Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
1/325
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
326 Terms
biology
study of life or living things
one aim is to discover patterns in the diversity
the study of living organisms
have several features that distinguish them from non-living things
common functions of all living things
responsiveness (irritability)
growth
reproduction
movement
metabolism
bio
life
logos
study of
responsiveness (irritability)
responding to a change in the immediate environment
e.g. pulling your hand from the stove
longer term change is called adaptation
wolf fur is 3x thicker in the winter than in the summer but polar bear fur always has thicker fur than wolves
adaptation
longer term chage
growth
increase in cell size or cell number
individual cells become specialized for particular functions (cellular differentiation)
e.g. gametes (egg and sperm) are produced by meiosis that is needed for reproduction to happen
cellular differentiation
individual cells becoming specialized for particular functions
skin cells are differentiated cells specialized for protection
eukaryotes
eu = “true”; karyotes = “enclosed nucleus”
yeasts, many protists
prokaryotes
pro = “before”; karyotes = “enclosed nucleus”
bacteria and archaea
unicellular
single-celled
consists of eukaryotes and prokaryotes
multicellular
animals, plants, all other fungi, and some protists
reproduction
creation of new generations of the same kind of organisms
can be asexual or sexual
mitosis
allows us to grow and to replace damaged or worn-out somatic (“body”) cells
asexual reproduction
cell that divides once to produce genetically identical cells to the parent cell and sister cell
binary fission
binary fission; occurs in prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea)
mitosis
found in our body (let’s us grow and replace damaged and worn out somatic cells (all cells in our body except for egg and sperm)) e.g. liver cells, pancreatic cells
crossing over
where genetic material is transferred between homologous chromatin or homologous chromosomes; occurs during prophase I of meiosis I)
independent assortment
the way one gene is inherited does not affect how another gene is inherited
movement
consists of internal and external movement, a common function of all living things
internal movement
