Measuring Productivity to the End
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
How to Measure Productivity
- 1) Using the rate of photosynthesis of producers.
- 2) Using the rate of increase in the biomass of producers.
-3) Using satellite imagery to measure the amount of Chlorophyll.
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
The amount of energy that is left over after respiration to be made into new plant biomass.
Gross Primary Production (GPP)
The amount of light or chemical energy fixed by producers in a given length of time in a given area.
1) Rate of Photosynthesis
Found by looking at the change in either the oxygen of carbon dioxide concentrations.
For Example, If photosynthesis is taking place the concentration of carbon dioxide will be lower but an increase in oxygen.
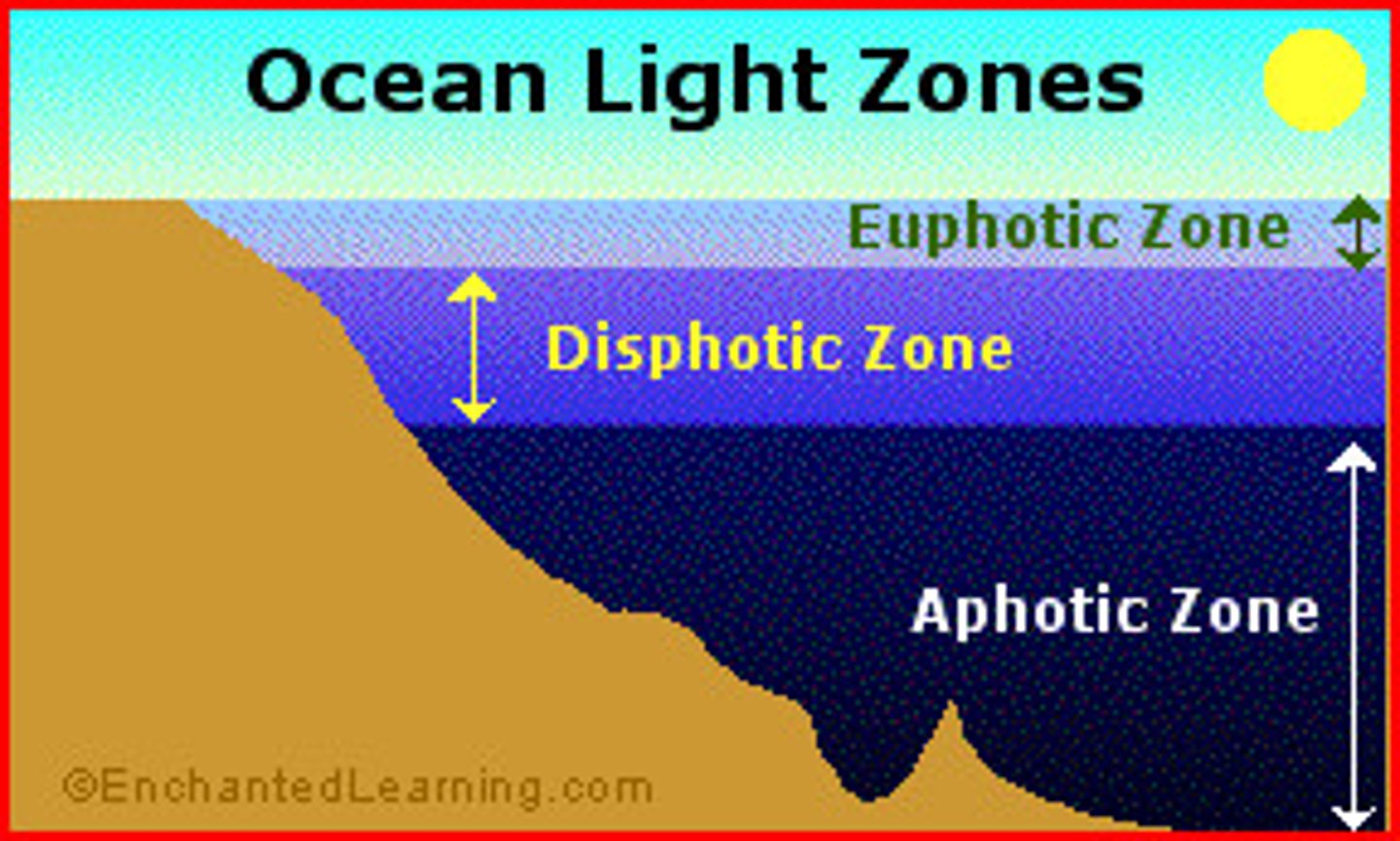
Compensation Point
The light intensity at which the rate of photosynthesis and the rate of respiration are equal.

