Stereochemistry
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Isomer Family Tree
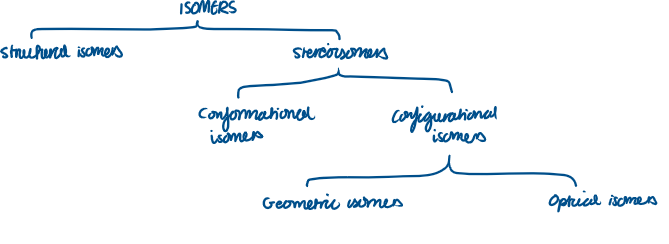
What are structural isomers?
Different compounds having the same molecular formula

What type of isomer is this?
What are their names?
What is it about these type of isomers?
Structural isomers
Butane
2-methylpropane
They are different compounds, so will have different physical properties
What does stereoisomer mean?
Same constitution, same formula, but different spatial arrangement.
Stereoisomers are molecules made of the same atoms joined in the same order, but arranged differently in space.
Structural isomer Vs Stereoisomer
Structural isomer have the same molecular formula, but different connectivity of atoms
Stereoisomer have the same molecular formula and the same connectivity, but different spatial (3D) arrangements of atoms.
So all atoms are connected in the same way, but positioned differently in space.
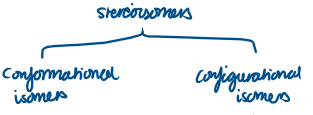
Name the 2 different types of stereoisomers:
Conformational isomers
Configurational isomers
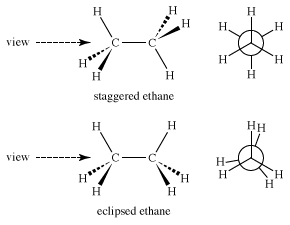
What are conformational isomers?
Conformational isomers are different 3D arrangements of the same molecule caused by rotation about single bonds, not bond breaking.
Different arrangements of atoms from bond rotation (NOT bond breaking)
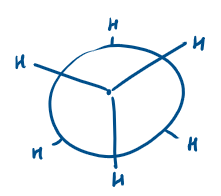
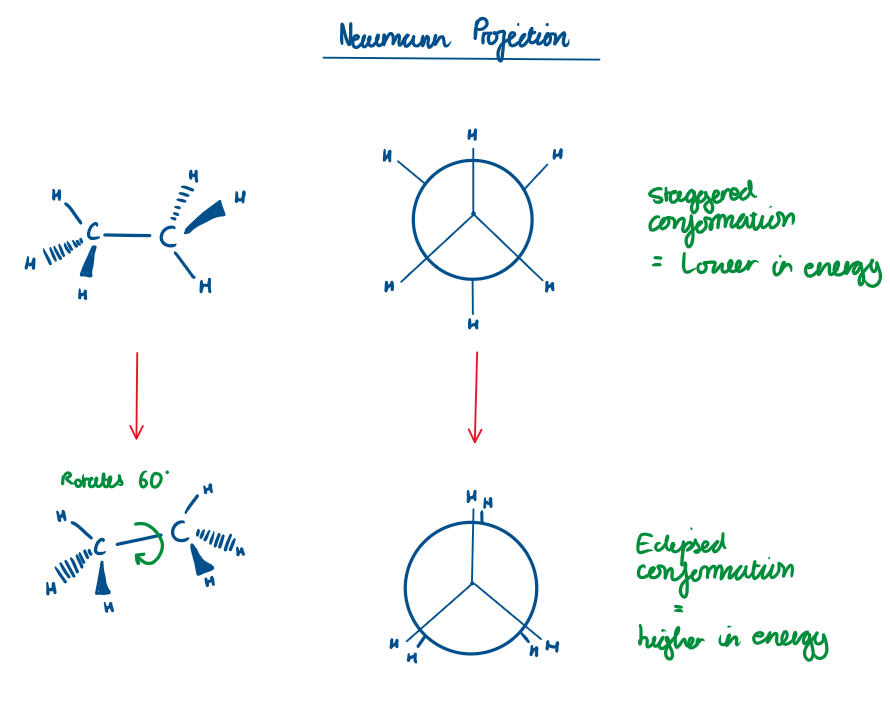
What is a Newman projection?
A Newman projection helps you visualize the conformation of a molecule by looking straight down a C–C bond.
What is this conformation called?
Staggered conformation
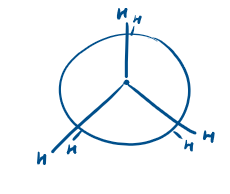
What is this conformation called?