transporting blood food, or other material within the body e.g. movement of air through the respiratory tract; inside
external movement
moving through the environment e.g. running, swimming, walking; outside
metabolism
one of the common functions of all living things; sum of all chemical reactions in the body, consisting of anabolism and catabolism
anabolism
when large molecules are created from smaller ones and energy is used; energy must be supplied, endergonic
endergonic
ender - inside gonic - energy; e.g. building amino acids requires energy to happen
catabolism
when large molecules are broken down to smaller ones and energy is released; exergonic
exergonic
exer - outside; gonic; energy; e.g. breaking down of proteins to amino acids in the digestive tract to release energy
anatomy
study of internal and external structure and the physical relationships between body parts
gross (macroscopic anatomy
microscopic anatomy
gross (macroscopic) anatomy
studies structures visible with unaided eye
microscopic anatomy
studies structures that cannot be seen without magnification or micrscope
3 forms of gross anatomy
surface anatomy
regional anatomy
systemic anatomy
surface anatomy
study of superficial markings; gross anatomy
regional anatomy
study of a specific region of the body; gross anatomy
systemic anatomy
study of organ systems; gross anatomy
2 forms of microscopic anatomy
cytology
histology
cytology
study of cells; microscopic anatomy
histology
study of tissues; microscopic anatomy
physiology
study of how living organisms carry out their functions
human physiology
studies functions of the human body
cell physiology
functions of living cells
special physiology
physiology of specific organs
systemic physiology
functions of organ systems
pathological physiology (pathology)
effects of diseases on organ or systems functions
levels of organization
chemical level
cellular level
tissue level
organ level
organ system level
organism level
chemical level
includes atoms, micromolecules, and macromolecules; e.g. actin protein
atoms
interact to form molecules; e.g. H2O
molecules
join ot form complex contractile protein filaments
macromolecules
e.g. carbohydrates, proteins, lipids (steroids, fats, and phospholipids), nucleic acids (DNA and RNA)
actin
protein found in our body that comes together to form actin filaments (thin filaments)
