CELL BIO TEST 2
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Imagine that you have added the ER retention (KDEL) signal to the C-terminus of a cytoplasmic protein. If the gene was expressed in a cell, predict the final location in which your protein will localize.
cytoplasm
Which protein is responsible for the ATP-dependent uncoating of the clathrin from the nascent vesicle?
Hsc 70
Coat proteins such as Clathrin would dissociate from the newly internalized vesicles so that ____.
Rab proteins can associate with their proper tethering proteins
What is Hsc 70 responsible for ?
for the ATP-dependent uncoating of the clathrin from the nascent vesicle
During the process of macropinocytosis, ____.
significant amount of fluid will be internalized
Animal cells contain numerous membrane proteins that are decorated with oligosaccharide. Which of the following statements is false?
When an oligosaccharide is linked to a protein through the N-Linked glycosylation, the oligosaccharide is covalently linked to the amino terminus of the protein
When is significant amount of fluid internalized?
During the process of macropinocytosis
Animal cells contain numerous membrane proteins that are decorated with oligosaccharide. Which of the following statements are true?
The glycosylated membrane proteins gain the oligosaccharide in the ER.
The oligosaccharides decorated on the glycosylated proteins are transferred as a preformed bloc called Dolichol.
Which is a member of local mediators?
Nitric Oxide
Which are not members of local mediators?
Delta
Acetylcholine
Adrenaline
T/F: The same signal molecule can induce different outcomes from target cells only when they express different types of receptors.
F: they can induce different outcomes even if receptor is the same
T/F: A cell can respond differently to different extracellular signals, but the responses occur within fairly similar time ranges, i.e., in a few minutes.
F (occurs at diff speeds)
T/F: signal receptors must be localized to the plasma membrane of the signal receiving cells.
F (not all signal receptors are on the plasma membrane)
T/F: The neurotransmitter acetylcholine directly binds to and activates guanylyl cyclase in the smooth muscle cell
F (acetycholine works indirectly/doesn’t directly bind to guanylyl cyclase)
The activation of the cdk kinase signals that a particular set of separate upstream events has been completed. Thus, cdk acts as a specific _____.
signal integrator
Cell surface receptors fall into three basic classes. Which one of the followings is not one of them?
cortisol receptor
Cell surface receptors fall into three basic classes: _______.
ion-channel coupled receptor
GPCR receptor
RPTK receptor
In muscle cells, adrenaline binds to the beta-adrenergic receptor to initiate a signaling cascade that leads to the breakdown of glycogen. At what points in this pathway is the signal amplified?
during the production of cAMP by AC
The ligand bound GPCR proteins activate the heterotrimeric G proteins through _____.
facilitating GDP exchange of Ga to GTP
Upon activation, which of the heaterotrimeric G proteins can function as a specific signal transmitting protein?
both G-alpha and G-beta/gamma
RGS proteins inhibit _____.
G-alpha
G-olf and Transducin are members of _____ protein.
G-alpha
Examples of G-alpha proteins include:
G-olf and Transducin
Acetylcholine activates heterotrimeric G proteins and induces opening of K+ channels in the plasma membrane of heart pacemaker cells. As a consequence, the pacemaker cells will be ______.
hyperpolarized
Which of the following is an intracellular second messenger molecule?
Calcium
Which of the following aren’t intracellular second messenger molecule?
Adenylyl Cyclase
PI3K
PLC
Adrenaline binds to GPCR, which increases the level of intracellular cAMP. One of the major intracellular targets of cAMP is PKA. What kind of molecule is PKA?
cAMP activated protein kinase
Adrenaline binds to GPCR, which increases the level of intracellular cAMP. One of the major intracellular targets of cAMP is PKA. What kind of molecules aren’t PKA?
GEF
Calcium activated kinase
cAMP activated lipid kinase
Acetylcholine activates PLC in smooth muscle in order to increase the level of _____?
IP3
Which of the following opens the ligand gated calcium channel of endoplasmic reticulum?
IP3
The cytoplasmic calcium ions associate with _____ to induce cellular effects.
Calmodulin
A rod photoreceptor cell (noncolor vision in dim light) from the retina is exquisitely sensitive to light. Upon activation Rhodopsin molecules activate transudcin, which in turn activates cGMP specific phosphodiesterase (PDE). Which of the following is the consequence of the activation of transducin and cGMP PDE?
Hyperpolarization
Wnt signal transduction pathway includes multiple components. Which one of the following will facilitate the effect of Wnt ligand?
beta-catenin
Which of the statements below about intermediate filaments is false?
They show dynamic instability
Which of the statements below about intermediate filaments is true?
They can stay intact in cells treated with concentrated salt solutions.
They can be found in the cytoplasm and the nucleus.
They can be anchored to the plasma membrane at cell-cell junction.
Which of the following is not a microtubule organizing structure?
Centromere
Which are a microtubule organizing structure?
Centrosome
Spindle Pole
Basal Body
Which of the following statements about microtubules is true?