Eclipsed conformation
Conformational Isomers of ethane:
As you rotate around the C-C bond, the molecular passes through staggered conformation (lowest energy) to eclipsed conformation (highest energy because of electron repulsion)
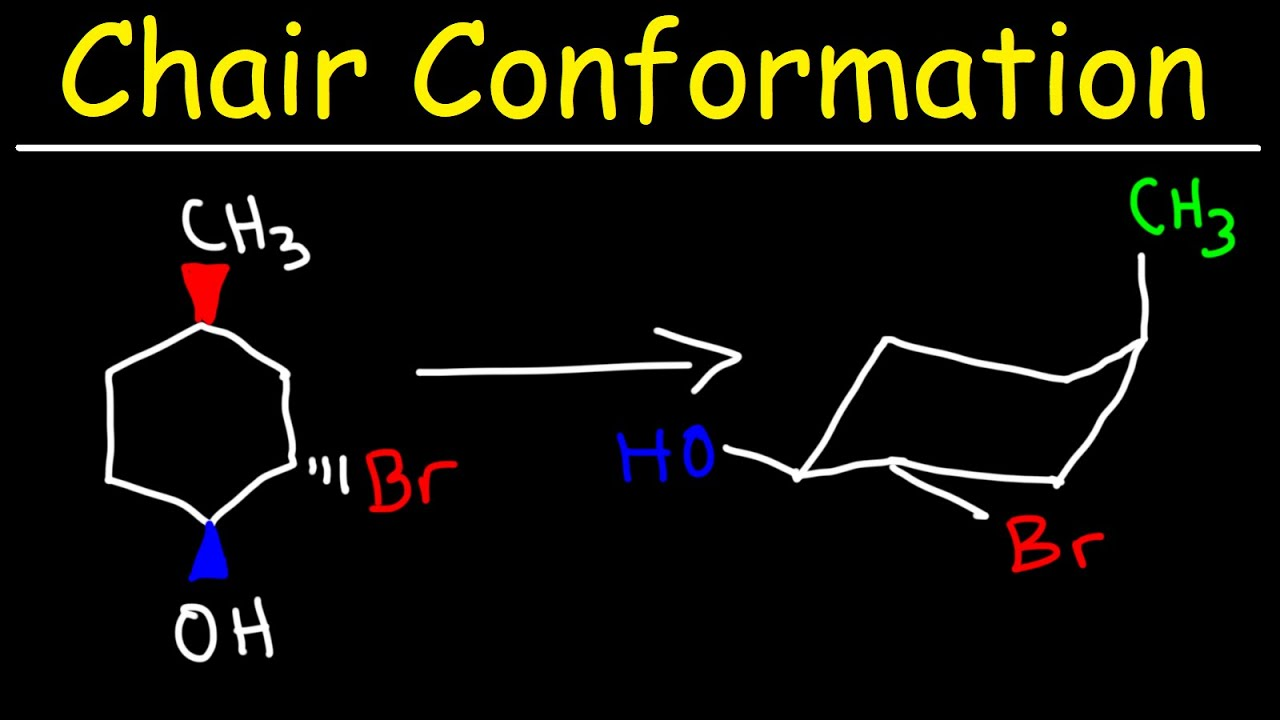
Does cyclohexane experience conformational isomerism?
Yes, the C-C single bonds can rotate and form different conformations
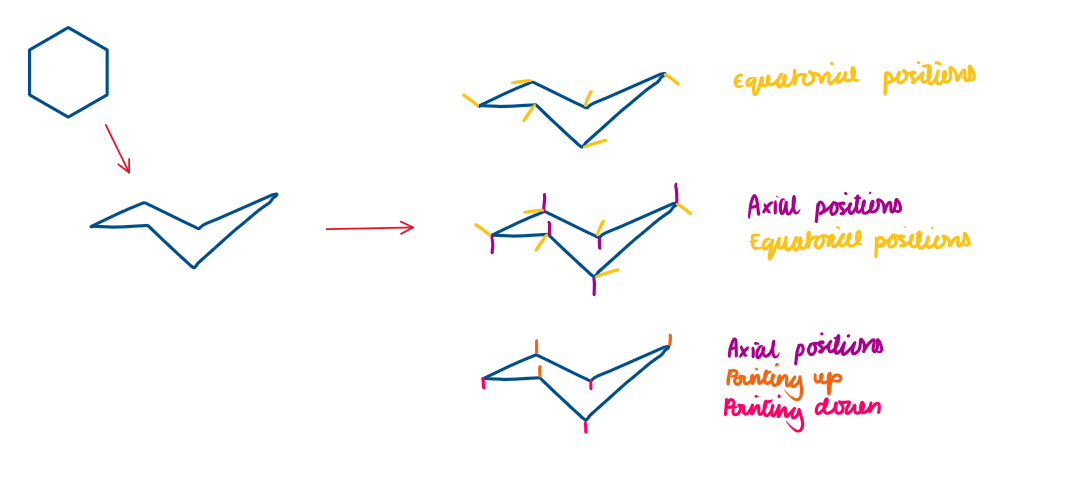
Cyclohexane adopts the chair conformation as it is the most stable and minimises strain
Axial positions in cyclohexane
Axial = H atoms that point up or down, parallel to the ring’s axis
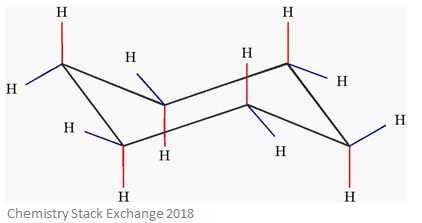
Equatorial positions in cyclohexane
Equatorial = H atoms that point outwards, to the equator of the ring
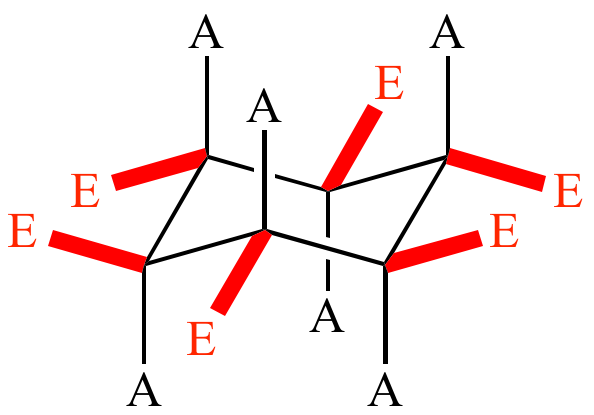
Axial and equatorial positions in cyclohexane
In cyclohexane, each C has 2 types of H atoms
Axial = H atoms that point up or down, parallel to the ring’s axis
Equatorial = H atoms that point outwards, to the equator of the ring
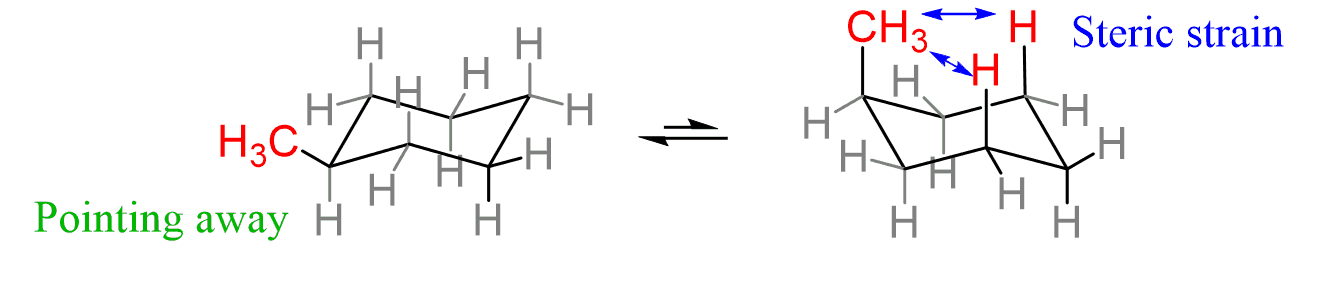
Are axial or equatorial positions more stable?
