growth like this because everything occurs close to SAM, and the primary thickening meristem thickens the base early allowing it to just grow up and be wide at the start
T/F everything occurs close to SAM in palm
True
what is PTM
Primary thickening meristem
a plant meristem responsible for the primary thickening (radial growth) of a stem, primarily found in monocots like Palms
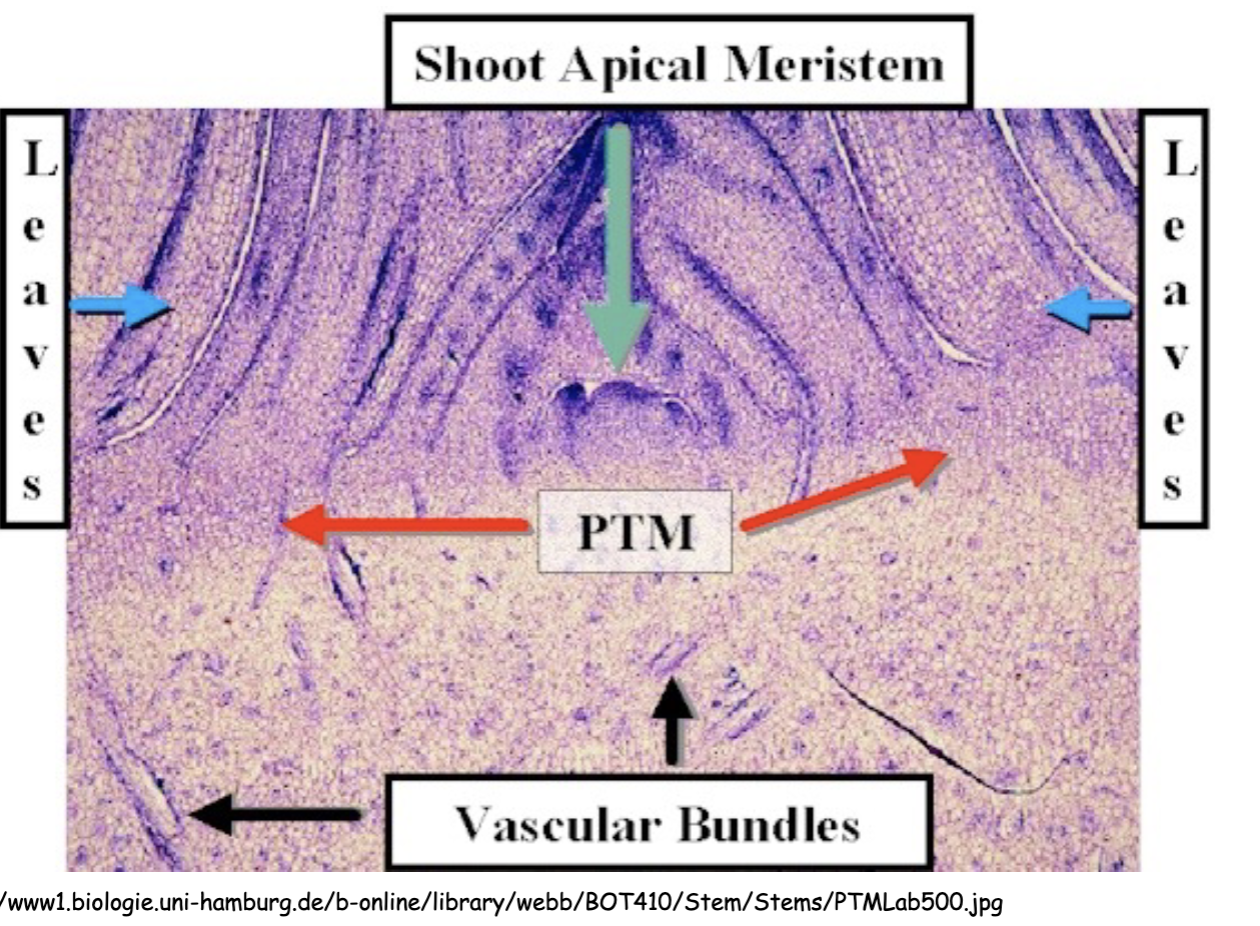
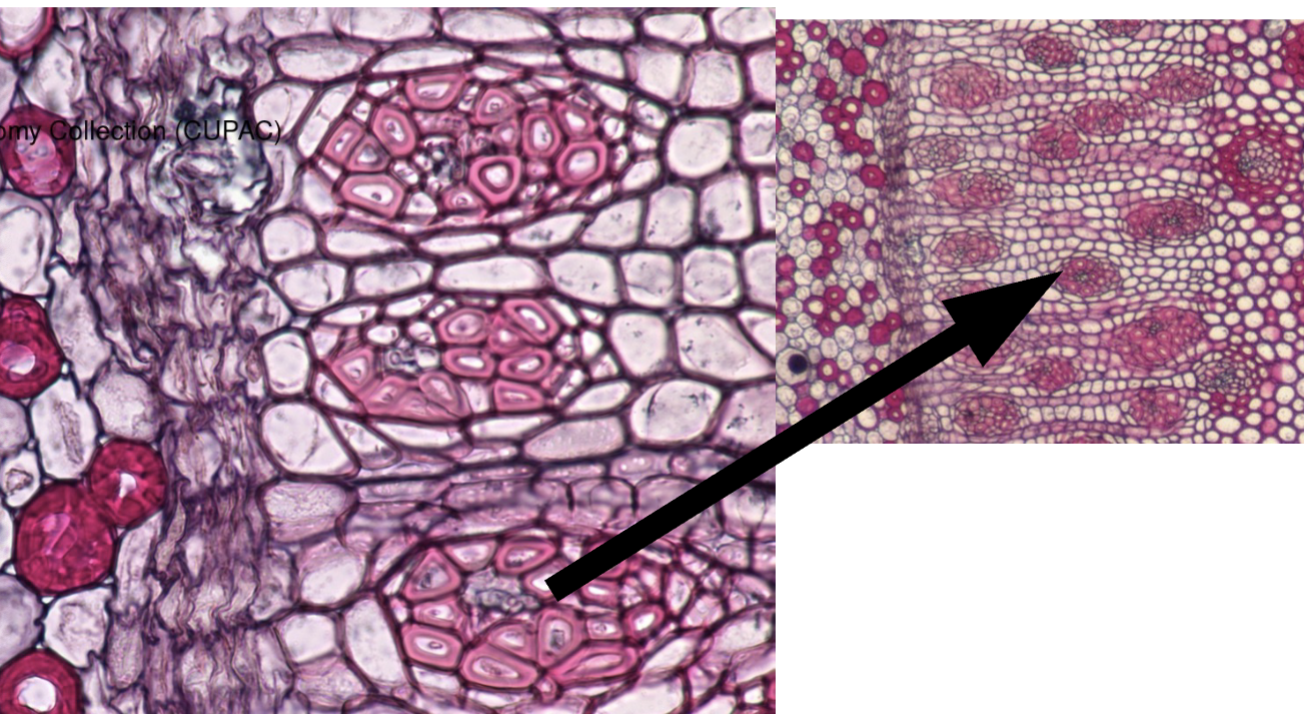
Describe this image
This is the formation of secondary growth in palms
How do Palms thicken
Via primary thickening meristem
_________ make up most of the root mass of woody
perennials.
Secondary tissues
(In roots) The ______ continues to __________, with the
normal tissue differentiation, producing root hair and lateral
roots.
