Chpt 17: Special Senses
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
The special senses include what 5 senses?
Taste
Smell
Sight
Hearing
Balance
*NOT TOUCH
Provide protection, lubrication, and support
Accessory Structures of the Eye
What are the 4 accessory structures of the eye?
Palpebrae (eyelids)
The superficial epithelium of eye
The lacrimal apparatus (tears)
Extra-occular muscles (movement of eye)
Gap that separates free margins of upper and lower eyelids
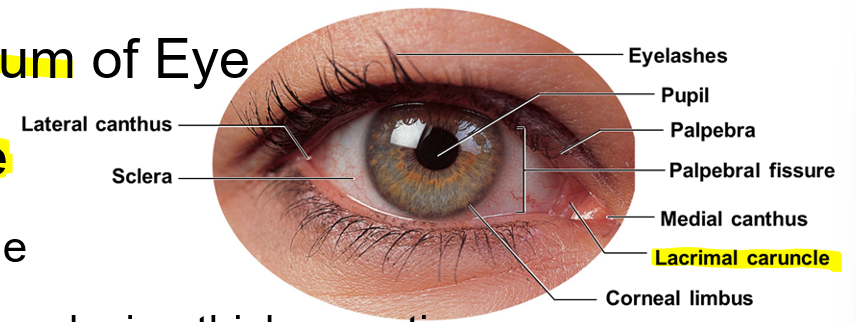
Palpebral fissure
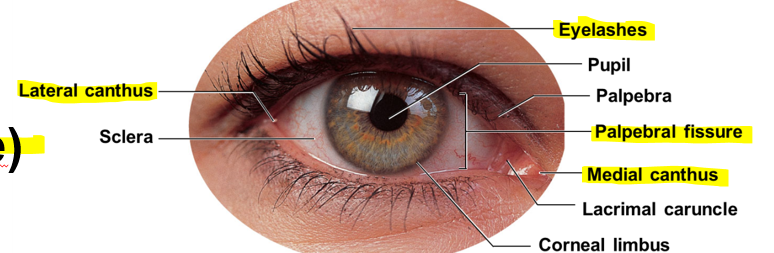
Where two eyelids are connected
Medial canthus and lateral canthus
Hairs that prevent foreign matter from entering
Associated sebaceous glands (coats eyelids so they don’t stick)
Inflammation=sty
Eyelashes
Secrete lipid-rich product that helps keep eyelids from sticking together
cyst=chalazion
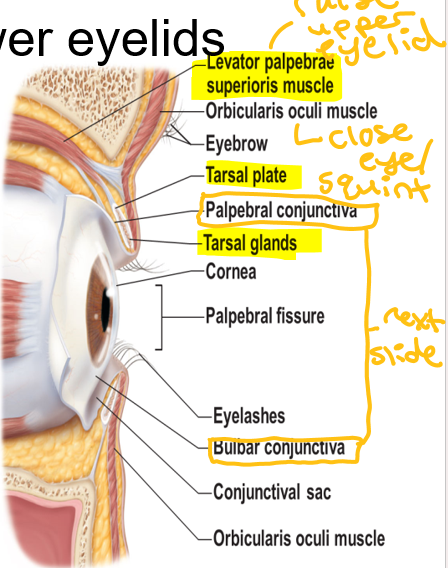
Tarsal glands
On the superficial epithelium of the eye
Mass of soft tissue
Contains glands producing thick secretions
Contributes to gritty deposits that appear after good night’s sleep
Lacrimal caruncle
Epithelium covering inner surfaces of eyelids (palpebral conjunctiva)
Outer surface of eye (occular conjunctiva)
Conjunctiva
Protects the eye from outside objects
Eyebrows
Inflammation of mucous membrane —> pink eye
Conjunctivitis
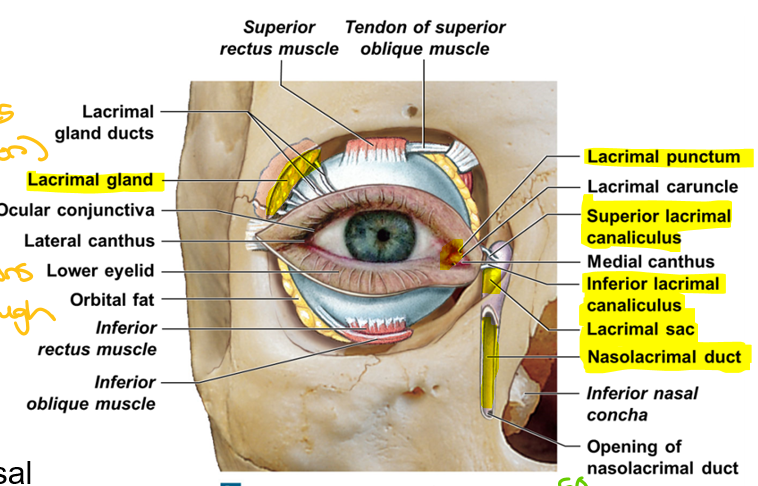
Lacrimal Apparatus Order
Lacrimal gland: Produces tears (lacrimation)(Great)
Lacrimal puncta: Openings drain lacrimal secretions(Pandas)
Lacrimal canaliculi: Tubules that tears pass through(Came)
Lacrimal sac:Tears pass through(Souring)
Nasolacrimal duct: To reach inferior meatus in nasal cavity(Near)
Cranial nerve 6 (Abducens) associates with what eye muscle?
Lateral rectus
