UPCAT - Chemistry
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 8:04 PM on 5/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
1
New cards
Organic Chemistry
the study of the structure and properties of carbon-containing compounds
2
New cards
Inorganic Chemistry
the study of the structure and properties of inorganic compounds or compounds not composed of carbons
3
New cards
Analytical Chemistry
* determination of composition and properties of matter
* studies what is in a sample of an object/matter or what is that sample composed of
* studies what is in a sample of an object/matter or what is that sample composed of
4
New cards
Physical Chemistry
* studies the physical and fundamental aspects of chemical system and processes
* one major topic discuseed is the energy involved in chemical reactions and physical changes in matter
* one major topic discuseed is the energy involved in chemical reactions and physical changes in matter
5
New cards
Biochemistry
studies the chemicals and chemical reactions found in living organisms
6
New cards
Law of Conservation of Mass
matter cannot be created nor destroyed, but only changed from one form to another
7
New cards
Law of Constant Composition
a given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by mass
8
New cards
Law of Multiple Proportions
the amount of elements that react with each other can be reduced to small whole numbers
9
New cards
mass of an atom
protons + neutrons
10
New cards
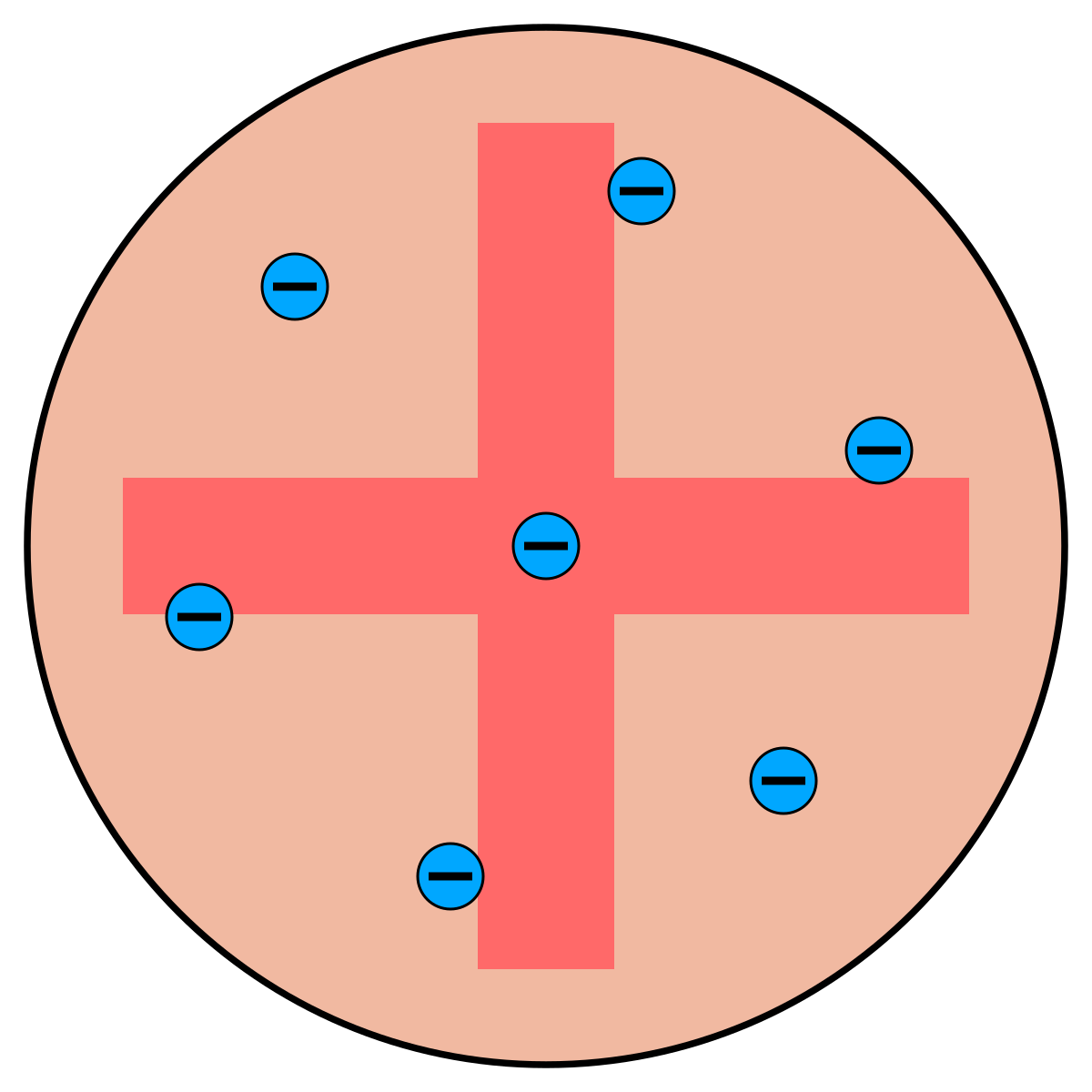
plum-pudding model
positively-charged sphre dotted with electrons
11
New cards
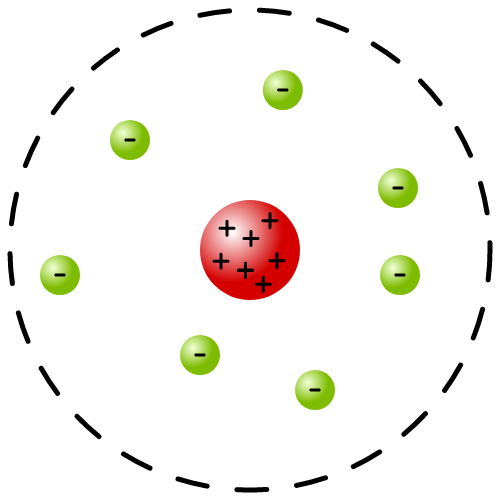
Rutherford model
atom is mostly empty space with most of its mass in the nucleus with electrons moving around it
12
New cards
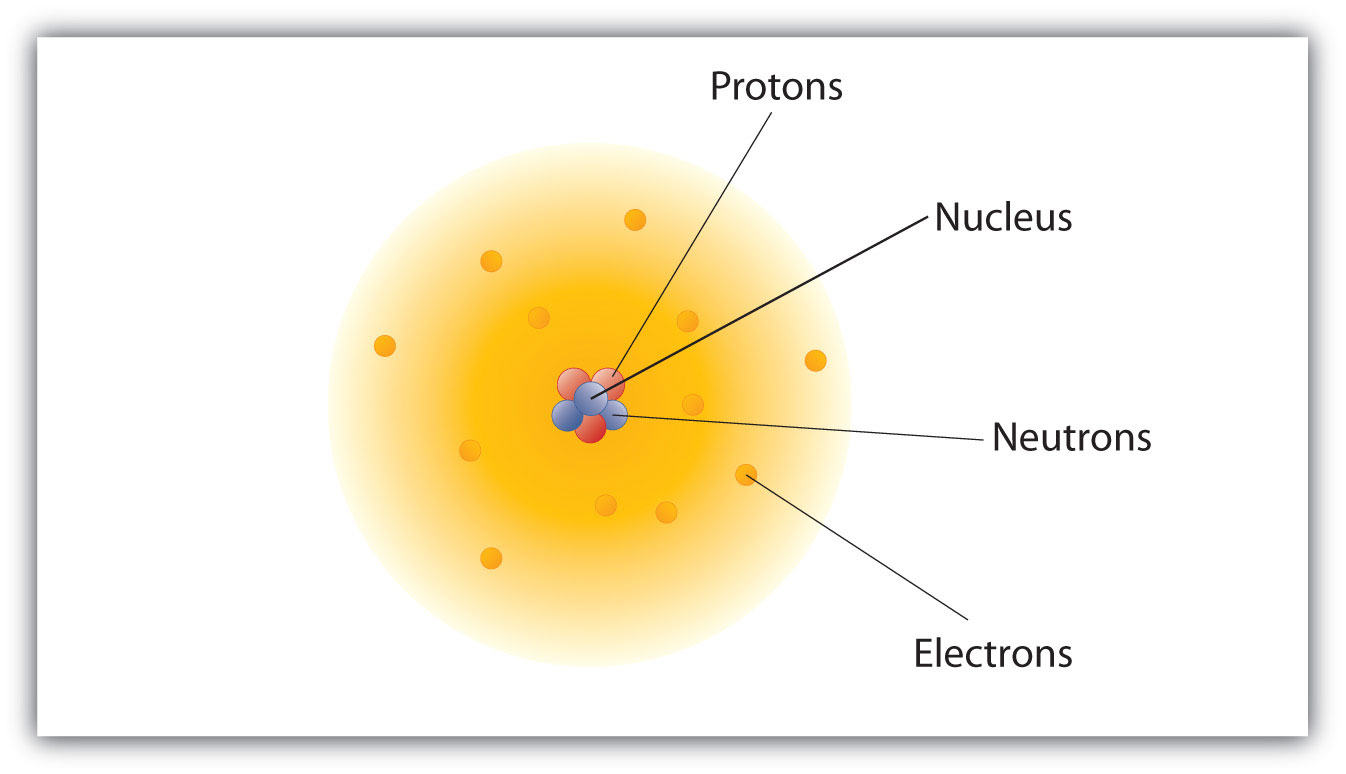
modern atomic theory
atoms are made out of protons, neutrons, and electrons with the protons and neutrons residing in the nucleus while the electrons move around
13
New cards
Group IA (Alkali Metals)
Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidium, Cesium, Francium
14
New cards
Group IIA (Alkaline Earth Metals)
Beryllium, Magnesium, Calcium, Strontium, Barium, Radium
15
New cards
Group VIA (Chalcogens)
Oxygen, Sulfur, Selenium, Tellerium, Polonium, Livermonium
16
New cards
Group VIIA (Halogens)
Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine, Astatine, Tennessine
17
New cards
Group VIIIA (Noble Gas)
Helium, Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon, Radon, Oganesson
18
New cards
Isotopes
atoms with identical atomic nmbers but different mass numbers (that is th same number of protons but a different number of neutrons)plasma
19
New cards
cations vs anions
cations are postively charged isotopes which lack electrons while anions are negatively charged isotpoes which lack protons