This is critical for root absorptive function
RAM
make primary root tissues
In secondary root growth
support for the secondary body made above ground
comes from __________ produced by the __________, the _________, and the _________
secondary tissues
lateral meristems, vascular cambium, and cork cambium
The underground root systems of trees are as extensive as the
aerial plant body. The provide the ________ for the
aboveground weight keeping the tree stable
support
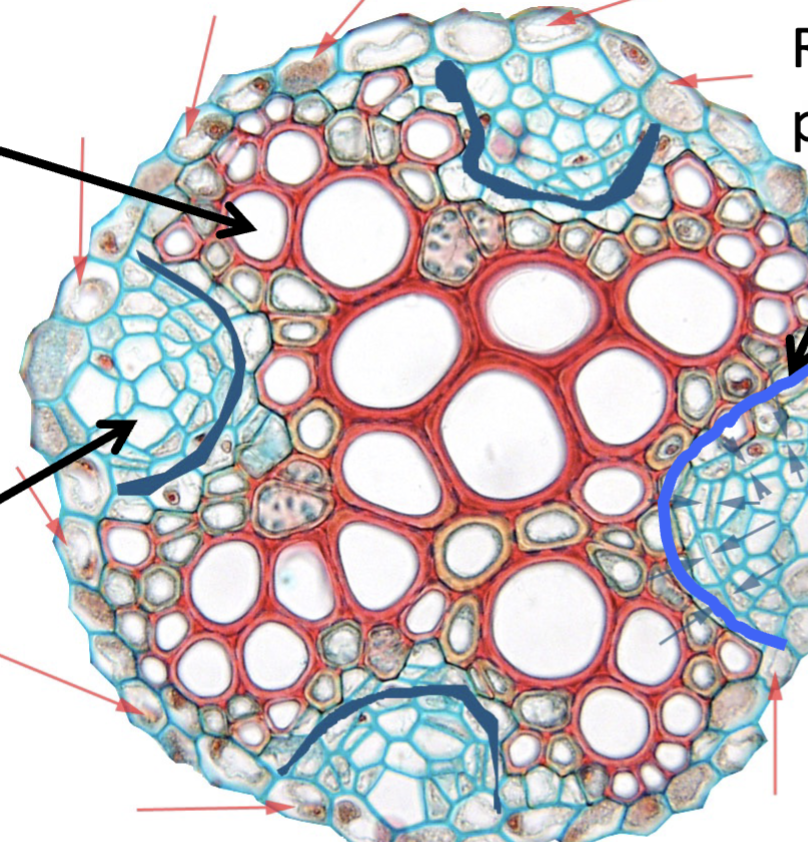
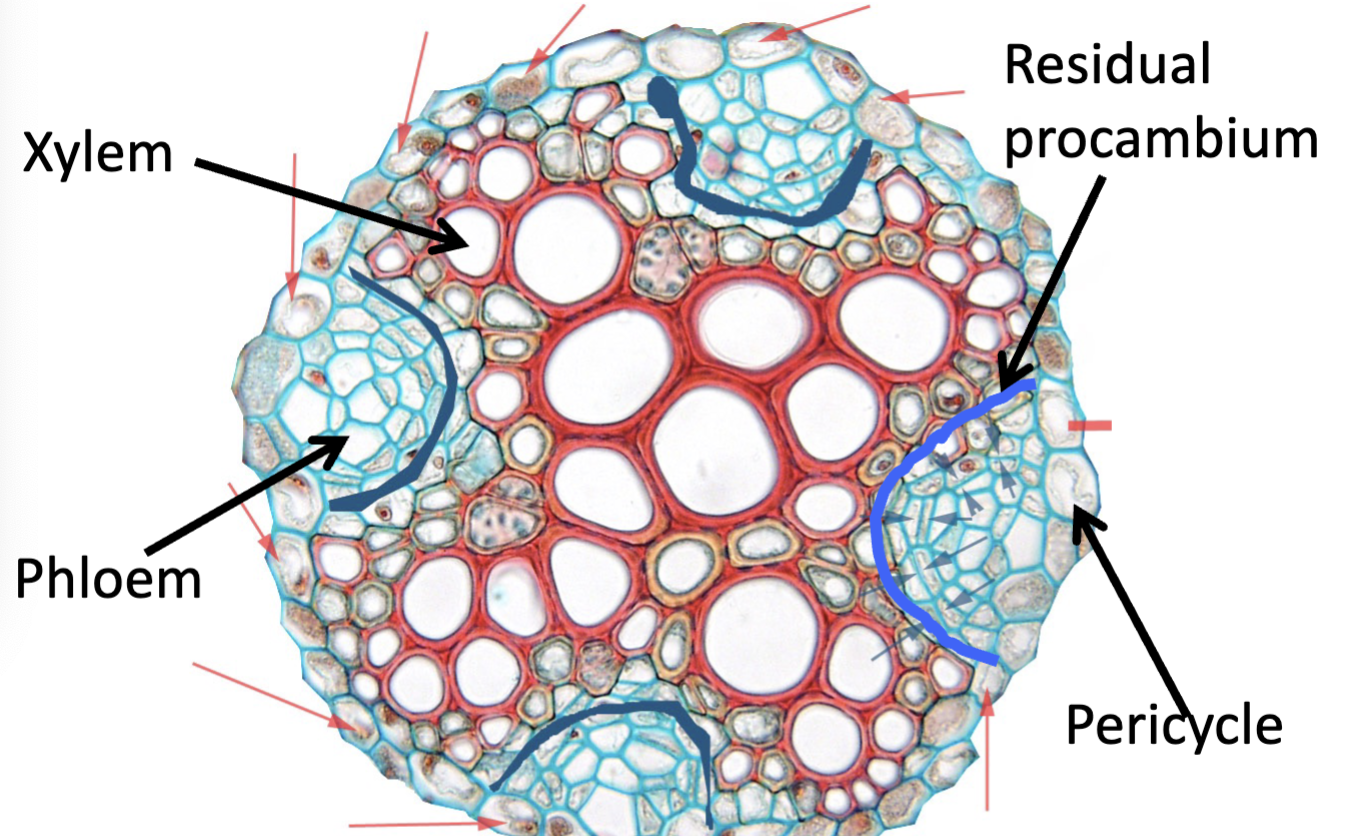
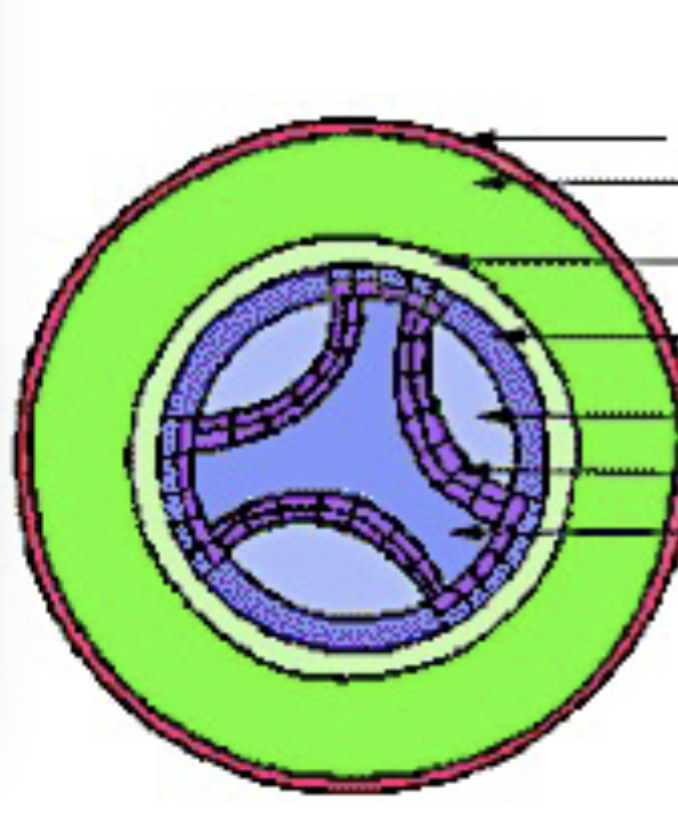
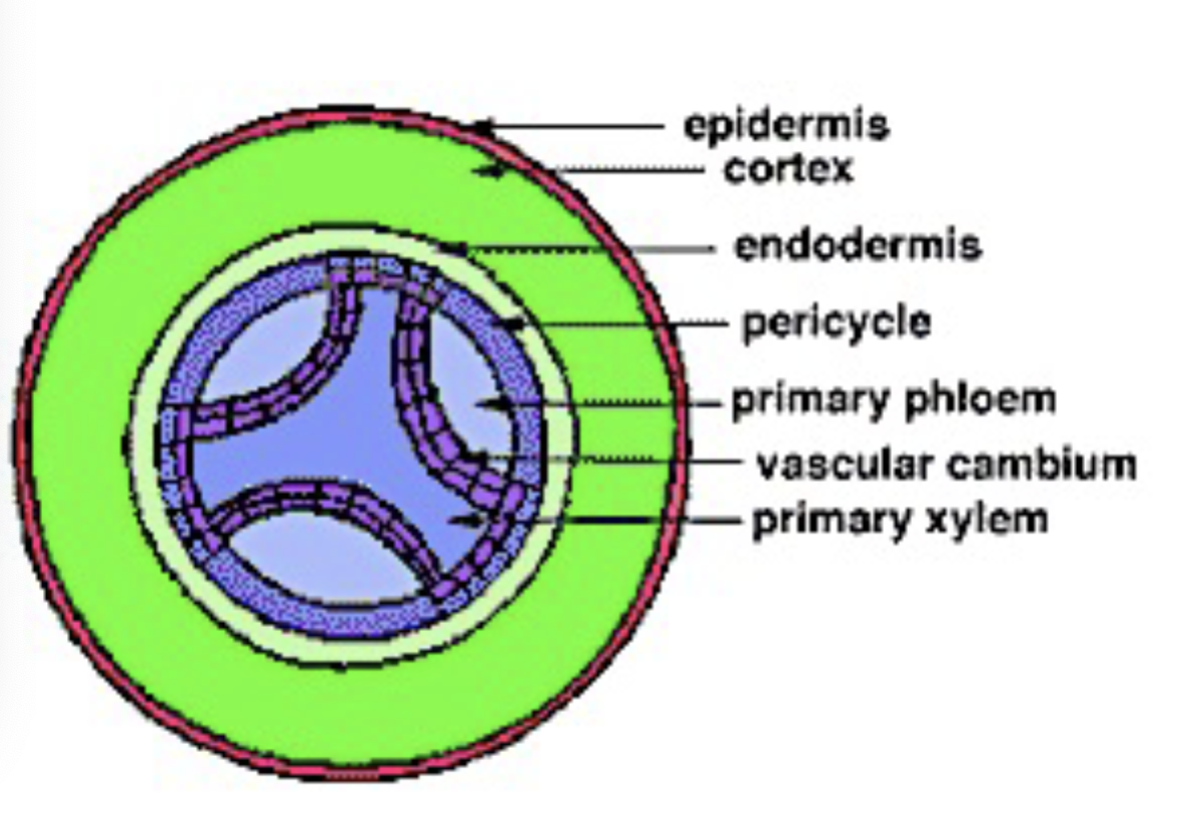