Cranial nerve 4 (trochlear) associates with what eye muscle?
Superior oblique
Cranial nerve 3 (oculomotor) associates with what eye muscle?
All remaining muscles (medial rectus, inferior rectus, superior rectus, inferior oblique)
How many tears do we produce per day?
1ml/day
What are tears composed of?
Water
Salt, Mucous, Lipids, Lysozyme, Antibodies
What are the functions of tears?
Protection
Cleanse the eye from debris in tears
Lubricate
What are the 3 layers of the eye?
Outer fibrous layer
Intermediate vascular layer
Deep inner layer
The white part of the eye, tendon like, provides support, attachment point for muscles
Sclera
What produces different colored eyes?
Melanin
This structure of the eye is avascular—no blood vessels, translucent, endothelial layer removes water to help keep this clear
Cornea

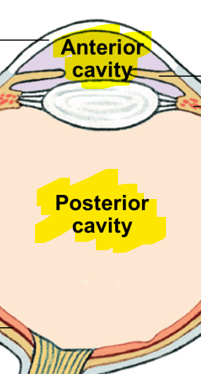
This structure is hollow and divided into two cavities:
Large posterior cavity
Smaller anterior cavity
Ant. Chamber
Post. Chamber
Eyeball
Border between cornea and sclera
Corneal limbus
Vascular layer that separates fibrous and inner layers posterior to ora serrata
The choroid
Contains ciliary processes, and ciliary muscle (when contracting, releases tension on lens) that attaches to suspensory ligaments (holds lens in place, aka zunule) of lens
Forms aqueous humor (fluid in eye)
Ciliary Body
Contains dilator (large) and constrictor (smaller) pupillary muscles
Change diameter of pupil
Iris
Axons of ganglion—cells exit here
Optic disc
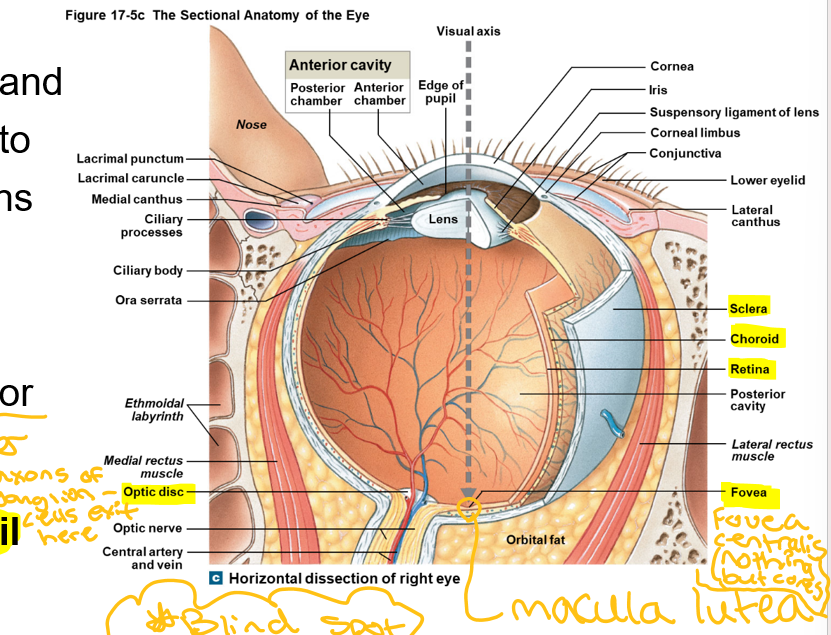
Controls the amount of light entering the eye
Pupil
Decreased light intensity
Increased sympathetic stimulation
Pupils become larger
Increased light intensity
Increased parasympathetic stimulation
Pupils become smaller
Why is the outer layer of the eye pigmented?