Disphotic zone ( twilight zone )
- Below the compensation point there is still light but not enough to survive because the rate of respiration would be greater than the rate of photosynthesis. Around 90% of marine life is found above the compensation point.
2) Changes in Biomass
Found by harvesting producers after a set amount of time, drying them to remove variations in the water content, then finding the mass.
If they know the size of the area the producers came from , they can work out the biomass per unit per year to give an estimate of the net primary production.
you cannot find estimate the gross primary production because you cannot measure the biomass that has already been consumed by heterotroph.
3) Satellite Imagery
found by using the color of surface layers from satellite imagery
- higher altitude = green and red ( most productive )
-lower ( least productive ) = Blue and Purple
- because the biomass is not fixed, it depends on the individual species present in their adaptations.
it cannot penetrate the whole euphotic zone.
Influence on Productivity
more productivity = more biomass = more for consumers to eat.
High light energy = thermocline
light levels are higher = more productivity
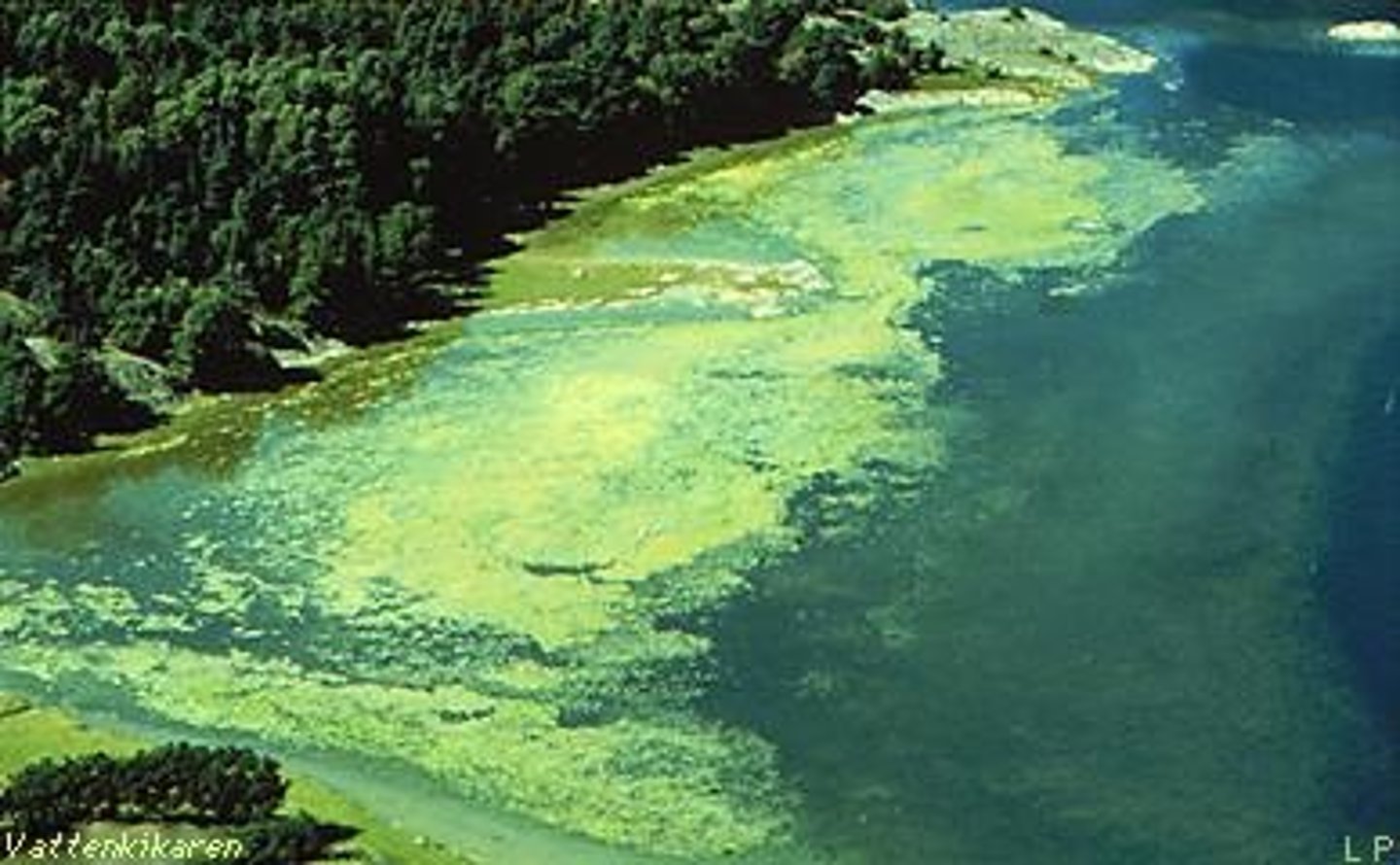
Eutrophication
a body of water becomes too enriched in dissolved nutrients like phosphates and nitrates that stimulate the growth of producers , resulting in a depletion of dissolved oxygen.