20
New cards
ionic copounds
made up of cations and anions and are bound by electrostatic forces (opposite charges attract)
21
New cards
electronic configuration mnemonic
Si Santos pumasok sa pinto, si Diego pumasok sa door. Pumunta si Fiona dumaan papunta sa faculty dala sila,
22
New cards
orbital capacities of s, p, d, and f
2, 6, 10, and 14
23
New cards
activity series of metals mnemonic
Please stop calling me a careless Zebra. Instead, try learning how Copper Saves Gold
24
New cards
activity series of metals from most reactive to least reactive
Potassium, Sodium, Calcium, Magnesium, Aluminum, Carbon, Zinc, Iron, Tin , Lead, Hydrogen, Copper, Silver, Gold
25
New cards
physical change
changes only the state of matter, not its composition
26
New cards
chemical change
alters the composition and identity of the substance and will inherit properties different to the chemicals before the change
27
New cards
indicators of chemical change
change in color, temperature, flame color, formation of precipitate, and formation of bubbles
28
New cards
physical property of matter
* property that involves physical change
* can be measured without converting matter into another substance (e.g. boiling point, hardness)
* can be measured without converting matter into another substance (e.g. boiling point, hardness)
29
New cards
intensive physical property vs. extensive physical property
* intensive: does not depend on amount (e.g. color)
* entensive: depends on amount (e.g. volume, mass)
* entensive: depends on amount (e.g. volume, mass)
30
New cards
chemical property
* matter will be converted into another substance during measurement of this property
* example: flash point, toxicity
* example: flash point, toxicity
31
New cards
pure substance
* matter that is constant in composition and properties does not vary
* cannot by phusically separated
* cannot by phusically separated
32
New cards
element
* simplest form of matter and cannot be broken down into simple substances
* composed of atoms
* composed of atoms
33
New cards
compound
* composed of two or mroe elements
* can be broken down into individual elements
* have different properties than parent elements
* can be broken down into individual elements
* have different properties than parent elements
34
New cards
mixtures
* composed of two or more pure substances of varying composition
* can be physically separated
* can be physically separated
35
New cards
homogeneous mixture (solution)
* occurs in a single phase
* components cannot be distinugished from each other
* components cannot be distinugished from each other
36
New cards
heterogeneous mixture
* occurs as two or more phases
* components can be distinguished from each other
