Y10 Chem: Energy Consumption and Fuel
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Energy
Capacity to do work or produce heat. It can be transferred between bodies and transformed between types but never created or destroyed
Energy Consumption
Energy consumption refers to ALL the energy used to perform an action and this energy can come from different sources
Explain how energy is used in everyday life
Produce goods and services
Infrastructure
Lighting, heating
Transformation
Direct energy use
Direct energy use is the energy consumed in forms that people actively use
Give an example of direct energy use
Electricity powers lightbulbs
Indirect energy use
Indirect energy use refers to the energy use behind the scenes to support daily life
Give an example of indirect energy use
Manufacturing and transporting garments require electricity and fuel
What is the difference between direct energy use and indirect energy use
The difference between direct energy use and indirect energy use is that indirect energy is consumed in the production process whereas direct energy directly powers the task at hand
How is indirect consumption of energy associated with production of consumer goods
Factories consume electricity and fuel for machinery, package and logistics
How is indirect consumption of energy associated with building homes and infrastructure
Mining raw materials, manufacturing bricks, glass, and concrete and transporting all of them consumes energy
How is indirect consumption of energy associated with energy for transporting goof
Trucks, ships and planes burn fossil duels
How is indirect consumption of energy associated with production of growing food
Tractors, irrigation systems, fertilisers and refrigeration systems all require energy
Fossil Fuels
Fossil duels are mixtures of hydrocarbons that form from remains of plants and animals (diatoms) that lived millions of years ago. They only compose of hydrogens and carbons.
Examples of fossil fuels
Crude oil, coal, natural gas
Name common Greenhouse gases
H2O - Water Vapour
CO2 - Carbon Dioxide
CH4 - Methane
N2O - Dinitrogen Monoxide/Nitrous oxide
O3 - Ozone
CFCs - Chlorofluorocarbons
HFCs - Hydrofluorocarbons
Crude Oil
Mixture of hundreds of different compounds. It is used to make fuels for transport, heating and generating electricity
What are most of the hydrocarbons in crude oil called?
Alkanes
How do you extract crude oil?
It is found trapped in rocks of the sea bed. Oil rigs or drilling platforms are used to drill through the sea bed to obtain the oil. Once the oil has been removed from the sea bed, it is pumped in long pipelines to an oil tanker terminal or an oil refinery on land
How is crude oil made? *
It was made from the remains of marine plants and animals that died millions of years ago. The remains sank to the bottom of the sea where they were buried in layers of sand and mud, which prevented them from rotting. These layers gradually became sedimentary rocks
Problems with Crude Oil
Burning the products of crude oil as fuel produces gases and prickles that contribute to climate change and air pollution
Removing oil from the ground, as well as oil spillages and slicks, can be very damaging to wildlife and the environment
The high value of oil means it is sometimes the cause of military conflict, especially because a large amount of oil comes from countries that are politically unstable.
Explain what happens to the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere with the burning of fossil fuels
When the fossil fuels are burned during combustion, carbon atoms in the fuel react with oxygen to form carbon dioxide:
CH4 + 2 O2 —> CO2 + 2 H2O
This process increases the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere as the carbon stored underground for millions of years is suddenly released into the air.
What happens when lots of fossil fuels are burned
The more fossil fuels are burned, the more CO2 accumulates, which disrupts the natural carbon cycle
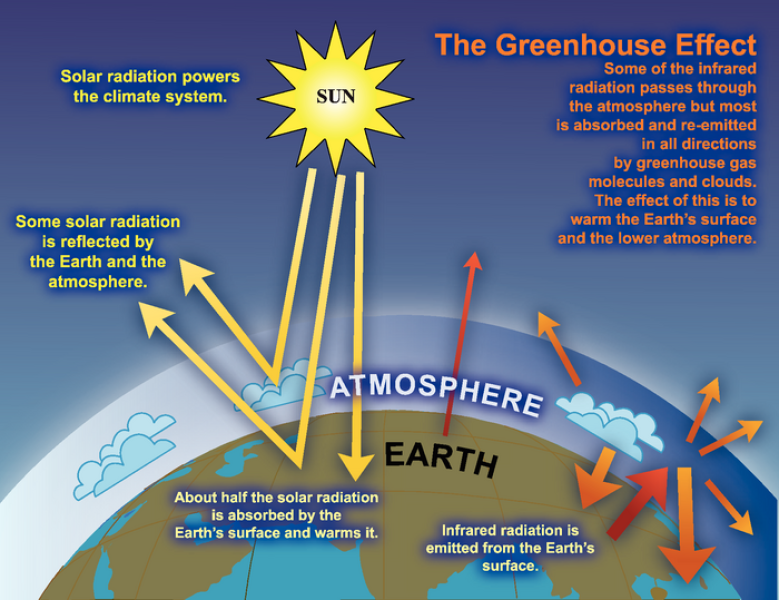
State the steps of the Greenhouse Effect
Earth’s surface absorbs visible light from the sun
Earth’s surface increases in temperature
Earth’s surface emits infrared radiation
Most infrared radiation passes through the atmosphere
Some infrared radiation is absorbed by molecules of greenhouse gases
Molecules of greenhouse gases increase in vibrational energy
Increased vibration causes more collisions
Kinetic energy of gases increases the atmosphere it resides
Temperature of atmosphere increases
Describe some effects of greenhouse gases (local and global)
Mean global temperatures will have increased by 1.4 to 5.8C
Sea levels will rise by 0.09m to 0.88m
There will be more precipitation (rain, snow, hail etc) in some areas and less than others
There will be more hot days and fewer cold days