Pediatric Development and Milestones Review for Health Assessment Exam 4
1/310
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
311 Terms
Describe the posterior fontanel.
This is TRIANGULAR in shape and usually less than 1 cm in size. It is usually soft and flat, not bulging or sunken. This closes from 6 WEEKS TO 2 MONTHS.
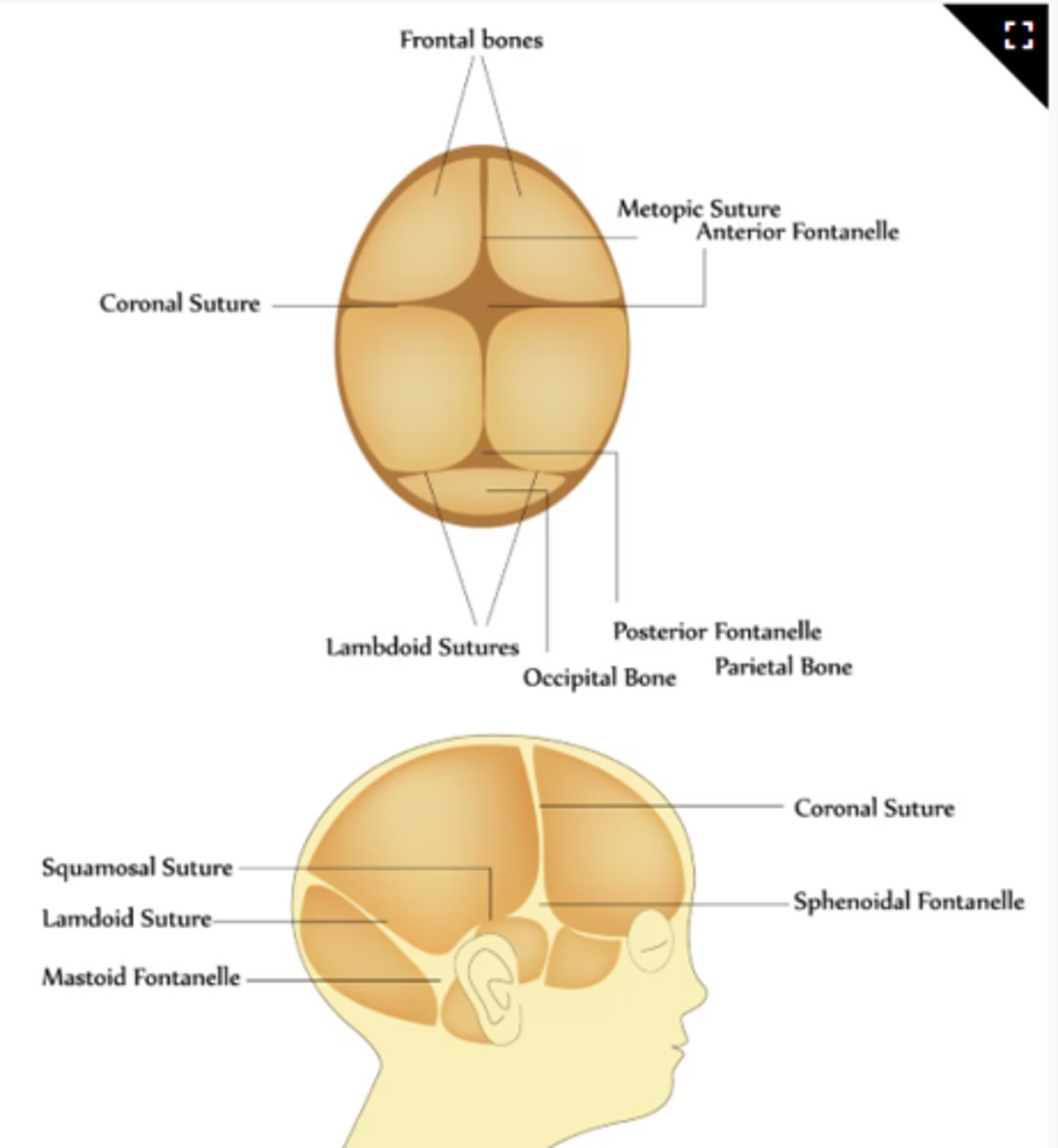
Describe the anterior fontanel.
This is DIAMOND-shaped and may vary in size. It is usually soft and flat, not bulging or sunken. This closes from 12-18 MONTHS.
What are retractions and why are they important?
IN-DRAWING of the chest muscles on inspiration and these commonly occur with RESPIRATORY ILLNESS/DISORDER especially in young children. Types include intercostal, subcostal, substernal, suprasternal, and supraclavicular.
In infants, toddlers, and pre-schoolers, where is the apical impulse typically located?
At the left of the midclavicular line in the 4th intercostal space.
How are heart murmurs graded?
By the INTENSITY and QUALITY of the sound they create.
Define recumbent length.
This is measured in children 2 years of age and under. It is done using a measuring board OR a non-stretchable measuring tape. Length is measured from the top of the head to the bottom of the heel in the SUPINE position. EXPECTED is between 45 to 54 CM with an AVERAGE of 50 CM.
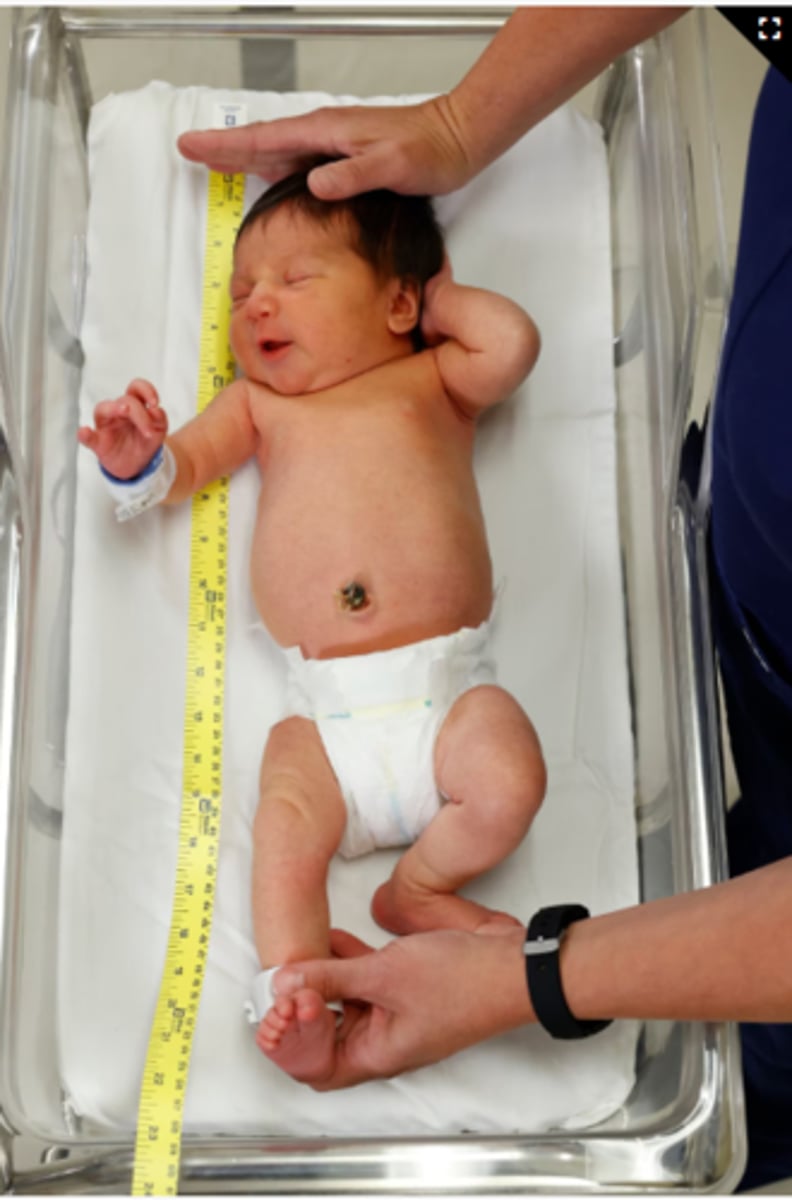
Why is head circumference measurement important for infants/toddlers?
It is reflective of brain growth and may also indicate problems such as microcephaly (<31 cm), craniosynostosis, or hydrocephalus. The average in a newborn is 35 CM and the normal is 31 to 37 CM. This is usually 1-2 CM LARGER than the CHEST.
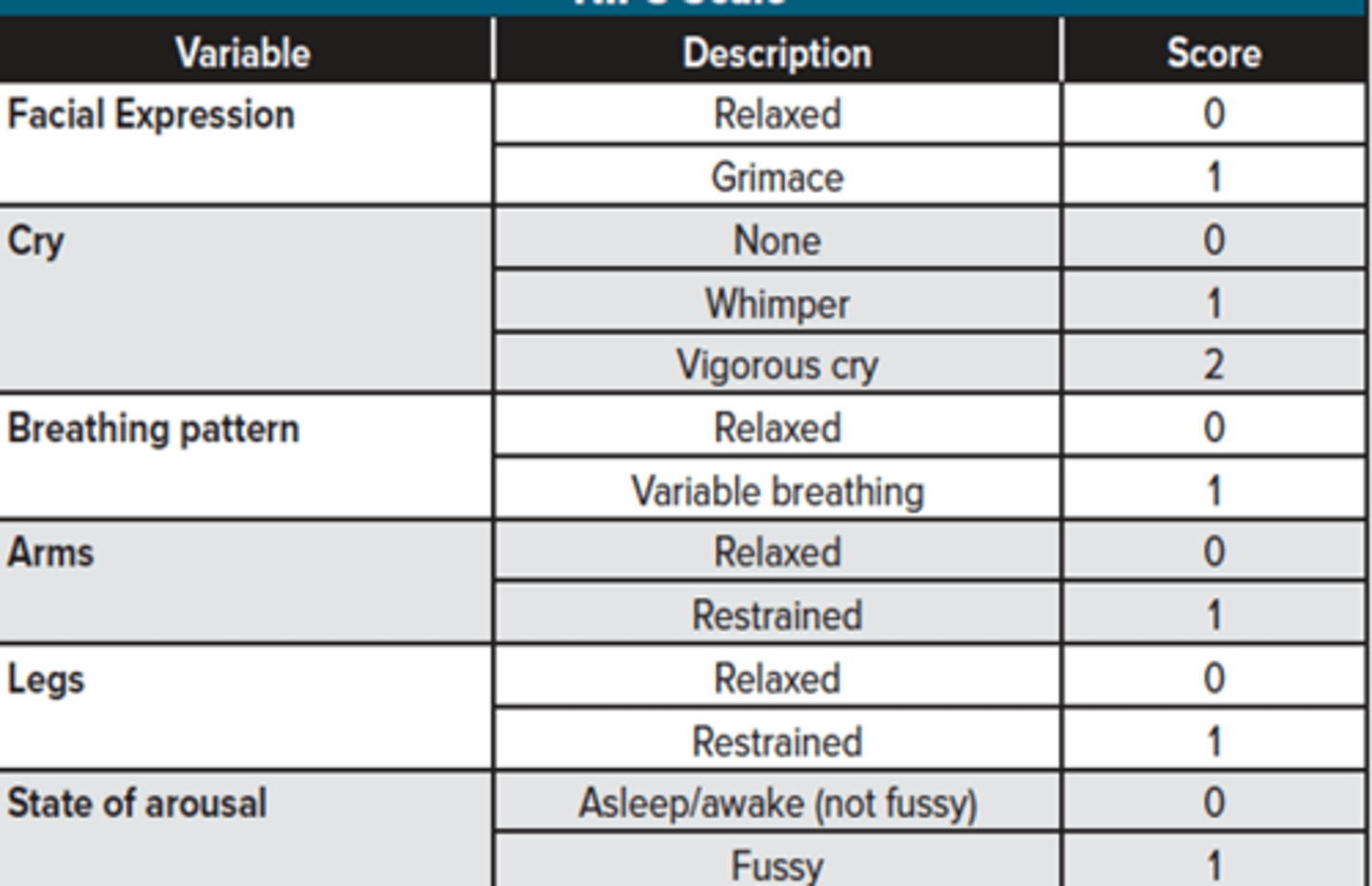
Which pain scale is used for neonates and infants (birth to 12 months)?