* two types: colloids and suspensions
* components can be distinguished from each other
* two types: colloids and suspensions
37
New cards
colloids
* large than the size of a molecule but smaller than what can be seen with the anked eye
* substance’s dimensions must be between 1 and 1000 nanometers
* exhibits the Tyndall Effect
* substance’s dimensions must be between 1 and 1000 nanometers
* exhibits the Tyndall Effect
38
New cards
suspension
* mixture between a liquid and particles of a solid
* particles do not dissolve and solid particles will settle and separate over time
* particles do not dissolve and solid particles will settle and separate over time
39
New cards
Solid sol
* a colloid between a solid and a solid
* example: Ruby glass
* example: Ruby glass
40
New cards
Solid emulsion/gel
* a colloid between a solid medium and a dispersed liquid
* example is pearl or cheese
* example is pearl or cheese
41
New cards
solid foam
* a colloid between a solid medium and dispersed gas
* example is lava and pumice
* example is lava and pumice
42
New cards
sol
* a colloid between a liquid medium and dispersed solid
* a colloidal suspension with solid particles in a liquid
* paints, cell fluids
* a colloidal suspension with solid particles in a liquid
* paints, cell fluids
43
New cards
emulsion
* is a colloid between two liquids
* examples are milk and oil in water
* examples are milk and oil in water
44
New cards
foam
* a colloid between a liquid medium and a gas
* is formed when many gas particles are trapped in a liquid
* examples are soap suds and whipped cream
* is formed when many gas particles are trapped in a liquid
* examples are soap suds and whipped cream
45
New cards
aerosol
* a colloid between a gas medium and dispersed solid or liquid
* contains small particles of liquid or solid dispersed in a gas
* examples are smoke, fog, and mist
* contains small particles of liquid or solid dispersed in a gas
* examples are smoke, fog, and mist
46
New cards
Tyndall Effect
the phenomenon in which light is scattered by particles of matter in its path
47
New cards
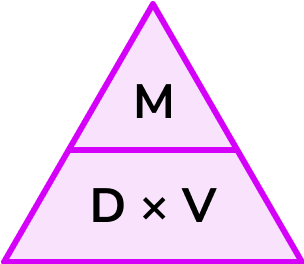
mass, density, and volume formula
M = DV
48
New cards
moles of reactant required in a reaction
moles of reactant \* (amount of product/amount of reactant)
49
New cards
Avogadro’s number
* the ratio that relates the number of constituent particles in a sample with the amount of substance in that sample
* equivalent to **6.02*10^23**
* equivalent to **6.02*10^23**
50
New cards
number of moles to molecules
number of moles \* Avogadro’s number
51
New cards
molarity
* a unit of concentration expressed as the number of moles of dissolved solute per liter of solution
* mol solute/L solution
* mol solute/L solution
52
New cards
ppm and ppb
