Ch. 4 Anatomy Lecture
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Epithelial tissue, connective tissue, and membranes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Tissue
A group of similar cells specialized to perform a specific function
What are the 4 types of tissues?
Epithelial, connective, muscle, and neural tissue
Epithelial tissue location
Cover surfaces
Line cavities
Form glands
Epithelial tissue function
Physical protection
Selective permeability
Secretion
Sensation
Epithelial tissue characteristics
Mainly cells; little extracellular material
Exhibits polarity; consists of apical (free/top) surface and basal (fixed/bottom) surface
Attached to basement membrane
Avascular
Richly innervated
High regeneration
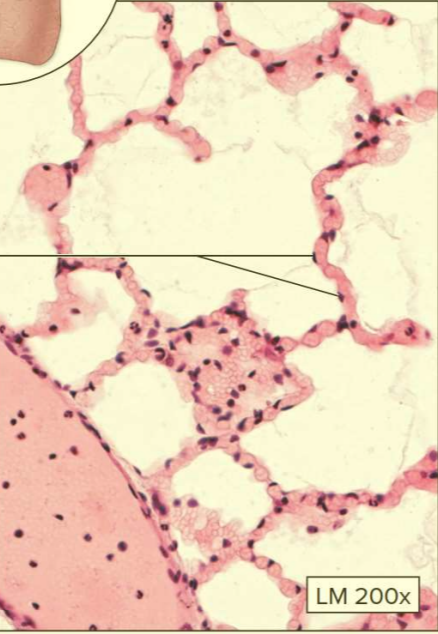
What type of tissue?
Simple squamous epithelium
Function: diffusion and filtration
Location: alveoli, endothelium (lines cardiovascular and lymphatic system), mesothelium (forms serous membranes of body cavities)
Flat and fast!

What type of tissue?
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Function: secretion and absorbtion
Location: kidney tubules; surface of ovaries; thyroid gland follicles; secretory glands (K.O.T.S.)
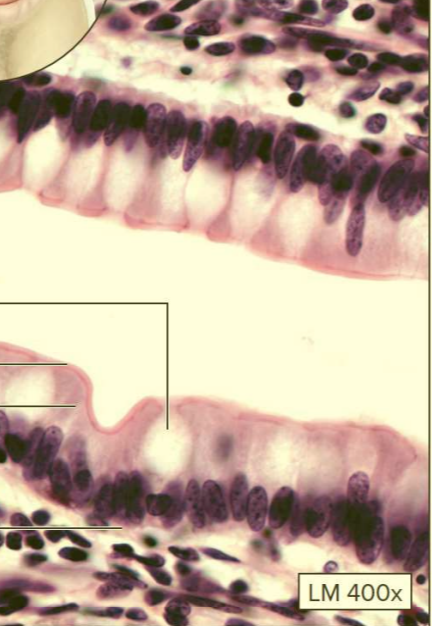
What type of tissue?
Non-ciliated simple columnar epithelium
Function: absorption and mucus secretion
Location: lining of digestive tract
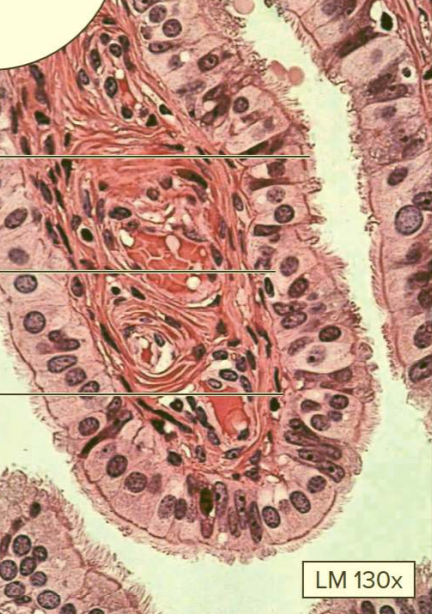
What type of tissue?