Equatorial positions are more stable (especially for bulky substituents) because they avoid 1,3-diaxial interactions with axial hydrogens, reducing steric hindrance.
What are 1,3-diaxial interactions?
These are repulsions between the axial substituent on C1 and the two other axial hydrogens (or groups) on C3 and C5, both on the same side of the ring.
It’s like two groups bumping into each other in a crowded space.
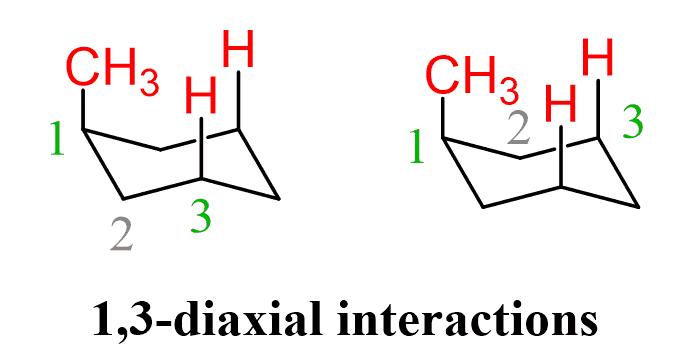
Which is higher in energy, axial or equatorial positions?
Axial positions
Axial substituents experience steric strain, specifically called 1,3-diaxial interactions.
In contrast, an equatorial substituent points outwards and avoids those clashes, so it’s more stable (lower energy).
Name the 2 different types of configurational isomers:
Geometric isomers
Optical isomers
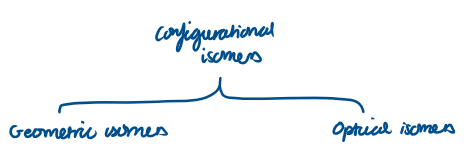
Geometric isomers
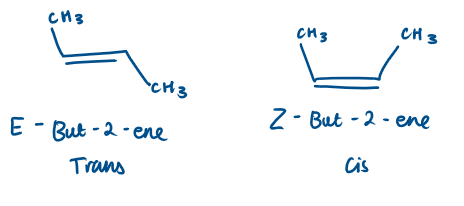
Can be classed as E/Z or cis/trans

Name these geometric isomers
What makes a molecule chiral?
If it does not have a plane of symmetry within
What is the only achiral amino acid?
Glycine
What are enantiomers?