What does the pericycle make / do
lateral roots
cork cambium
vascular cambium
root branching
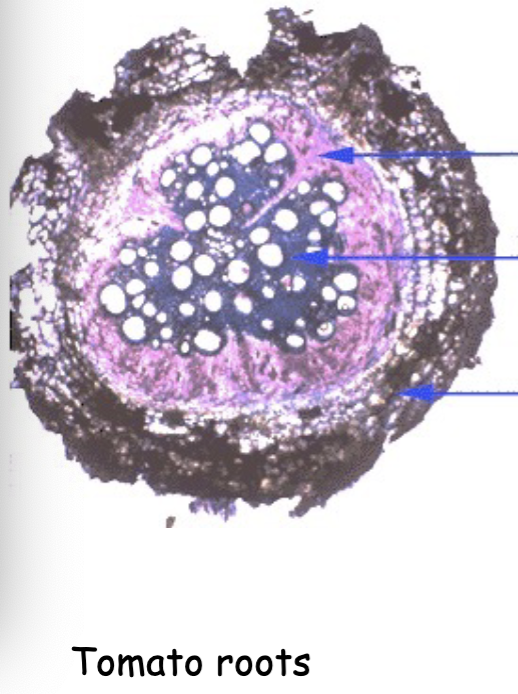
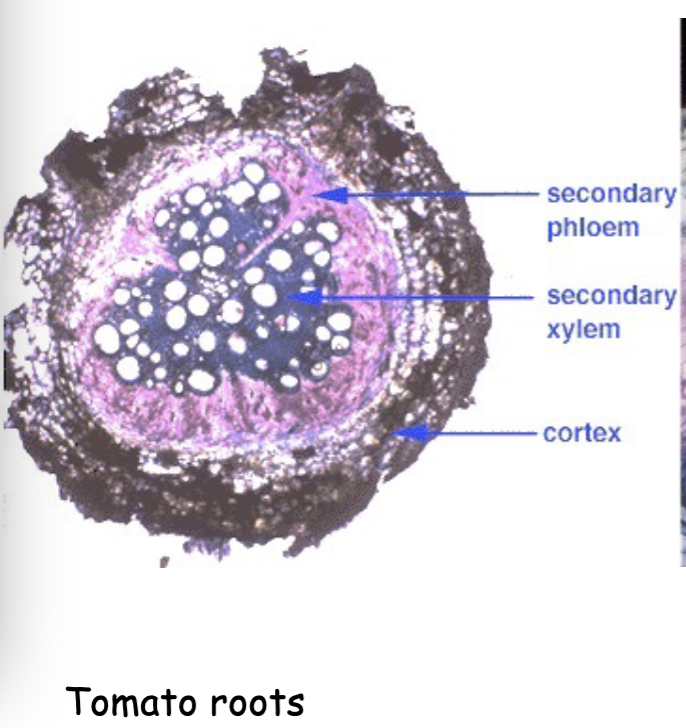
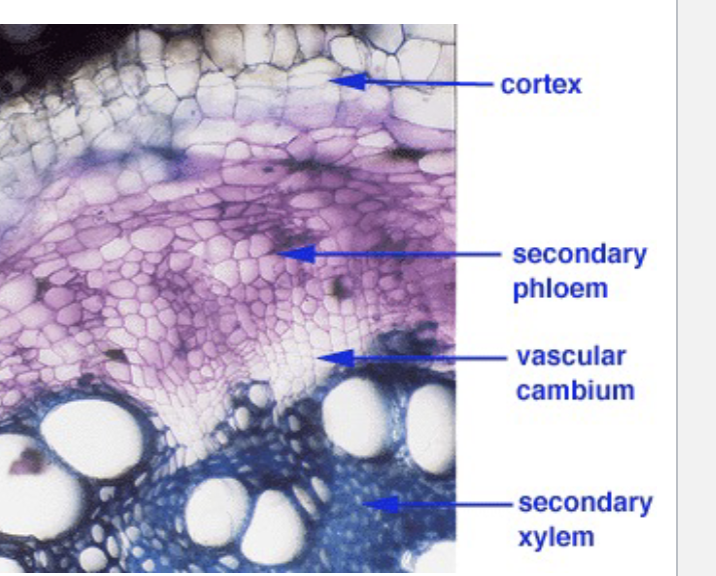
is this an example of normal secondary growth
Yes
Explain carrot secondary growth