- 5 million cells per litre can be produced when this happens damaging the ecosystem.
Phytoplankton rapidly increase causing an algal bloom.
- can clog gills of fish .
Once the algal cells die they reprise and take up oxygen in the water leading to hypoxic conditions, killing heterotrophs.

Eutrophication pt.2
algal species also produce toxins the effects can be worse because organisms that ingest them will be poisoned.
Energy transfer through the food chain
Only a small amount of sun gets absorbed by producers because it either reflects or is scattered by water.
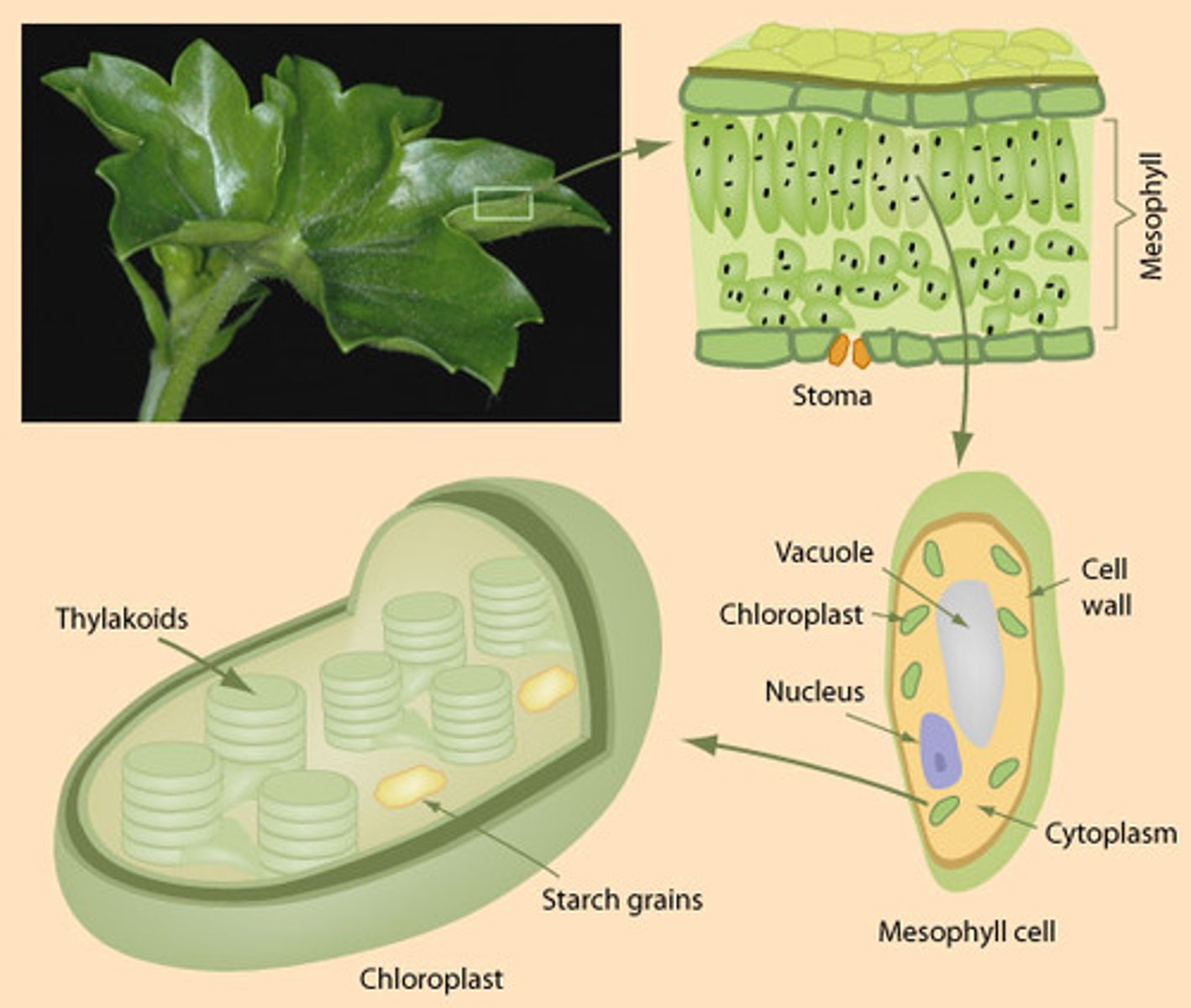
Chlorophyll
absorbs red and blue light but reflects green. That's why when the sun hits the water only the chloroplasts are absorbed.