Neonatal Infant Pain Scale (NIPS) which includes facial expressions, crying, breathing pattern, motor activity of the arms and legs, and state of arousal. A higher score indicates severe pain and a lower score indicates mild or no pain.
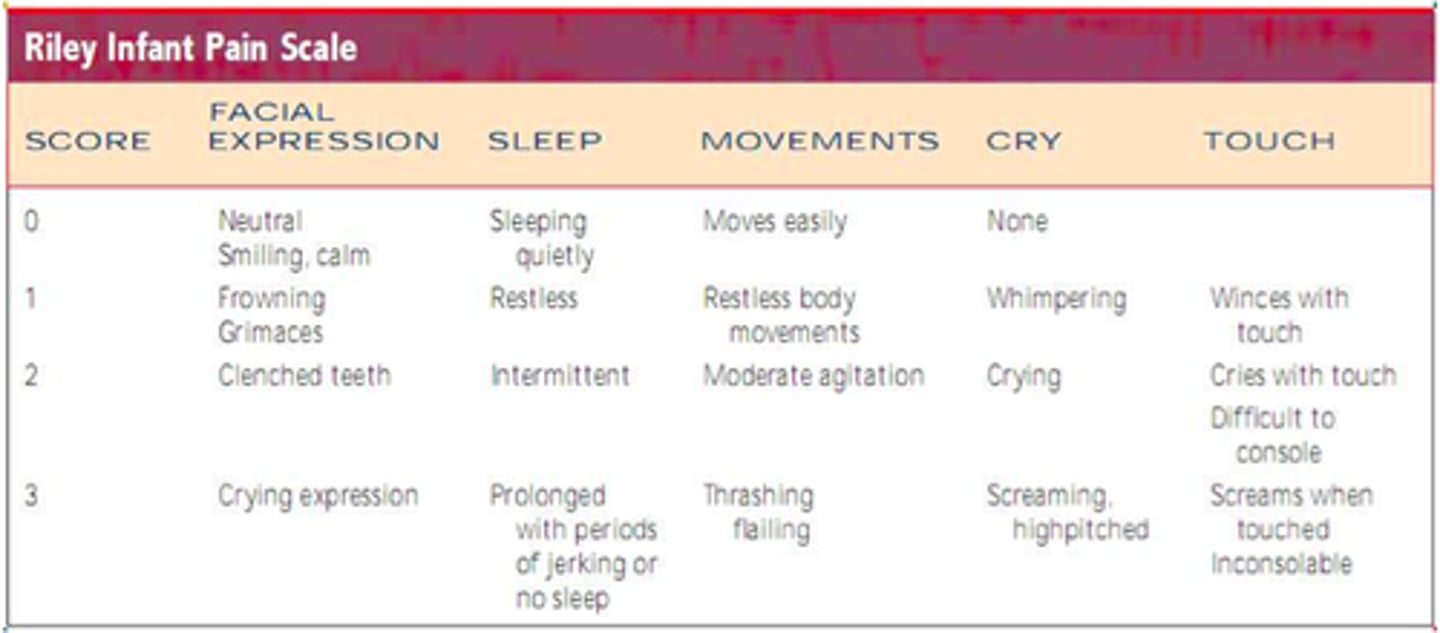
Which pain scale is used for infants (up to 12 months)?
Riley Infant Pain Scale (RIPS) which includes facial expressions, body movement, sleep, verbal/vocal consolability, and response to movement/touch. A higher score indicates higher pain and a lower score indicates minimal or no pain.
What is the age range for an infant?
1 month to 12 months
It is expected for newborns to lose 5 to 10% of their body weight over the first few days of life.
True
1 multiple choice option
When should newborns return to their birth weight after initially losing weight?
Returns within 10 TO 14 DAYS.
What birth weight is appropriate for gestational age (AGA) in a full-term newborn?
Between 2500 g (10TH PERCENTILE) and 4000 g (90TH PERCENTILE). Below 2500 g (less than the 10th percentile) would be low birth weight (SGA) and higher than 4000 g (more than the 90th percentile) would be high birth weight (LGA).
Which PRIMITIVE reflexes be present in newborns?
Moro, rooting, stepping, tonic neck, sucking, corneal, palmar grasp, plantar grasp, gag, blinking, and swallowing
Describe the assessment for muscle tone in a newborn.
Observe for passive (RESTING POSITION) and active tone.
Observe FLEXION of extremities.
Movements should be smooth, symmetrical, and spontaneous (SSS) in all extremities.
Posture at rest reflects position IN-UTERO.
HYPOTONIA or poor muscle tone requires follow-up.
Describe the assessment of motor function in a newborn.
Evaluate active and passive muscle function.
Expected resting posture for term newborns shows strong flexion in all 4 extremities.
By age 32 TO 34 WEEKS of gestation, they have a symmetric, smooth, and spontaneous movements in all extremities.
What is the typical range of the newborn's heart rate?
110 TO 160/MIN and count for the FULL MINUTE. This may decrease during sleep and increase during activity, feeding, and crying.
What is the typical newborn's respiratory rate?
30 TO 60 BREATHS/MIN and count for the FULL MINUTE to account for expected variations in rhythm and rate.
How should the newborn's temperature be measured and what is the range?
Via AXILLARY method to minimize invasiveness and 36.5 to 37.5 degrees C or 97.7 degrees F to 99.5 degrees F.
Define lanugo.
Fine, soft DOWNY hair, especially that which covers the body and limbs of a very young infant or newborn.
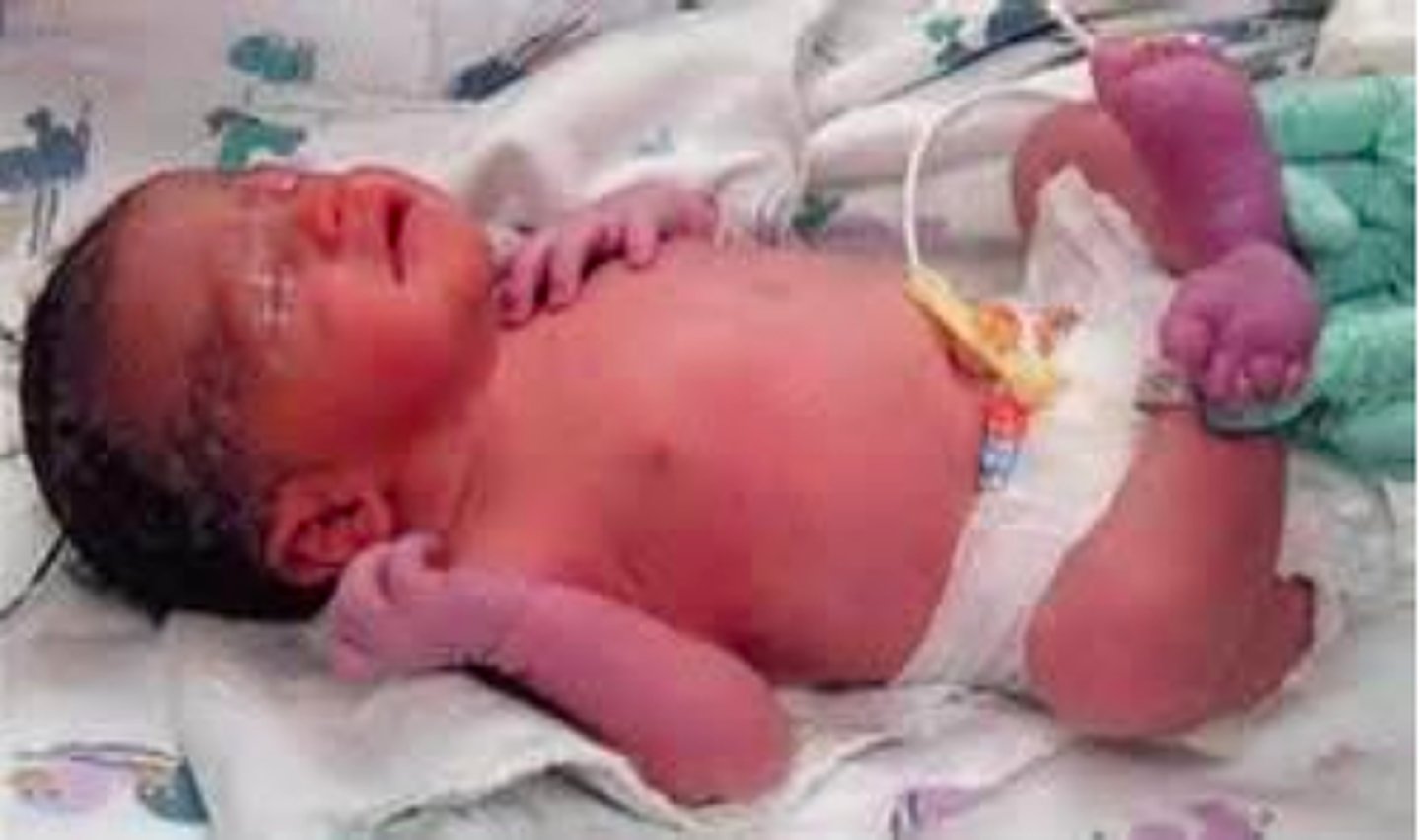
Define acrocyanosis.
A newborn's skin will initially be deep red to purple with central pink color/BLUENESS of the hands and/or feet and is typical in THE FIRST FEW DAYS AFTER BIRTH. In lighter-skinned infants, the entire foot or hand may appear blue in color. In darker-skinned infants, acrocyanosis may be noted on the soles or palms. This should fade to the color of their genetic background.
Is jaundice in newborns abnormal?
This is considered pathologic if observed in the first 24 hours after birth, however, it can also appear on the 3RD DAY OF LIFE due to increased BILIRUBIN then it will decrease spontaneously.
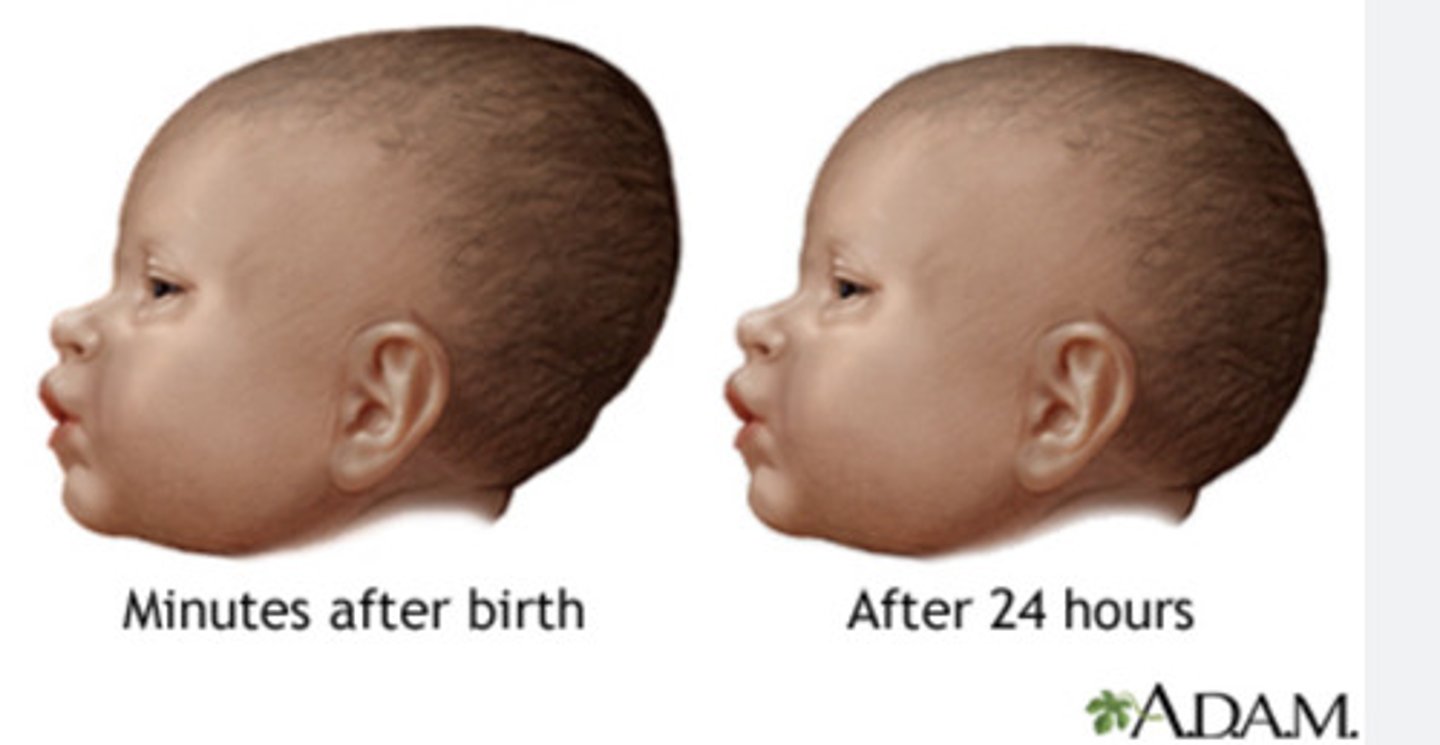
Define molding.