Pairs of molecules that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other
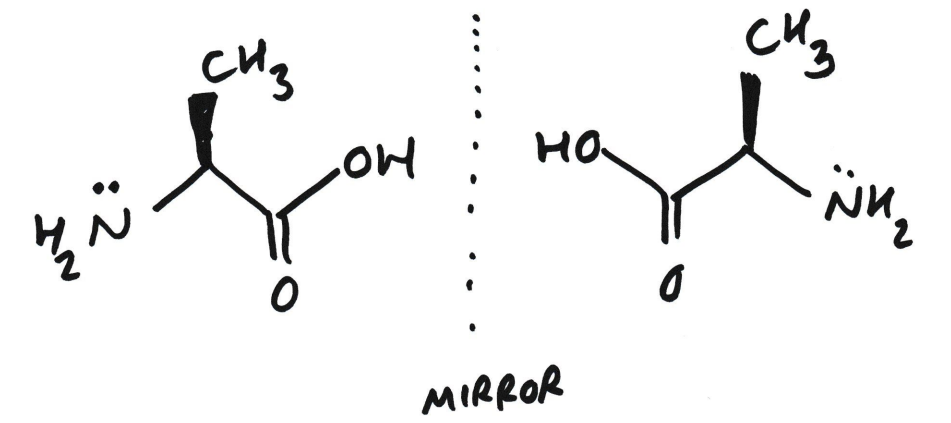
What is this also known as?
Non superimposable enantiomers
Enantiomers have identical physical properties, like mp, bp, and NMR. However….
….enantiomers rotate PPL in equal but opposite directions
What does PPL stand for?
Plane Polarised Light
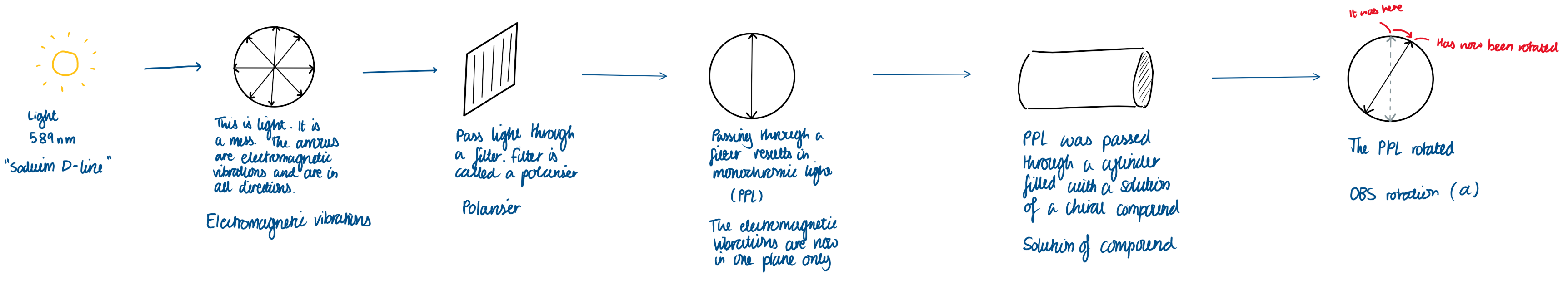
Light has electromagnetic vibrations in all directions.
Light is passed through a filter called a polariser.
This results in monochromic light (PPL).
The electromagnetic vibrations are now in one plane only.
PPL was passed through a cylinder filled with a solution of a chiral compound.
The PPL rotates.
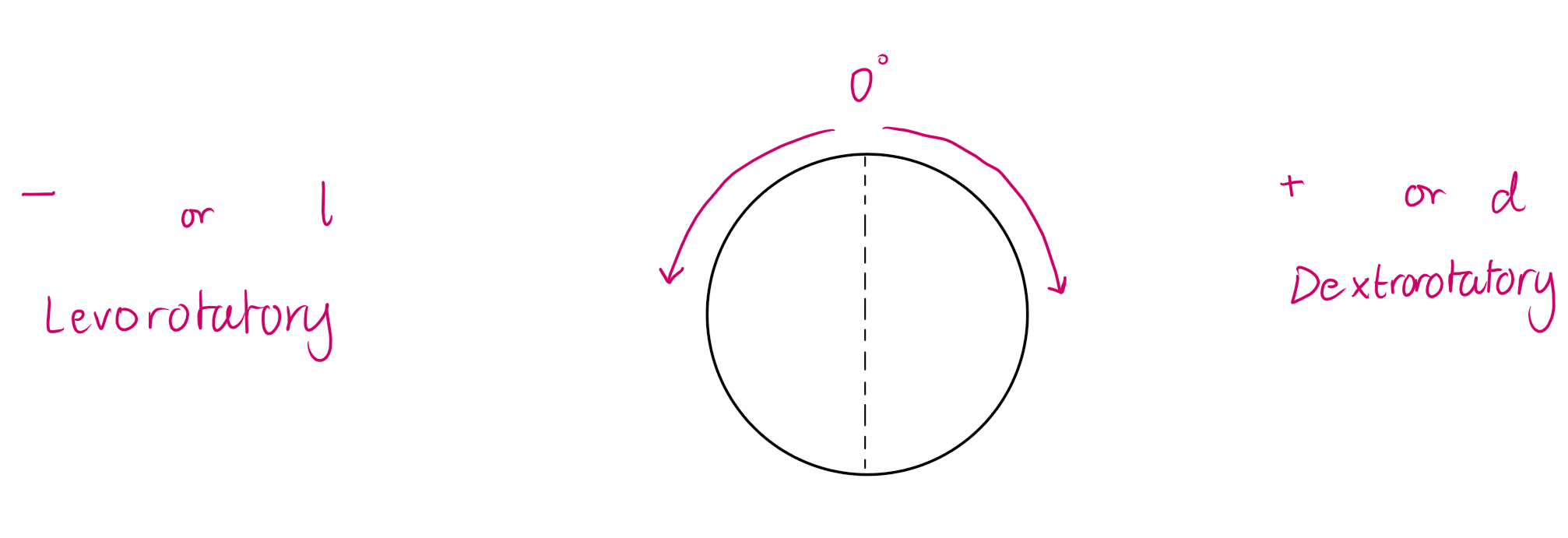
If the PPL rotates - or +, what is that called?