protein
macromolecule; part of chemical level or organization
actin filament
made up of actin protein; part of the cellular level of organization
protein filaments
e.g. contractile protein filaments are structures within a heart muscle cell; myosin (thick) filament; acting (thin filament); cellular level of organization
myosin (thick) filament
consists of many proteins called myosin; cellular level of organization
heart muscle cell
eukaryotic cell; part of the cellular level of organization
nucleus
stores genetic material (DNA)
tissue level
e.g. cardiac muscle tissue makes up the heart
cardiac muscle tissue
makes up the heart; consists of many heart muscle cells
organ level of organization
consists of more or equal to 2 different tissues; e.g. the heart is a complex organ composed of different tissues
heart
complex organ that is composed of different tissues; made up of cardiac muscle and other tissues; part of the organ level of organization
organ system level
consists of different organs working together; e.g. the cardiovascular system; have a total of 11 organ systems in the human body
cardiovascular system
includes the heart, blood, and blood vessels
organism level
e.g. human’s 11 organ systems must work together in order to remain alive and healthy
11 organ systems of the human body
integumentary
skeletal
muscular
nervous
endocrine
cardiovascular
lymphatic
respiratory
digestive
urinary
reproductive
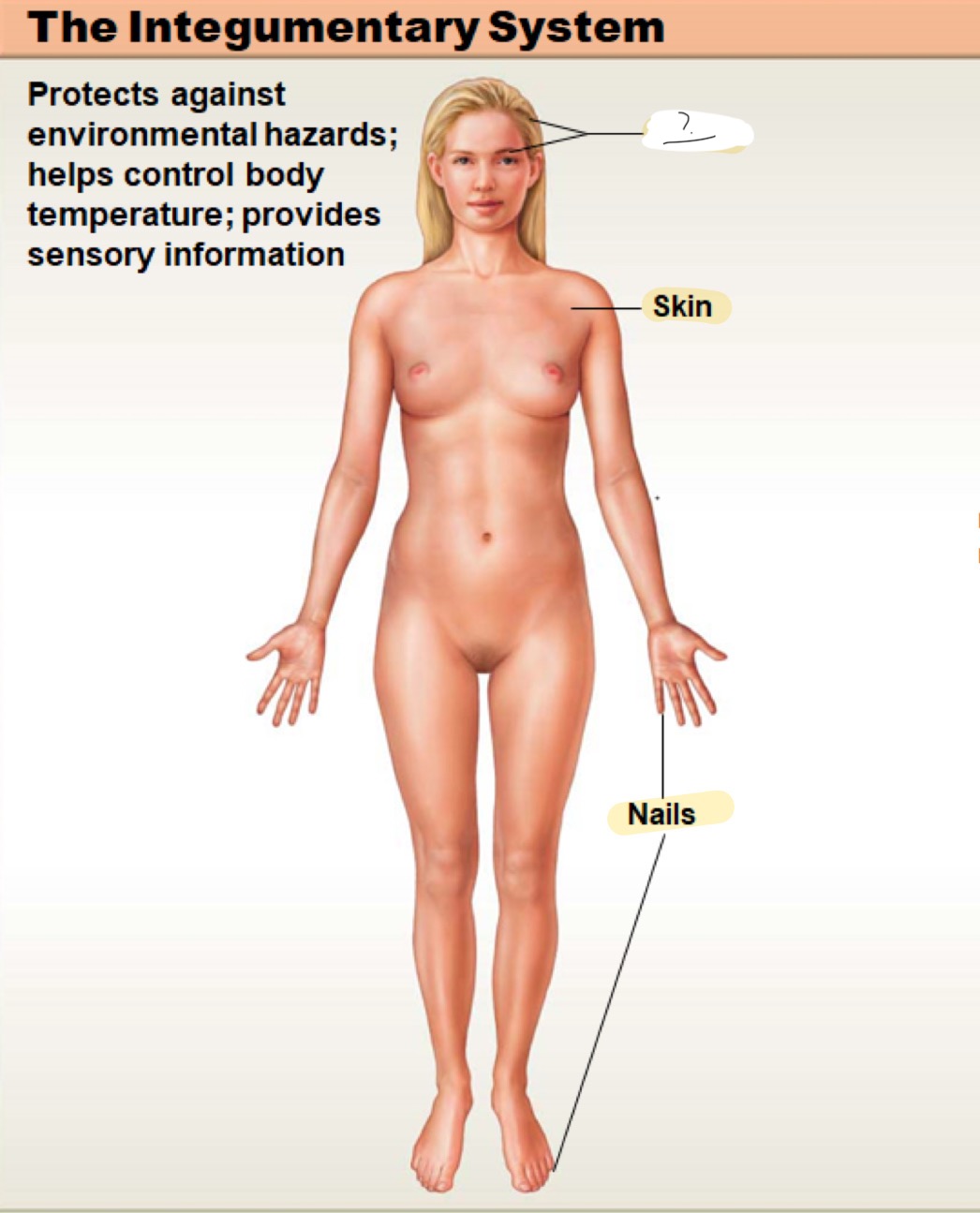
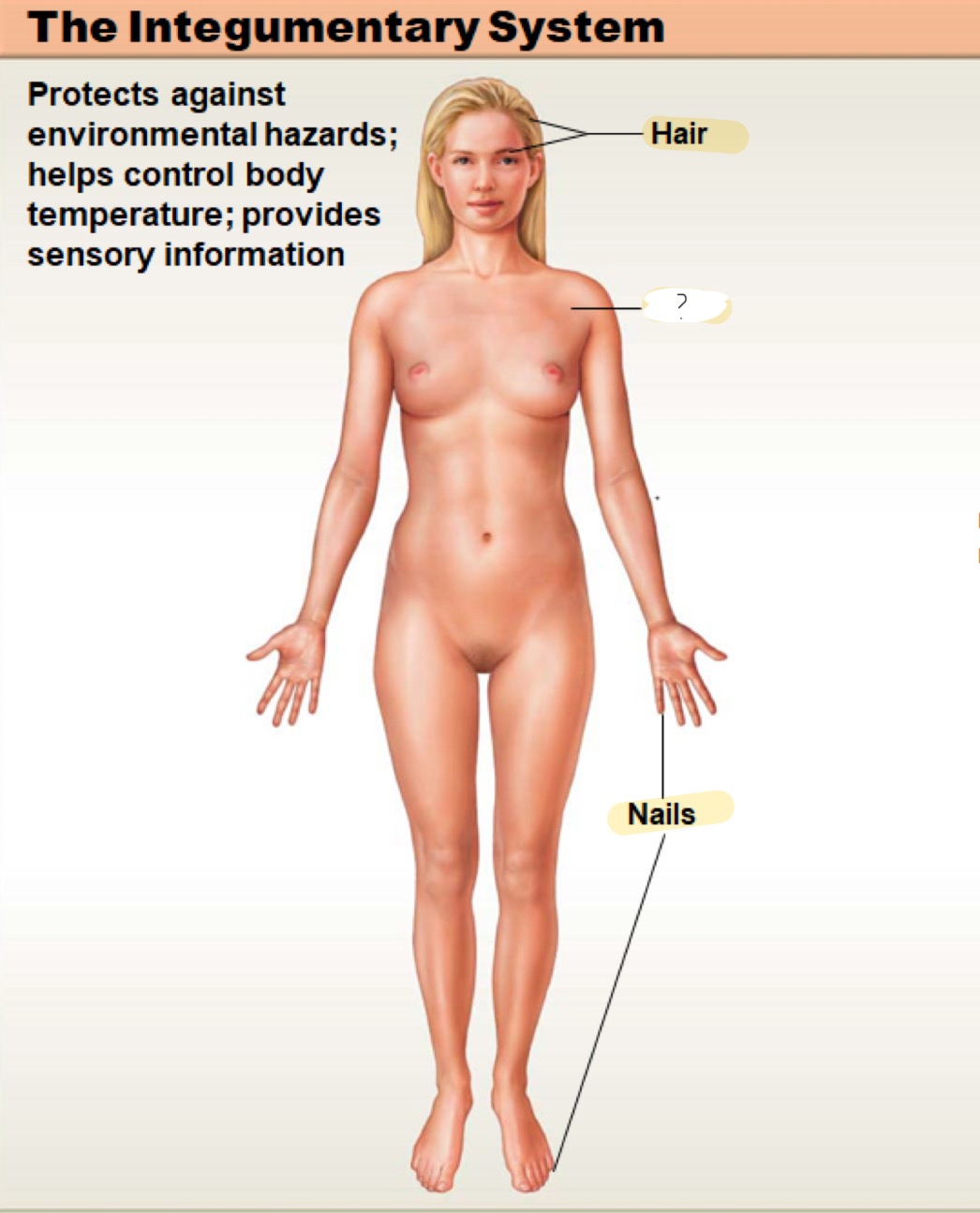
integumentary system
protects against environmental hazards; helps control body temperature; provides sensory information; (not shown) mammary and sweat glands
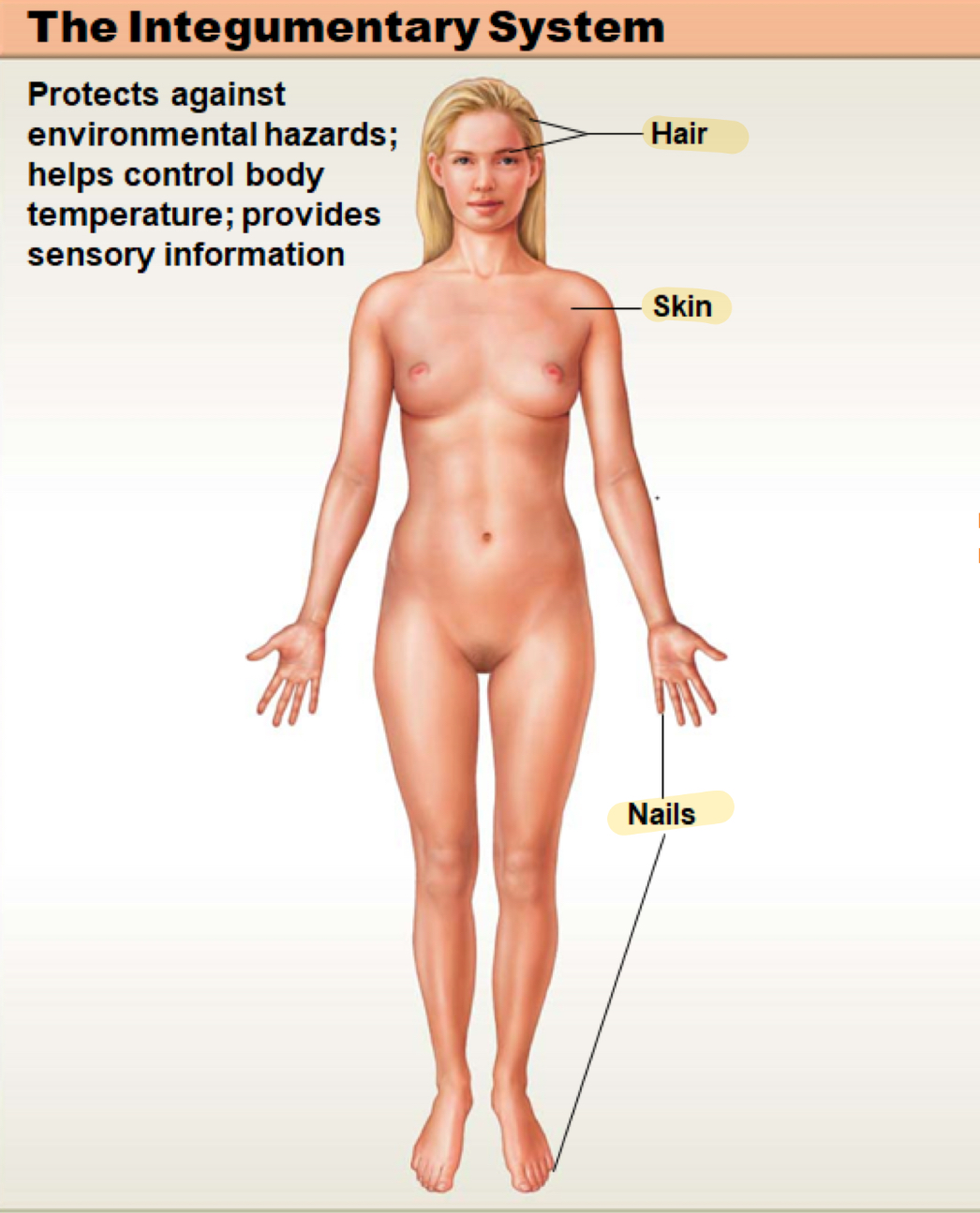
hair
skin
nails
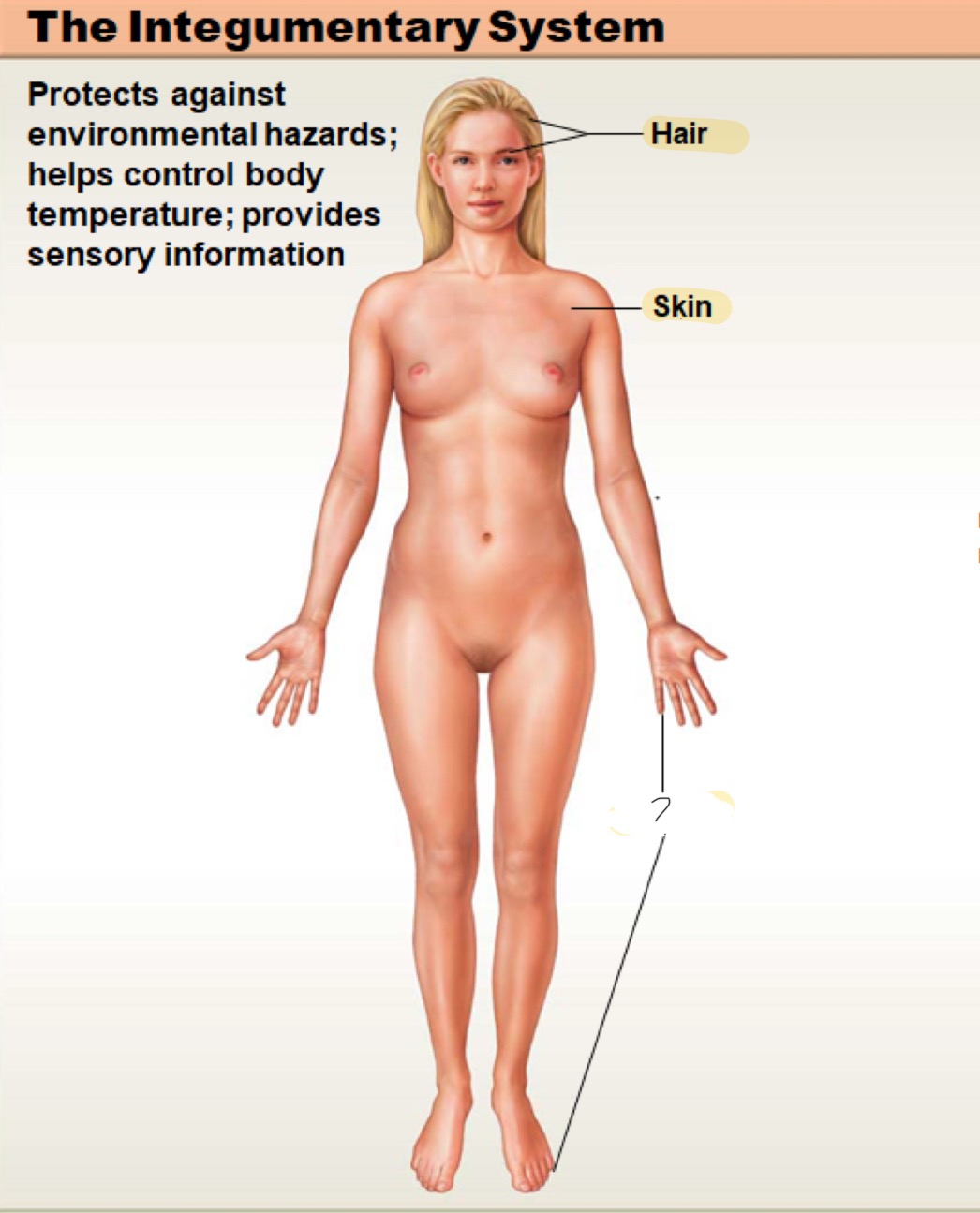
mammary glands
produce milk; exocrine gland; part of the integumentary system
sweat (sudoriferous) glands
part of integumentary system; exocrine glands
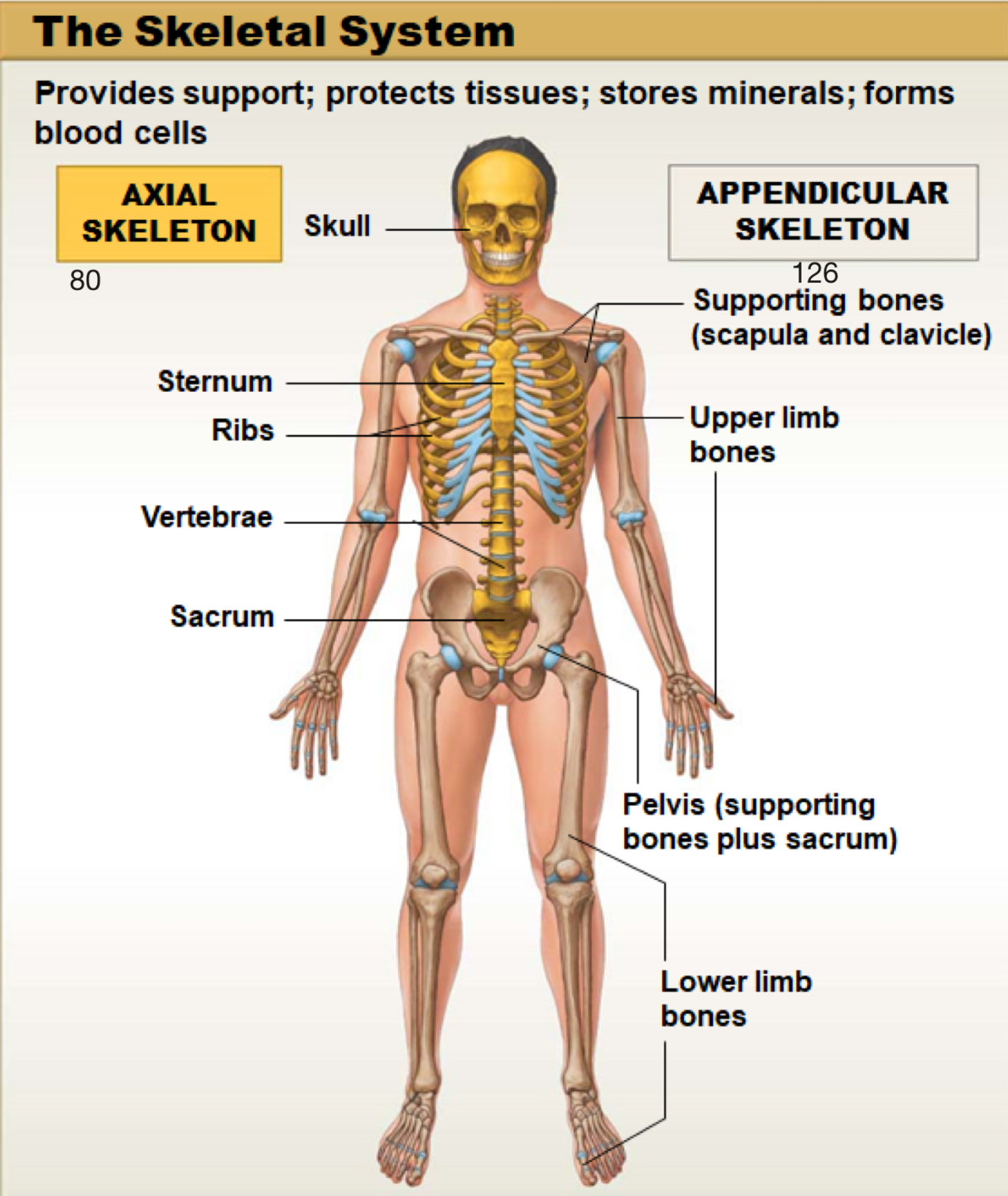
skeletal system
made up of bones, cartilages, ligaments (connect bone to bone) and bone marrow; supports and protects tissues, stores minerals, and produces blood cells
platelets
blood cells produced in the bone marrow that repair dermal damages
bone marrow
component of skeletal system
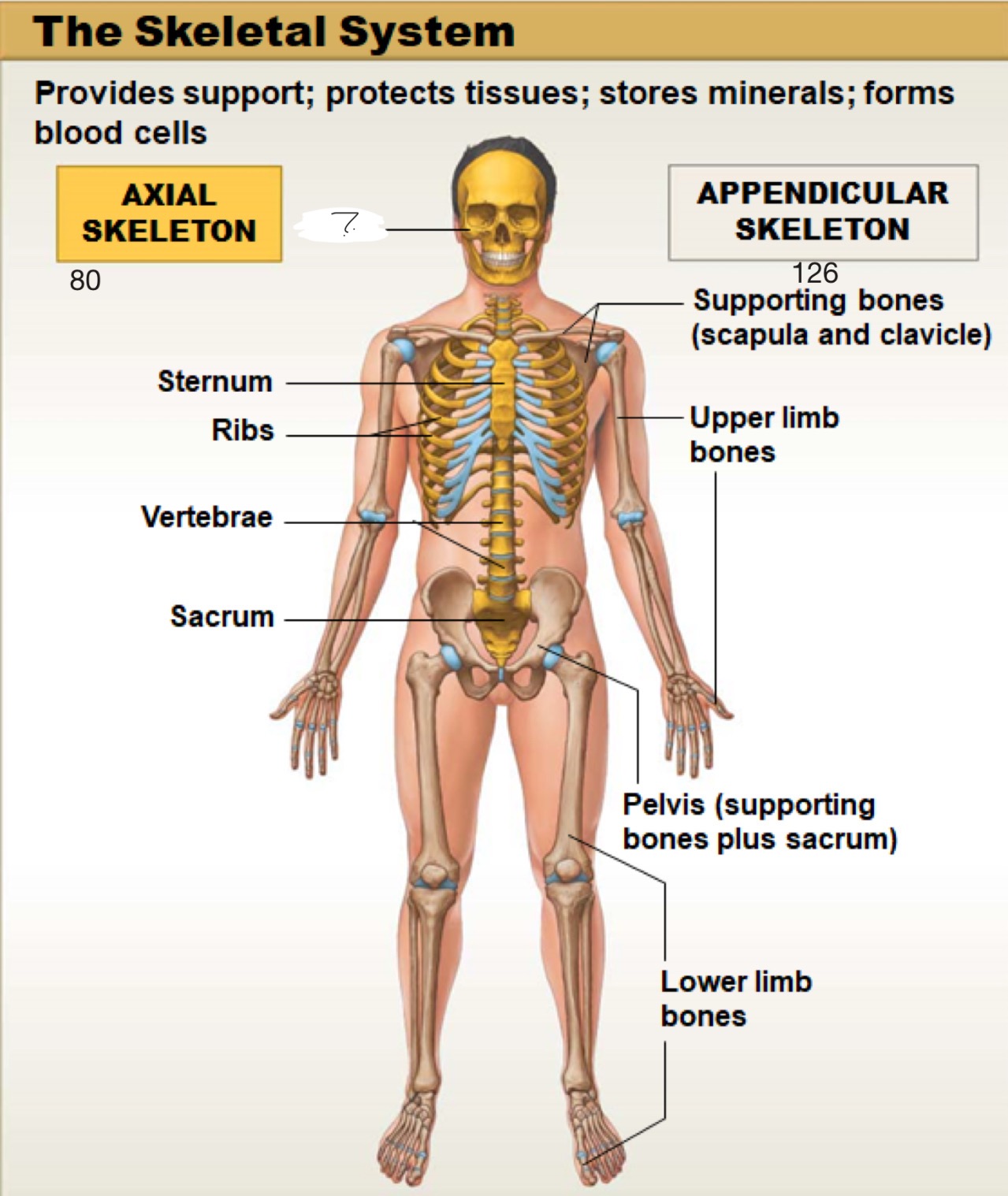