ELONGATION of the newborn's head related to passage through the BIRTH CANAL and should resolve in the FIRST FEW DAYS OF LIFE.
Define caput succedaneum.
EDEMA or swelling over the presenting part of the newborn's head which CROSSES SUTURE LINES. This is COMMON and should resolves within A FEW DAYS.

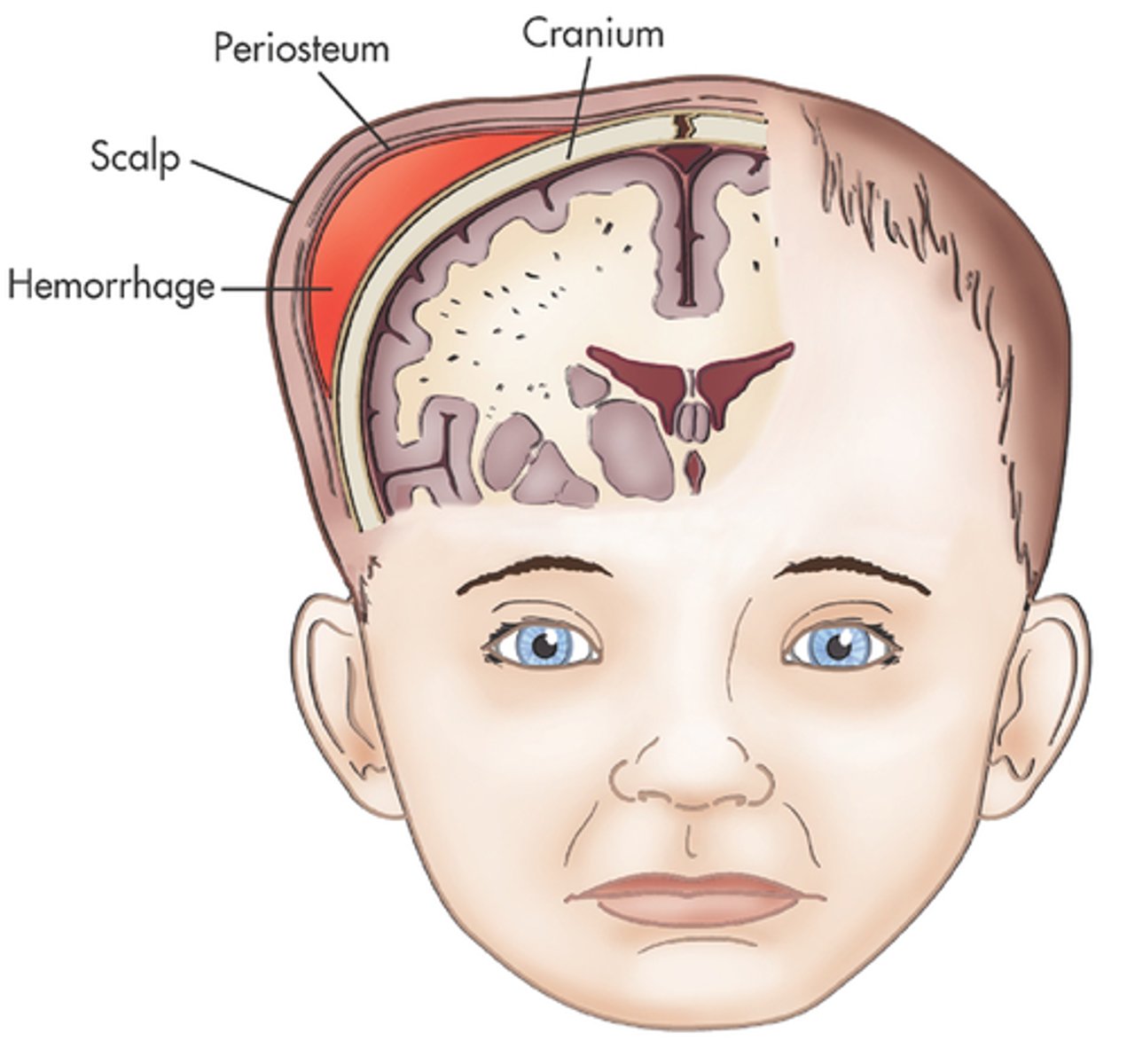
Define cephalohematoma.
Accumulation of BLOOD under the subperiosteum that results in SWELLING of the scalp and this does NOT cross suture lines. It may increase in size after birth and can up to WEEKS OR MONTHS TO RESOLVE.
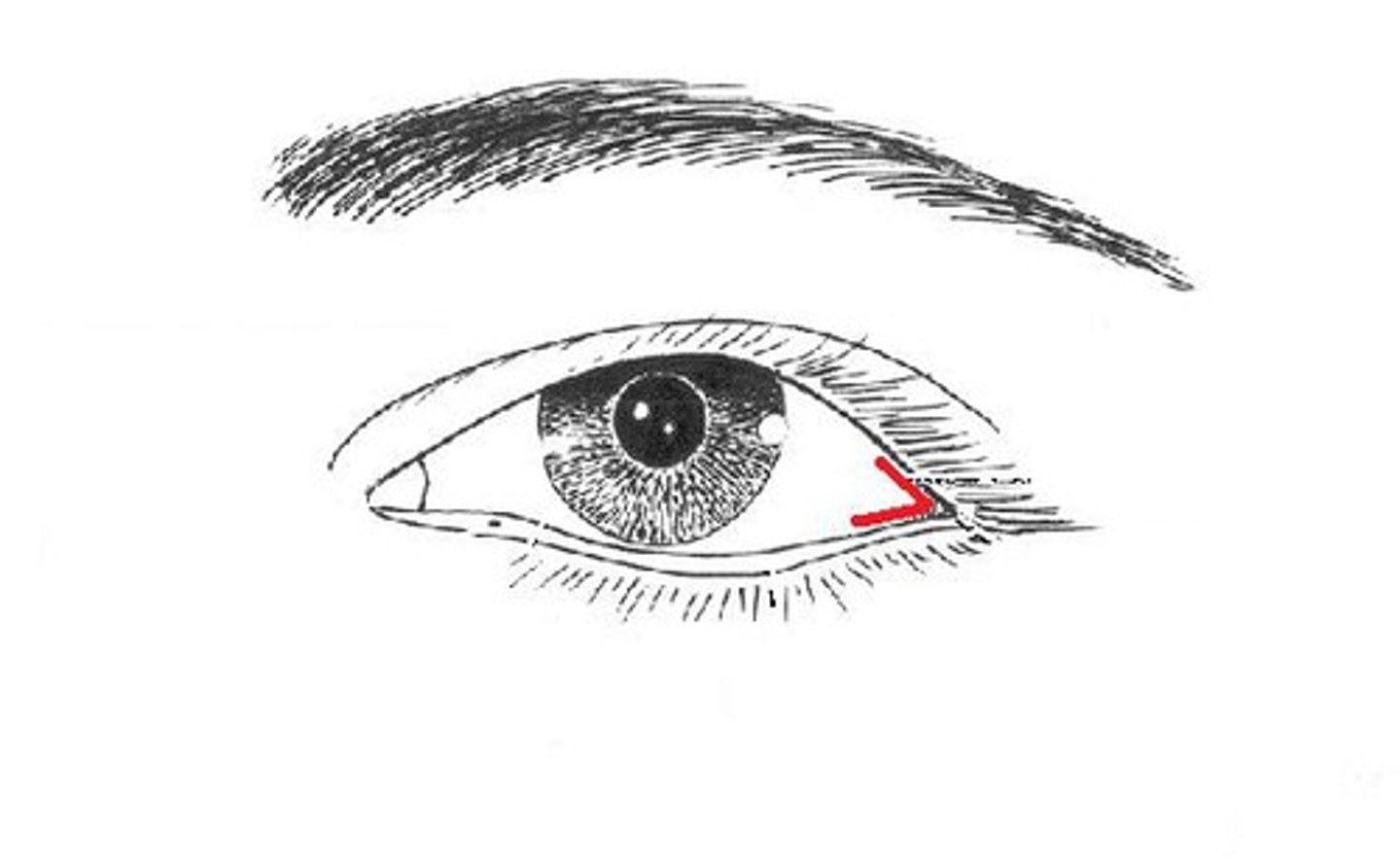
What should the helix or auricle or pinna of a newborn's ear be aligned with?
When it intersects or is above the level (10 degrees) of the OUTER CANTHUS of the eye. If it is lower, it is low-set which can indicate a syndrome or renal disease.
How is patency of the nares in a newborn assessed?
Noting the MOVEMENT of a piece of thread or cotton in front of each.
How does the newborn breathe?
Diaphragmatic and has a barrel chest (1:1)
What are some signs of respiratory distress?
Grunting (newborns), retractions, nasal flaring, rhonchi, crackles, prolonged expiratory phase, shallow rapid breaths, coughing or strong crying may clear upper airway congestion (makes it easier to hear true lower airway sounds in infants/toddlers)
What are expected findings of a newborn's nipples?
Engorgement and a milky white discharge (galactorrhea) due to maternal hormonal influences (also called witch's milk)
Is a murmur an unexpected finding in a newborn?
No, this is expected for the FIRST 24 HOURS of their life due to the foramen ovale. This will occur until the ductus arteriosus closes. If it persists after 24 hours, further cardiology evaluation may be necessary.
What should a newborn's abdomen be like?
Slightly protuberant and soft to light palpation
How is anal patency of a newborn determined?
The passage of MECONIUM stool within 24 to 48 hours after birth.
Milky or slightly blood vaginal discharge (pseudomenstruation) from a newborn may occur in the first few weeks of life in response to maternal circulating hormones.
True
1 multiple choice option
Define syndactyly.
FUSION of fingers or toes. This can happen incidentally in healthy infants or be associated with genetic syndromes.