* used in solutions with low concentrations of a solute
* ppm = (grams of solute/grams or mL of solution) \* 10^6
* ppb = (grams of solute/grams or mL of solution) \* 10^9
* ppm = (grams of solute/grams or mL of solution) \* 10^6
* ppb = (grams of solute/grams or mL of solution) \* 10^9
53
New cards
mass percent
(mass of component of solution/total mass of solution) \* 100%
54
New cards
mole fraction formulas
* (n/n)% = moles of solute/total number of moles
* (n/n)% = partial pressure/total pressure
* (n/n)% = partial pressure/total pressure
55
New cards
partial pressure formula
P_A = X_A \* P_T
56
New cards
Dalton’s Law
* total pressure is equal to all partial pressures
* all mole fractions is equal to 1
* all mole fractions is equal to 1
57
New cards
volume percent formula
volume% = (volume of component of solution/total volume of solution)\*100%
58
New cards
constitution of a chemical equation
* on the left are the reactants
* on the right are the products
* the initals written in parenthesis (e.g. HCl(aq)) defines their states
* solid, liquid, gas - (s), (l), (g)
* substance is dissolved in water - (aq)
* on the right are the products
* the initals written in parenthesis (e.g. HCl(aq)) defines their states
* solid, liquid, gas - (s), (l), (g)
* substance is dissolved in water - (aq)
59
New cards
Combination (Synthesis) Reaction
* two or more products form a single product
* 2Na(s) + Cl_2(g) → 2NaCl(s)
* 2Na(s) + Cl_2(g) → 2NaCl(s)
60
New cards
Decomposition Reaction
* a single compound breaks down into two or more products
* 2KClO_3(s) → 2KCl(s) + 3O_2(g)
* 2KClO_3(s) → 2KCl(s) + 3O_2(g)
61
New cards
Single displacement reaction
* one of the components of one of the reactants is replaced by another reactant
* always a redox reaction
* Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl_2(aq) + H_2(g)
* always a redox reaction
* Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl_2(aq) + H_2(g)
62
New cards
Double displacement (metathesis) reaction
* reactants exhange parts
* BaCl_2(aq) + Na_2SO_4(aq) → BaSO_4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
* BaCl_2(aq) + Na_2SO_4(aq) → BaSO_4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
63
New cards
Combustion reaction
* carbon-containing compounds react with oxygen to form CO2 and H2O **as water vapor**
* CH_4(g) + 2O_2(g) → CO_2(g) + 2H_2O(g)
* CH_4(g) + 2O_2(g) → CO_2(g) + 2H_2O(g)
64
New cards
Redox reaction
this is the reaction that involves the transfer of electrons
65
New cards
reducing agent
* the element that loses electrons in a redox reaction (a.k.a. the one that is oxidized)
* metals
* metals
66
New cards
oxidizing agent
* the element that gains electrons in a redox reaction (a.k.a. the one hat is reduced)
* non-metals
* non-metals
67
New cards
oxidation number of a pure element