Ciliated simple columnar epithelium
Function: movement of mucus and oocytes via cilia
Location: lining of uterine tubes; bronchioles of respiratory tract
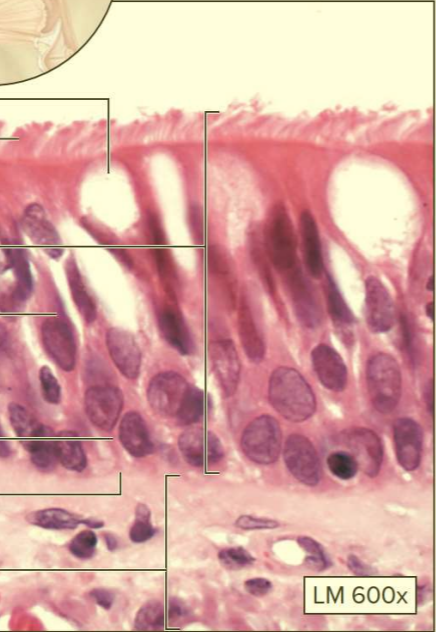
What type of tissue?
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Function: movement of mucus via cilia
Location: lining of respiratory tract
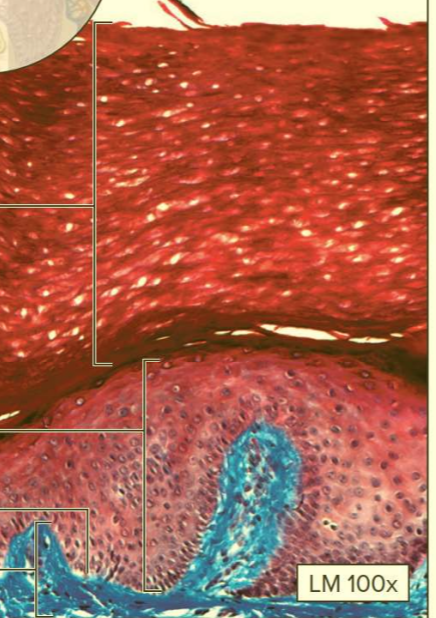
What type of tissue?
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Function: protection of underlying tissue
Location: epidermis of skin
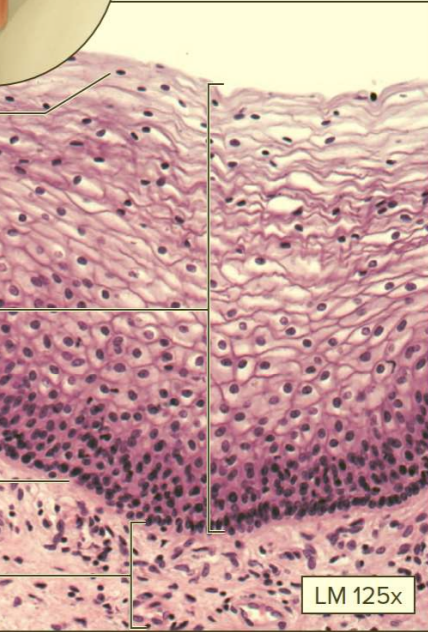
What type of tissue?
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Function: protection of underlying tissue in a moist environment
Location: oral cavity; pharynx; esophagus; anus; vagina
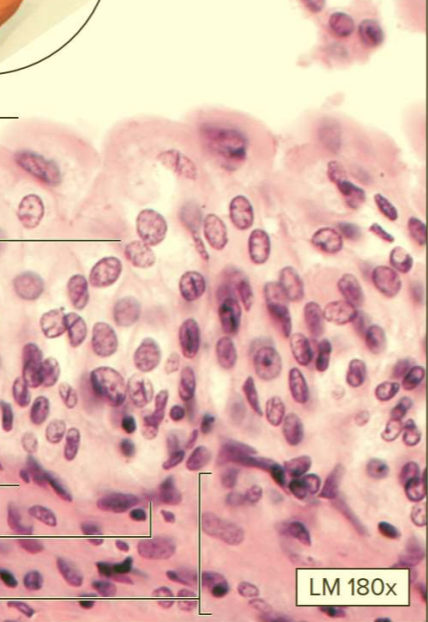
What type of tissue?