Cells have melanin
Inner layer of eye
Retina (neural part)
Membranous discs
See black + white
Blurry images
Sensitivity to light
Respond to almost any photon, regardless of energy content
Fovea centralis
Macula lutea
Rods
Folded membrane
Have characteristic ranges of sensitivity
Color (blue-shorter wavelength, red-larger wavelength, green)
Color blindness
Clear images
More active in day
Less sensitive to light
Cones
6 parts of inner layer of eye
Rods and cones (Red)
Outer synaptic layer (Octopuses)
Bipolar layer (2 processes, axon + dendrite)(Best)
Inner synaptic layer (In)
Ganglion layer (Green)
Axonal layer (axons of ganglion cells) (Algae)
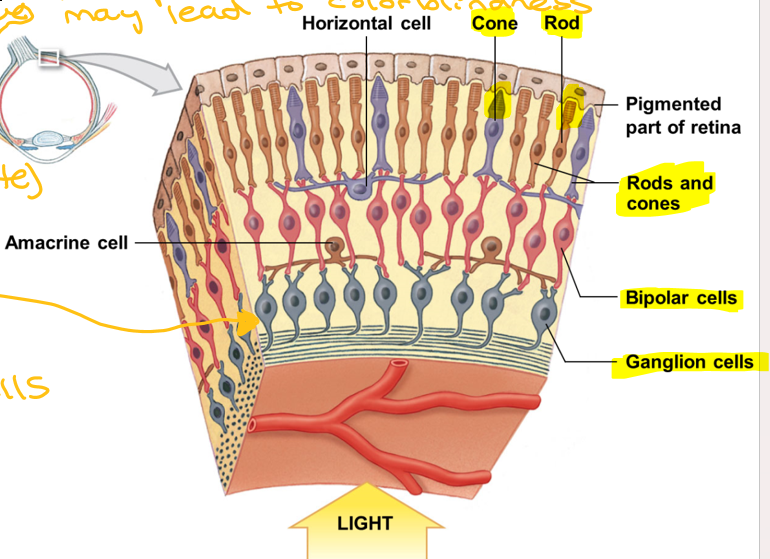
Receptor colors of rods and cones layer, may lead to colorblindness
Red, blue, green
Fluid circulates within the eye
Diffuses through walls of anterior camber in pupil into scleral venous sinus (canal of Schlemm)
Re-enters circulation
Aqueous Humor
Fluid pressure in aqueous humor
Helps retain eye shape
Intraocular Pressure (12-22 mm of Hg)
Higher ocular pressure leads to what?