- is levorotatory
+ is dextrorotatory
![<p>How do you calculate the [α]<sup>20</sup><sub>D</sub></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/30a84793-5e61-4030-ab51-226aa35a81b1.png)
How do you calculate the [α]20D

What is the [α]20D of achiral compounds?
[α]20D = 0
This is because passing an achiral compound through a cylinder results in no rotation - achiral compounds don’t rotate in PPL.
![<p>[α]<sup>20</sup><sub>D </sub>=<sub> </sub>0</p><p>This is because passing an achiral compound through a cylinder results in no rotation - achiral compounds don’t rotate in PPL.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6d3c8923-02b1-48b7-bc59-229fa5c64fe1.png)
What’s a racemic mixture?
An equal mix of opposite enantiomers in a 50:50 proportion
What is the [α]20D of a racemic mixture?
[α]20D = 0
This is because the enantiomers will rotate in equal but opposite directions.
One is dextrorotatory (+) → Rotates light clockwise
One is levorotatory (-) → Rotates light anticlockwise
They’re in equal proportion, so their optical rotation cancel each other out exactly
![<p>[α]<sup>20</sup><sub>D </sub>=<sub> </sub>0</p><p>This is because the enantiomers will rotate in equal but opposite directions.</p><p>One is dextrorotatory (+) → Rotates light clockwise</p><p>One is levorotatory (-) → Rotates light anticlockwise</p><p>They’re in equal proportion, so their optical rotation cancel each other out exactly</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c29aa948-e5dd-45e9-9353-936c0a2a7af0.png)
Is a compound with a negative OBS the -ve enantiomers?
Yes but we cannot decipher whether it is the R or S enantiomer without more information
Exam Q)
1.2g of cocaine in 7.5mls CHCl3 sample tube
OBS: 5cm
Rotation: -1.3°
What is the [α]20D = ?
cm → dm
5cm → 0.5dm
1.2g in 7.5ml
0.16 g/ml
(-1.3)/(0.5 × 0.16) = -16
One of the pure enantiomers is -16

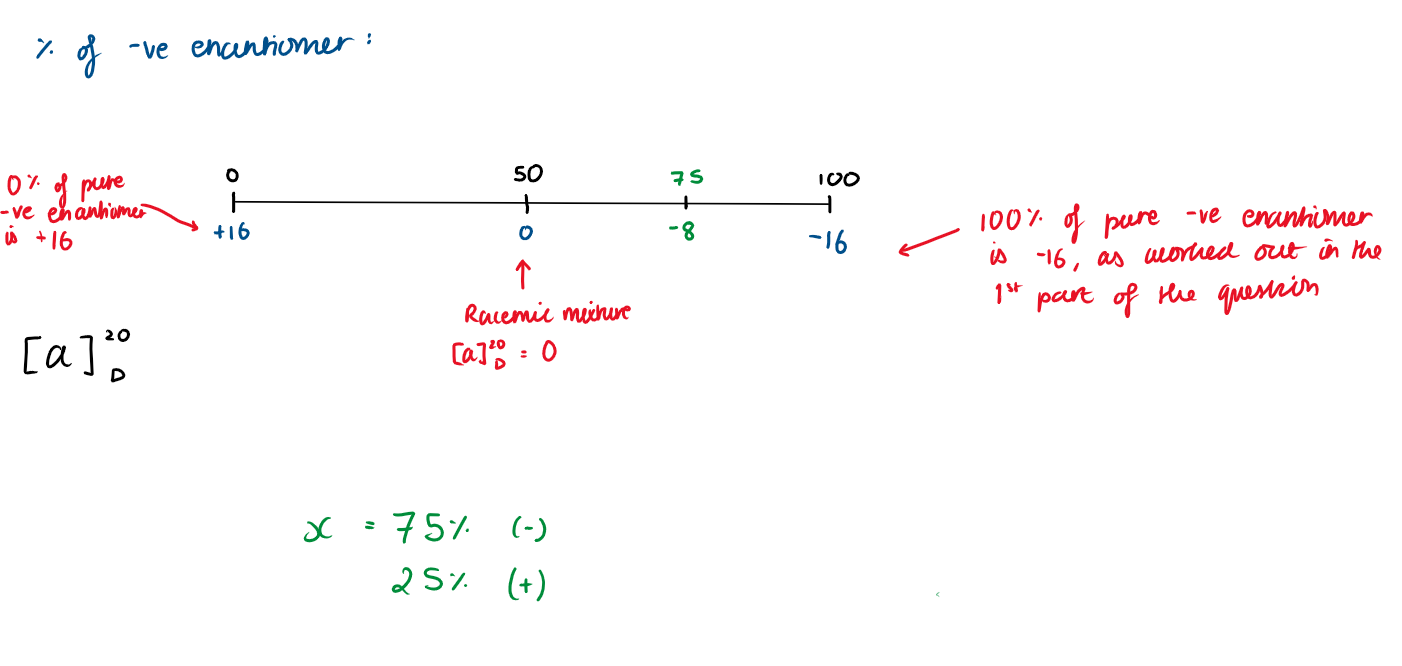
What is the mixture of a sample with [α]20D = -8°
100% of the pure -ve enantiomer is -16 (we calculated earlier)
That means 0% of the -ve enantiomer is +16
50% is the racemic mixture, so it is 0.
