AP Psychology Unit 1.1 Vocab
1/201
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
202 Terms
nature-nurture issue
longstanding controversy over the relative contributions that genes and experience make to the development of psychological traits and behaviors
evolutionary psychology
study of the evolution of behavior and the mind, using principles of natural selection
behavior genetics
study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on behavior
environment
every non-genetic influence, from prenatal nutrition to our experiences of the people and things around us
genome
complete instructions for making an organism
interaction
interplay that occurs when the effect of one factor (such as environment) depends on another factor (such as hereditary)
epigenetics
study of the molecular mechanisms by which environments can influence genetic expression (without DNA change)
adverse childhood experiences (ACEs)
traumatic events that happen between the ages of one and seventeen that affect the child’s brain and health
central nervous system (CNS)
body’s decision maker (brain and spinal cord)
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
sensory and motor neurons that connect the CNS to the rest of the body
sensory (afferent) neurons
neurons that carry incoming information from the body’s tissues and sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
motor (efferent) neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord; they communicate internally and process information between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
somatic nervous system (skeletal nervous system)
division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body’s skeletal muscles
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and muscles of the internal organs (such as the nerves)
sympathetic nervous system
division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy
parasympathetic nervous system
division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
dendrites
neuron’s often bushy, branching extensions that receive and integrate messages, conducting impulses toward the cell body
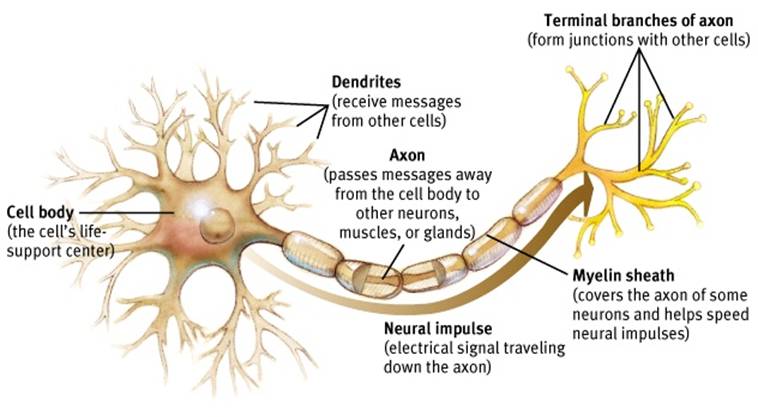
axon
segmented neuron extension that passes messages through its branches to other neurons or to muscles or glands
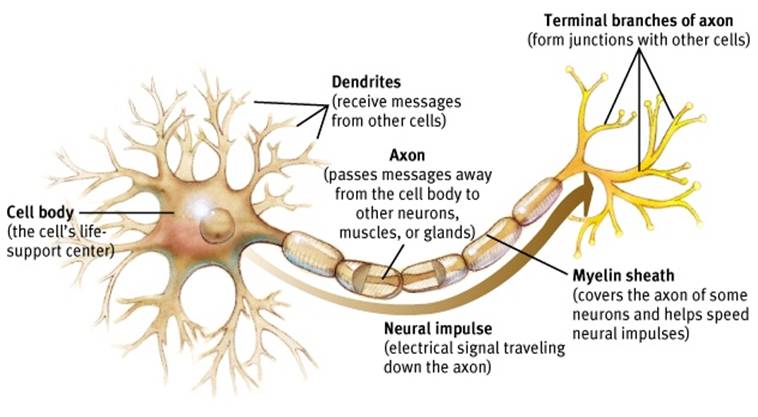
myelin sheath
fatty tissue layer segmentally encasing the axons of some neurons; it enables vastly greater transmission speed as neural impulses hop from one node to the next
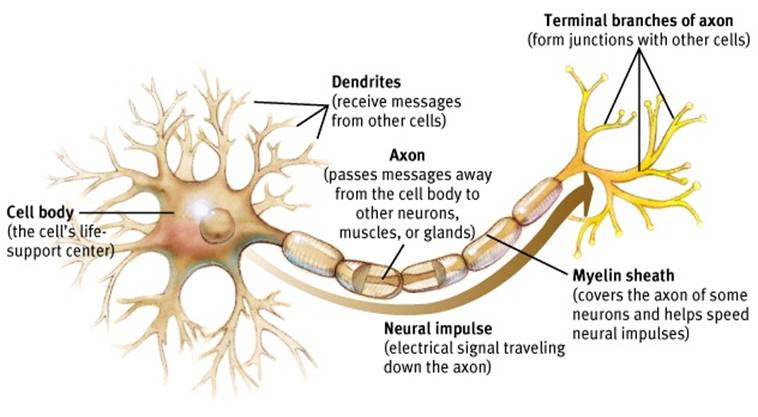
glial cells
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons; they may also play a role in learning, thinking, and memory
action potential
brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
threshold
level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
refractory period
brief resting pause that occurs after a neuron has fired; subsequent action potentials cannot occur until the axon returns to its resting state
all-or-none response (all-or-nothing principle)