0
68
New cards
oxidation number of monoatomic ions
equal to their charge (e.g. Fe-2 = -2)
69
New cards
oxidation number of Group I and II
if in a compound with other elements or is in its ionic form, +1 and +2 respectively (excluding H)
70
New cards
oxidation number of H
if in a compound with metals (a hydride compound), then -1 else +1
71
New cards
oxidation number of Al and F in compounds
\+3 and -\`1
72
New cards
oxidation number of O
\-2 except in hydrogen peroxide (H_2O_2) and peroxide anion (O_2 -2) where it is -1
73
New cards
oxidation number of halogens
negative oxidation number on halide compounds and positive oxidation number of oxygen-containing compounds
74
New cards
oxidation number of polyatomic ions
the algebraic sum of the oxidation number of each element is equivalent to the ion’s charge
75
New cards
oxidation number for neutral compounds
the algebraic sum of the oxidation number of each element is equivalent to zero
76
New cards
Kinetic-Molecular Theory
* a model that explains the behavior of gases where external forces are applied
* the higher the temperautre, the faster the particles move
* at the same temperature:
* larger particles move slower
* smaller particles move faster
* the higher the temperautre, the faster the particles move
* at the same temperature:
* larger particles move slower
* smaller particles move faster
77
New cards
Boyle’s Law
* pressure is in an inverse relationship with volume
* P1V1 = P2V2
* P1V1 = P2V2
78
New cards
Charles’s Law
* the temperature of a gas is directly proportional to its volume
* T1/V1 = T2/V2
* T1/V1 = T2/V2
79
New cards
Gay-Lussac’s Law
* pressure is directly propertional to temperature
* T1/P1 = T2/P2
* T1/P1 = T2/P2
80
New cards
Avogadro’s Law
* the volume of a gas is directly propertional to its amount (mol)
* n1/V1 = n2/V2
* n1/V1 = n2/V2
81
New cards
Ideal Gas Law
PV = nRT; R = 0.08206 L-atm/mol-k
82
New cards
effusion vs. diffusion
* effusion is the ability of a gas to pass through a small orifice into an evaculated chamber
* diffusion is the ability of a gass to distribute itself homogeneously
* diffusion is the ability of a gass to distribute itself homogeneously
83
New cards
Graham’s Law of Effusion and Diffusion
* the rate of an effusion/diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to its molar mass
* r1/r2 = sqrt(M1)/sqrt(M2)
* r1/r2 = sqrt(M1)/sqrt(M2)
84
New cards
open system
there is an exchange of heat and matter between the system and its surroundings
85
New cards
closed system
there is only an exchange ofheat between the system and its surroundings
86
New cards
isolated system
netiher energy nor matter is exchanged
87
New cards
thermochemistry
branch of chemistry that deals with the energy changes during a chemical reaction