-8 therefore equals to 75%
75% is the -ve enantiomer
25% is the +ve enantiomer
What is enantiomer excess (ee)?
The excess of one enantiomer over another
How to calculate enantiomer excess (ee)?
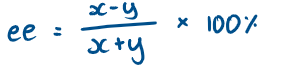
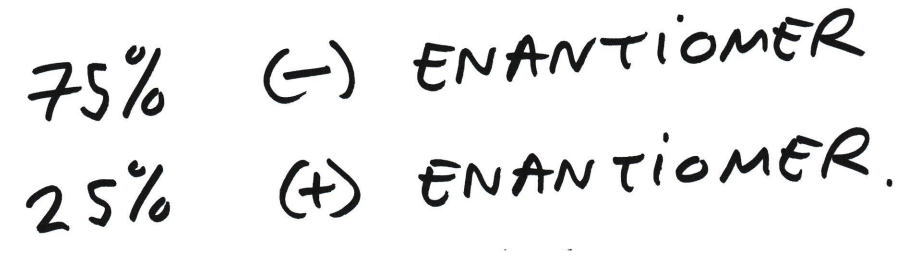
Calculate the ee
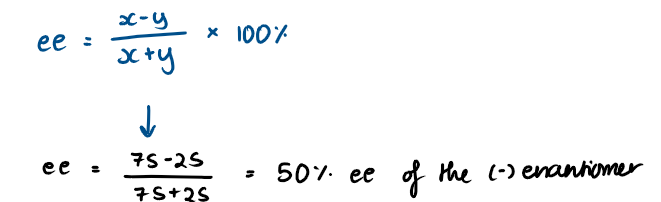
Molecules are chiral, centres are….
stereogenic
R
Clockwise
S
Anticlockwise
You use CIP rules to work out if an enantiomer is R or S. What are the rules?
Assign priority according to atomic number
If a decision cannot be made with the 1st set of atoms, apply to the 2nd set of atoms, and so forth
Double bonds count as 2 σ bonds to 2 same atoms. Same for triple
Lone pair counts as zero
Orientate the 4th (lowest priority) at the back and follow the sequence
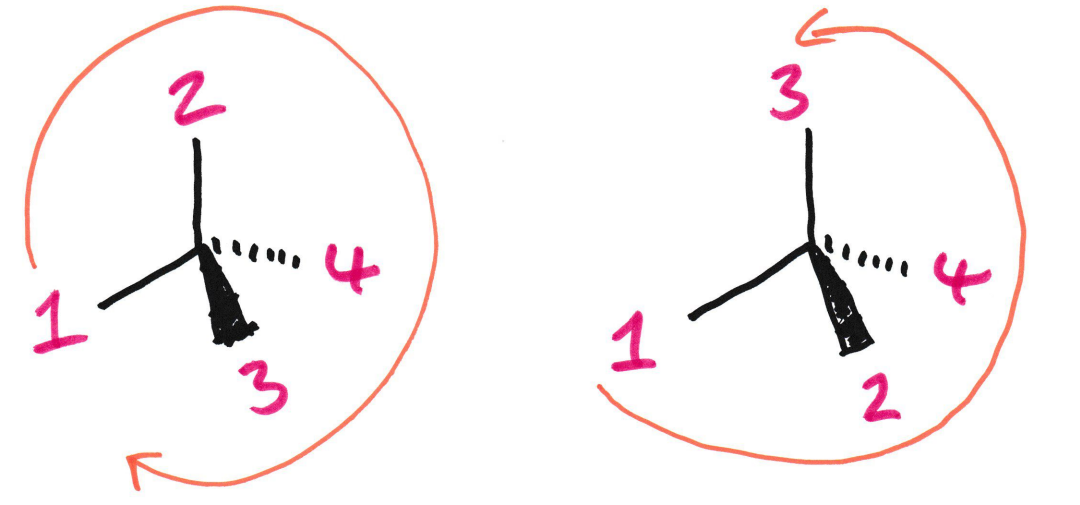
Is Alanine an R or S enantiomer?