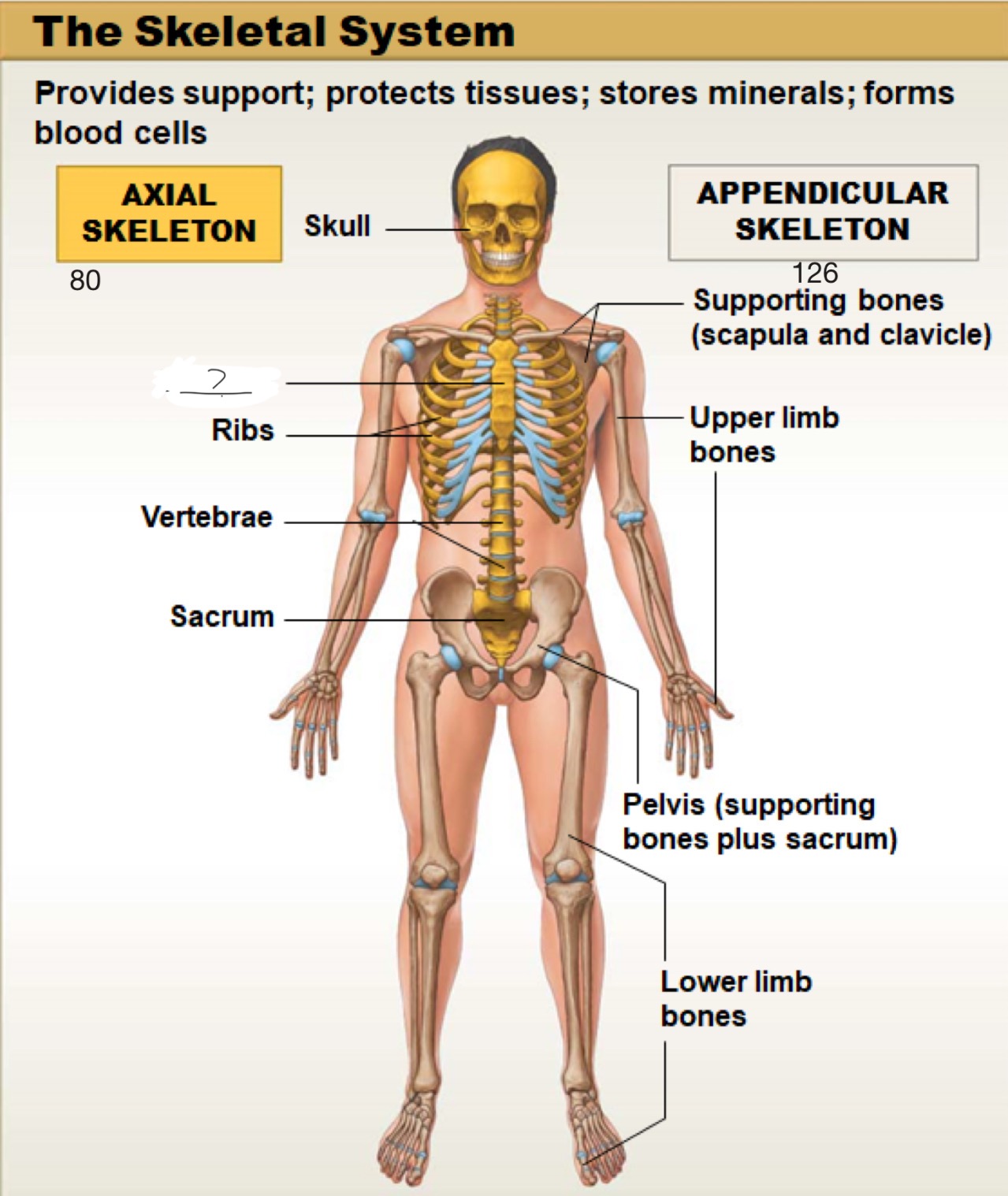
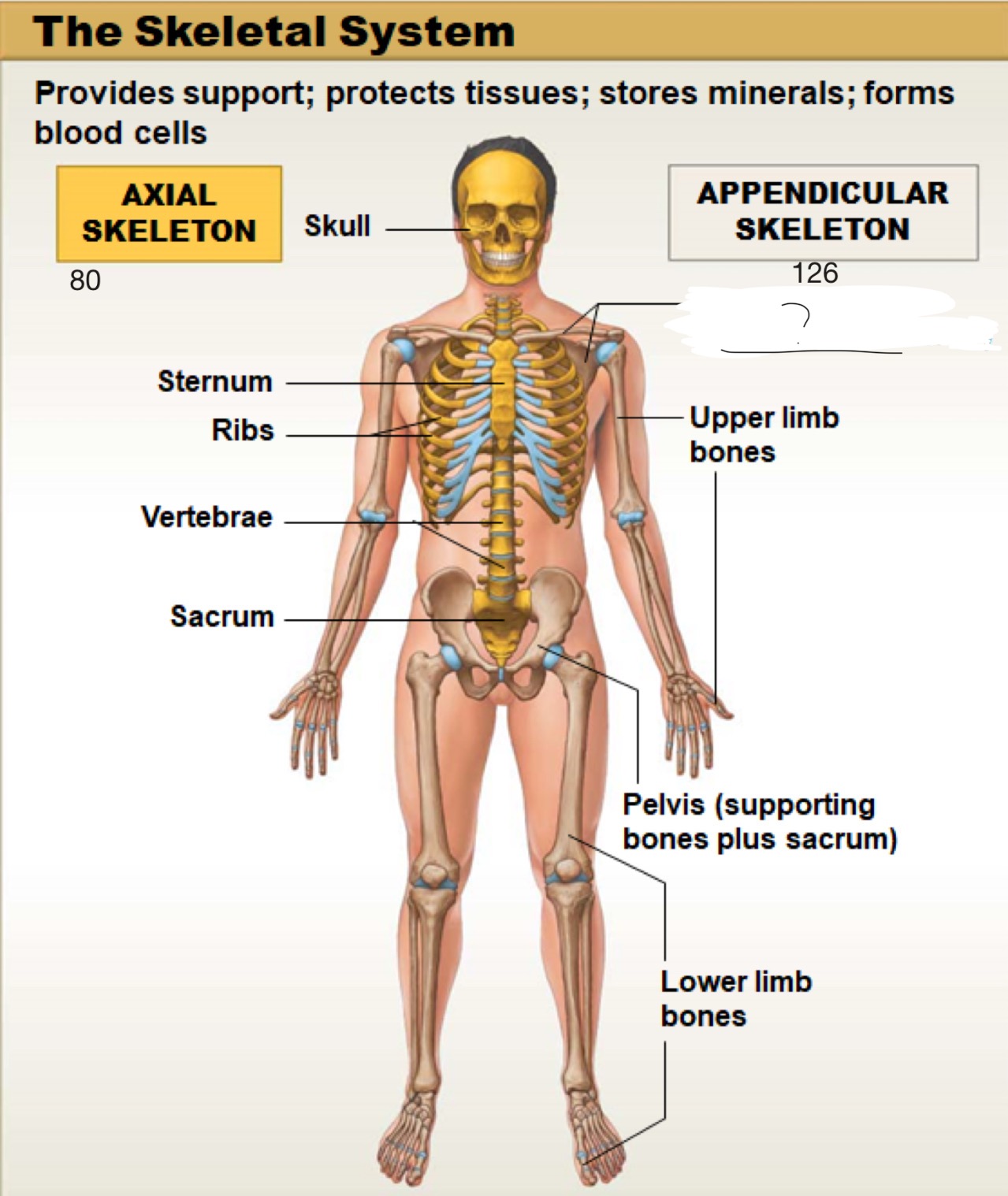
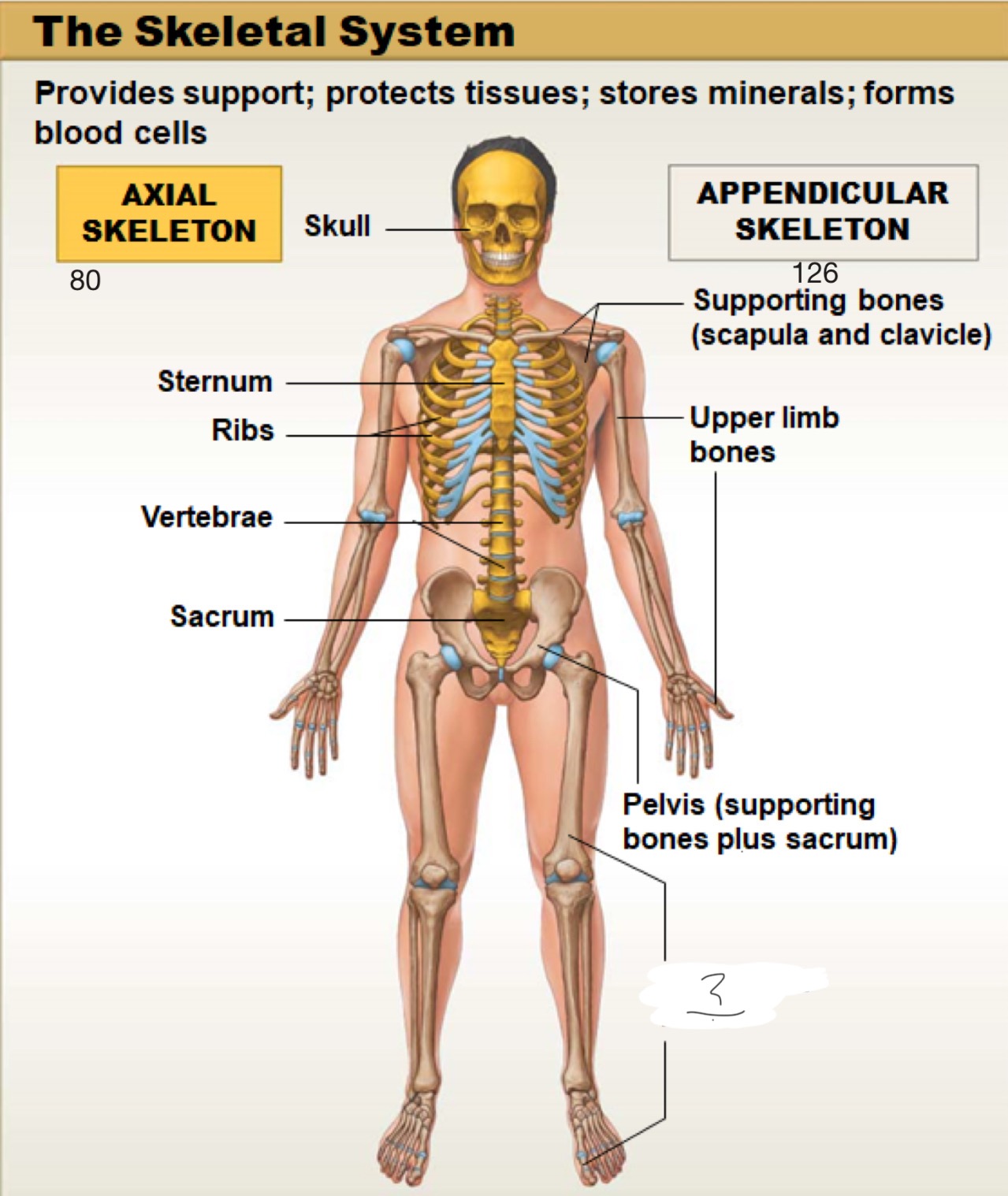
axial skeleton
includes the bones of the skull, spine (vertebral column), ribs, and sternum. It forms the main framework of the body and helps protect the brain, heart, and lungs
appendicular skeleton
includes the bones of the arms, legs, shoulders (pectoral girdle), and hips (pelvic girdle). It helps the body move and interact with the environment
skull
axial skeleton
sternum
axial skeleton
ribs
axial skeleton
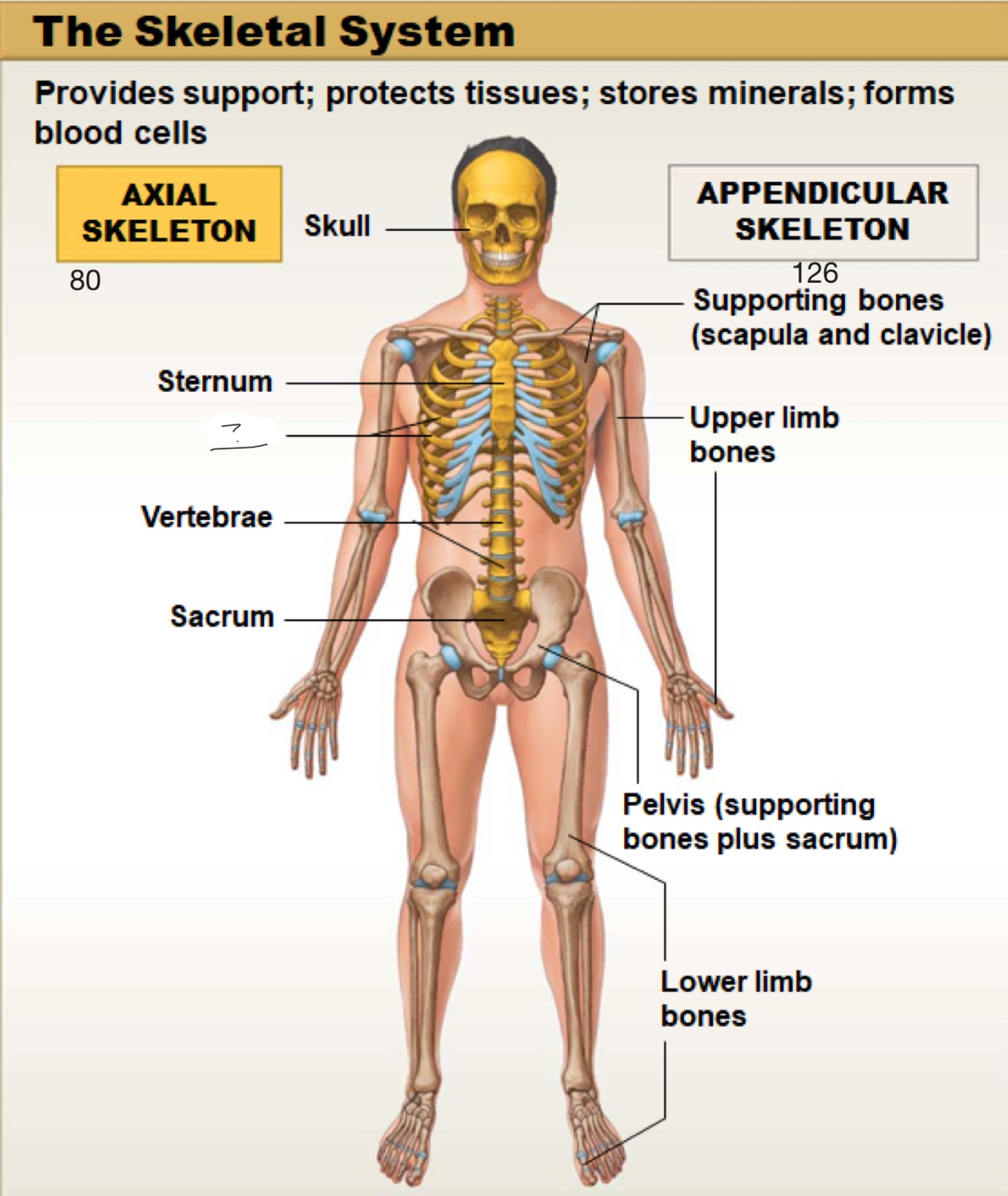
vertebrae
axial skeleton
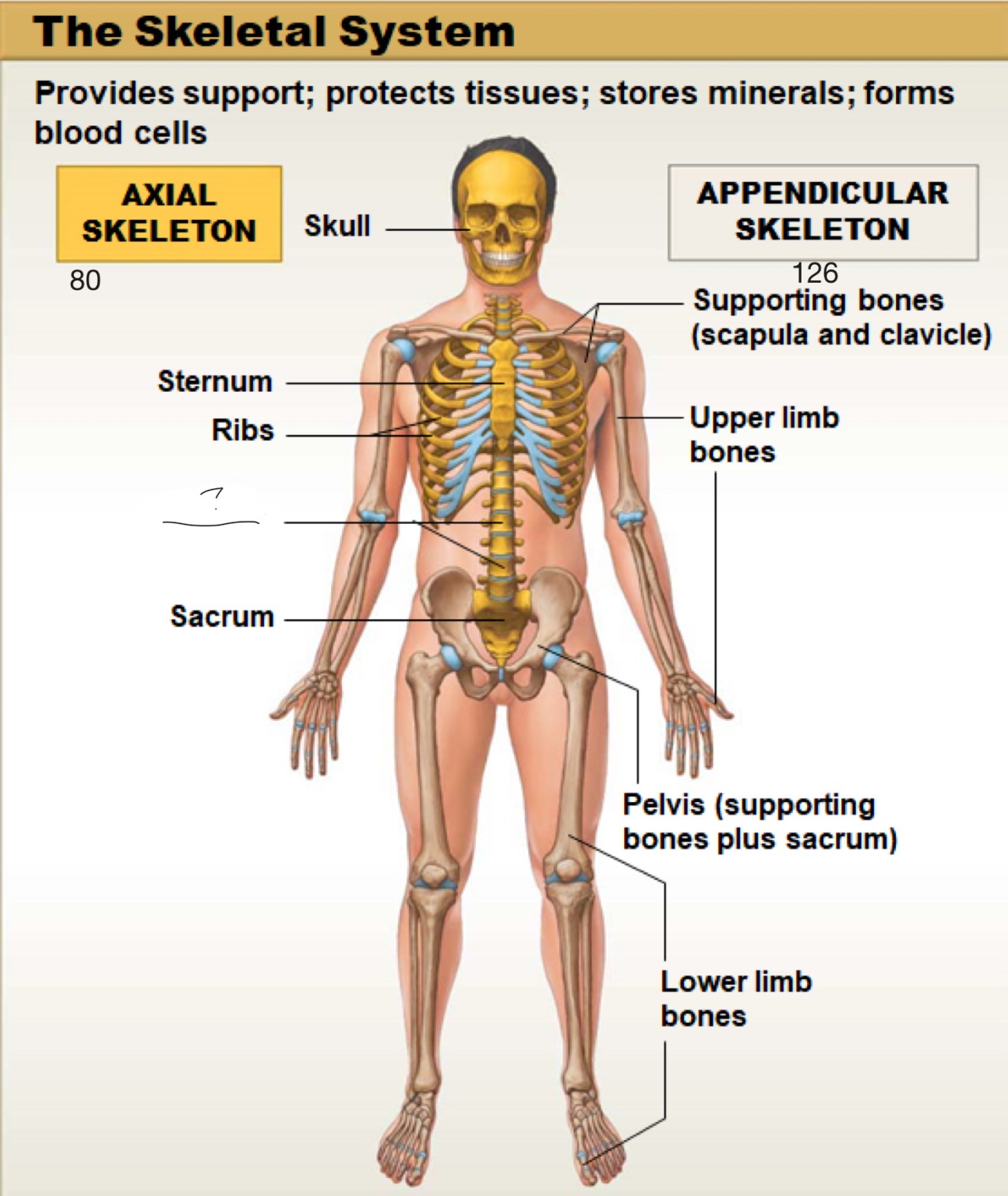
sacrum
axial skeleton
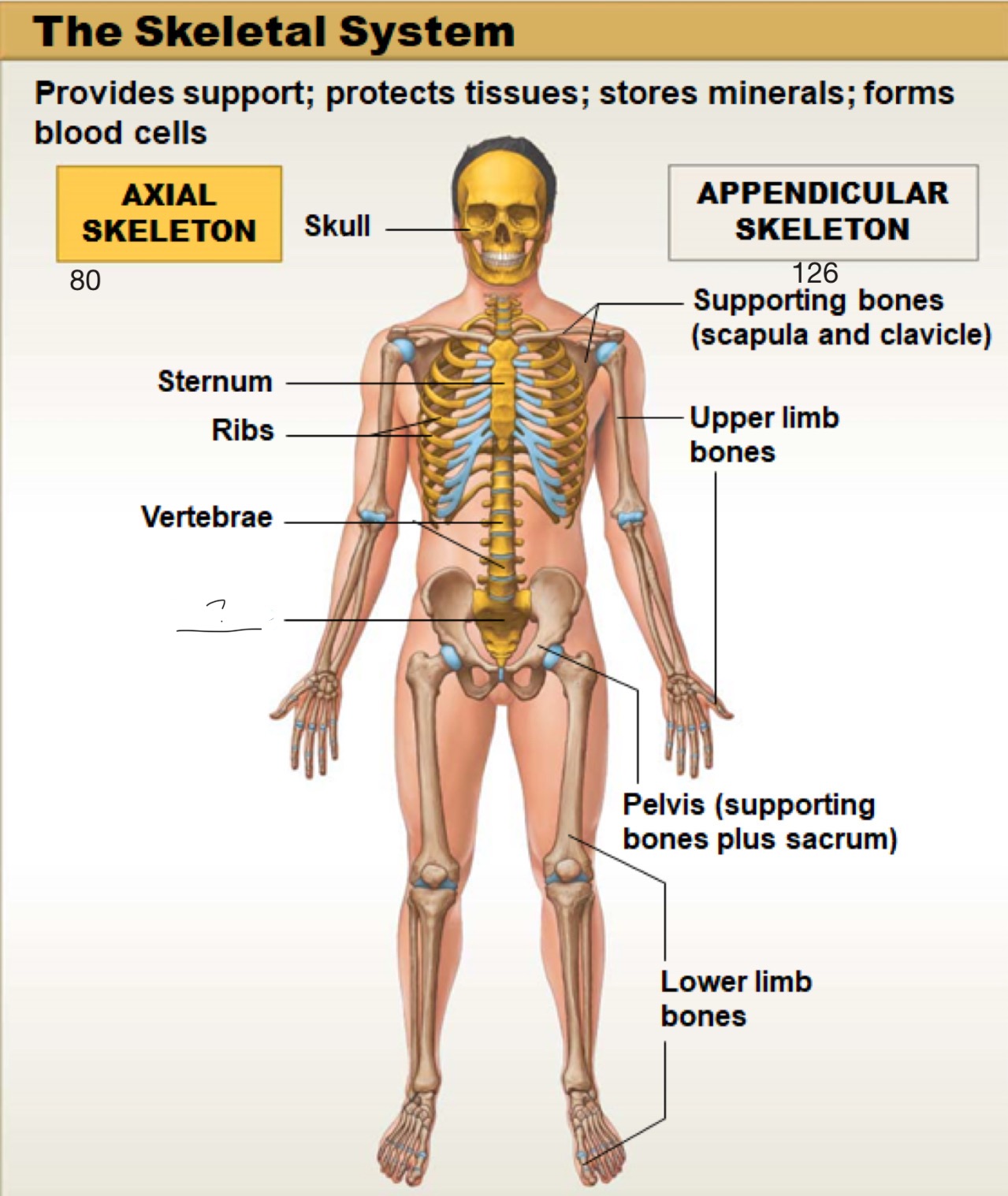
supporting bones (scapula and clavicle)
appendicular skeleton
upper limb bones
appendicular skeleton
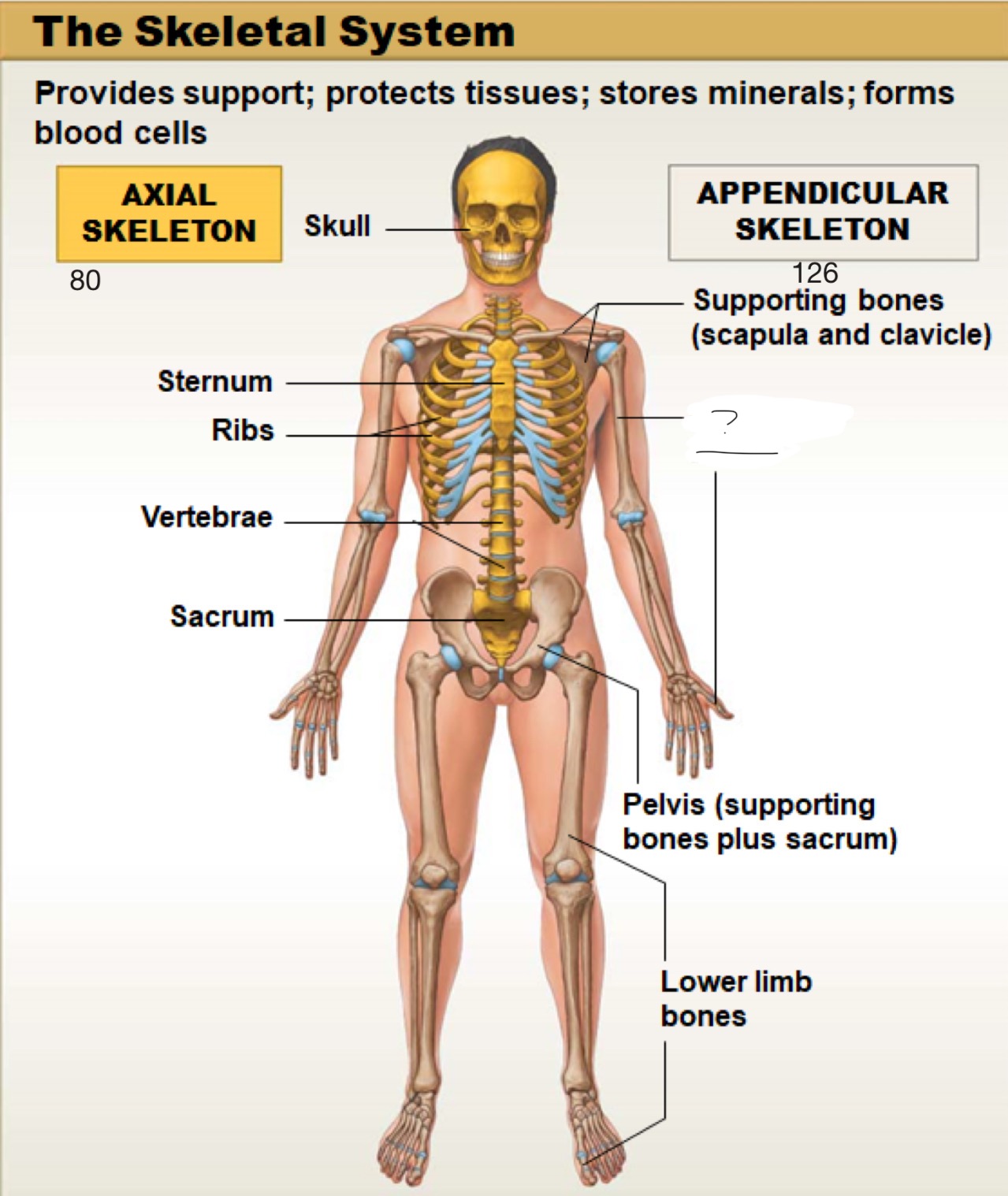
pelvis (supporting bones plus sacrum)
appendicular skeleton
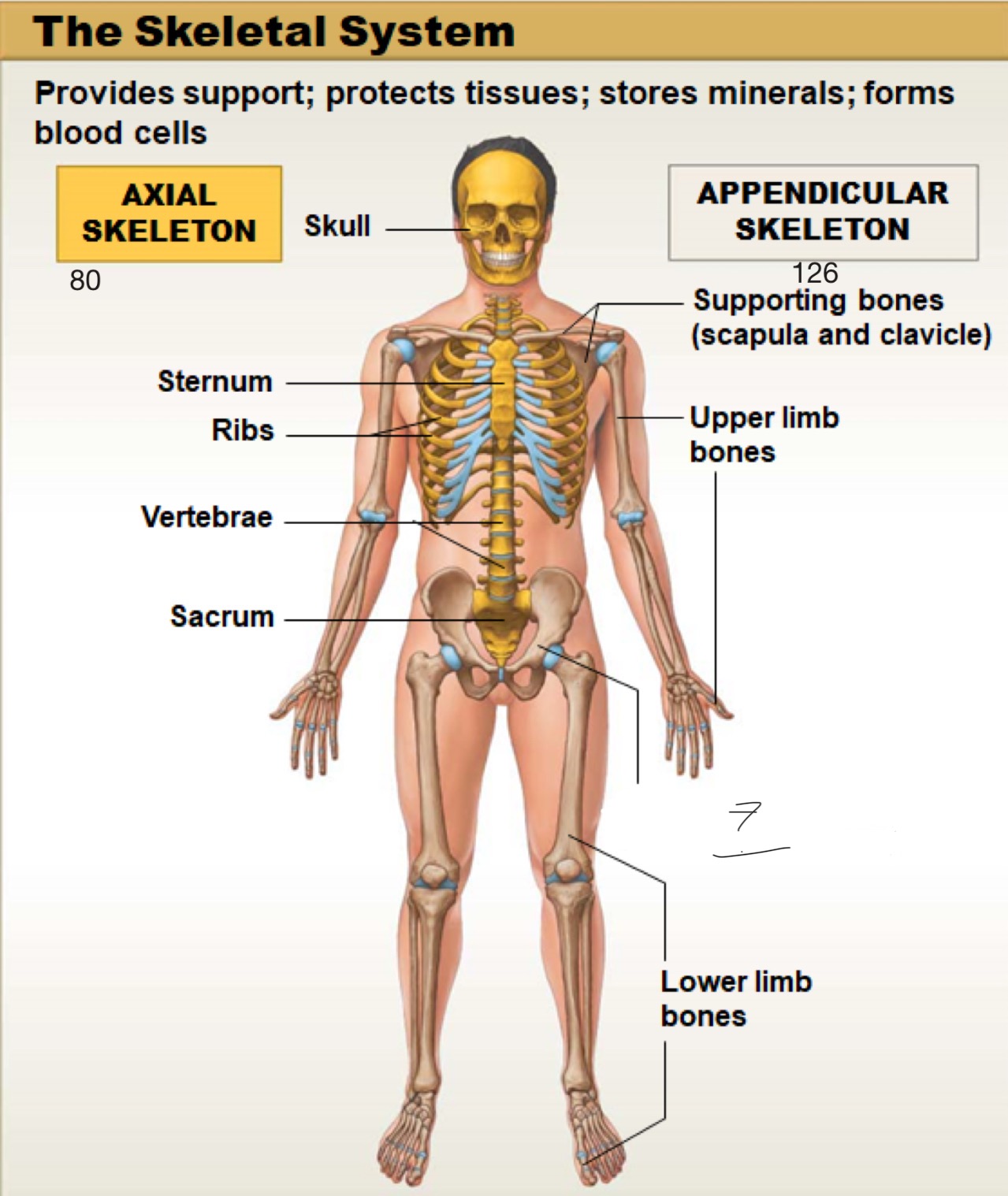
lower limb bones
appendicular skeleton
muscular system
provides movement; provides protection and support for other tissues; produces heart
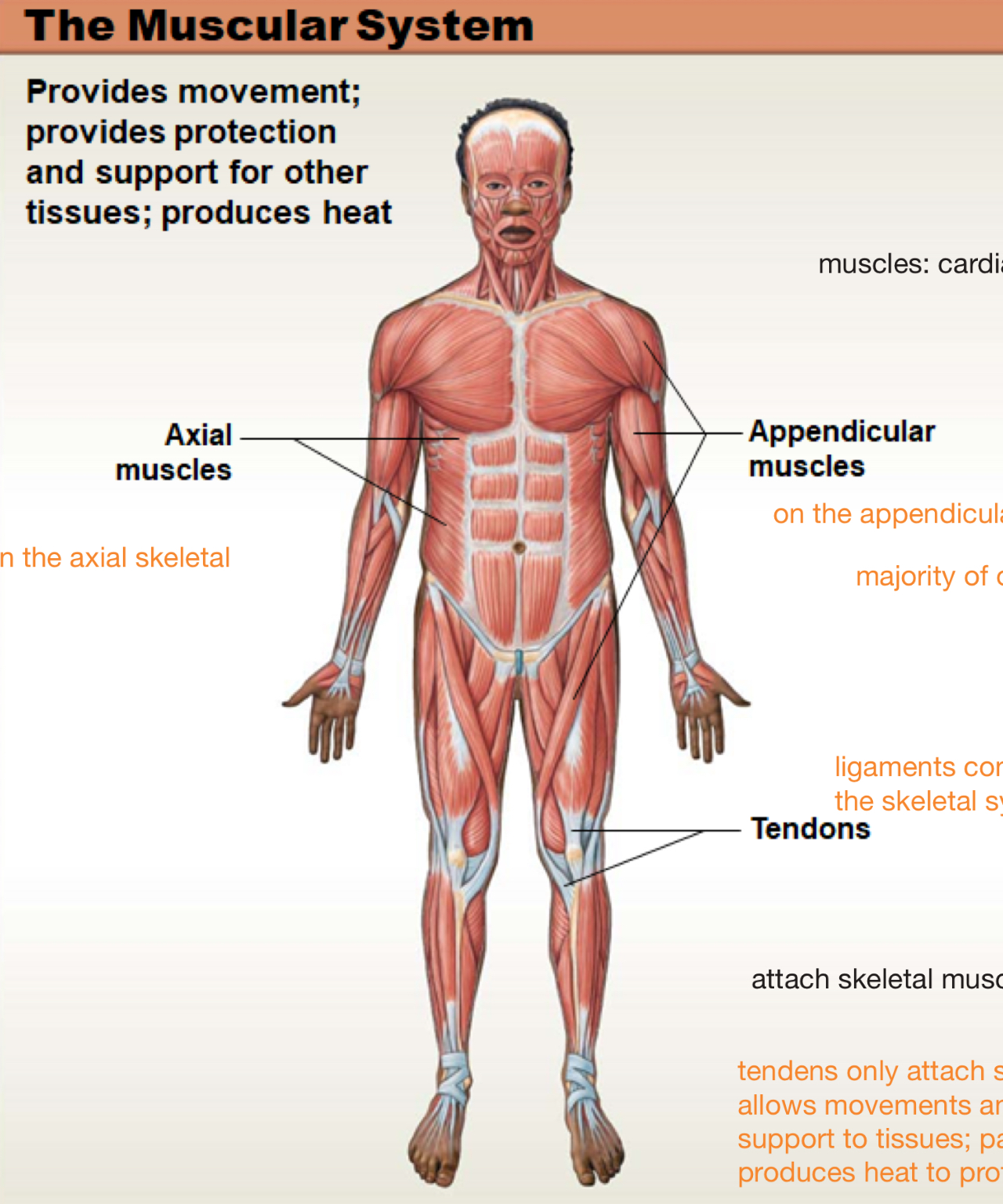
muscles