Secondary Production
the production of new biomass by the consumers. can involve animals eating phytoplankton, macro algae and seagrass or animals and animals.
DEPENDS ON
- the biomass available in the producers
- the amount of energy lost through respiration by the consumers.
- the amount of energy lost in waste products such as urine.
Energy transfers
C= P+R+F+U
c= consumed r= energy used in respiration
u= energy in urine p= energy left over after production of biomass
Typically the efficiency of transfer between trophic levels is 10% but it varies depending on :
- how much of food is eaten
- how easy it is for consumer to digest and assimilate the nutrients
- how much energy is used for movement
- how much is lost in the waste products of metabolism.
Pyramid of Numbers
a diagram that shows the number of organisms in each trophic level of a food chain.
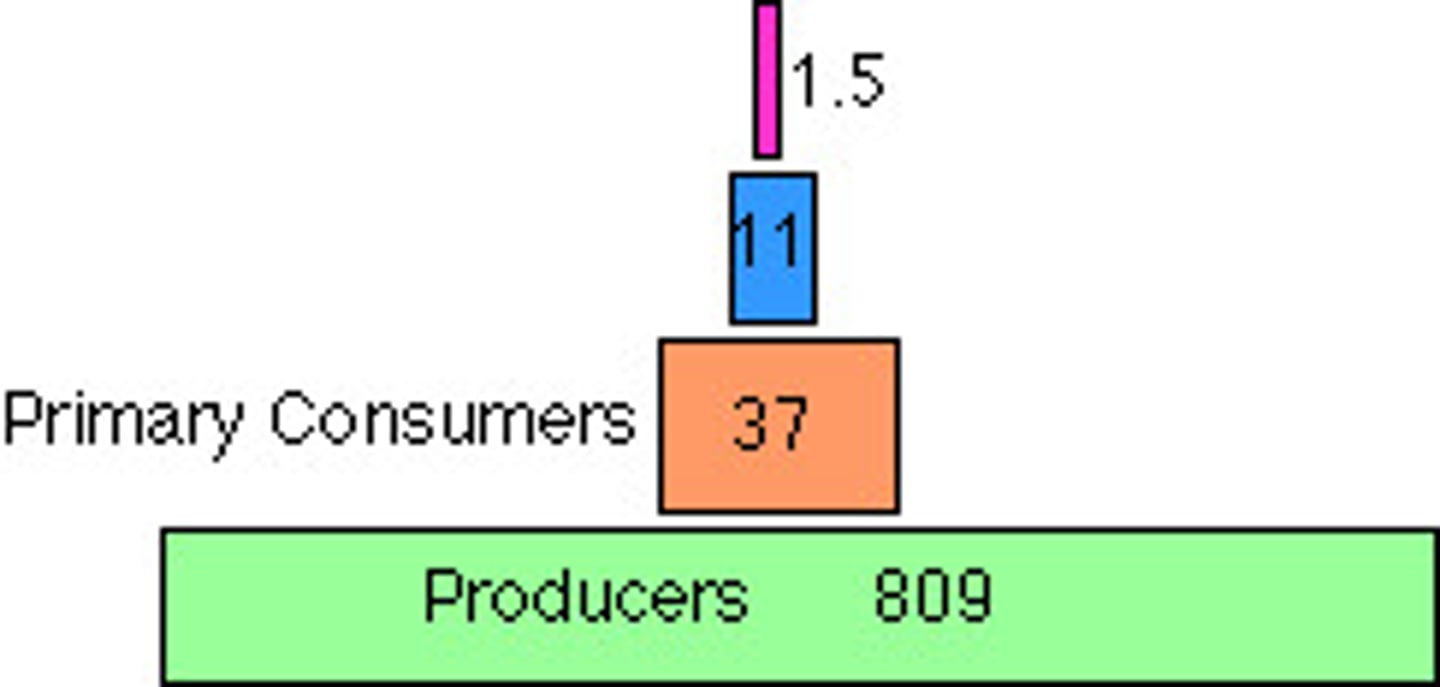
Pyramid of Biomass
instead of finding the number of each organism you find the total biomass of each organism.