Transitional epithelium
Contain binucleated cells
Function: stretches and relaxes to accommodate urine
Location: Lining of urinary bladder, ureters, and urethra
Gland
Epithelial cells that produce a secretion
Exocrine glands
Release secretions via ducts onto the surface of epithelial tissue
Goblet cells
Unicellular exocrine glands
Serous glands
Produce a watery secretion (ex. sweat, milk, tears, and digestive juices)
Mucous glands
Produce a slimy secretion that contains mucin protein
Mixed glands
Produces serous and mucous gland secretions (ex. saliva)
Connective tissues
Function: fill internal spaces; support other tissues; transport materials; store lipids
Characteristics: specialized cells, extracellular protein fibers, and ground substance
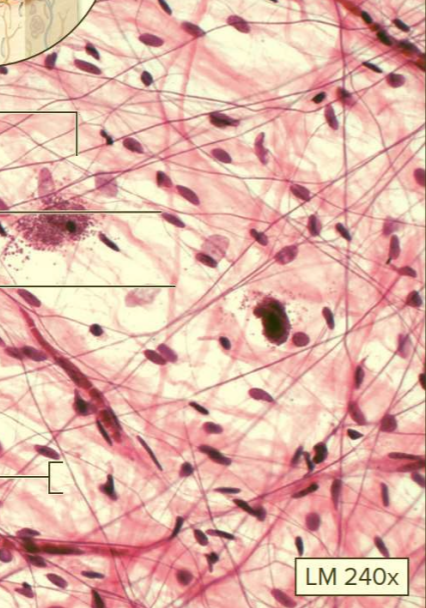
What type of tissue?
Areolar connective tissue
Type of loose connective tissue proper
Contains a variety of cells and fibers
Function: packs around and binds organs
Location: surrounds nerves, vessels, and organs; subcutaneous layer
Areolar = around
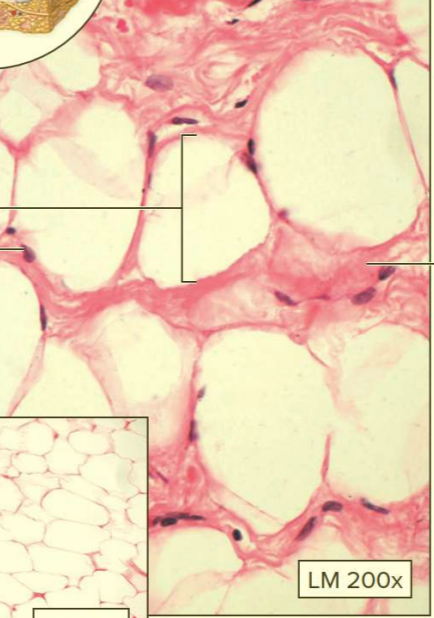
What type of tissue?
Adipose connective tissue proper
A type of loose connective tissue proper
Contains mostly adipocytes
Function: protects; stores fat; insulates
Location: around organs; subcutaneous layer
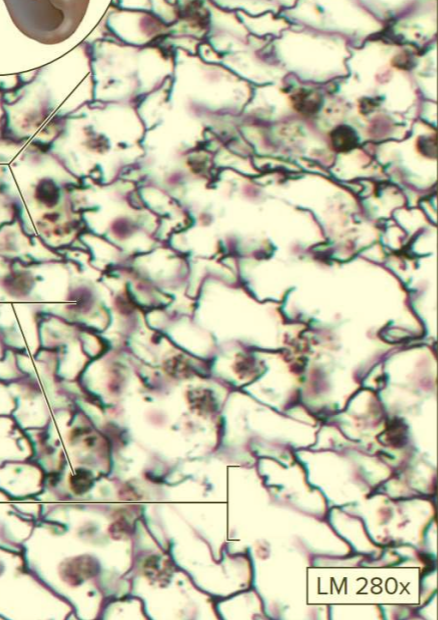
What type of tissue?