neuron’s reaction of either firing
synapse
junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
reuptake
neurotransmitter’s reabsorption by the sending neuron
acetycholine (ACh)
enables muscle action, learning, and memory
ex of malfunctions: with Alzheimer’s disease, ACh-producing neurons deteriote
dopamine
influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion
ex of malfunctions: oversupply = schizophrenia, undersupply = tremors and decreases mobility in Parkinson’s disease
serotonin
affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
ex of malfunctions: undersupply = depression, oversupply = hep with depression
norepinephrine
helps control alertness and arousal
ex of malfunctions: undersupply can depress mood
gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
major inhibitory neurotransmitter
ex of malfunctions: undersupply = seizures, tremors, and insomia
glutamate
major excitatory neurotransmitter, involved in memory
ex of malfunctions: oversupply = overstimulate the brain producing migraines or seizures
endorphins
neurotransmitters that influence the perception of pain or pleasure
ex of malfunctions: oversupply with opioid drugs can suppress the body’s natural endorphin supply
substance P
involved in pain perception and immune response
ex of malfunctions: oversupply = chronic pain
agonist
molecule that increases a neurotransmitter’s action
antagonist
molecule that inhibits or blocks a neurotransmitter’s action
endocrine system
body’s “slow” chemical communication system; a set of glands and fat tissue that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
reflex
involuntary and nearly instantaneous movement in response to a stimulus
reflex arc
controls a reflex
psychoactive drugs
chemical substance that alters the brain, causing changes in perceptions and moods
substance use disorder
disorder characterized by continued substance use despite resulting life disruption
tolerance
diminishing effect with regular use of the same dose, requiring the user to take larger and larger doses before experiencing the drug’s effect
depressants
drugs that reduce neural activity and slow body functions
barbiturates
drugs that depress the CNS activity, reducing activity but impairing memory and judgement
opioids
depress neural activity, temporarily lessening pain and anxiety
hallucigens
psychedelic drugs that distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input
near-death experience
altered state of consciousness
excitatory
neurotransmitters that increases the likelihood of neuron firing
inhibitory
neurotransmitters that decrease the likelihood of neuron firing
neuroplasticity
brain’s ability to change, especially during childhood, by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience
lesion
tissue destruction
electroencephalogram (EEG)
amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity sweeping across the brain’s surface
magnetoencephalography (MEG)
brain-imaging technique that measures fields from the brain’s natural electrical activity