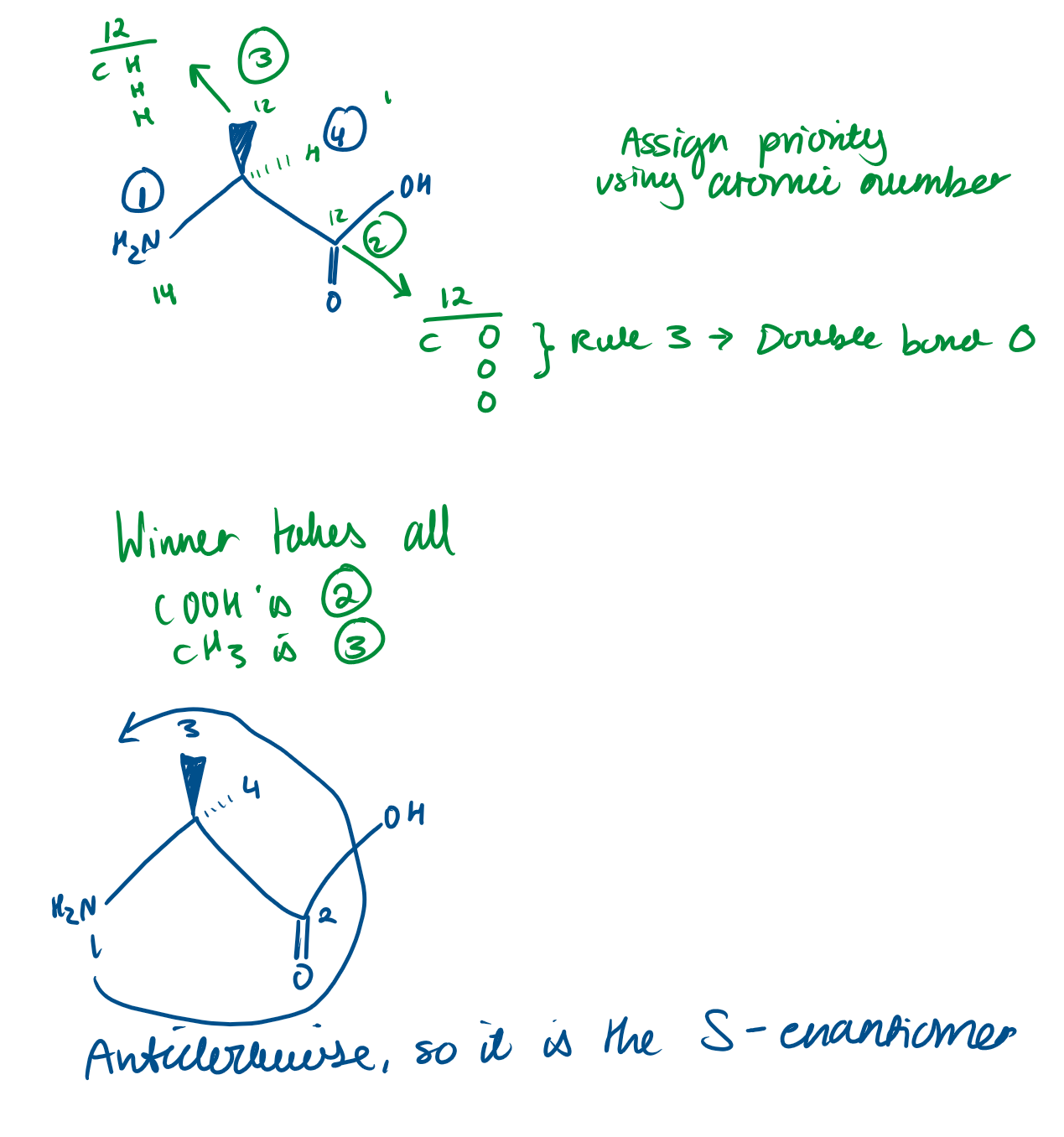
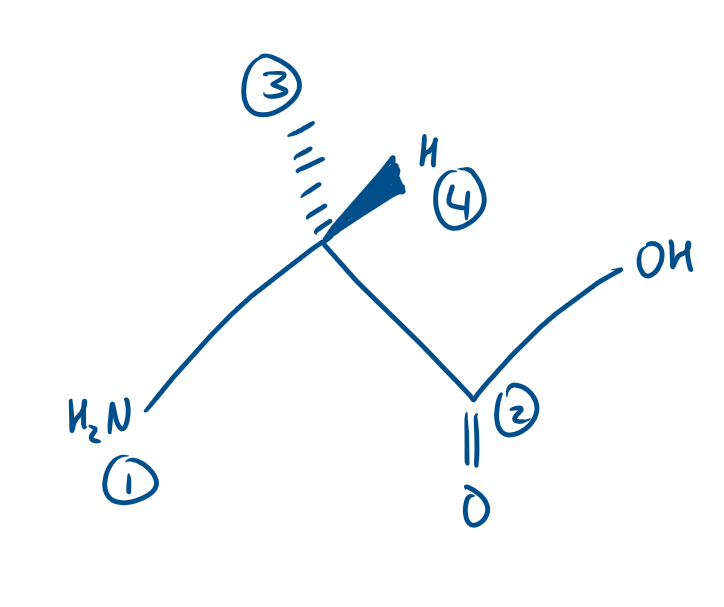
Here H is at the front. Isn’t Alanine still an S enantiomer here?