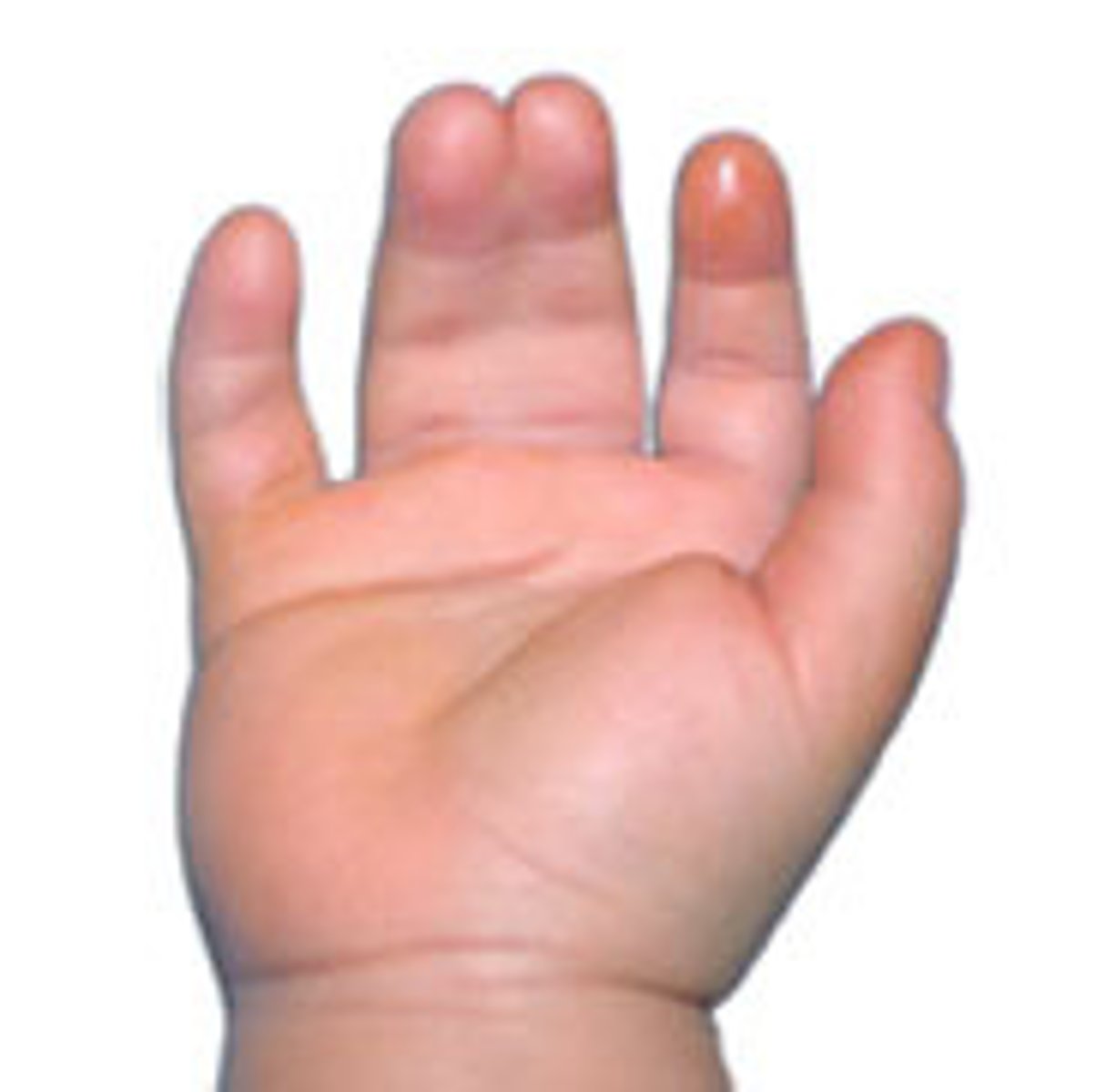
Define polydactyly.
Having EXTRA digits. This can happen incidentally in healthy infants or be associated with genetic syndromes.

What characteristc of the hand is associated with Down syndrome (Trisomy 21) but can also be present in healthy infants?
A single palmar crease
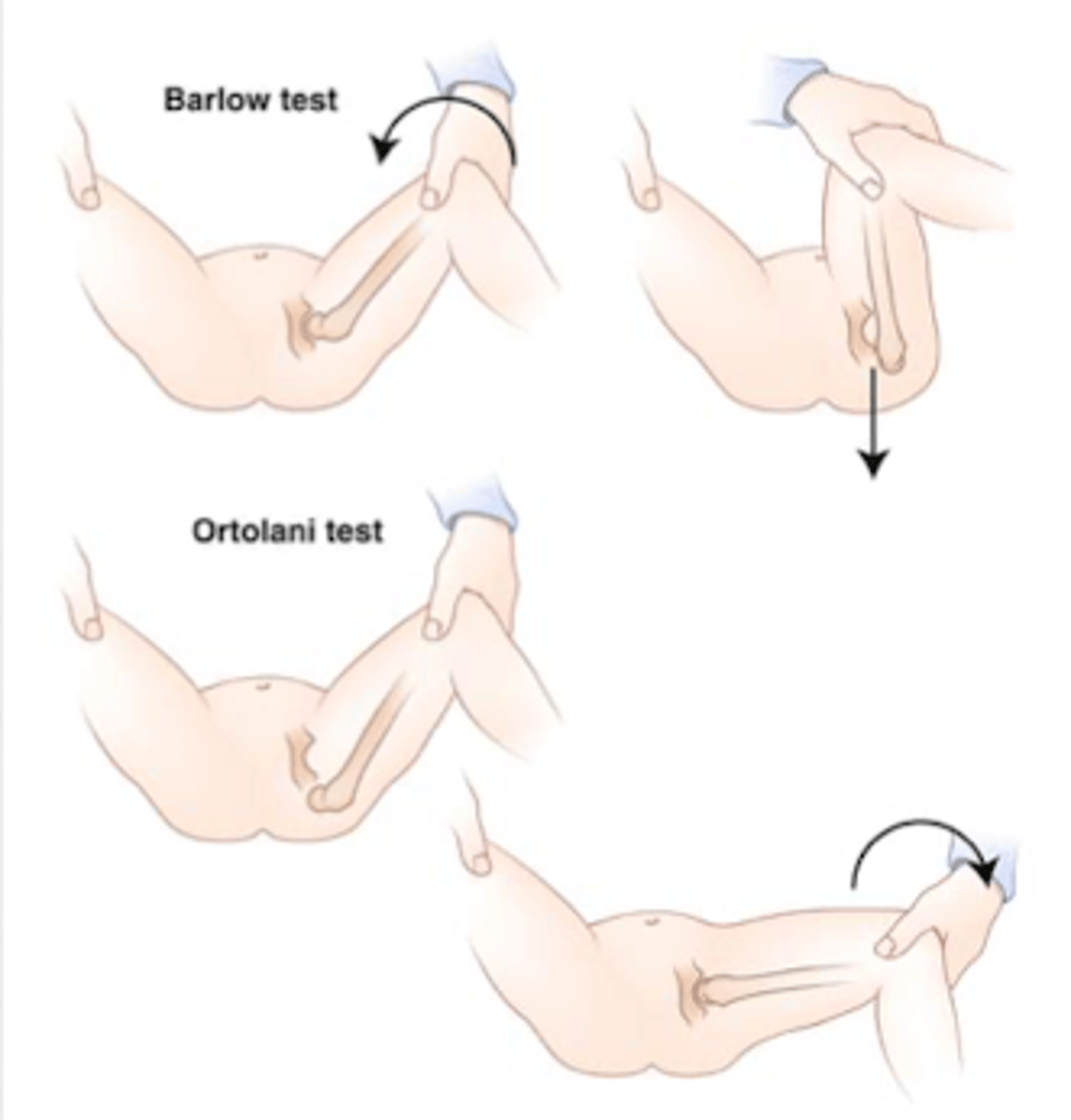
Describe the Ortolani test.
Place the thumb on the newborn's inner thigh and index finger over the greater trochanter.
With the knees flexed 90 degrees, abduct the upper leg applying gentle pressure on the trochanter.
A positive test indicate possible DDH is noted by a CLUNK or JERK with this maneuver.
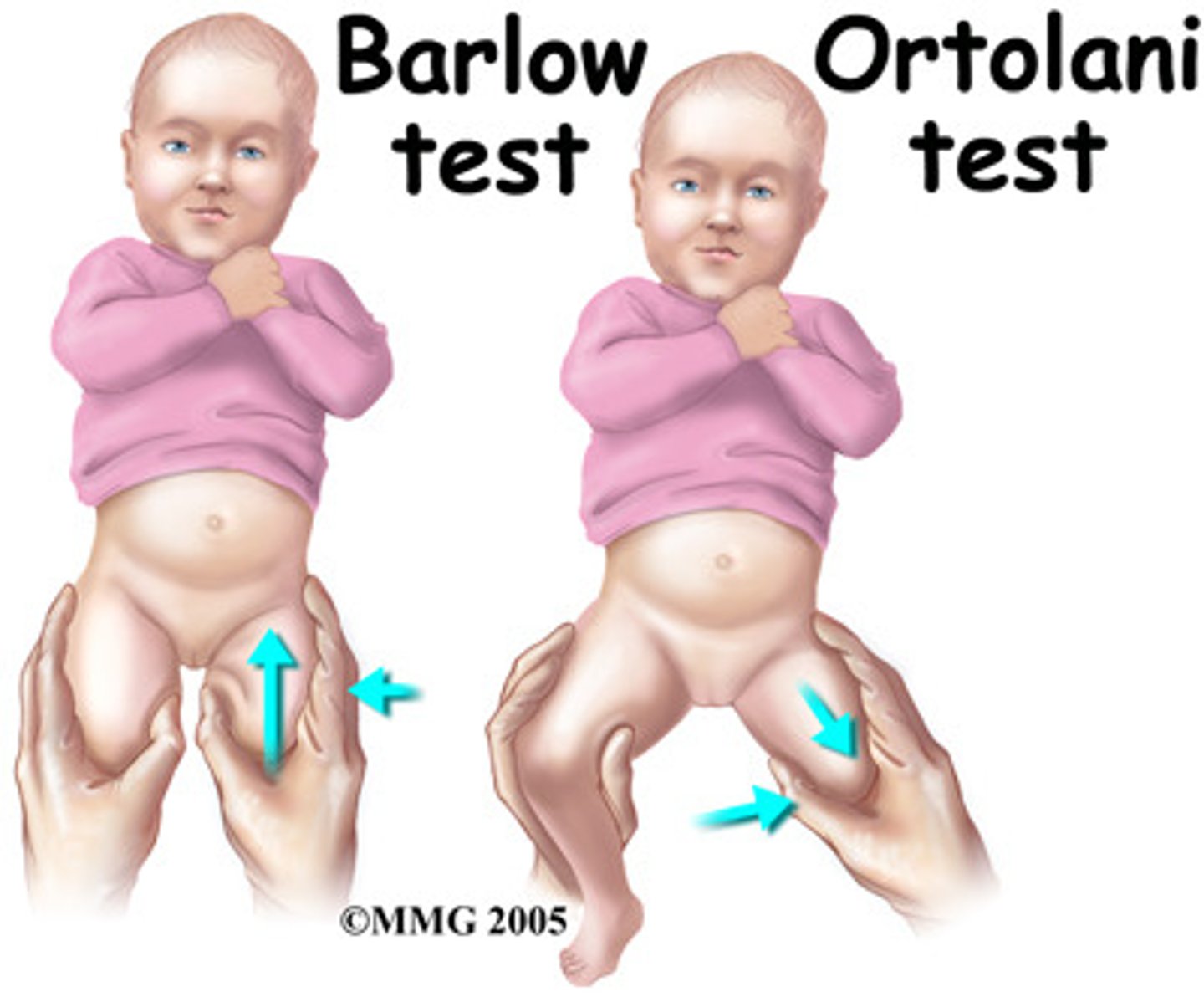
Describe the Barlow test.
With the hips abducted, gentle apply pressure to the posterior hip.
A positive indicating possible DDH is noted by a clunk or jerk with this maneuver.
How do you assess for the Moro or startle reflex?
The examiner holds the newborn in SUPINE position and lets the head drop slightly or performs a loud hand clap over the newborn while they are laying supine. The newborn should symmetrically ABDUCT and EXTEND their arms and fingers, while the legs FLEX UP towards the trunk.
How do you assess for the rooting reflex?
Tickle the corner of the mouth or brush the side of the cheek near the mouth. The newborn should TURN ITS HEAD towards the stimulus, open its mouth, and begin to suckle.