Glocoma (damage to retina + vision)
Gel-like body present in posterior cavity
Gelatinous mass
Helps stabilize eye shape and supports retina
Vitreous body
Biconvex, avascular, flexible, layered like onion
Contains fibers and cataract
The lens
Cells in interior of lens
No nuclei or organelles
Filled with crystallins, which provide clarity and focusing power to lens
Lens fibers
Condition in which lens has lost its transparency
Cataract
Bending of light by cornea and lens
Light Refraction
Specific point of intersection of light rays
Focal point
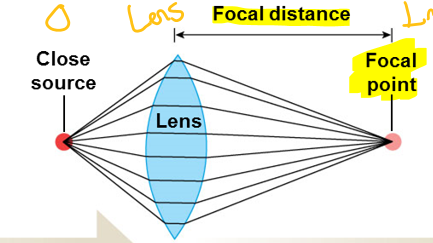
Distance between center of lens and focal point
Focal distance
The closer the light source, the _____the focal distance
Longer
The rounder the lens, the _______ the focal distance
Shorter
Shape of lens changes to focus image on retina
Accommodation
Condition where light passing through cornea and lens is not refracted properly
Visual image is distorted
Astigmatism
Clarity of vision
“Normal” rating is 20/20
Visual acuity
Eye is elongated
Can see close objects clearly, NOT distant objects
Corrected with a diverging, concave lens
Myopia (nearsightedness)
When object moves closer, image falls behind retina
Not enough retraction to focus image on retina
Hyperopia (farsightedness)
Older people become farsighted as their lens lose elasticity
Hyperopia due to age
Presbyopia
Normal vision
Emmetropia
Blindness (partial and complete)
Anopia
Narrow stalk connects outer segment to inner segment
Inner segment of rods and cones
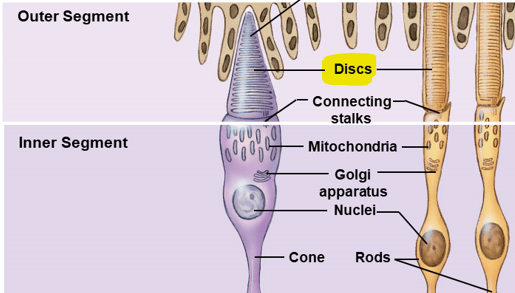
Is where light absorption occurs
Visual pigment
Derivatives of rhodopsin molecule
Opsin + retinal
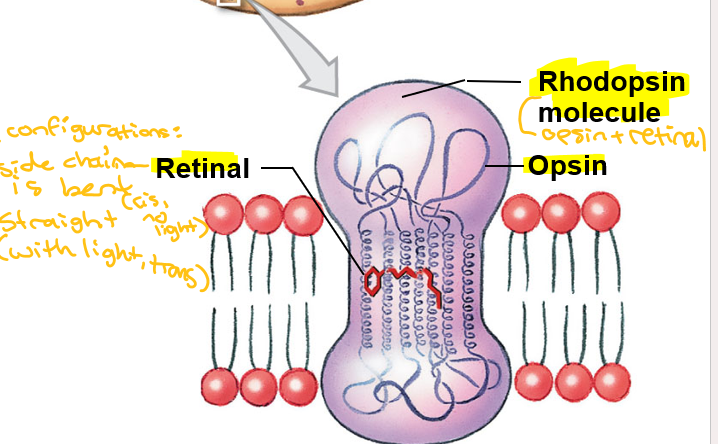
Retinal synthesized from what?
Vitamin A
Retinal with side chain bent
Can combine with opsin
No light, cis
Retinal with side chain straight
Cannot combine with opsin
Light, trans
Photon strikes retinal portion of rhodopsin molecule embedded in membrane of disc
Opsin is activated
Photoreception
Events of Phototransduction (5)
Light (photons) activate visual pigment
Visual pigment activates transducin (G protein)
Transducin activates phosphodiesterase (PDE)
PDE converts cGMP (controls sodium + calcium channels) into GMP, causing cGMP levels to fall
As cGMP levels fall, cGMP-gated cation channels close, resulting in hyperpolarization
Signal transmission in the retina in the dark
cGMP-gated channels open, allowing cation influx; the photoreceptor depolarizes (releasing neurotransmitters)
Voltage-gated Ca+ channels open in synaptic terminals
Neurotransmitter is released continuously
Neurotransmitter causes IPSPs in bipolar cell; hyperpolarization results
Hyperpolarization closes voltage-gated Ca+ channels, inhibiting neurotransmitter release
No EPSPs occur in ganglion cell
No action potentials occur along the optic nerve
Signal transmission in the retina in the light
cGMP-gated channels are closed, so cation influx stops; the photoreceptor hyperpolarizes
Voltage-gated Ca+ channels close in synaptic terminals
No neurotransmitter released
Lack of IPSPs in bipolar cell results in depolarization
Depolarization opens voltage-gated Ca+ channels; neurotransmitter is released
EPSPs occur in ganglion cell
Action potentials propagate along the optic nerve
Rhodopsin molecule breaks down into retinal and opsin
Bleaching
Most visual pigments are fully receptive to stimulation
Dark Adaptation
Pupil constricts
Bleaching of visual pigments occurs
Light Adaptation
Begin at photoreceptors
End at visual cortex of cerebral hemispheres
Message crosses two synapses before it heads toward brain
Photoreceptor to bipolar cell
Bipolar cell to ganglion cell
Visual Pathways
3-Step Neuron
Bipolar—> Ganglion—> Thalamic
Pituitary gland tumor affects what structure?