- difficult to do accurately
Pyramids of Energy
the amount of energy typically throughout a year. the units for pyramids of energy are kJ m^-2year^-1
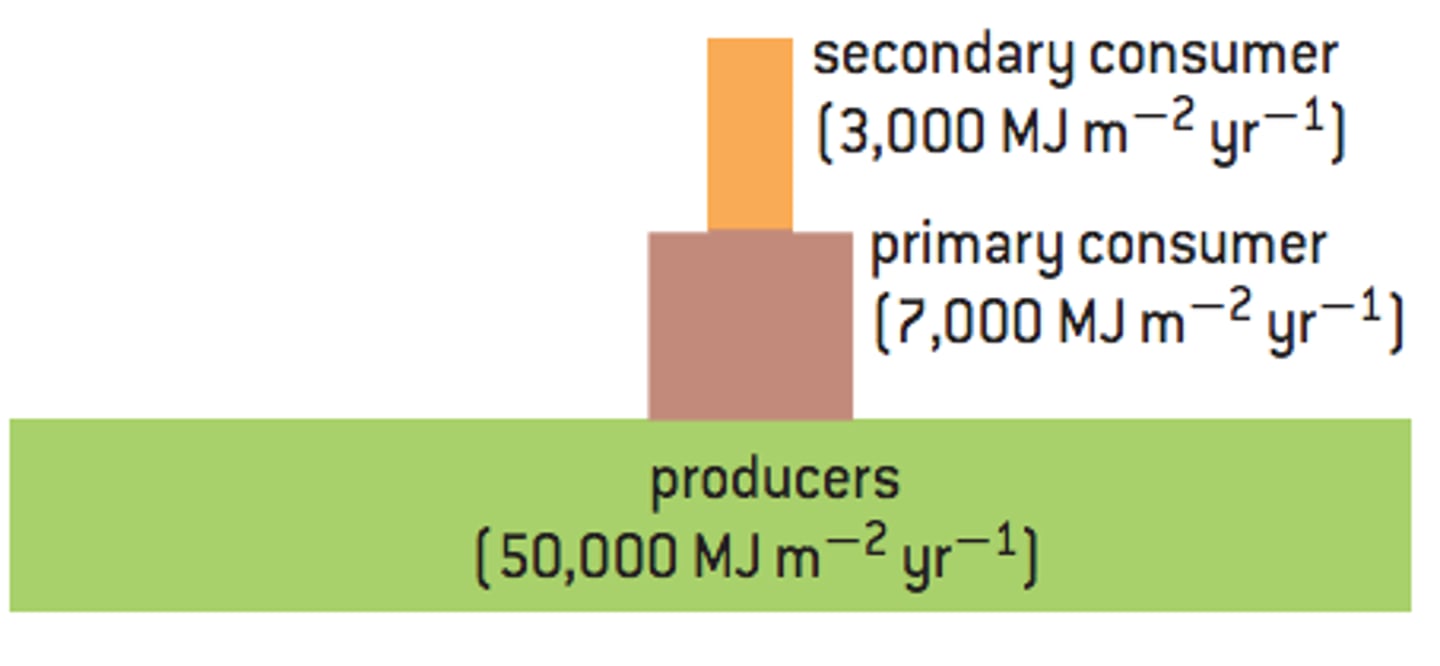
Pyramids of Numbers, Biomass, and Energy during an Algal Bloom.