How do you assess for the stepping reflex?
Hold the infant in a VERTICAL position with the feet contact with a flat surface. The infant lifts their feet alternatively as if to walk.
How do you assess for the tonic neck reflex?
With the newborn in a SUPINE position, turn the head quickly to one side. The newborn should assume a "FENCING" position where the arm and leg on the side to which the head was turned extend while the opposite arm and leg flex.
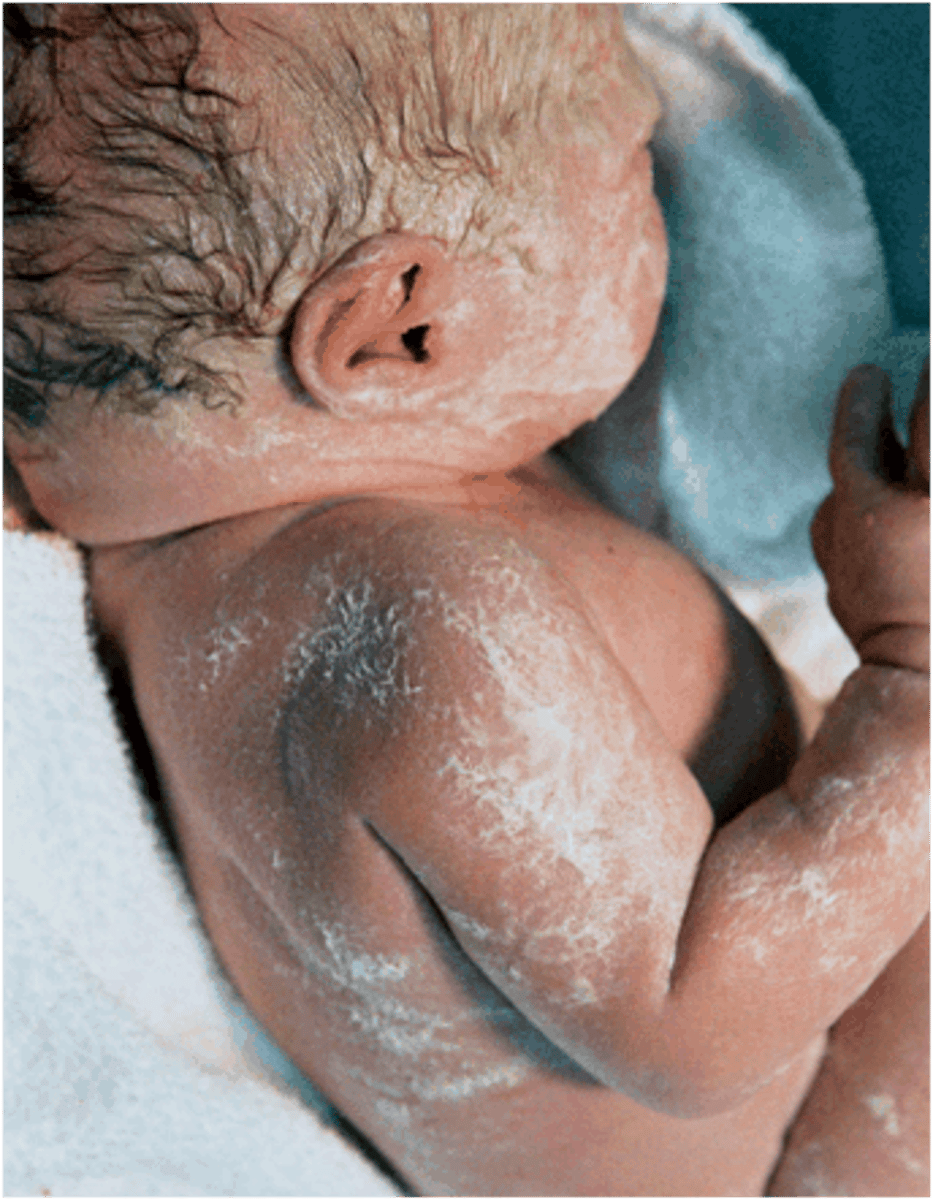
What is vernix caseosa?
A thick cheesy substance found coating the skin of newborns.
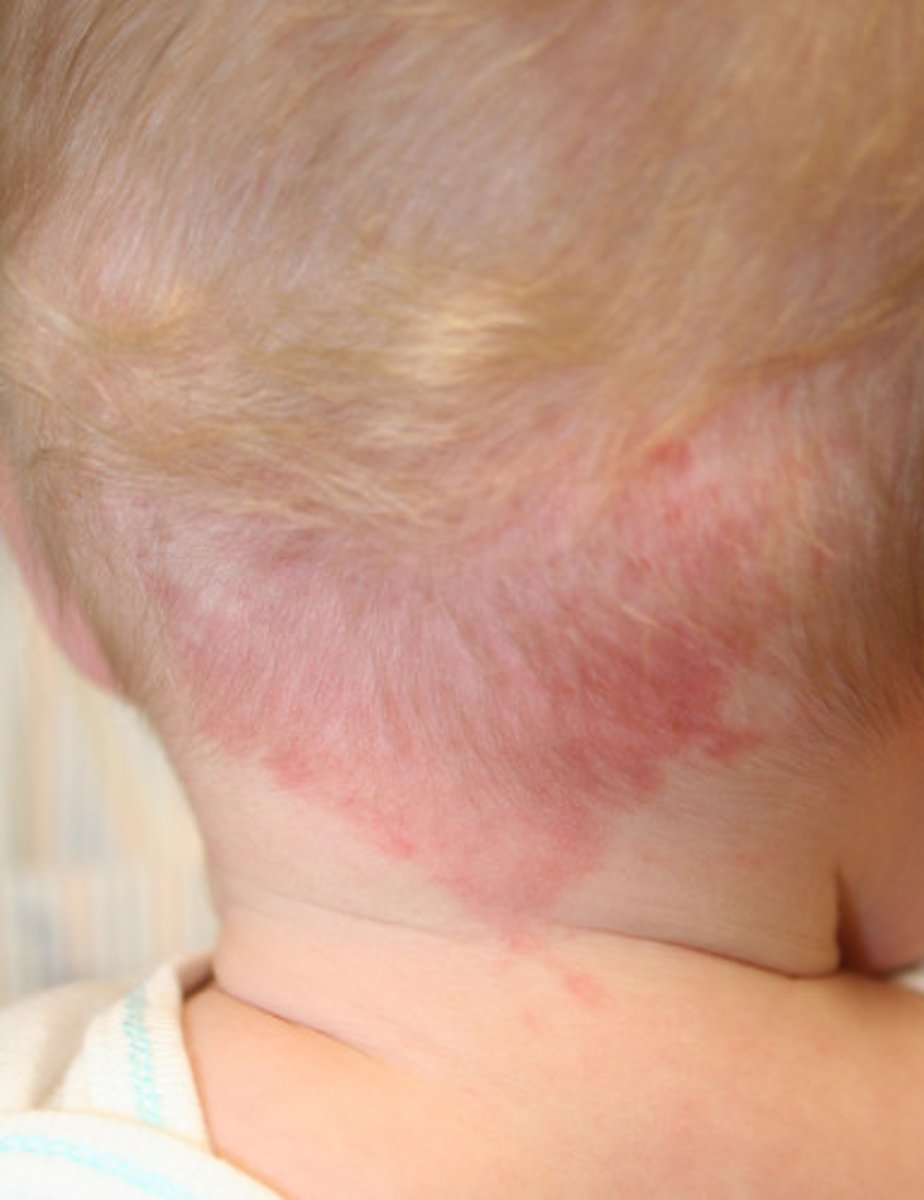
What are "stork bites"?
FLAT PINK and RED PATCHES that are caused by a cluster of capillaries that usually appears on the back of the neck or head. These are harmless and fade over time usually by age 2.
Define erythema toxicum (erythema neonatorum).
A COMMON and non-threatening PINK RASH in newborns that is typically present in the first 3 weeks of life then disappears.
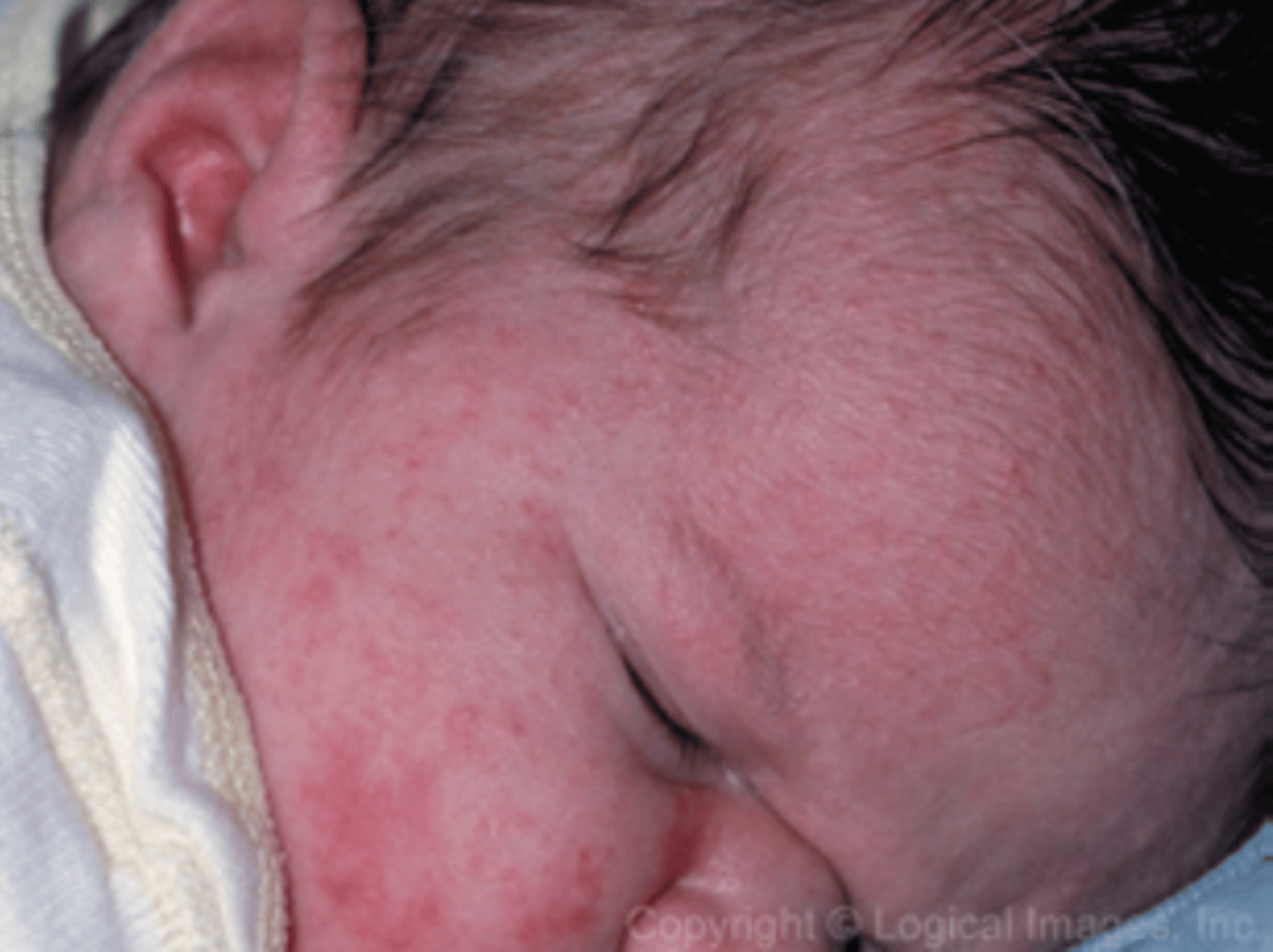
Define milia.
Common skin condition causing SMALL WHITE BUMPS (cysts) under the skin caused by clogged sebaceous glands which are very active due to maternal hormones and usually appear on the NOSE and CHEEKS.

