med surg 40 disorders of liver, gallbladder, pancreas
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
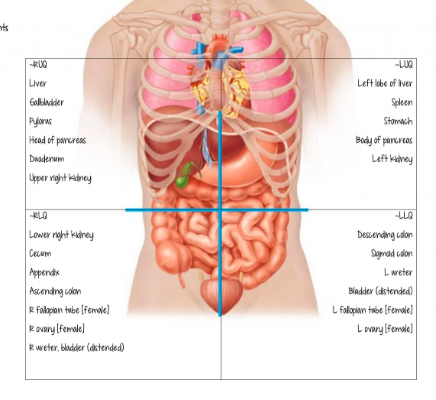
organs in quadrants of GI
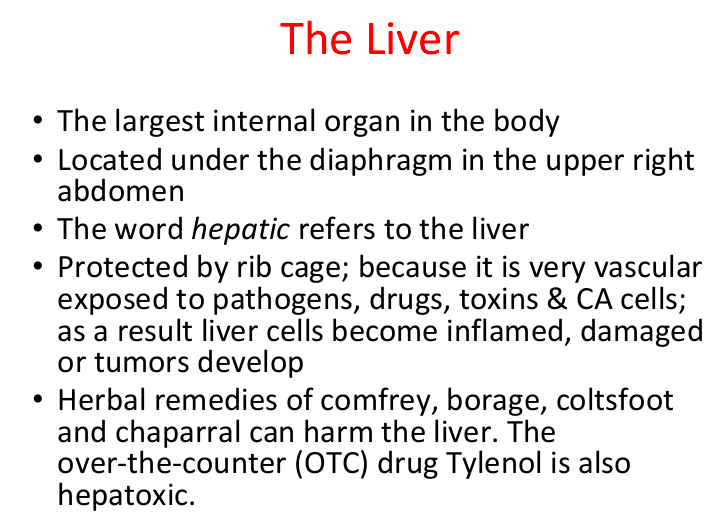
overall of liver
URQ
protected by ribcage
“hepa”
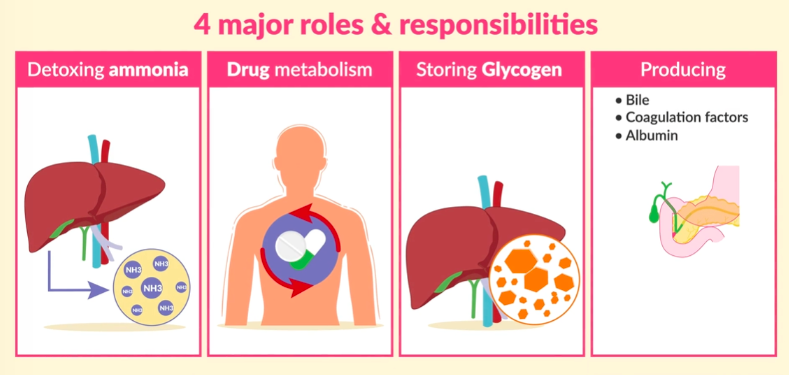
4 major roles of liver
detoxifying ammonia
drug metabolism
stores glycogen
produces bile, coagulation factors, albumin
(albumin helps keep fluid where they belong)
bile
produced in liver → cystic duct → gallbladder
absorption of soluble vitamins, help remove toxins
bilirubin can be increased when one is
anemic, cirrhosis, or bile duct obstruction
history & assessment
changes in weight/ skin color. itching, easy bruising, headaches, enlarged lymph nodes, dyspnea, breast enlargement in men
anorexia, ab pain, n&s, diarrhea, GI bleeding
alcohol use, use of acetaphetomin
dx tests and procedures
check ammonia levels, coagulation, bilirubin, liver enzymes
with ammonia, reduce protein. take Lactose (laxative)
HIDA nuclear scan: isotope injected into vein, collects in liver, shows diseases
CT
MRI
ultrasound to visualize organs
dx tests and procedures
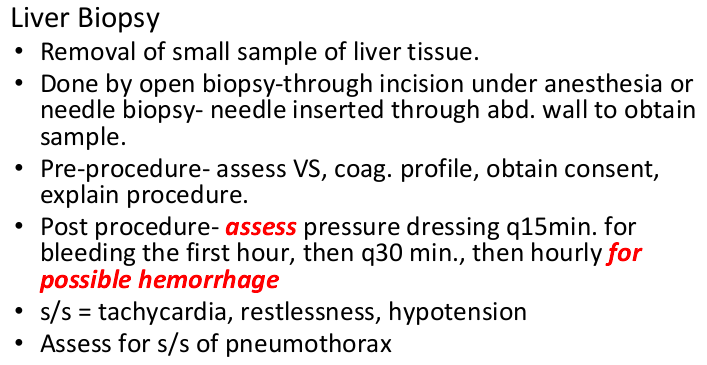
liver biopsy
lay 2 hours post-op on right side to keep pressure on liver (think coagulation factors, prevent hemorrhaging)
hepatitis
inflamed liver. virus grows & damages cells
s&s: fever, rash, angioedema (hives), arthritis, fever, malaise
risk: tylenol, alcohol
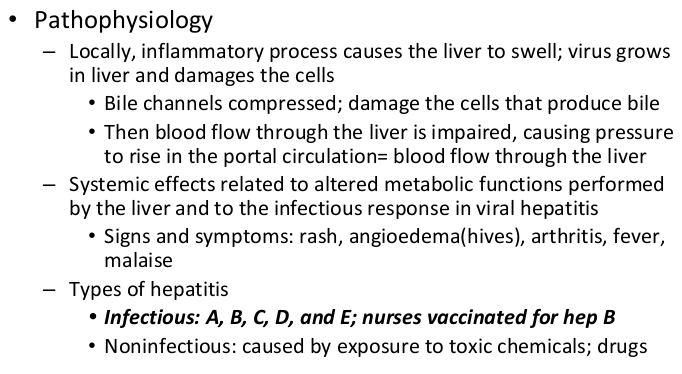
types of hepatitis
A: fecal → oral route. contaminated foods
B: blood and body. sexual. newborns may be affected
C: blood and body (no vaccine available) cause cirrhosis
D: body fluids. cause infection only when B is present
E: fecal → oral route