Due to loss of oxygen and animals will die due to hypoxic conditions so the numbers will decrease affecting the ecosystem completely but the phytoplankton growing fast. but the zooplankton don't
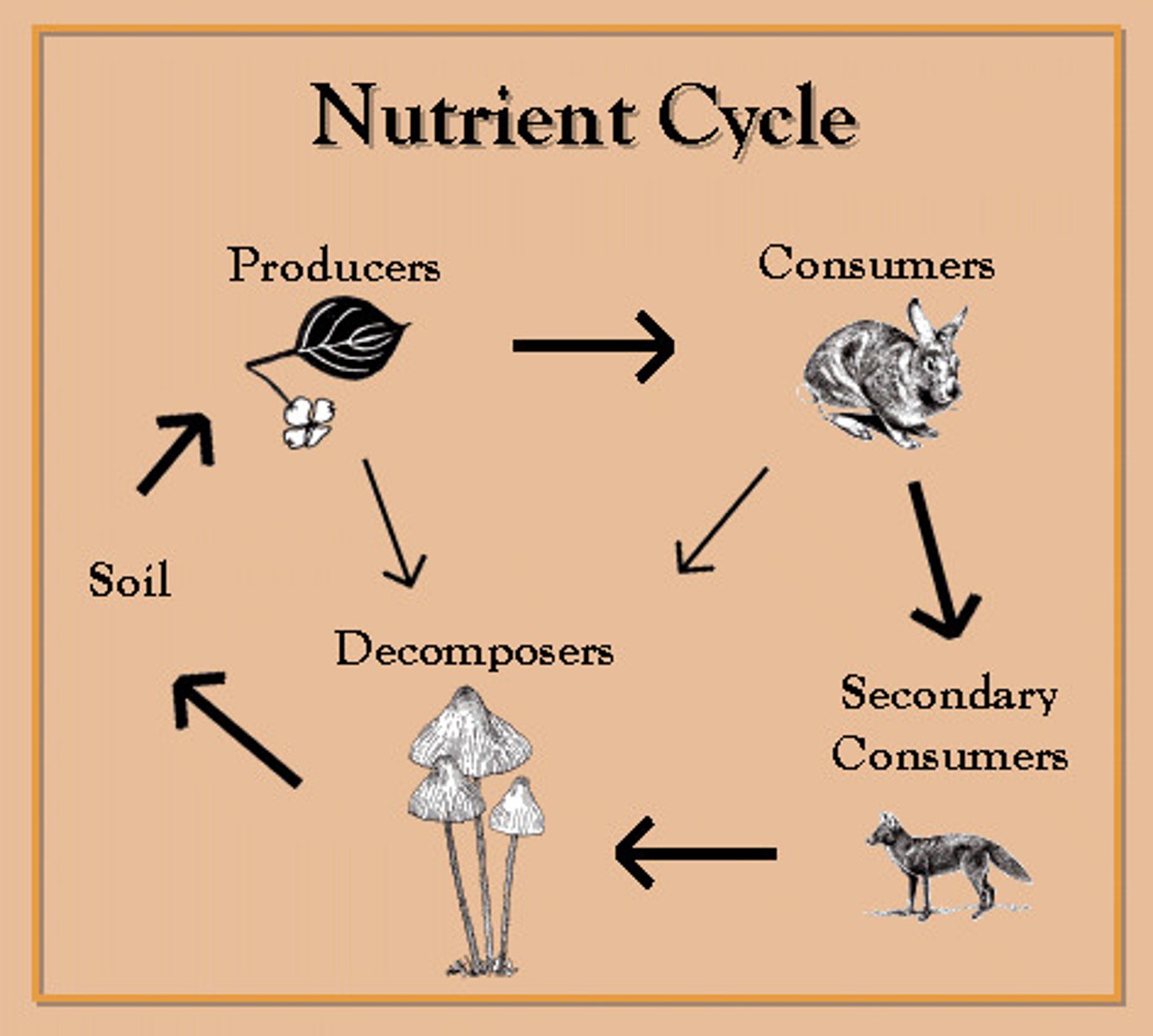
Nutrient Cycle
The movement and exchange of elements that are essential to life, from inorganic molecules, through fixation and then into living organisms, before being decomposed back into inorganic molecules.
Assimilation
The conversion of a nutrient into a useable form that can be incorporated into the tissues of an organism.
The Biotic Phase
During the Biotic Phase, nutrients are moved from one organism to the next by feeding. So nutrients move along the food chain from producers to consumers.
primary consumers-->consumers---->decomposers.
Carbohydrates, Lipids and Protiens
-They are three very important polymers ( large molecule made from other sub-units called MONOMERS )
Starch
Made of Glucose Molecules joined together
Cellulose
Important component of cell walls made by mostly glucose molecules.
Lipids
Made from Carbon, Hydrogen, and oxygen. Triglycerides are formed by carbon, hydrogen and oxygen made from long fatty acid molecules joined to a glycerol molecule by ester bonds which are hydrophobic. Joined by peptide bonds.
Proteins
polymers formed from amino acids and contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur. there are 20 amino acids that form proteins and determined by DNA and rely on:
- Enzymes which speed up chemical reactions
-horomones, chemical messangers
-part of bones, muscles, skin , cartilage
-part of the cell wall in plants