position emission tomography (PET)
technique for detecting brain activity that displays where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task
functional MRI (fMRI)
technique for revealing blood flow, and therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans
hindbrain (medulla, pons, and cerebellum)
directs essential survival functions (e.g. breathing, sleeping, wakefullness, coordination, and balance)
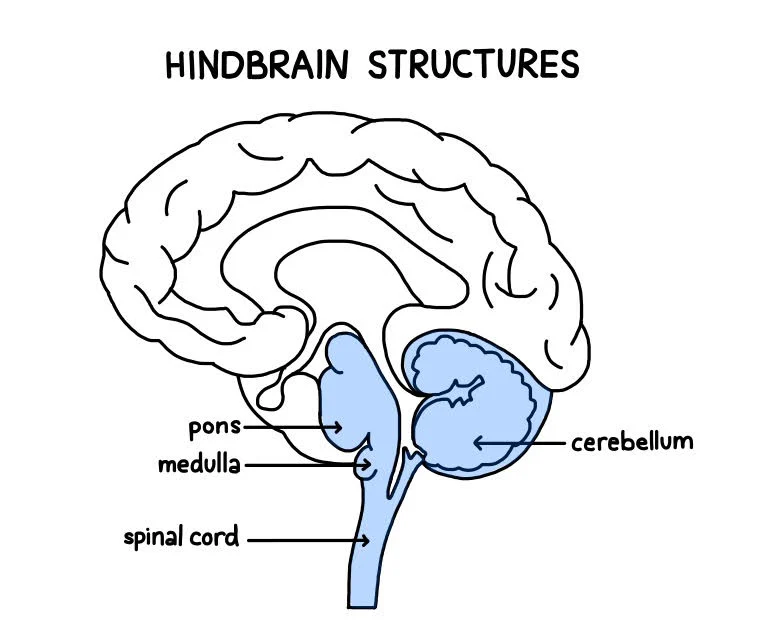
midbrain (atop the brainstem)
connects the hindbrain with forebrain (controls some motor movement, transmits auditory and visual information)
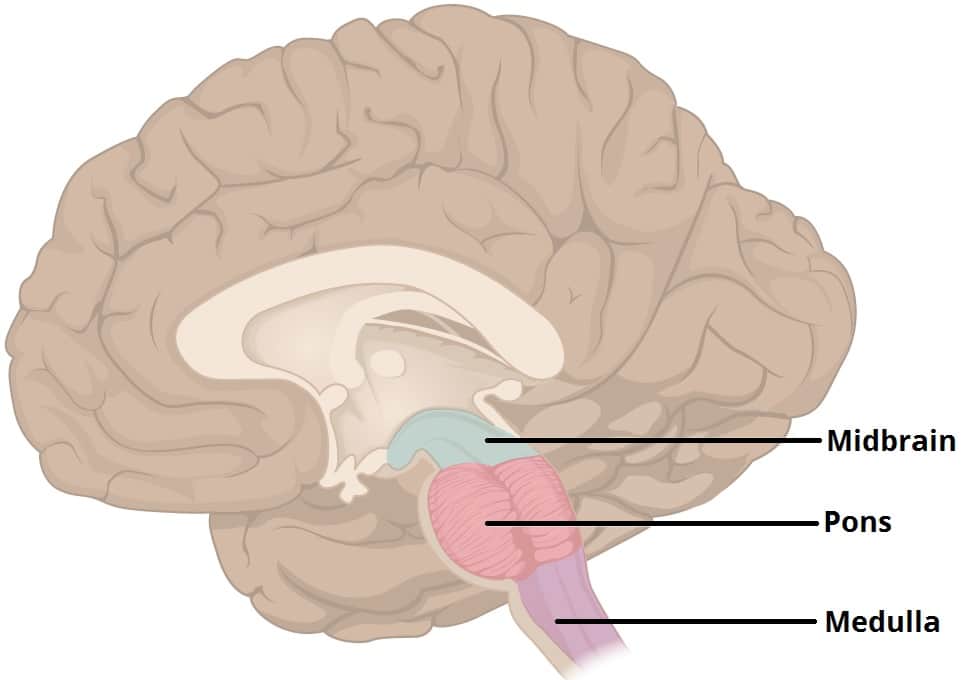
forebrain (cerebral cortex, thalamus, and hypothalamus)
manages complex cognitive activities, sensory and associative functions, and voluntary motor activities
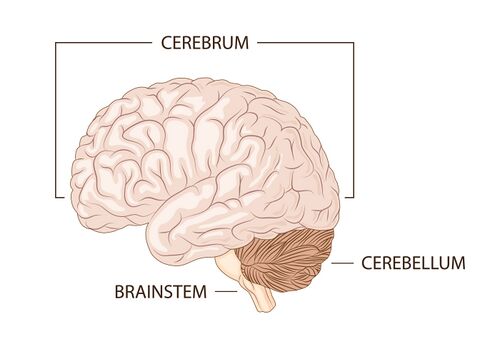
brainstem
central core of the brain; responsible for automatic survival functions
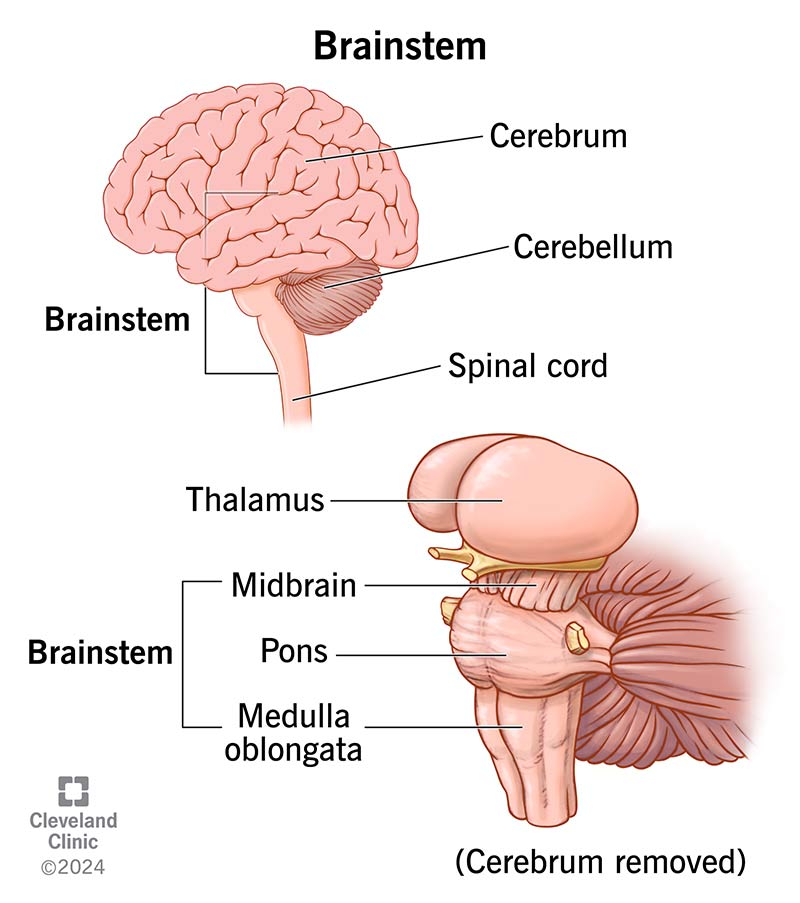
medulla
controls heartbeat and breathing
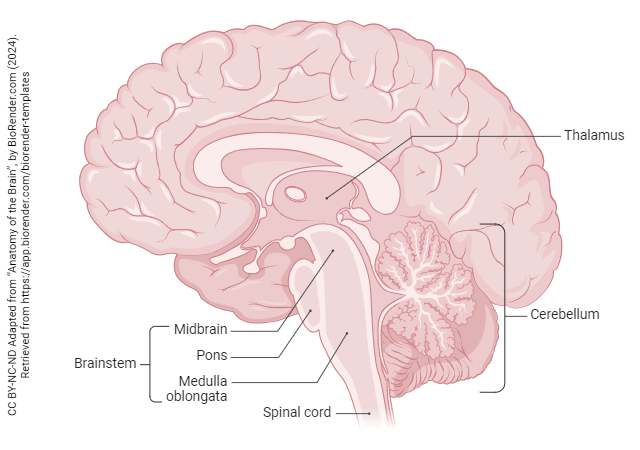
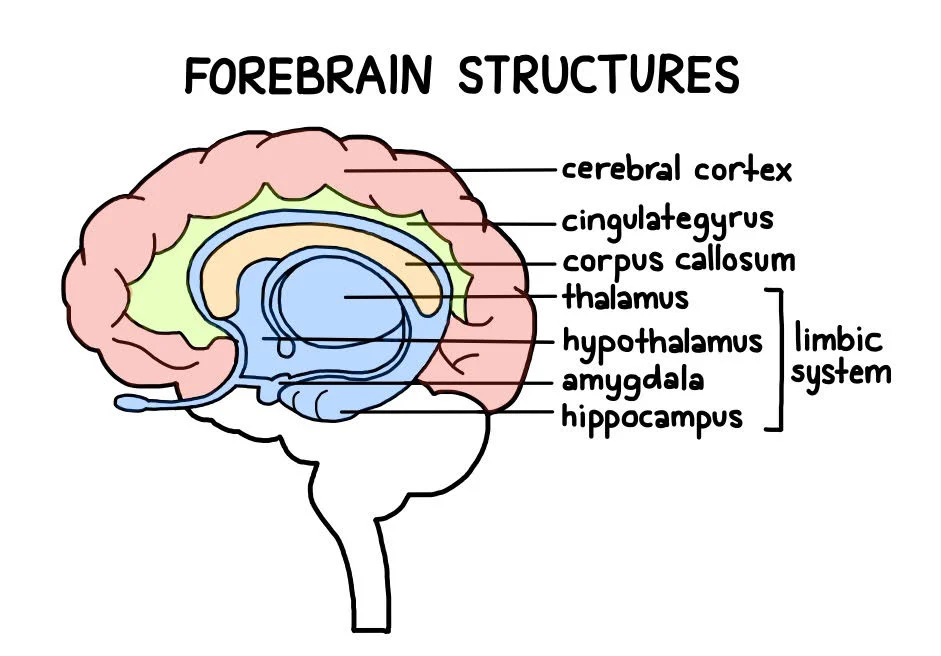
thalamus
forebrain’s sensory control center; directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
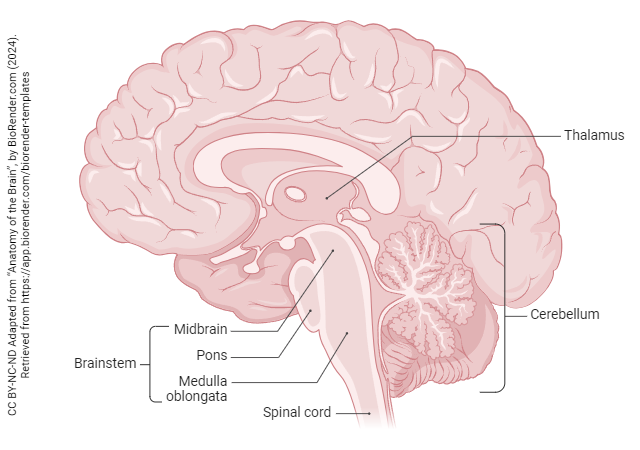
reticular formation
nerve network that travels through the brainstem into the thalamus; filters information and plays an important role in controlling arousal
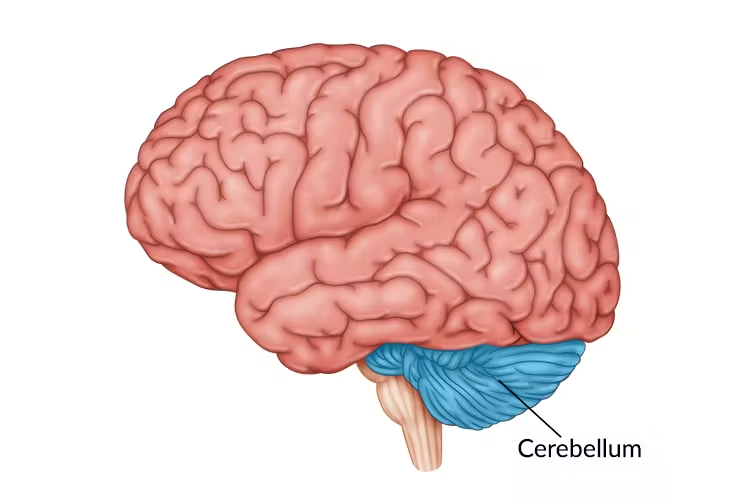
cerebellum
processes sensory input, coordinates movement output and balance, and enables nonverbal learning and memory