Reticular connective tissue proper
A type of loose connective tissue proper
Contains reticular fibers and leukocytes
Function: the framework of delicate organs
Location: organs in the lymphatic system (spleen, thymus, and lymph nodes); bone marrow
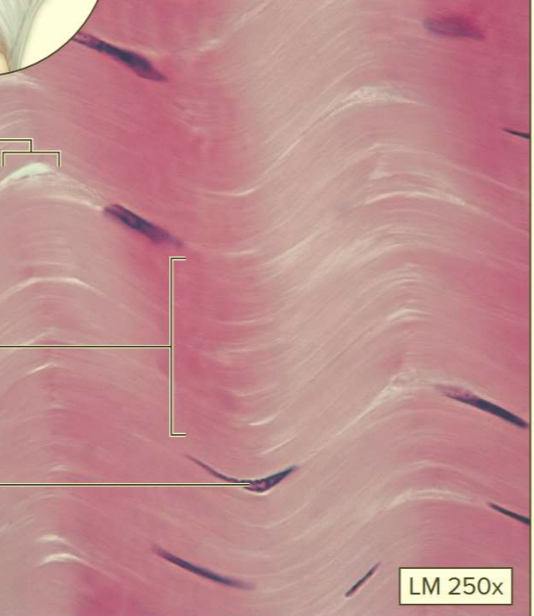
What type of tissue?
Dense regular connective tissue
A type of dense connective tissue proper
Contains mostly collagen fibers
Function: strength and flexibility in one direction
Location: tendons; ligaments

What type of tissue?
Dense irregular connective tissue
A type of dense connective tissue proper
Contains mainly collagen fibers
Function: strength in all directions
Locations: dermis of the skin; capsule of organs
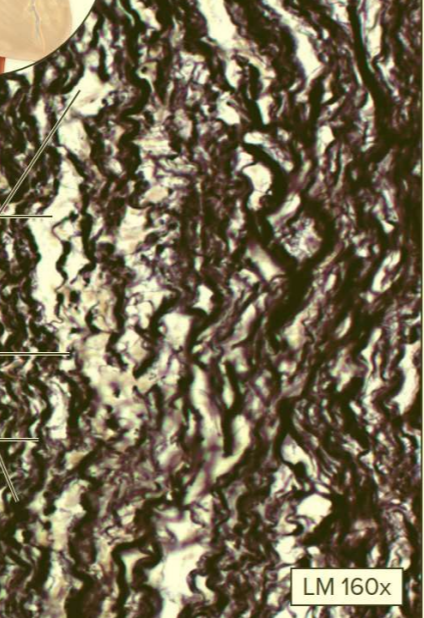
What type of tissue?
Elastic connective tissue
A type of dense connective tissue proper
Contains mainly elastic fibers
Function: allows stretching
Location: elastic connections of vertebral spinous processes; walls of arteries
Fibroblasts
Produce protein fibers and ground substance
Macrophages
Phagocytize foreign materials
Mast cells
Release histamine and heparin to stimulate local inflammation
Plasma cells
Form antibodies
Lymphocytes
Attack foreign materials
Neutrophils
Phagocytizes bacteria
Perichondrium
A layer of dense connective tissue proper that surrounds cartilage
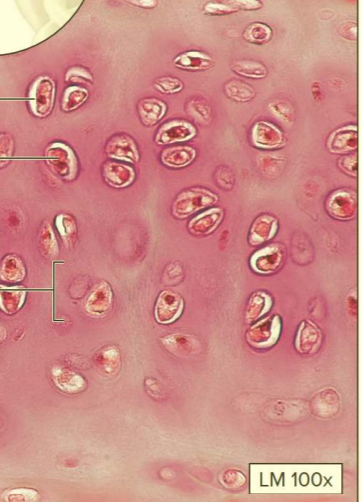
What type of cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage
A type of supporting connective tissue
Contains chondrocytes and dissolved protein fibers
Function: reduces friction; provides flexible support
Location: articular ends of long bones, larynx, trachea, and nose
Air, nose, and ends of bones!