GTP hydrolysis by a tubulin heterodimer discourages the growth of a microtubule
Which of the following statements regarding dynamic instability is true?
Each microtubule filament grows and shrinks independently of its neighbors.
The GTP cap helps protect a growing microtubule from depolymerization.
GTP hydrolysis by the b-tubulin promotes microtubule shrinking.
What type of motor protein causes the flagellum to bend?
Dynein
What does dynein do ?
causes the flagellum to bend
Which of the following statements about actin is false?
ATP hydrolysis increases actin filament stability
Which of the following statements about actin is true?
Actin at the cell cortex helps govern the shape of the plasma membrane.
Actin filaments are nucleated at the side of existing actin filaments in lamellipodia
Small G Protein Family members induce major cytoskeletal rearrangements. Which of the following is not one of them?
Ran
Small G Protein Family members induce major cytoskeletal rearrangements. These include _______.
Rho
Rac
Cdc42
Which of the following conditions below would decrease the likelihood of skeletal muscle contraction?
addition of a drug that blocks Ca2+ binding to troponin
What does addition of a drug that blocks Ca2+ binding to troponin do ?
decrease the likelihood of skeletal muscle contraction
Assembly of myosin II into thick bipolar myosin II filaments in smooth muscle is known to be dependent on the Myosin II Light- chain phosphorylation by Calmodulin dependent kinase (CamK, Myosin Light Chain Kinase is one of them). What second messenger would be responsible for Myosin II activation in smooth muscle?
Calcium
Skeletal muscle contraction is triggered by the release of Ca2+ from _______ into the cytosol.
the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Which two processes together constitute the M phase of the cell cycle?
Mitosis and cytokinesis
Different cyclin-dependent protein kinases (Cdks) trigger different stages of the cell cycle in part because ______.
their activities increase at different stages of the cycle
Which of the following statements about cyclins is false?
Cyclins help activate Cdks by phosphorylating them
Which statements about cyclins are true?
Cyclins vary in concentration at different stages of the cell cycle.
Cyclins are degraded at specific times in the cell cycle.
Cyclins have no enzymatic activity on their own.
The cell-cycle control system uses Cdk inhibitory proteins to _____.
arrest the cell cycle at specific checkpoints
Which of the following statements about cdk is false?
Activated M-Cdk triggers the onset of cytokinesis
Which statements about cdk are true?
Activated S- Cdk initiates DNA replication.
G1-Cdk helps drive cells through G1 into S phase.
The shortening and thickening of chromosomes in M phase depends on _____.
condensins
The shortening and thickening of chromosomes in M phase does not depend on _____.
microtubules.
actin and myosin.
E2F.
The mitotic spindle is made of ____.
microtubules
Microtubules make up the _____.
mitotic spindle
Microtubules capture chromosomes by binding to _____.
kinetochores on the sister chromatids
The anaphase promoting complex (APC) triggers the onset of anaphase by _____.
facilitating the destruction of the cohesins that hold the sister chromatids together
The contractile ring is made of _____.
actin and myosin
Actin and myosin make up the _____.
contractile ring
Which of the following statements about cell death is true?
Many cells die by apoptosis in many normal, adult, human tissues
Which of the following statements about apoptosis is false?
Bcl2 promotes apoptosis
Which of the following statements about apoptosis is true?
Bcl2 inhibits apoptosis
Bax and Bak promote apoptosis by inducing the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria into the cytosol
Which of the following statements describe how growth factors stimulate animal cell enlargement?
They stimulate intracellular protein synthesis
In connective tissues, the tensile strength of the tissue is chiefly provided by _____.
collagen
What does collagen do ?
provide the tensile strength of connective tissues
Fibroblasts are found in _____.
Connective tissue
Fibroblasts play a role in _____.
orienting collagen
A fibroblast can attach indirectly to collagen via which type of protein?
Fibronectin
Which protein in a fibroblast’s plasma membrane attaches to the extracellular matrix on the outside of the cell and (through adapter molecules) to actin inside the cell?
Integrin
In the extracellular matrix of animal tissues, which of the following molecules allows the matrix to resist compression?
Proteoglycans
What do proteoglycans do ?
allow the matrix of animal tissues to resist compression
Which of the following is NOT true of the basal lamina?
The basal lamina lines the inside of epithelia cells at the basal membrane surface
Which of the following is true of the basal lamina?
The basal lamina is a thin tough sheet of extracellular matrix.
The basal lamina contains a specialized type of collagen.
Which epithelial cell junctions serve to seal neighboring cells together so that water-soluble molecules cannot easily leak between them?
Tight junctions
What do tight junctions do?
seal neighboring cells together so that water-soluble molecules cannot easily leak between them
Cadherin proteins _____.
link epithelial cells together by binding to similar cadherins on adjacent epithelial cells
In a tissue, which of the following cell types divides to create a continuous supply of differentiated cells?