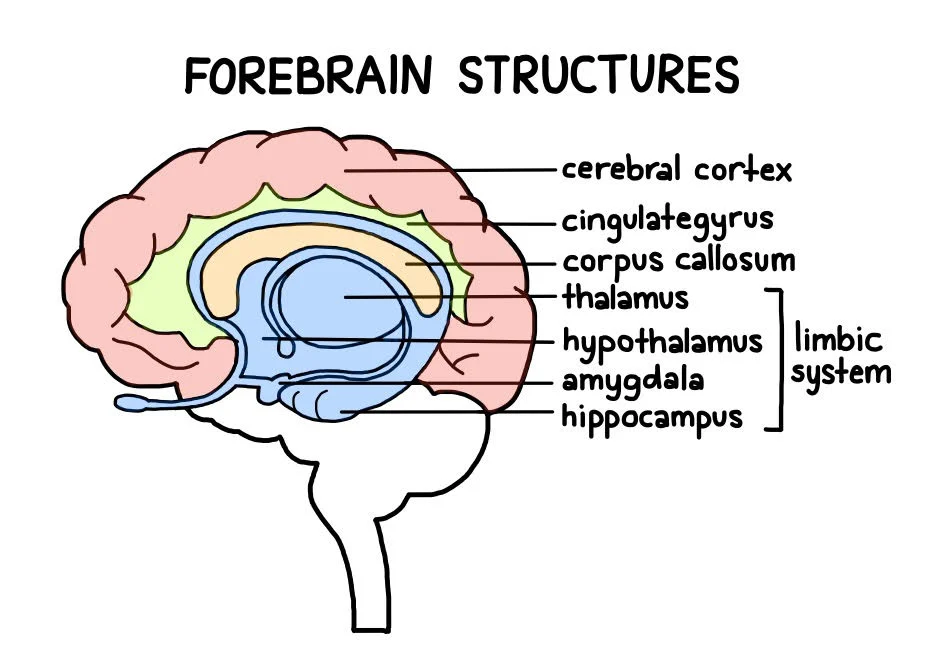
limbic system
neural system located mostly in the forebrain that includes the amygdala, hypothalamus, hippocampus, thalamus, and pituitary gland; associated with emotions and drives
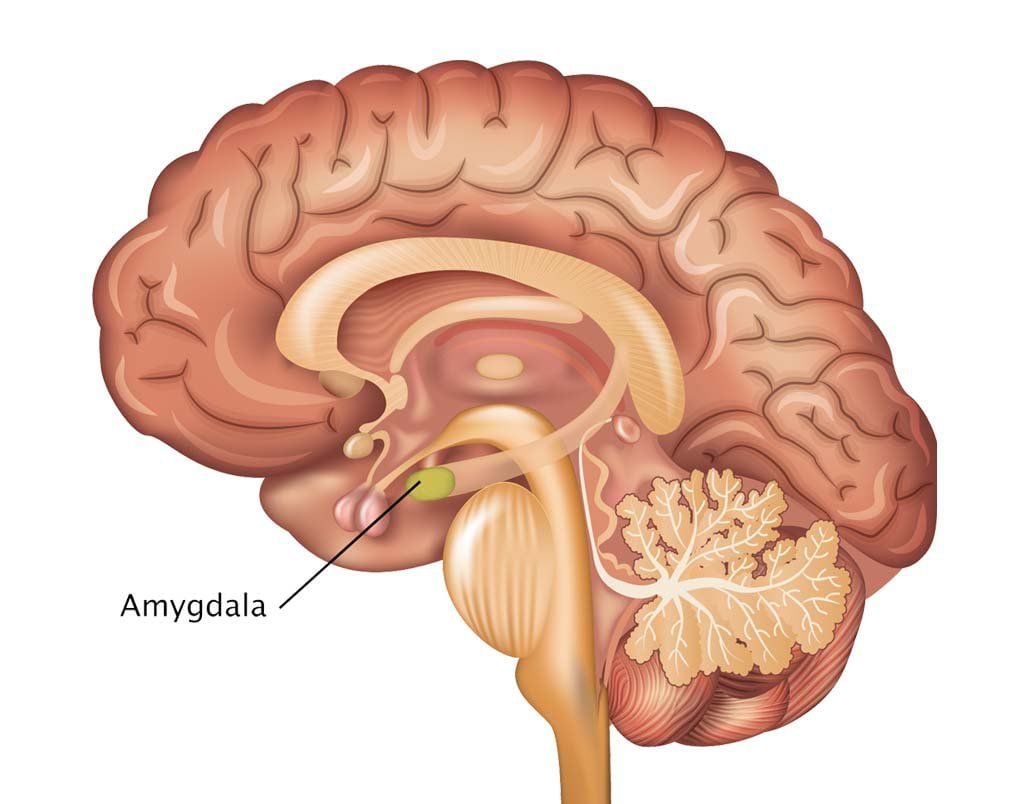
amygdala
two lima-bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion
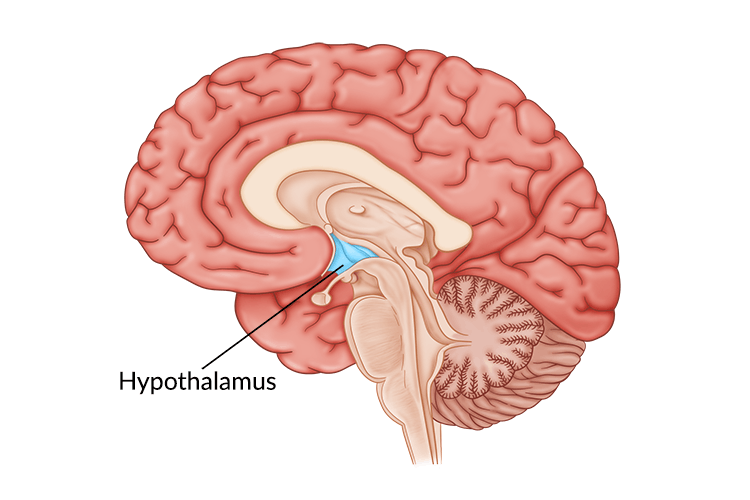
hypothalamus
directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temp), helps govern the endocrine system and is linked to emotion and reward
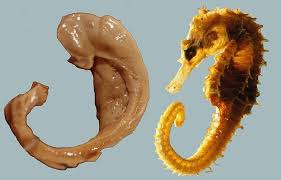
hippocampus
neural center in the limbic system that helps process explicit (conscious) memories for storage
cerebral cortex
intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the forebrain’s cerebral hemispheres; body’s ultimate control and information processing center
frontal lobes
enables linguistic processing, muscles movements, higher order thinking, and executive functioning
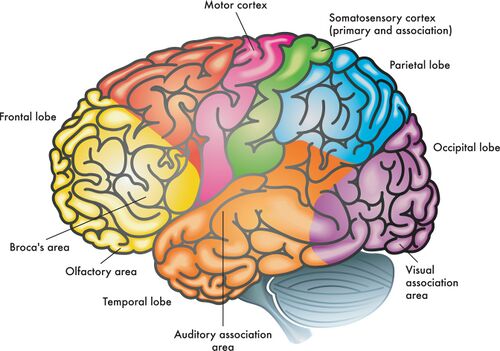
parietal lobes
receives sensory input for touch and body position
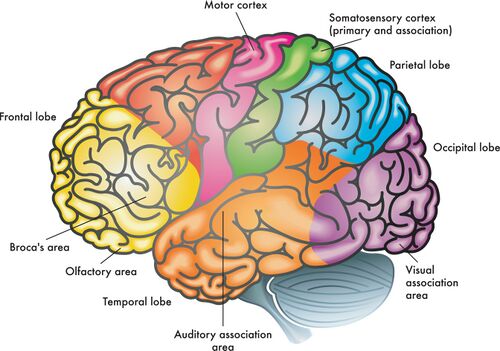
occipital lobes
receives information from the visual fields
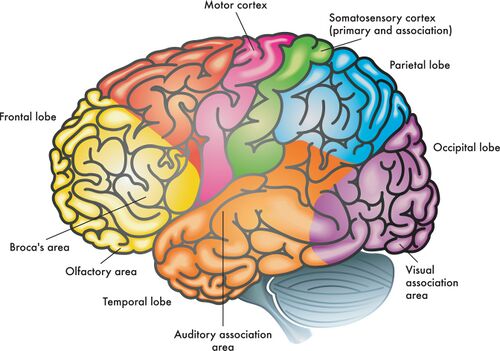
temporal lobes
receives information primarily from the opposite ear and enables language processing
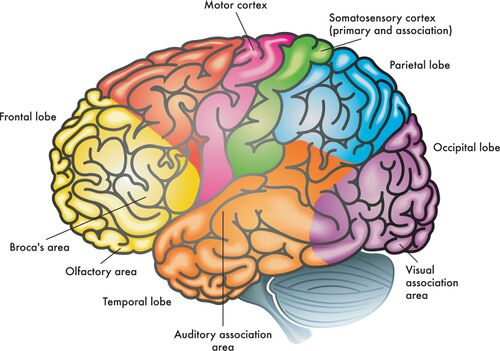
motor cortex
controls voluntary movements
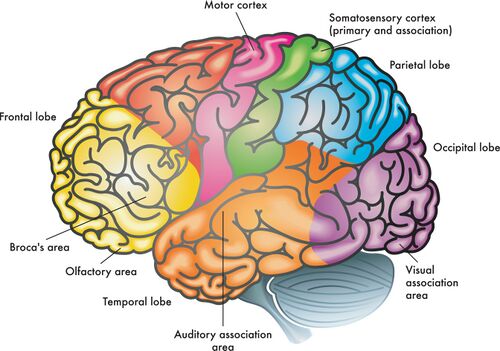
somatosensory cortex