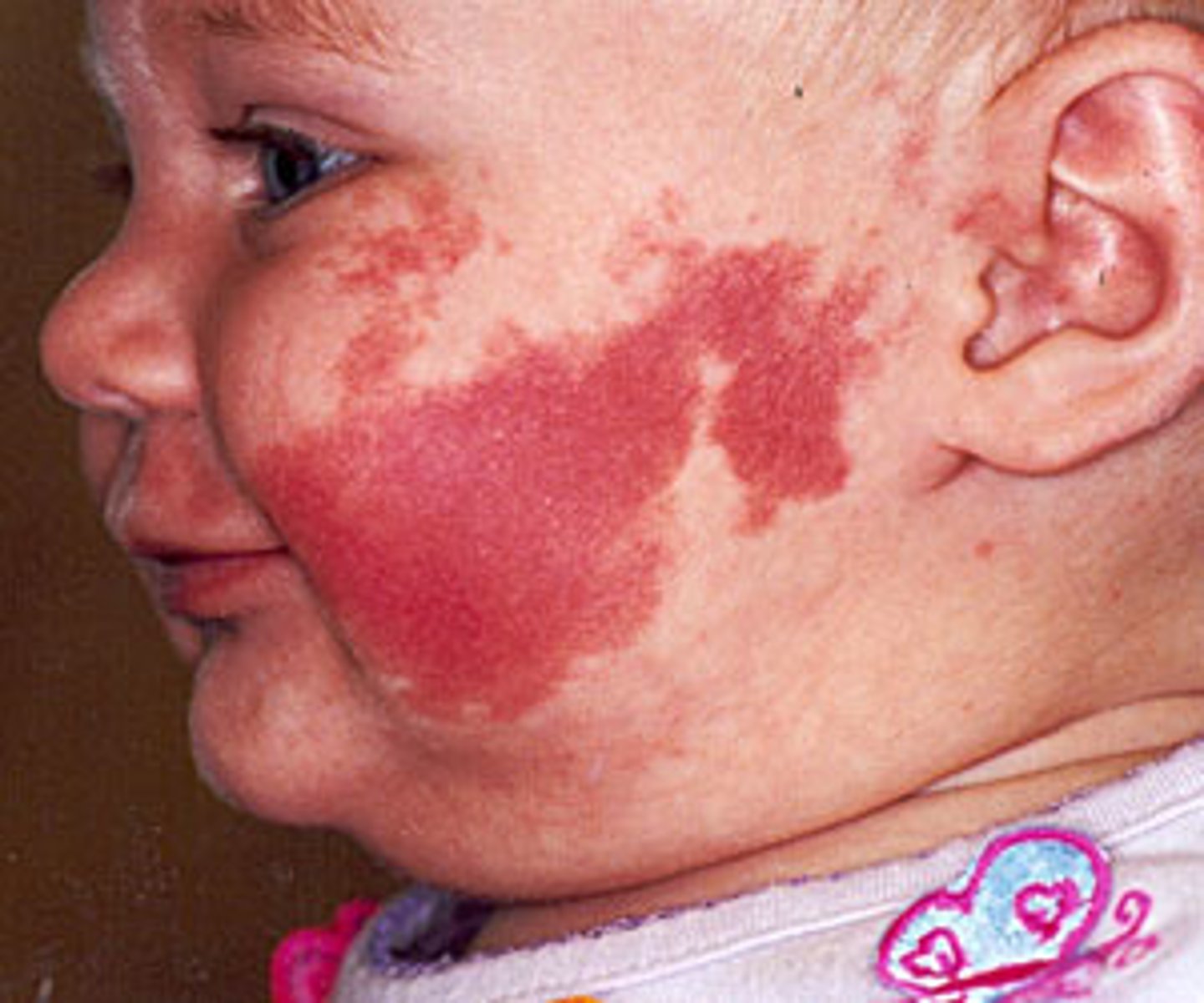
What does nevus flammeus (port-wine stain) indicate?
A congenital skin condition that can affect any part of the body and PERSISTS through life (does not disappear).
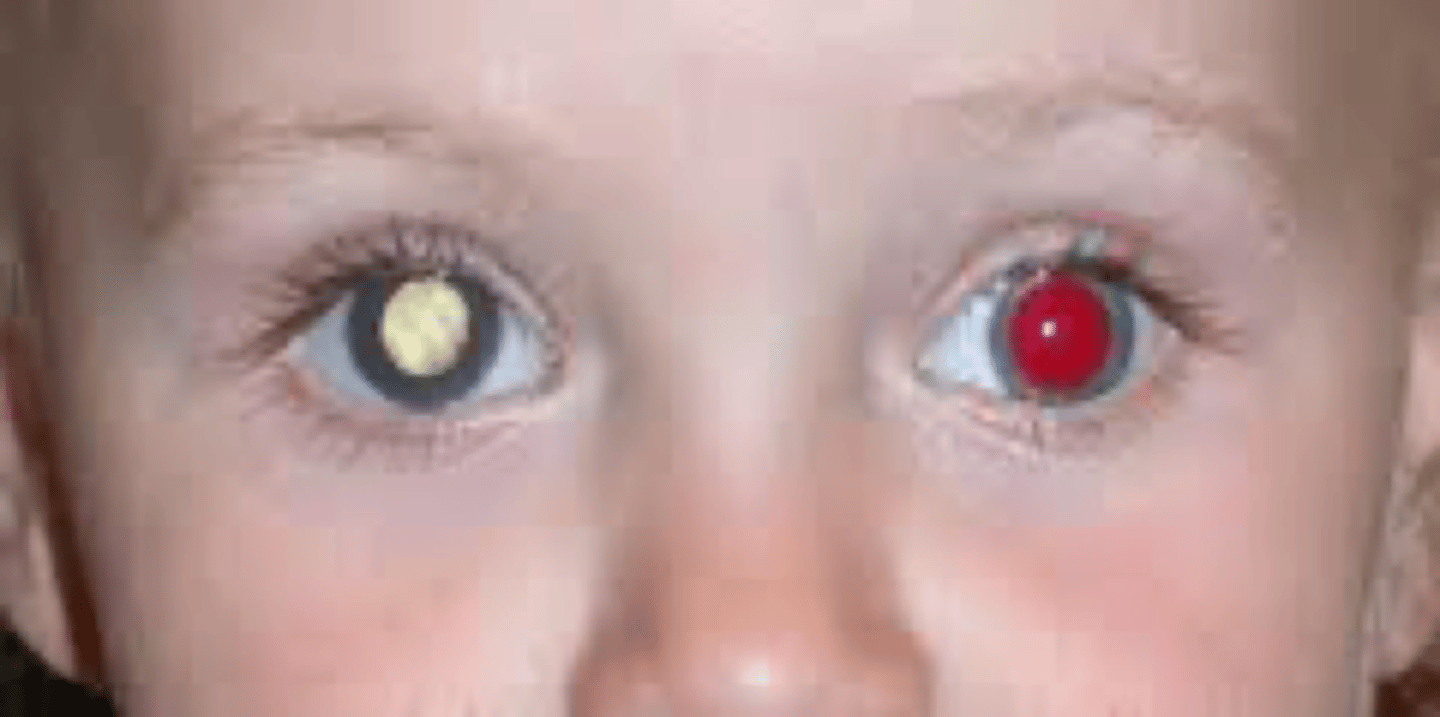
What is the red reflex?
Normal REDDISH coloration of the PUPILS that is visible when LIGHT SHINED into the pupil reflects off the inside surface of the eye. Conditions that may cause absent or abnormal results in a newborn include cataracts, retinal abnormalities, refractive errors, and strabismus.
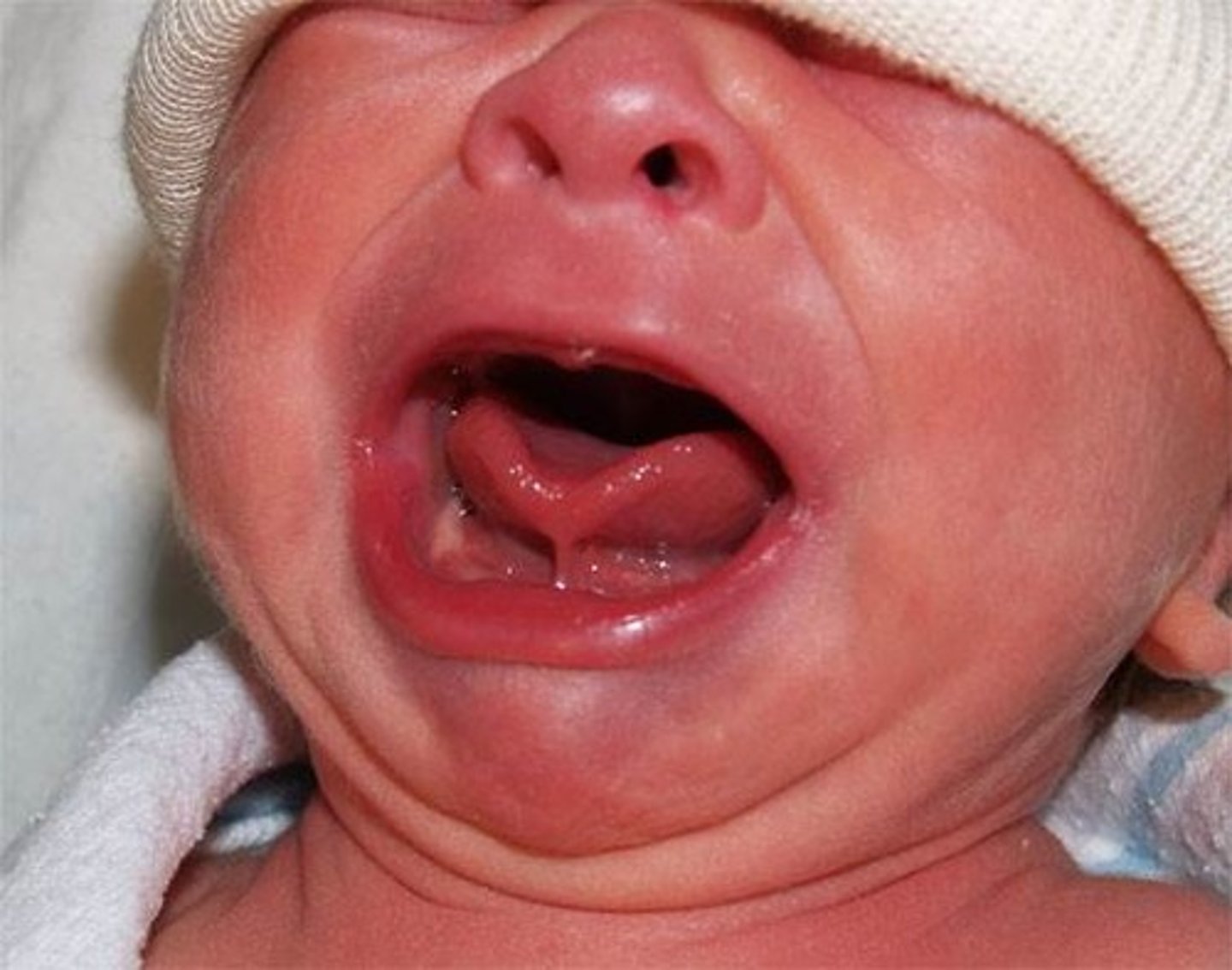
Define ankyloglossia.
Also called TONGUE-TIED. Short, lingual frenulum, fixed to tongue tip and floor of mouth and gums, limits mobility and speech. This is COMMON in newborns.