Stem cells
What do stem cells do ?
divide to create a continuous supply of differentiated cells
In the intestine, Wnt proteins ______.
promote the proliferation of the stem cells at the base of each intestinal crypt
Which of the following can give rise to cancer causing mutations?
Tobacco smoke.
Ionizing radiation.
Mistakes in DNA replication.
Which of the following is NOT a key behavior of cancer cells?
They digest neighboring cells to fuel proliferation
Which of the following is a key behavior of cancer cells?
They have a reduced dependence on signals from other cells for their growth, survival, and division.
They can often proliferate indefinitely.
Most are genetically unstable, with a greatly increased mutation rate.
In addition to stimulatory factors, some signal proteins such as ________ act negatively on their target cells, inhibiting their survival, growth, or proliferation.
TGF-beta
Which of the following cell has the shortest half-life?
a cell lining the gut
P53 is known as the king of Cancer research. It is essential for cells to either stop the cell cycle or commit apoptosis upon DNA damage. How does p53 induce apoptosis?
by inducing Bcl2 inhibitor PUMA
Beta-Catenin is the transcription factor that mediates Wnt signaling. What would facilitate the destabilization of beta-catenin in the absence of Wnt signal?
APC
what does APC do ?
facilitate the destabilization of beta-catenin in the absence of Wnt signal
Carcinoma is a cancer derived from _________.
Epithelial cells
Rb is a critical regulator of G1 to S transition. What inhibits Rb?
Cdk
The Na+/K+ ATPase (sodium-potassium pump) is an electrogenic transporter that moves 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ in, creating both ionic and electrical imbalances across the plasma membrane. Cells use several mechanisms to compensate for this imbalance (hyperpolarization) and maintain homeostasis. Which of the following activities would NOT be one of the compensating mechanisms ?
Voltage-sensitive chloride channel: leads to chloride influx (making it more negative = bad)
The Na+/K+ ATPase (sodium-potassium pump) is an electrogenic transporter that moves 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ in, creating both ionic and electrical imbalances across the plasma membrane. Cells use several mechanisms to compensate for this imbalance (hyperpolarization) and maintain homeostasis. Which of the following activities would be the compensating mechanisms ?
Sodium leak channel: sodium influx
Sodium calcium exchanger: 1 calcium efflux, 3 sodium influx.
Na+ glucose symporter (SGLT): uses Na+ influx to drive glucose uptake (important in intestines and kidneys).
Phase | Na channel | K channel |
Resting phase | ||
Depolarizing phase | ||
Repolarizing phase | ||
Late refractory phase |
Fill in the table with the following words: closed, open, inactivated
Phase | Na channel | K channel |
Resting phase | closed | closed |
Depolarizing phase | open | closed |
Repolarizing phase | inactivated | open |
Late refractory phase | closed | closed |
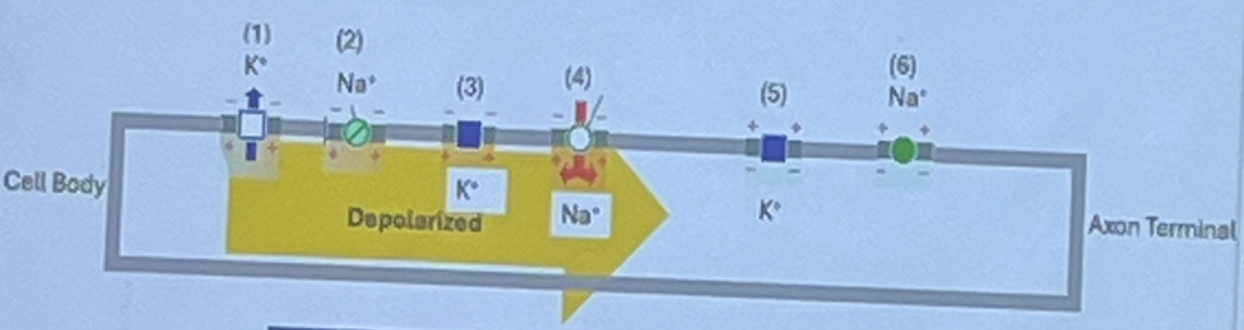
Fill in the table with the right words: open, closed, inactived.
Channel | State | |
1 | K channel | |
2 | Na channel | |
3 | K channel | |
4 | Na channel | |
5 | K channel | |
6 | Na channel |
Channel | State | |
1 | K channel | open |
2 | Na channel | inactivated |
3 | K channel | closed |
4 | Na channel | open |
5 | K channel | closed |
6 | Na channel | closed |
Molecules that make GABA-gated channels open more easily in response to the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA. This channel, when open, allows Cl- to flow into the neurons, making the cell more difficult to depolarize. These types of molecules are ____.
Tranquilizer (such as Diazepam (Valium))
Certain molecules block the reuptake of the neurotransmitter serotonin in the synaptic cleft. This results in a net increase in serotonin available for excitatory signaling to the postsynaptic neuron. These types of molecules are _____.
Antidepressant (such as Prozac)