processes body touch and movement sensations
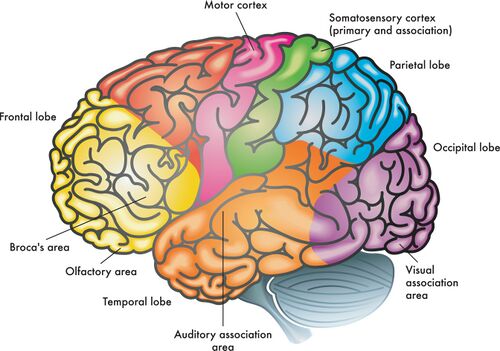
association areas
not involved in primary motor or sensory functions, but rather higher mental functions like learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking
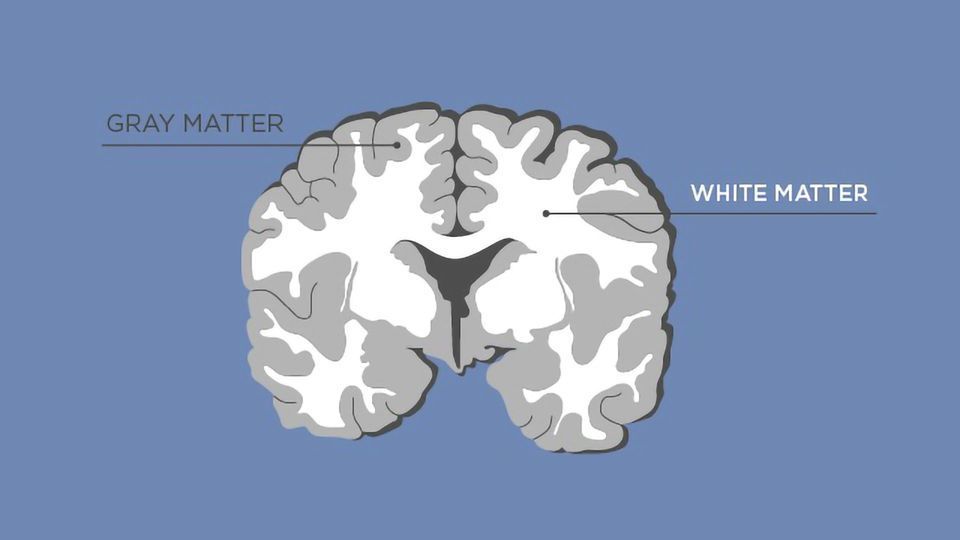
grey matter
contains cell bodies, dendrites, and axon terminals of neurons
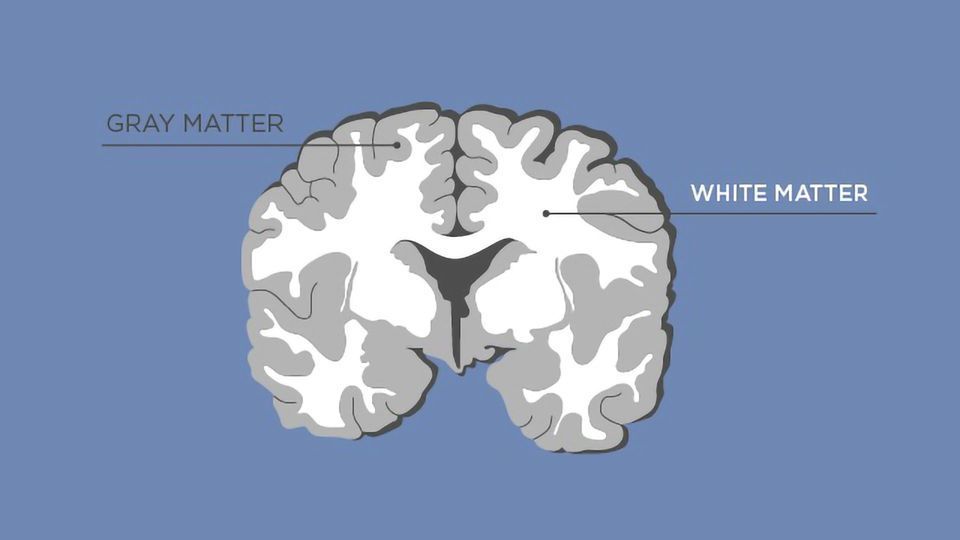
white matter
axons connecting different parts of grey matter to each other
glial cells
cells in central and peripheral nervous system that:
hold neurons in place
supply nutrients and oxygen to neurons
insulates neurons from one another
destroy pathogens and remove dead neurons
assist neurons in forming synaptic connections between each other
neurogenesis
formation of new neurons
split brain
separates the two hemispheres by cutting the fibers connecting them (usually happens to try and lessen epilepsy seizures)
gyrusli
bumps on brain
sulcusli
caves on brain
longitudinal fissure
corpus colossum
corpus colossum
connect left and right hemispheres
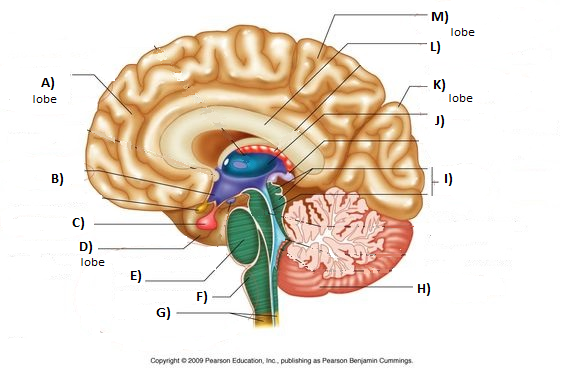
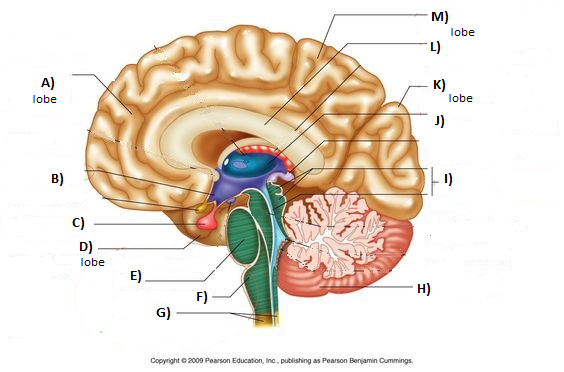
Broca’s Area
part of frontal lobe (left hemisphere) associated with speech production
brain damage (e.g. strokes) and genetics can lead to non-fluent/expressive aphasia: good comprehension, bad production
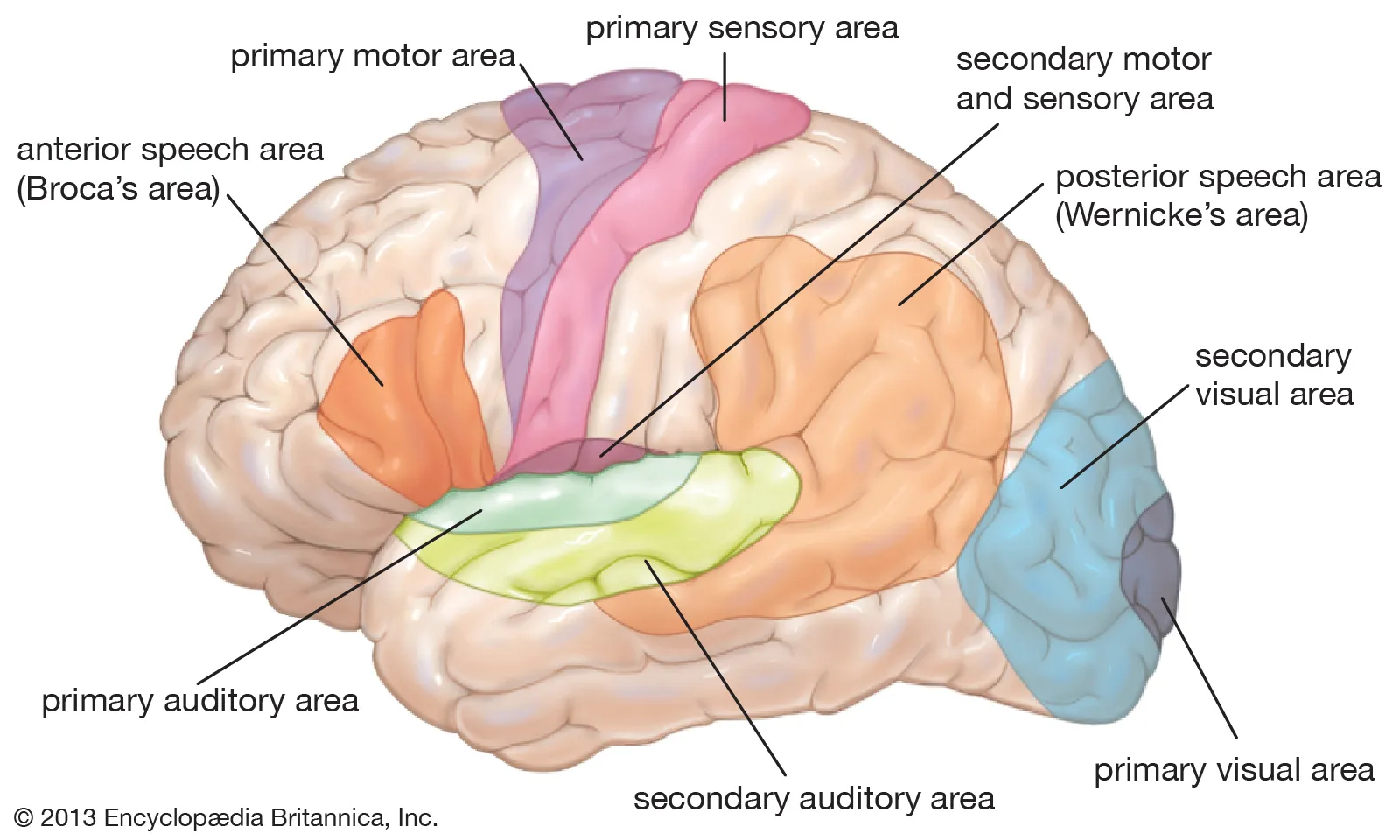
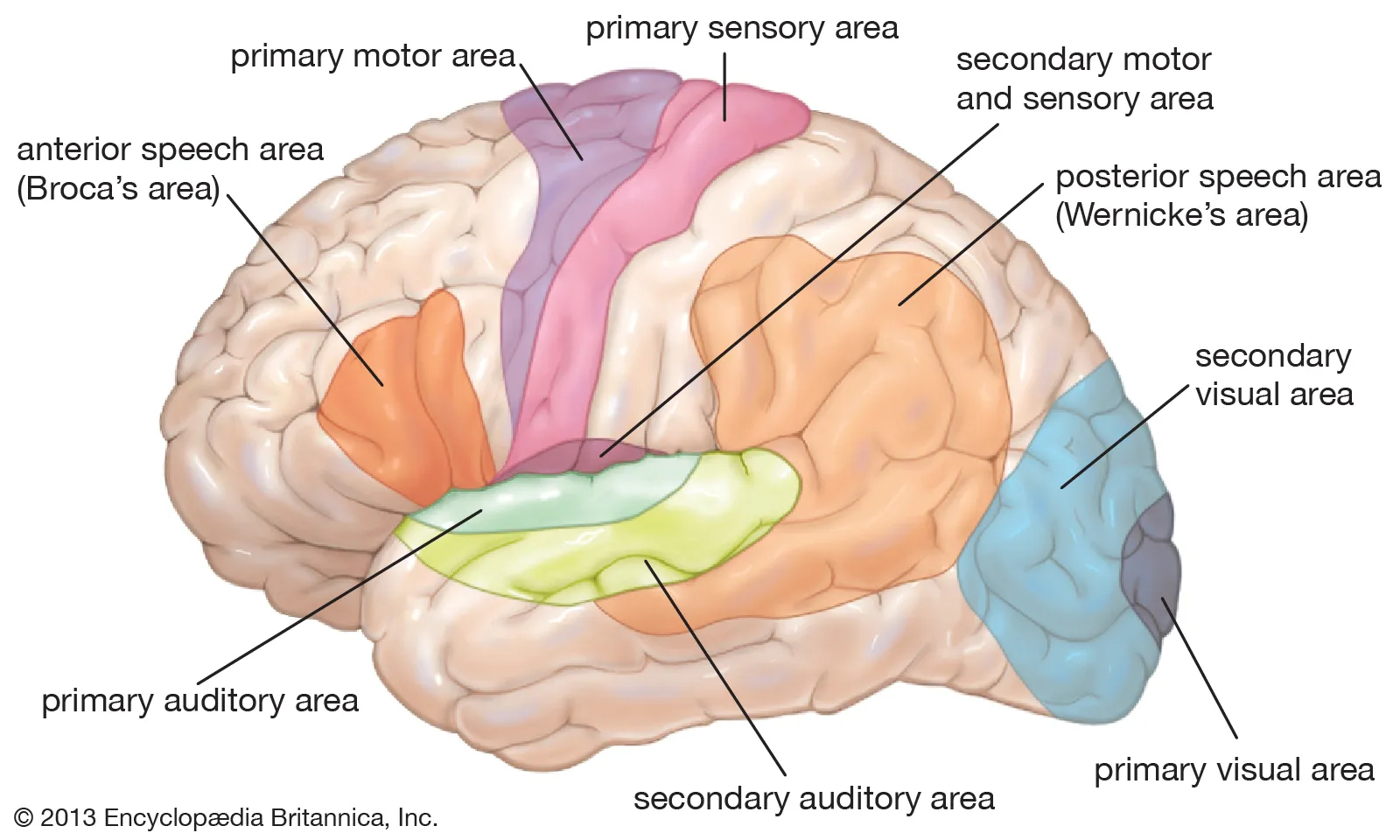
Werincke’s Area
part of temporal lobe concerned with comprehension of language