88
New cards
thermochemicals
any chemical equation that has heat on either the product or reactant side of the equation
89
New cards
exothermic vs endothermic
* exothermic: heat is released and is on the product side of the equation
* endothermic: heart is required for the reaction to proceed and is on the reactant side of the equation
* endothermic: heart is required for the reaction to proceed and is on the reactant side of the equation
90
New cards
heat
is a process of gaining or losing energy
91
New cards
work
is a transfer of energy, which does not involve temperature changes
92
New cards
First law of thermodynamics
* the net change of total energy of a system is equal to the heat added into the system minus the work done
* ΔU = q - w; q = heat added, w = work done
* ΔU = q - w; q = heat added, w = work done
93
New cards
Second law of thermodynamics
the total entropy must increase in every spontaneous process
94
New cards
spontaneous processes
* processes that occur wihtout intervention
* processes tend to havor states with low energy and high entropy
* processes tend to havor states with low energy and high entropy
95
New cards
enthalpy
* indicates the transfer of heat from or into the thermodynamic system
* ΔH = ΔU + pΔV
* ΔH = ΔP - RTΔn for gases
* ΔH = ΔU + pΔV
* ΔH = ΔP - RTΔn for gases
96
New cards
entropy
* measure of randomness or disorder in a system
* ΔS= qrev/T; qrev = amount of heat in a reversible process, T = temperature
* ΔS= qrev/T; qrev = amount of heat in a reversible process, T = temperature
97
New cards
Gibbs free energy (G)
* tells us the spontaneity of a process
* ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
* -ΔG = spontaneous, +ΔG = not spontaneous
* ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
* -ΔG = spontaneous, +ΔG = not spontaneous
98
New cards
molecular vs. emperical formula
* molecular formula presents the exact number of elements in a compound whileas emperical only has the ratio
* molecular: C6H14
* emperical: C3H7
* molecular: C6H14
* emperical: C3H7
99
New cards
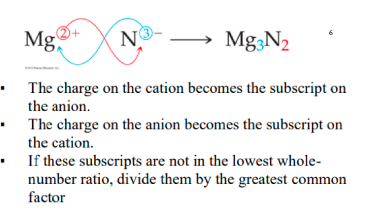
combining a cation and an anion
* the charge of the cation becomes the subscript of the anion
* the charge of the anion becomes the subscript of the cation
* divide by the GCF if possible
* the charge of the anion becomes the subscript of the cation
* divide by the GCF if possible
100
New cards
alkanes, alkenes, and acetylenes
* alkanes: single bond between carbon atoms; saturated hydrocarbons
* alkenes: double bond between carbon atoms: unsaturated hydrocarbons
* acetylenes: triple bond between carbon atoms; unsaturated hydrocarbons
* alkenes: double bond between carbon atoms: unsaturated hydrocarbons
* acetylenes: triple bond between carbon atoms; unsaturated hydrocarbons