No because we need to flip it
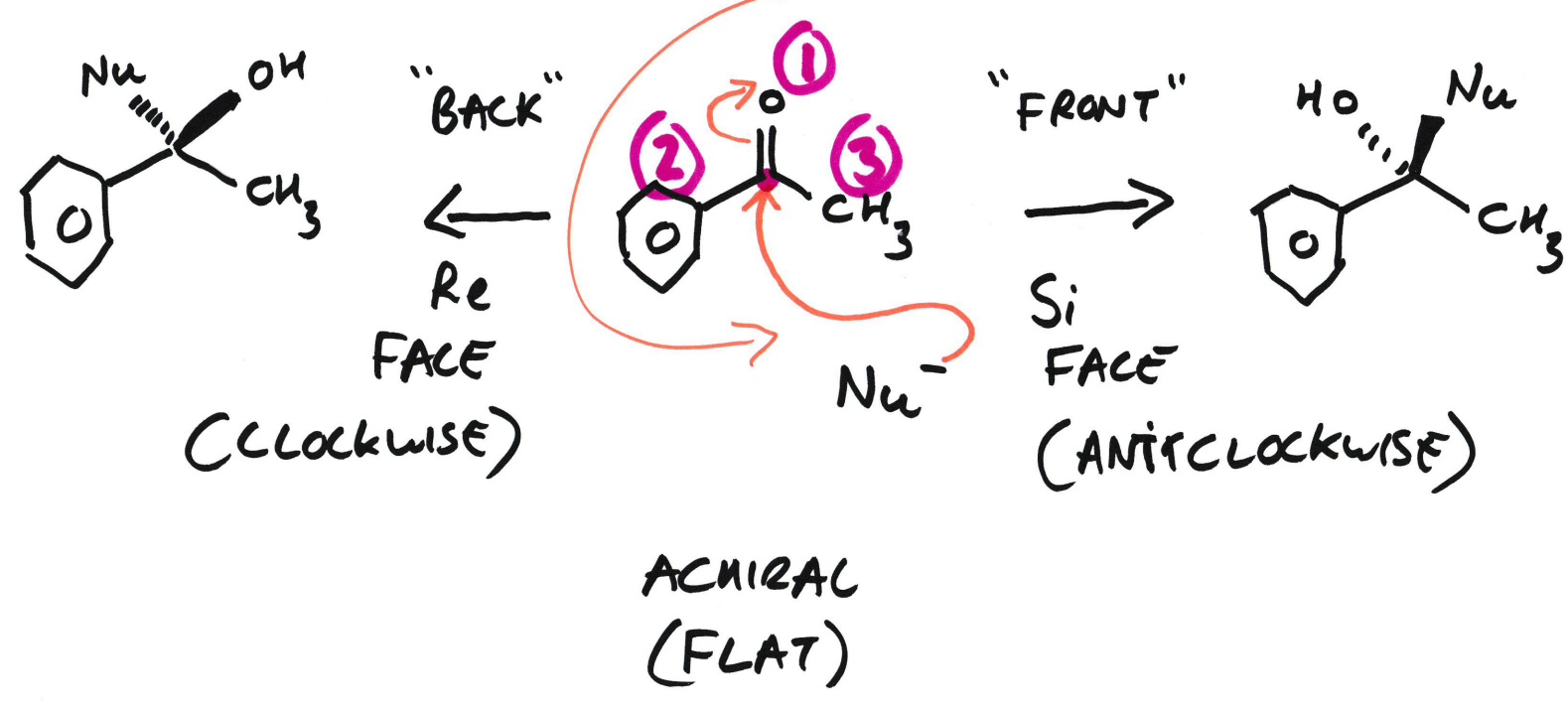
What’s the difference between R/S configurations and Re/Si faces?
R/S configurations = Chiral centres
R/S is used when the atom is already chiral, and CIP rules are used to assign them. R/S is a fixed property of a molecule’s 3D structure
Re/Si faces = Chiral faces
Re/Si is used when the atom is not chiral yet, but could become chiral after a reaction.
Example of Re/Si face
The Nu- could attack from front or behind and this would change which face it is, whether Re or Si.
What does racemisation mean?
The process of making a racemic mixture
What is a Diastereoisomers?
A stereoisomer that is not a mirror image of another
They differ in 3D arrangement at one or more (but not all) stereogenic centres and have different physical/chemical properties.
What’s the difference between diastereoisomer and an enantiomer?


When diasteroisomers differ at only one stereogenic centre, what is it called?
Epimers
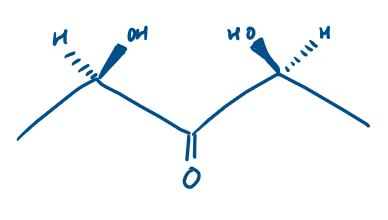
Is this chiral or achiral?
Achiral as there is a plane of symmetry down the centre, though it contains 2 stereogenic centres
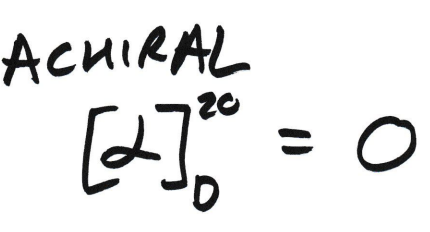
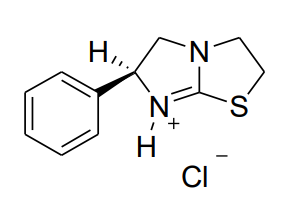
Does this have R or S stereochemical configuration?
S