brain damage (e.g. strokes) and genetics can lead to fluent/receptive aphasia: bad comprehension, good production
fusiform facial area (FFA) or fusiformgyrus
recognition of faces
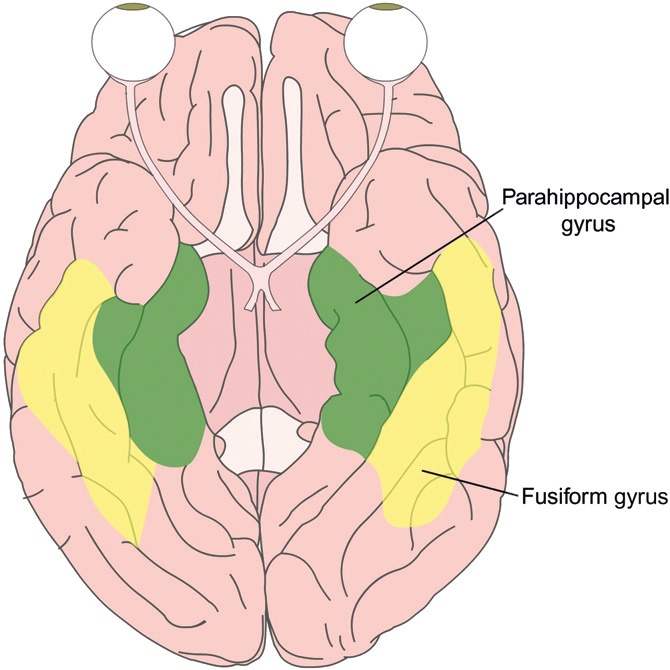
prosopagnosia
inability to recognize faces
sensation
process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment
perception
process by which our brain organizes and interprets sensory information, enabling us to recognize objects and events as meaningful
sensory receptors
sensory nerve ending that respond to stimuli
bottom-up processing
information processing that begins with the sensory receptors and works its way up to the brain’s integration of sensory information
top-down processing
information processing guided by higher-level mental processes, as when we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and expectations
transduction
conversion of one energy into another
example: in sensation, the transforming of physical energy (e.g. sights, sounds, and smells) into neural impulses the brain can interpret
psychophysics
study of relationships between the physical characteristics of stimuli, such as their intensity, and our psychological experience of them
absolute thresholds
maximum stimulus energy needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the time
signal detection theory
theory predicting how and when we detect the presence of a faint stimulus (signal) and background stimulation (noise)
subliminal
below one’s absolute threshold for conscious awareness