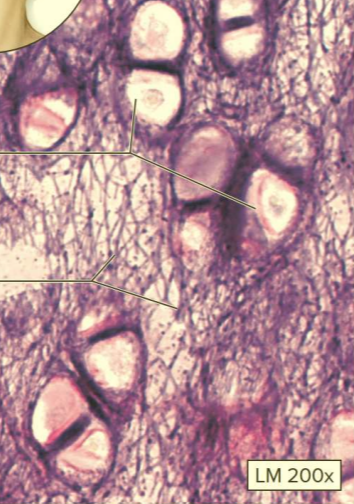
What type of cartilage?
Elastic cartilage
A type of supporting connective tissue
Contains chondrocytes and elastic fibers
Function: allows flexibility
Location: external ear; epiglottis of larynx
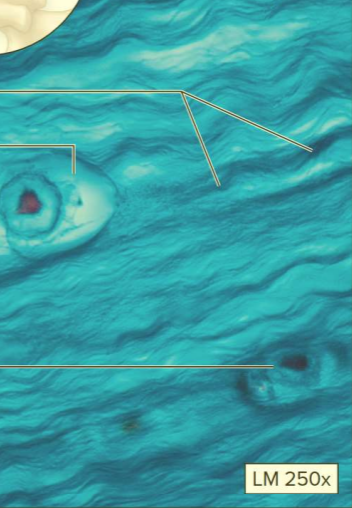
What type of cartilage?
Fibrocartilage
A type of supporting connective tissue
Contains chondrocytes and collagen fibers
Function: resists compression
Location: pads within knee joint; between pubic bones and pelvis; intervertebral discs
Bone
Ground substance is a semi-solid substance that hardens when mineral deposits are added
Contains osteocytes and collagen fibers
Two types: compact and spongy
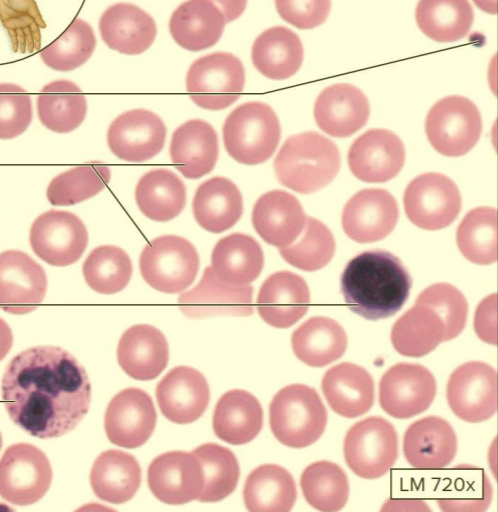
What type of tissue?
Blood
A type of fluid connective tissue
Contains red blood cells, white blood cells, and plasma
Lymph
Fluid connective tissue
Not viewable histologically
Membrane
A combination of epithelial and connective tissues
Serous membrane
Location: line internal body cavities (ex. pleura, pericardium, and peritoneum)
Epithelial cells secretes transudate
A combination of simple squamous epithelium and areolar connective tissue
Mucus membrane
Location: line passageways that open to the outside environment (ex. respiratory, digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts)
Epithelial cells secrete mucus
A combination of simple columnar epithelium or pseudostratified epithelium and areolar connective tissue
Synovial membrane
Location: line joint spaces
Epithelial cells secrete synovial fluid
A combination of areolar, fibrous, and adipose connective tissue; no true epithelium
Cutaneous membranes
Location: the skin
A combination of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium and connective tissue