Tiny vascular cambium, small 2 X, lts of 2 P
Explain storage secondary growth in Beets
successive cambium each with 2 X/P and spaced out with parenchyma
Explain sweet potato secondary growth
cambium with 2 Xylem and Phloem
rings of anmylus cambium each with secondary X / P and tertiary cambium within
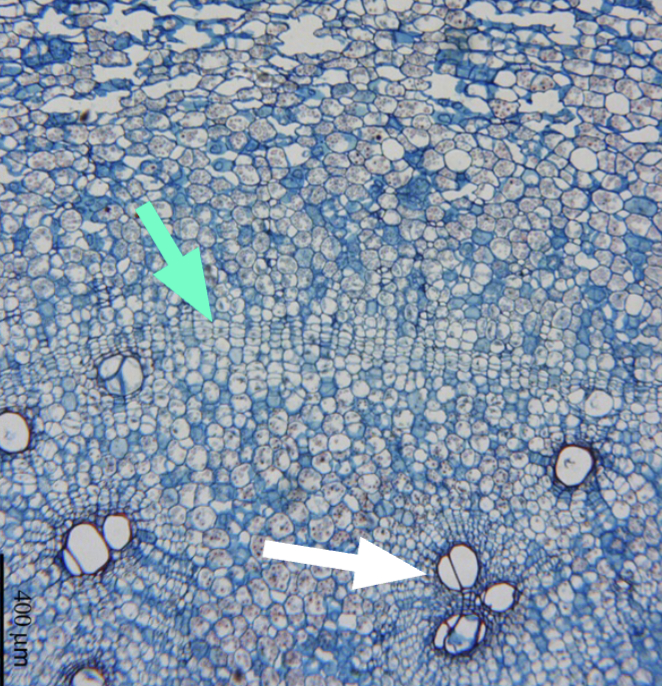
Green → vascular cambium
white → tertiary vascular cambia
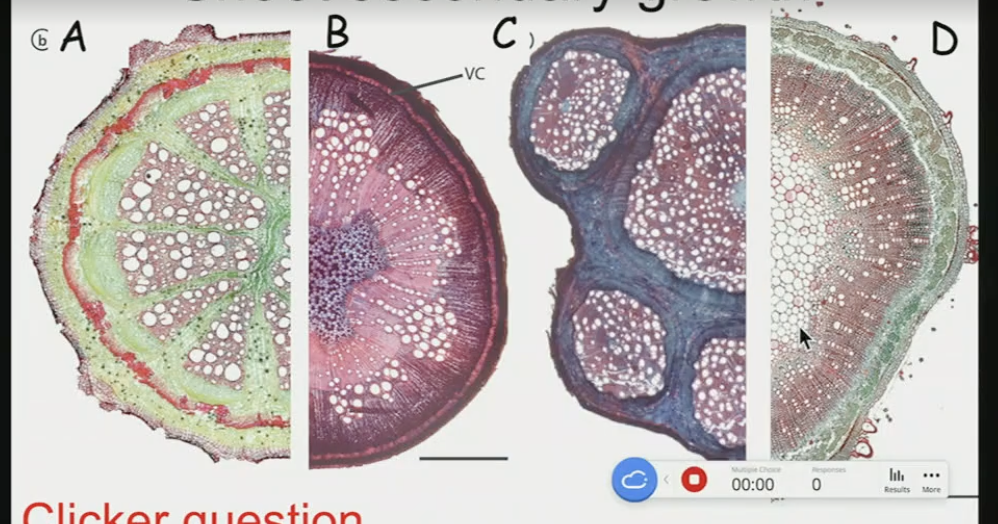
Which of the shoots is showing normal secondary growth
D
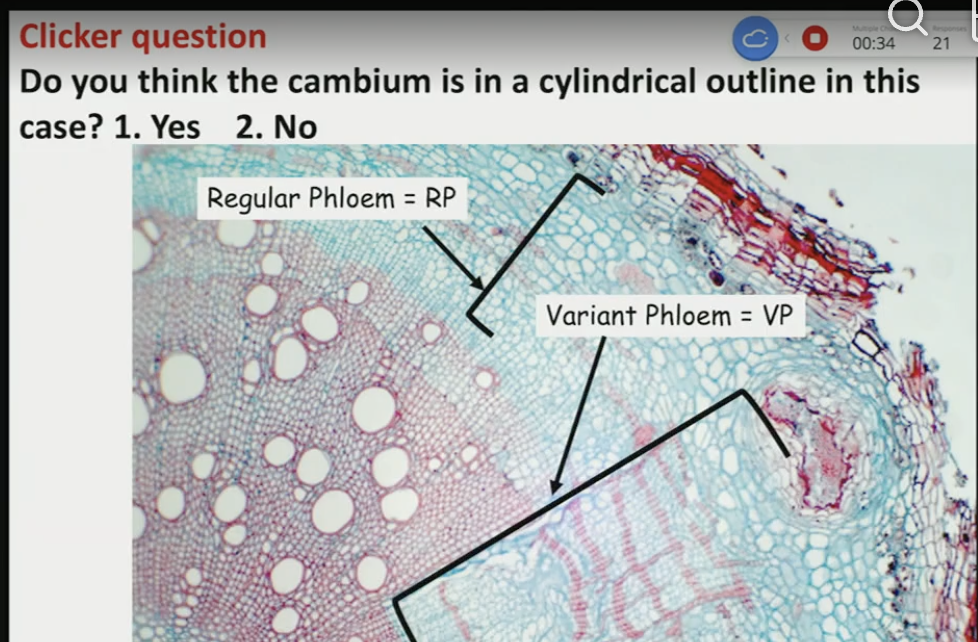
NO

ALL OF THE ABOVE
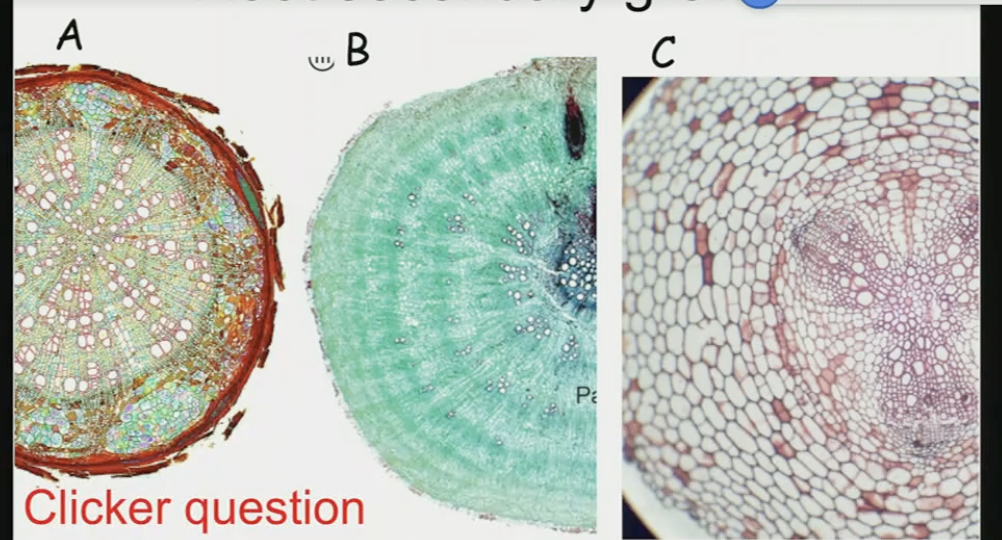
which of these roots is showing normal secondary growth
A
accessory cambium can be ______ or ______
arches or rings
accessory cambium can appear like asymmetric _________
steps
intraxylary phloem is made in _______ arrangements
files to thicken
do cordylene and palms have primary thickening meristems
Yes

help
sweet potato