phases of hepatitis
preicteric:
before jaundice. most infectious. headache, malaise, ruq pain, n&s, fever, joint point, rash, liver enlarged and tender
icteric:
jaundice. dark urine. light stool. increased bilirubin. edema bc low albumin. itchy
post icteric:
fatigue, malaise, liver enlargement, s&s start to subside. 2-12 weeks recovery

complications with hepatitis
esophageal varices (may bleed out) #1
hypertension
hepatic encephalopathy (enlarged head. confused)
ascites
tx for hepatitis
rest
anti-emetics, steroids, anti-pyretics
low fat and high protein (unless ammonia high)
avoid alcohol and tylenol
avoid sharing razors, toothbrush
protected sex

alcohol-induced liver disease
fatty liver:
too much alc. often no signs. can fix w/ good diet
alcoholic hepatitis:
inflammation bc heavy alc. heavy signs
alcoholic cirrhosis:
scar tissue replaces liver cells. need transplant (at end stage too. need steroids and immunosuppressant for life)
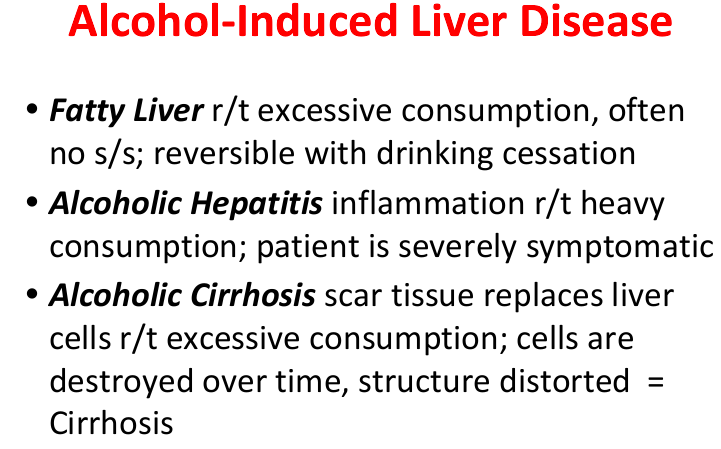
cirrhosis
chronic, progressive. scar tissue replaces liver cells
healthy liver → fatty liver → liver fibrosis → cirrhosis

complications w cirrhosis
esophageal varices & portal hypertension
ascites
hepatic encephalopathy (due to high ammonia levels → must be on seizure precautions and mild protein)
tx for cirrhosis
rest
diet high in vitamins and moderate protein unless ammonia
water and salt likely restricted
IV fluids
anemic → blood transfusion
paracentesis
tx for bleeding esophageal varies
to constrict bv and lower pressure: octreotide
vitamin K
Protonix (ppi)
sclerotherapy: solution into vein → hardens and closes it
dx tests for bile / gallbladder disorders

cholecystitis
inflammation of gallbaldder
causes: gallstones, bacteria, toxins & chemicals, starvation, tumors, anesthesia, opioids
cholelithiasis
gallstones
can be anywhere in biliary tract: gallbladder, cystic duct or common bile duct
cause: high cholesterol / high calorie
female, fat, fair, 40+, fertile
s&s of cholecystitis and cholelithiasis
clay-colored stool if bile duct obstructed / steatorhea
pancreli-paste (enzymes) given for digestion of fats, carbs, proteins. give w meals. capsule

complications & tx for cholecystitis and cholelithiasis
pancreatitis
abscesses
cholangitis (inflamamtion of bile duct)
rupture of gallbladder

pancreatitis
inflammation of pancreas. causes irreversible damages. severe abdominal pain
can develop diabetes
causes: alcohol, gallbladder disease, cystic fibrosis. ERCP
s: ab pain ulq, vomiting, jaundice, flushing, dyspnea, fever, hypotensive
distended abdomen. absent bowel sounds

complicaitons & dx pancreatitis
psudeocyst, abscess, hypocalcemia
will see elevated levels of everything & higher coagulation time
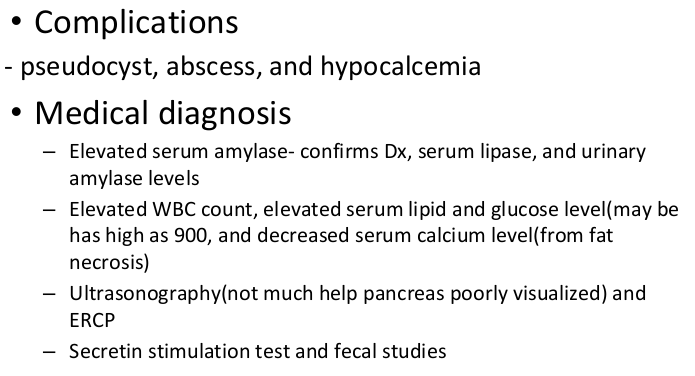
tx pancreatitis
low fat & low sugar diet. enzymes w meals

what is the first sign of rejection for transplant?
fever