Optic chiasm
Enopia
Blindness
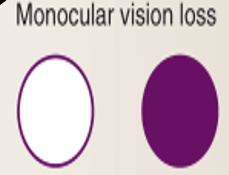
A lesion to the optic nerve of one eye will lead to loss of the complete visual field of that eye
Monocular vision loss
A lesion to optic chiasm that leads to loss of the temporal (lateral) visual field in both eyes
Bitemporal hemianopia

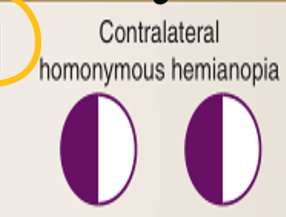
A lesion of the optic tract will lead to the loss of the contralateral visual field in both eyes (lateral on one side and medial on the other)
Contralateral homonymous hemianopia
Obtained by comparing relative positions of objects between left-eye and right-eye images
Need input from both eyes
Depth perception
Integumentary glands along external acoustic meatus
Secrete waxy material (cerumen)
Ceruminous glands in external ear
Also called tympanic cavity
Communicates with nasopharynx via auditory tube
Equalization of pressures
Communication with mastoid antrum via epitympanic recess
Otitis media (infection of middle ear) and Mastoiditis
The Middle Ear
What are the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear?
Malleus (hammer)
Incus (anvil)
Stapes (stirrup)
What are the two muscles of the middle ear?
Tensor tympani (attached to meatus)
Stapedius (attached to stapes)
What is the fluid of the membranous labyrinth of the internal ear?
Endolymph (rich in K+)
The bony labyrinth that surrounds and protects membranous labyrinth in the internal ear contains what?
Perilympth (rich in Na+)
The internal ear is subdivided into what three divisions of the bony labyrinth?
Vestibule: Cochlea connects here
Semicircular canals
Cochlea: snail-like portion
The membranous labyrinth of the internal ear contains what three structures?
Semicircular ducts
Utricle and saccule
Cochlear duct (scala media)
Semicircular canals + ducts’ function and receptor
Equilibrium; rotational (angular) acceleration
Crista ampullaris
Vestibule + utricle + saccule function and receptor
Equilibrium; head position relative to gravity, linear acceleration
Macula
Cochlea + cochlear duct (scala media) function and receptor
Hearing (auditory)
Spiral organ
Sensations provided by receptors of vestibular complex
Equilibrium
Basic receptors of inner ear
Provide information about direction and strength of mechanical stimuli
Hair cells
These ducts are continuous with utricle
Semicircular Ducts
Each semicircular duct contains this
Ampulla
Resemble long microvilli on surface of hair cell in semicircular duct
Stereocilia
Single large cilium in semicircular duct
Kinocilium
2 oval structures where hair cells cluster (saccule-vertical, utricle-horizontal), can detect change in movement
Maculae
Densely packed calcium carbonate crystals on surface of gelatinous mass
Statoconia
Ear stone
Gelatinous matrix and statoconia
Otolith
What do cochlear duct receptors (aka organ of corti) provide?
Sense of hearing
Spongy bone core of cochlea
Modiolus