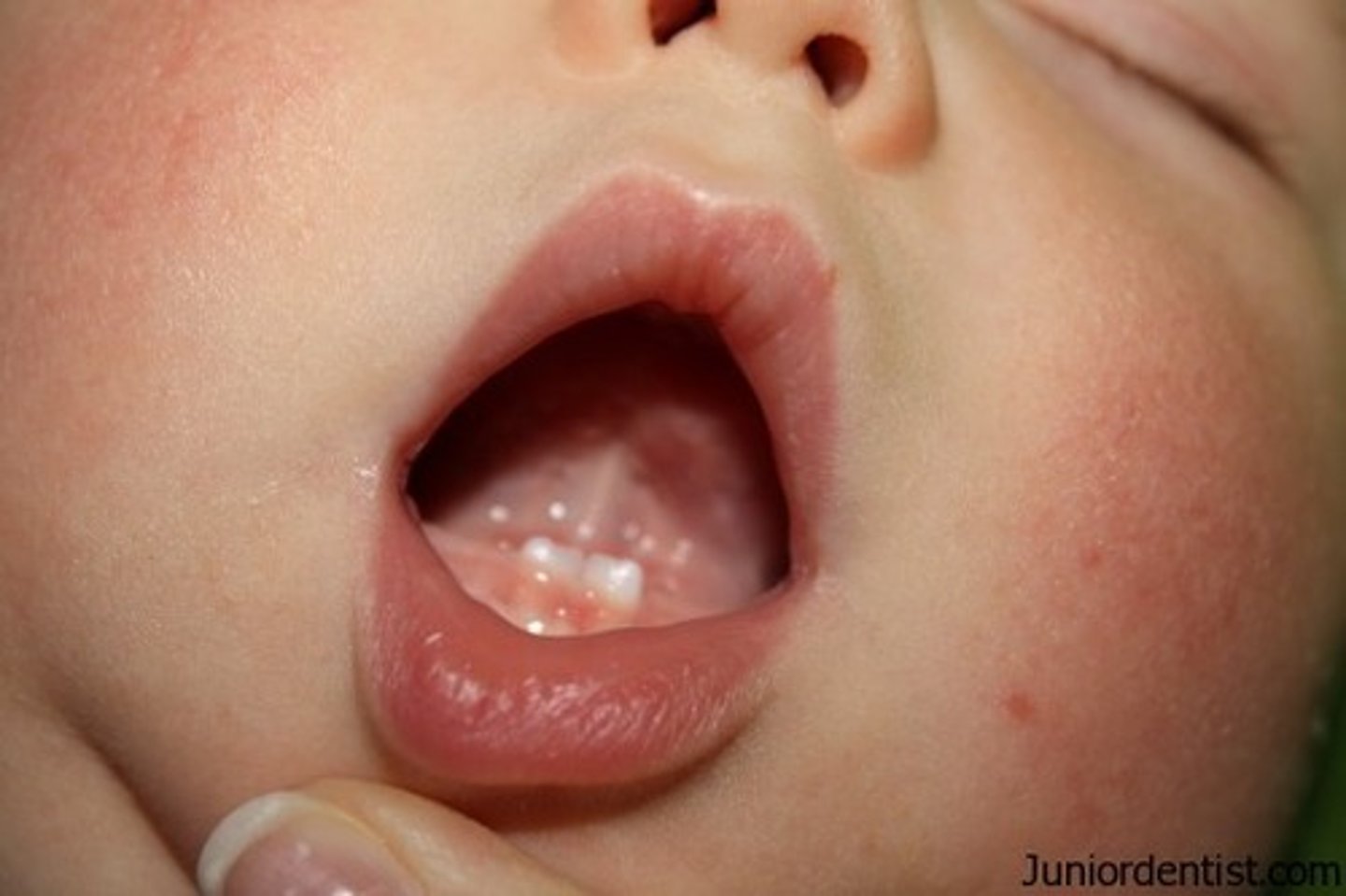
Define inclusion cysts.
Also called EPSTEIN'S PEARLS. Small, harmless, white or yellow NODULES that may appear along the newborn's GUMS or on the ROOF of their mouths. These are COMMON.
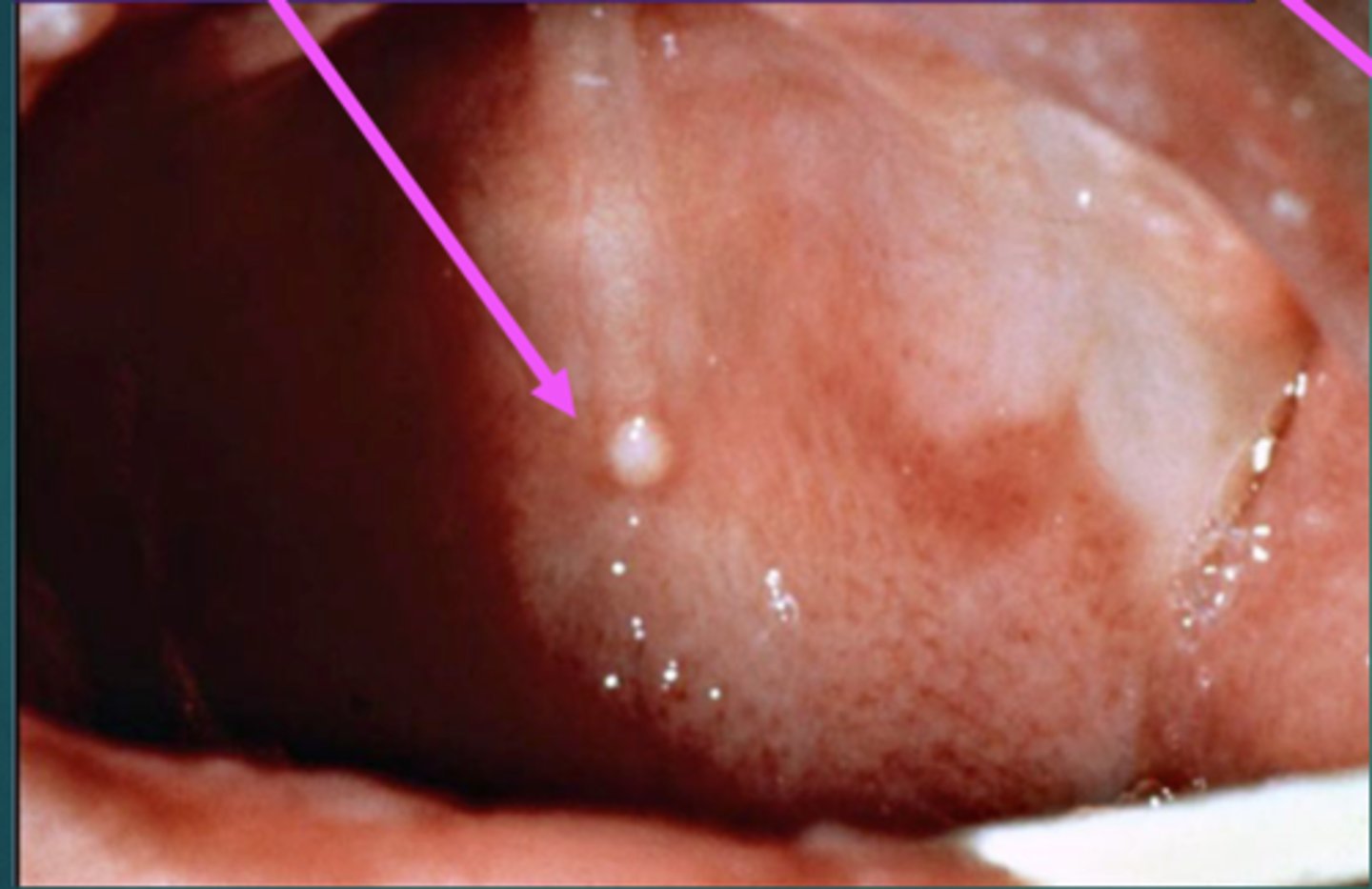
What are supernumerary nipples?
EXTRA nipples that congenitally form along the milk line and occurs in 1/40 BIRTHS.
Define anticipatory guidance.
COUNSELING by the healthcare provider to assist parents or guardians to understand UPCOMING EXPECTED growth and development their infant/child, including safety and injury prevention, healthy lifestyle, and disease prevention.
What is APGAR and why is it important?
A scoring system used to assess newborns and consists of appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, and respiratory effort. A score of 7 TO 10 usually requires MINIMAL to NO intervention; a score of 6 OR LESS indicates distress and requires PROMPT intervention.
What is the SUN scale used for?
For neonatal ACUTE PAIN assessment which incorporates heart rate, breathing, MAP, state of alertness, movement, muscle tone, and facial expression.
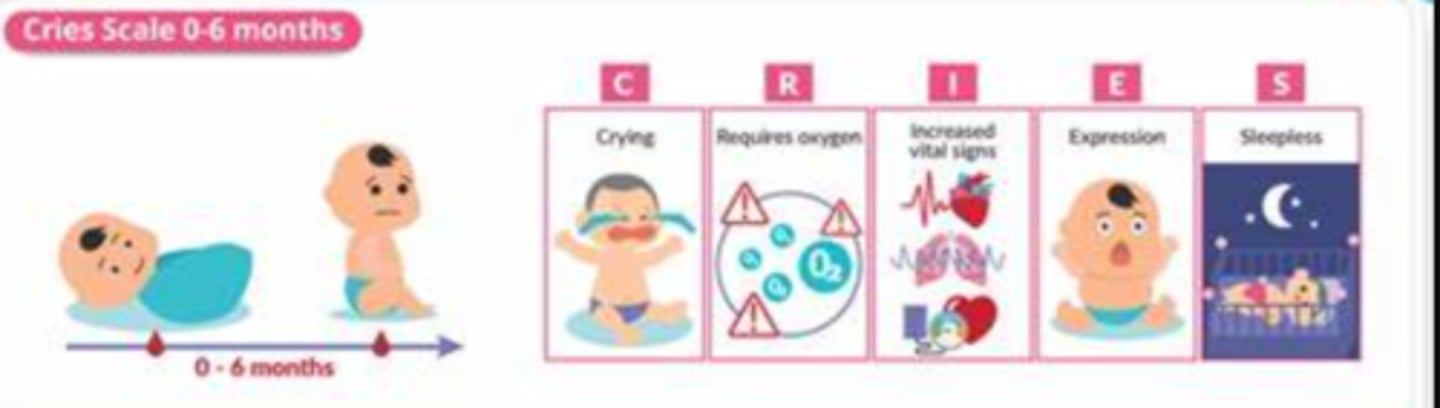
What is the CRIES scale used for?
A 10-point pain assessment tool designed for neonates which consists of crying, requires oxygen, increased vital signs, expression, and sleeplessness. Higher scores indicate greater pain intensity.
What is done during the transitional period?
This is the FIRST 4-6 HOURS after birth. Newborns are assessed EVERY 30 TO 60 MINUTES (vital signs, muscle tone, color, etc.).
What do you use to determine a newborn's physical and neurological assessment?
BALLARD assessment and scores are given 6 for physical and 6 for nerve and muscle development signs of maturity. The scores for each range from -1 to 5. The scores are added to together to determine the gestational age. The total score may range from -10 TO 50. PREMATURE babies have LOW scores and babies born LATE have HIGH scores.
What are signs of hypoxemia in a newborn?
Central CYANOSIS or a bluish discoloration of the TONGUE and MUCOUS MEMBRANE
What may bruising come from in newborns?
SOFT TISSUE INJURY from the birthing process
Where would bruising of the newborn be located especially in a breech (bottom first) birth?
Genitalia
What may be present in a newborn who underwent a facial presentation birth?
PETECHIAE of the head and face
Are paradoxical breathing movements an abnormal finding in newborns?
No, this is EXPECTED and is when the chest moves INWARD while the abdomen moves OUTWARD with INSPIRATION.
What sort of adventitious breath sounds are expected in newborns?
RALES for a few hours IMMEDIATELY after birth
When is apnea considered an unexpected finding in a newborn?
If it lasts longer than 20 seconds
Where is S1 on a newborn best heard?
At the APEX and is when the TRICUSPID and MITRAL valves closes SIMULTANEOUSLY.
Where and how is S2 on a newborn best heard?
At the LEFT UPPER STERNAL BORDER and is caused by the CLOSURE of the PULMONARY and AORTIC valves. It is usually heard as a SPLIT sound.
What are some unexpected findings of the newborn's abdomen?
DIstention, diastasis recti, and umbilical hernia (can be seen when crying or straining and may close on its own by several years of age)
What is a scaphoid-shaped abdomen a characteristic of?
Diaphragmatic hernia
Define Wharton jelly.
The connective tissue around the umbilical cord (AVA) that serves crucial protective functions during fetal development.
When should all newborns urinate?
Within 24 HOURS after birth
When does the transitional stool pass?
This is after the meconium and occurs ON THE 3RD DAY.
What will the stool of a newborn who is breastfed look like?
Yellow to golden, pasty, sour milk smell
What will the stool of a newborn who is formula-fed look like?
Pale yellow to light brown, firmer, more foul odor
What shape should the spine of the newborn be?
C-shaped
Define pilonidal cyst or sinus.
A condition that occurs between the BUTTOCKS and near the TAILBONE. It can range from painful abscesses to sinuses that lead to persistent bloody drainage. The cysts typically contain HAIR or other debris and can become infected, causing discomfort.

What can asymmetrical posterior thigh folds indicate in a newborn?
DDH
What can decreased movement in one limb in a newborn indicate?
Pain associated with fracture, or paralysis like brachial nerve injury
What are the 5 levels or states of alertness in newborns?
QUIET sleep state: eyes are closed and there are nonrapid eye movements (occasional fluttering)
ACTIVE sleep: eyes are closed with rapid eye movement (frequent fluttering)
AWAKE/DROWSY: eyes are open but periodically close
ALERT state: eyes are opened and there is an increase in muscle tone and movement, which is often seen as the newborns begin to indicate hunger
CRYING: eye may be open or slightly, crying is audible--muscle tone at its maximum
When is a newborn considered lethargic?
If they appear SLEEPY AND have a slightly diminished AROUSAL and response to STIMULI. This is a manifestation of neurologic complication or an infection.
Define the Babinski reflex.
When the sole of the foot on a newborn is stroked, the normal response is when the toes FAN OUT (especially the greater toe) and HYPEREXTEND (positive). After 1 year, flexion should occur (negative).

How do you assess for the plantar grasp reflex?
Place a thumb firmly against the the ball of the newborn's foot. The toes should FLEX SLIGHTLY DOWN in a grasping motion.
How do you assess for the palmar grasp reflex?
Place a finger in the newborn's palm. The newborn should GRASP the examiner's finger TIGHTLY.
How do you assess for the blinking reflex?
A flash of light or puff of air is presented to the newborn and they should CLOSE their eyes.
When is a newborn's level of alertness considered within the expected limits?
Awake, arouse to stimuli, or respond easily to noxious stimuli
Is desquammation (peeling) abnormal in newborns?
No, this may occur after the FIRST FEW DAYS.
What are mongolian spots?
BENIGN blue, green, grey, black discoloration usually on the back and is more common in newborns who are AFRICAN American, HISPANIC American, and ASIAN American.
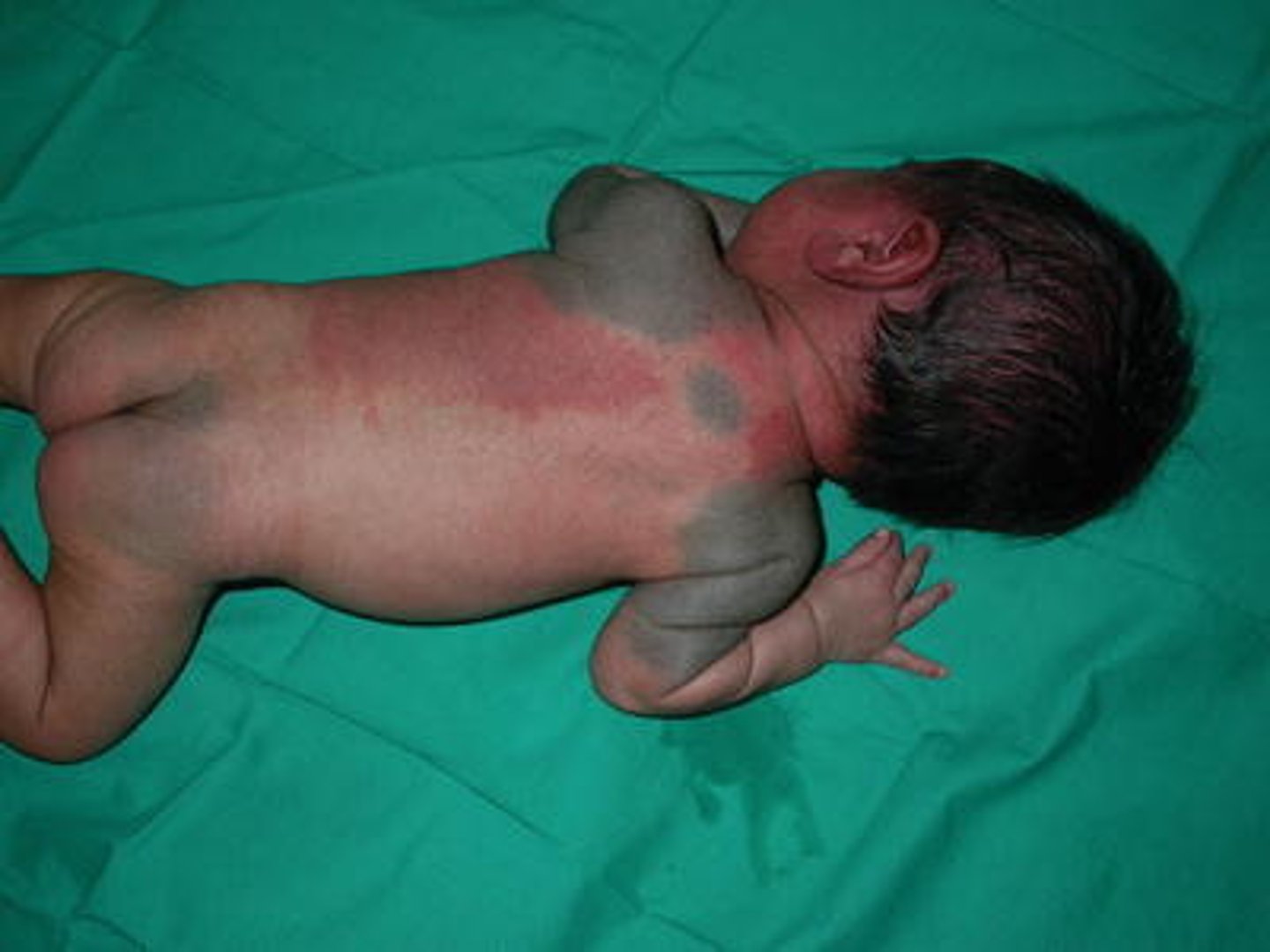
What is transient pustular melanosis?
Generalized ERUPTIONS of superficial PUSTULES overlying hyperpigmented MACULES and are consistent in DARK-SKINNED newborns.

What are signs of adequate hydration and nutrition in a newborn?
At least one void per day of age
At least one stool per day
Moist mucous membranes
Normal skin turgor
Steady weight gain
What should the diameter of a newborn's cornea be?
10 mm
What can indicate craniosynostosis in newborns?
An asymmetrical head shape or craniofacial deformities
Define the corneal reflex.
The STIMULATION of the cornea with a bright light, loud sound, or touching with and foreign object.
When are tear glands functional in a newborn?
By 2-4 weeks of age
What distance should newborns be able to focus on?
Objects 8-12 inches away
What kind of objects do newborns prefer to see?
Black and white geometric objects
Large, shiny objects
When can newborns differentiate between their mother's voice from others'?
AT 3 DAYS and TURN towards the direction of the sound
What is associated with a deviated nasal septum?
Birth injuries
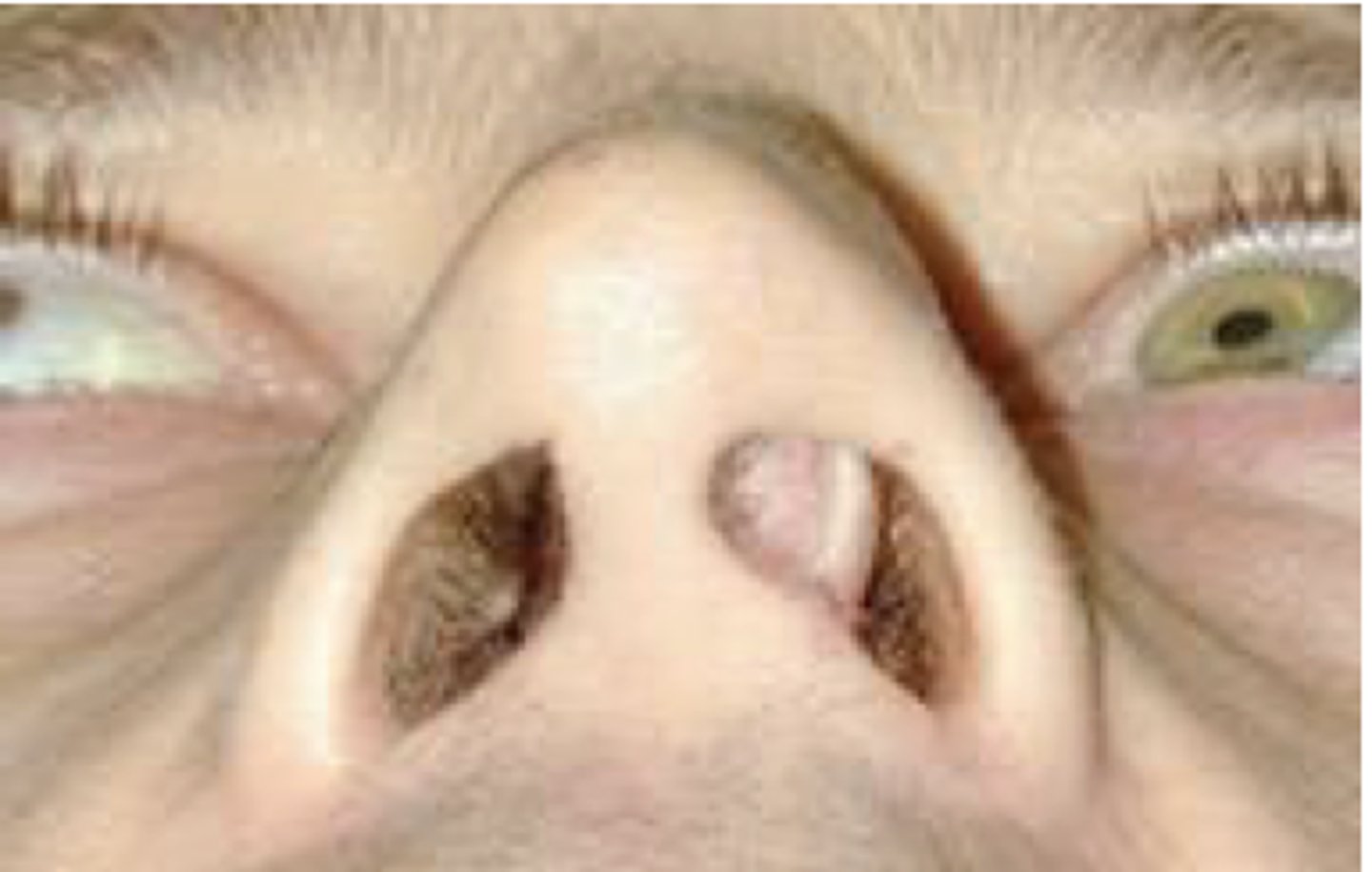
What is asymmetrical appearance of the mouth associated with?
Usually with INTRAUTERINE POSITION and resolves with time.
Define cleft.
Its an OPENING in a normally closed structure. Often associated with cleft lip (an opening in the lip). However cleft palate is not often associated with cleft lips.
Are natal teeth common in newborns?
Yes, and the cause is unknown. They may be small, discolored, loose, and often not fully developed.