cardiac, skeletal (majority of our body), and smooth
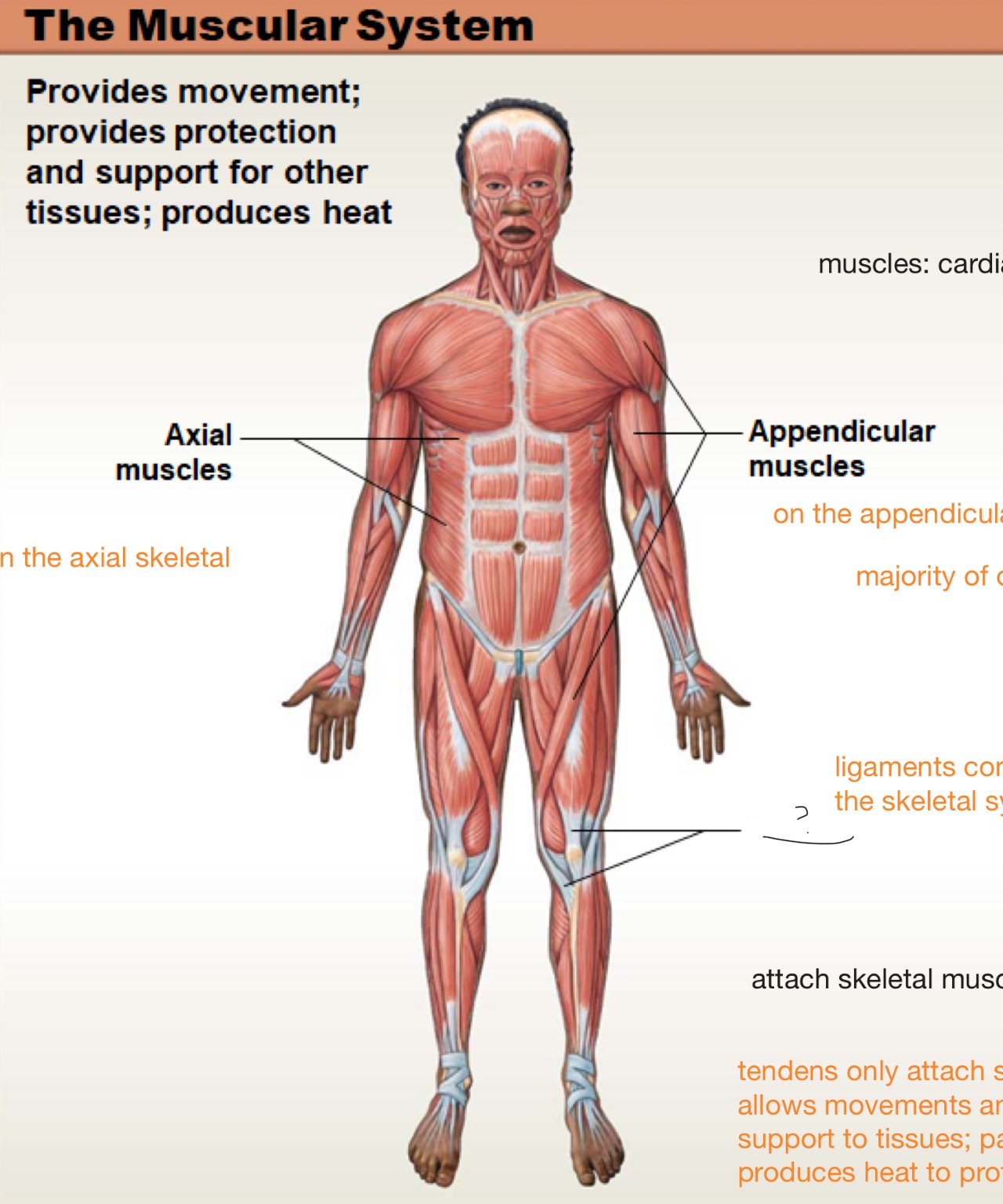
ligaments
connect bone to bone
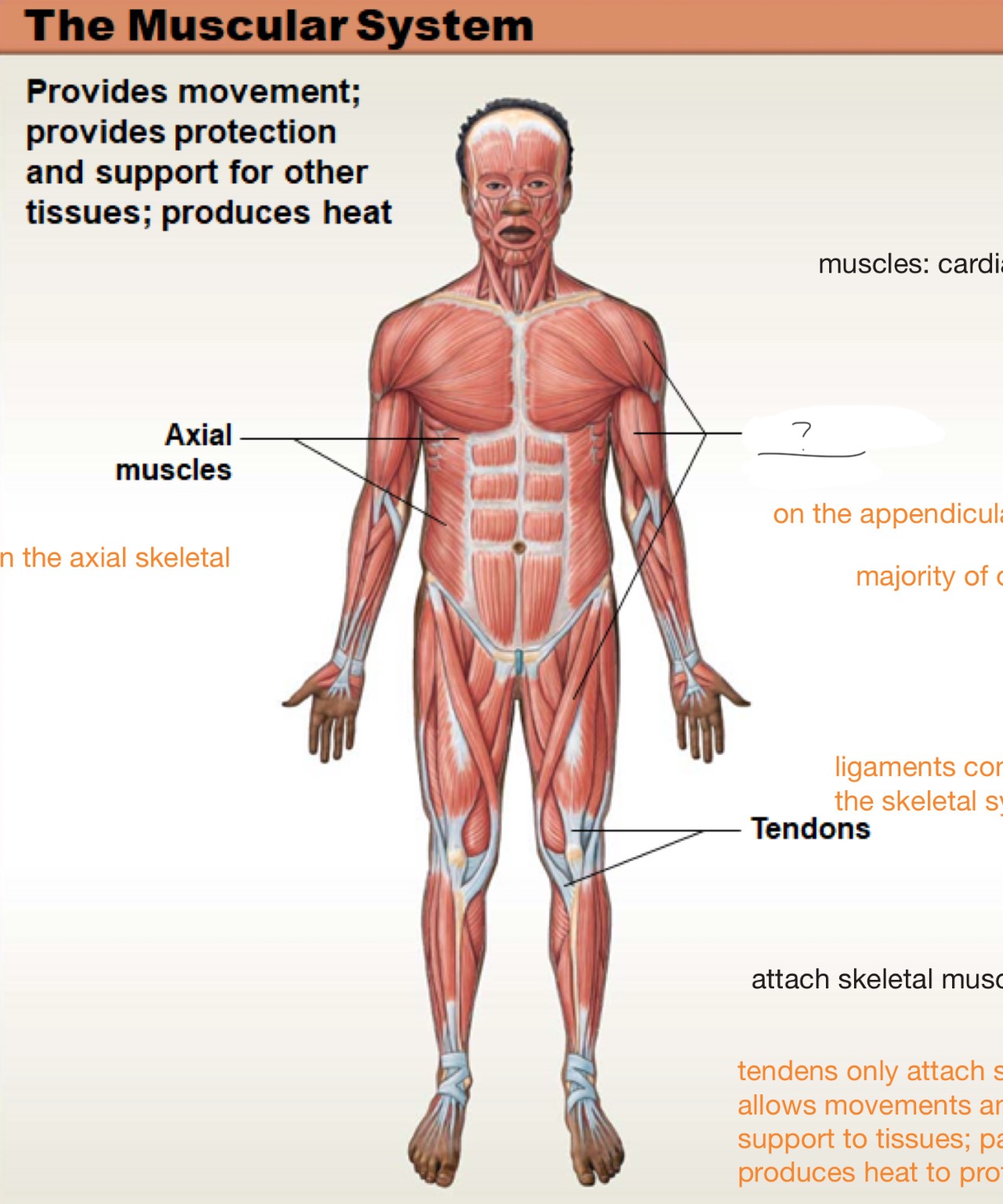
axial muscles
on the axial skeleton
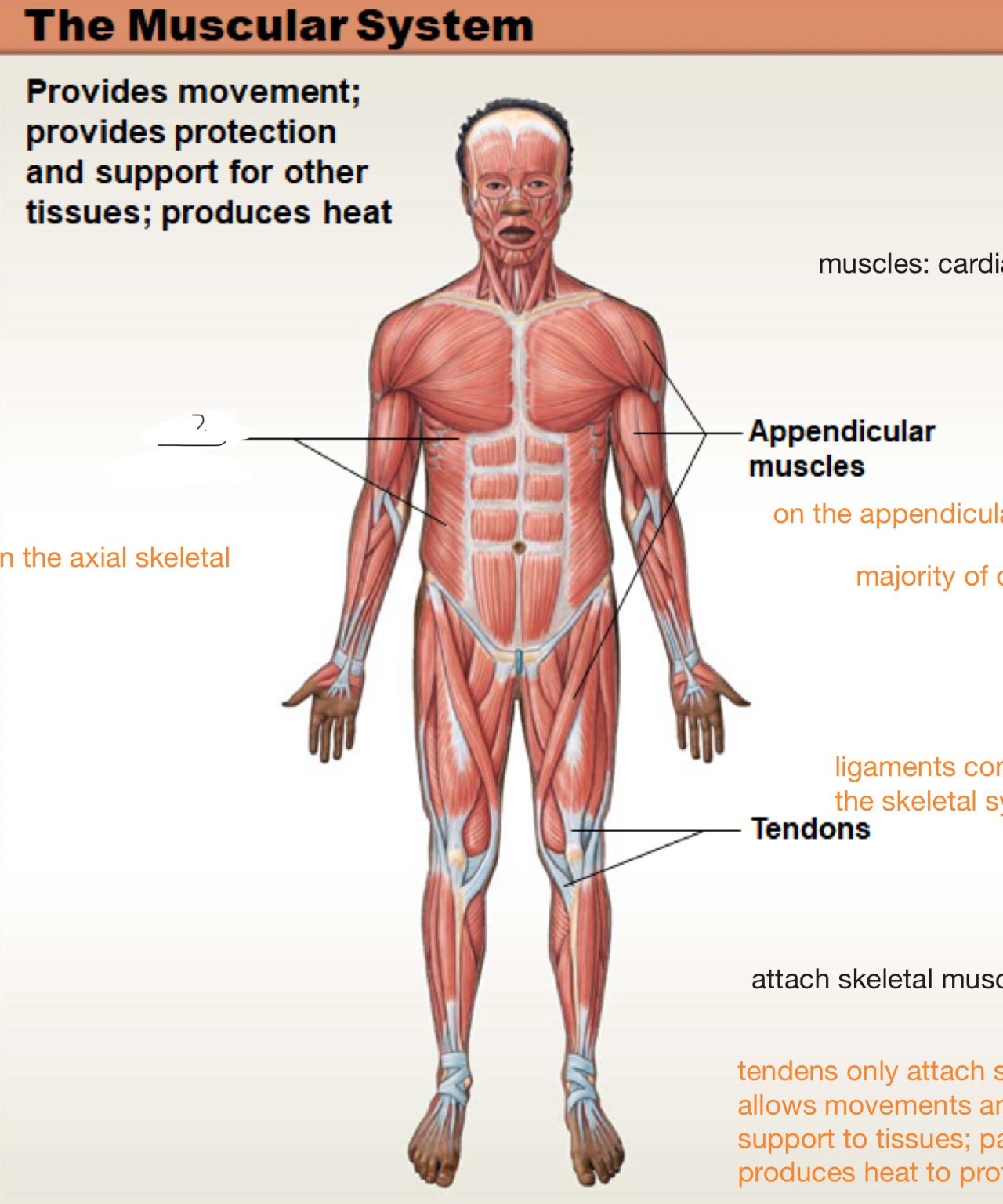
appendicular muscles
on the appendicular skeleton
tendons
attach skeletal muscle to bones and allows movement and provides protection and support to tissues
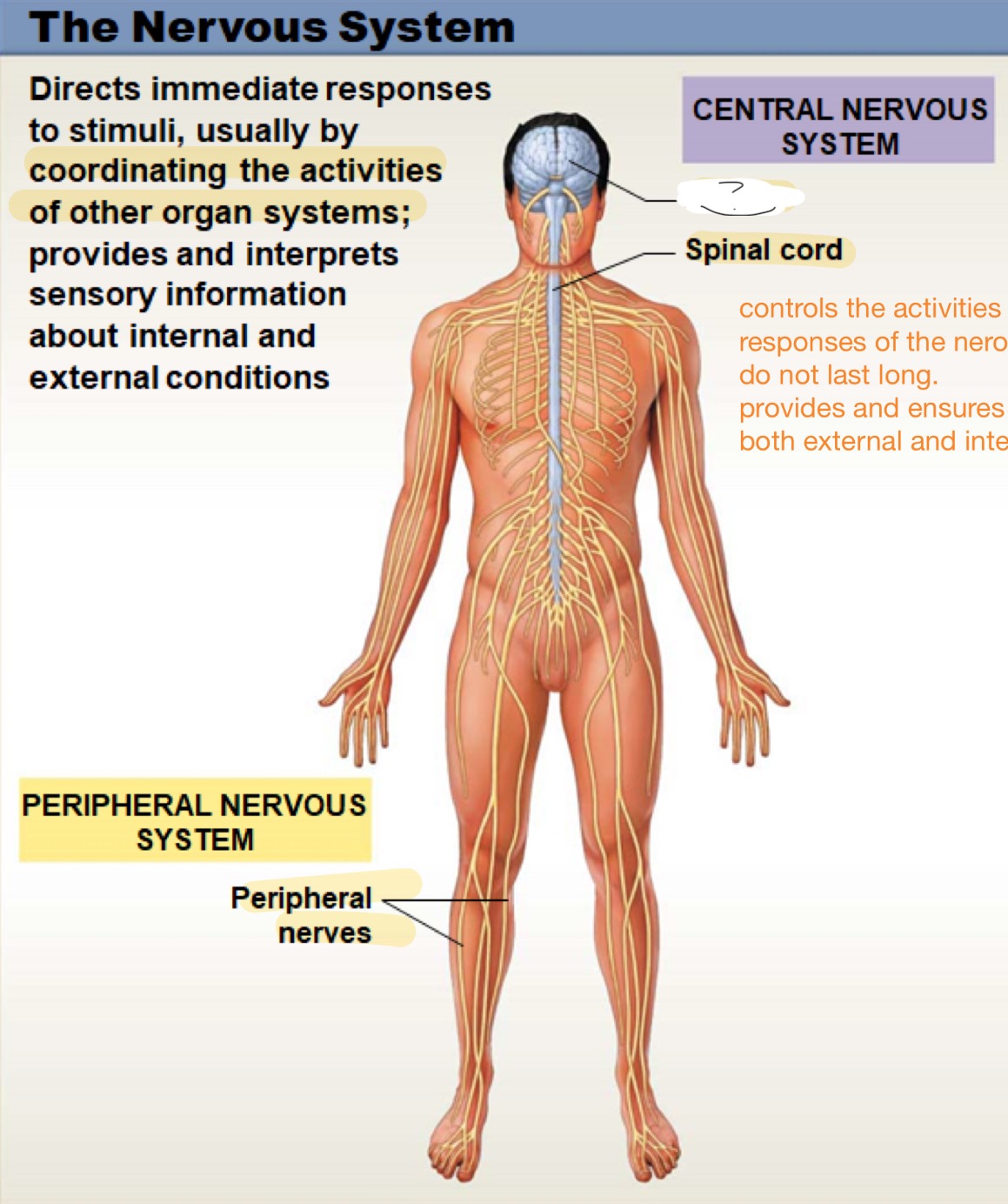
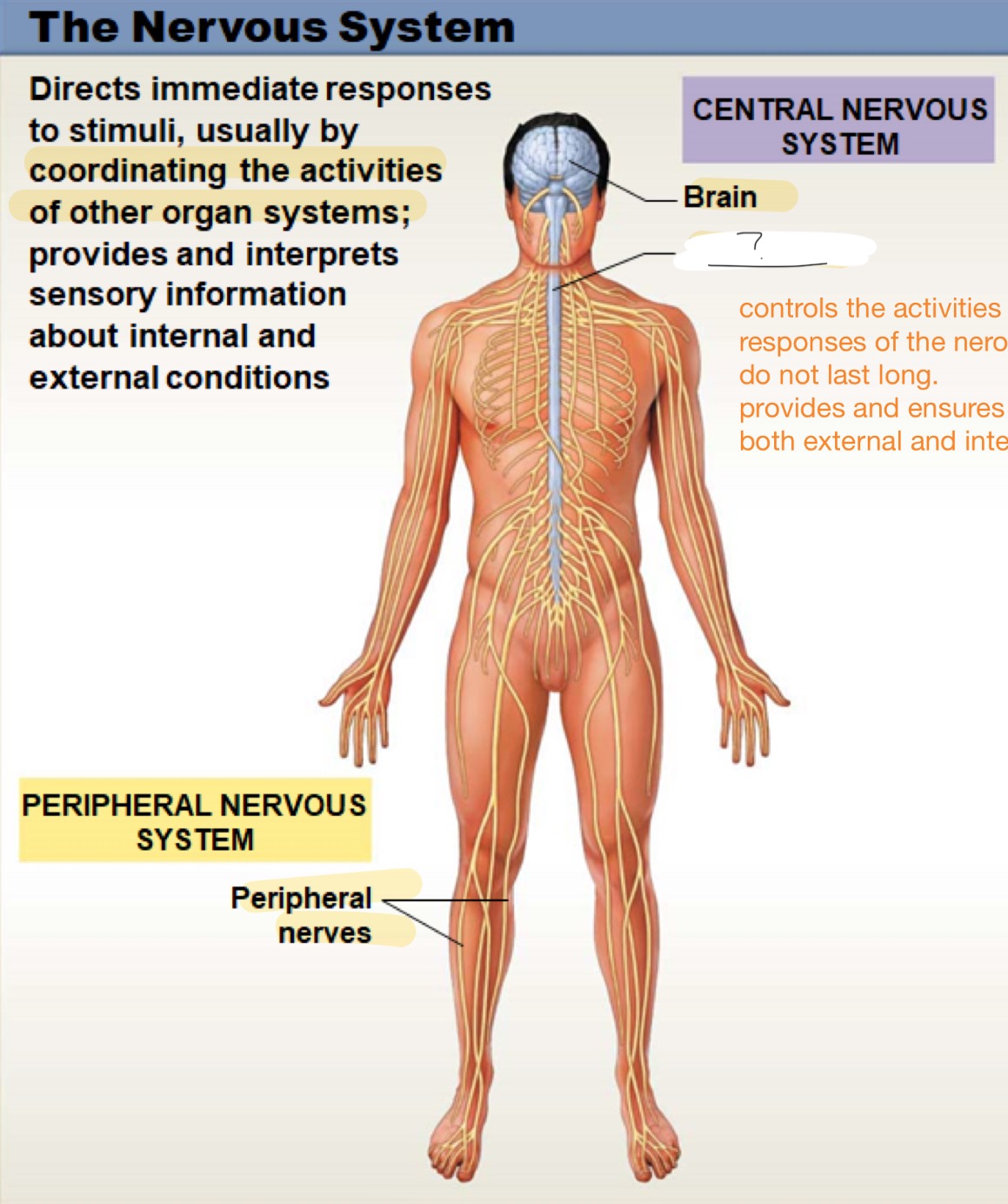
the nervous system
directs immediate responses to stimuli, usually by coordinating the activities of other organ systems; provides and interprets sensory information about internal and external conditions
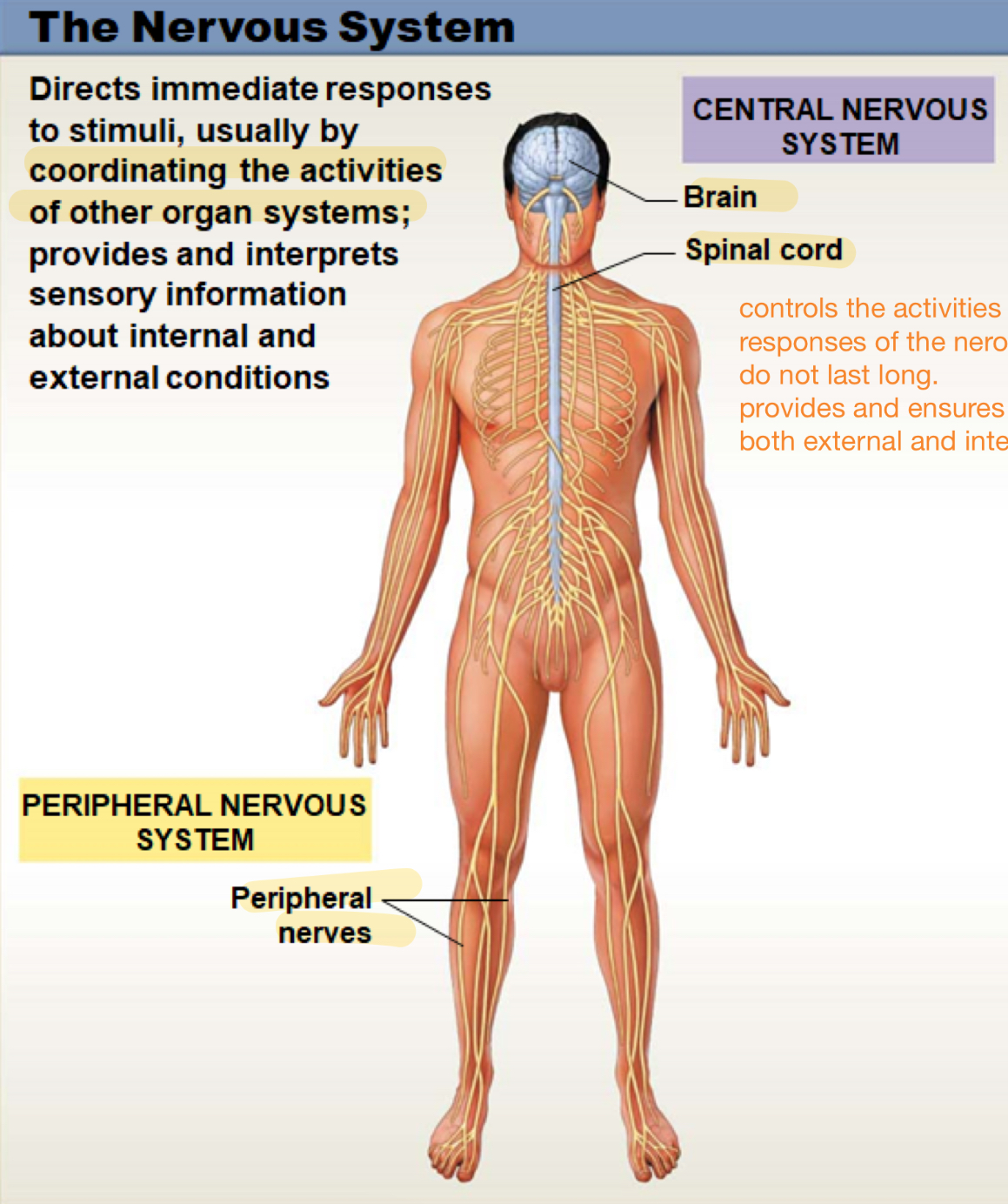
peripheral nervous sytem
includes all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord; helps carry messages between the central nervous system and the muscles, organs, and skin, allowing the body to move and respond to the environm
central nervous system
controls the activites of other organ systems; responses are quick and do not last long; provides and ensure sensory information from both external and internal environments
peripheral nerves
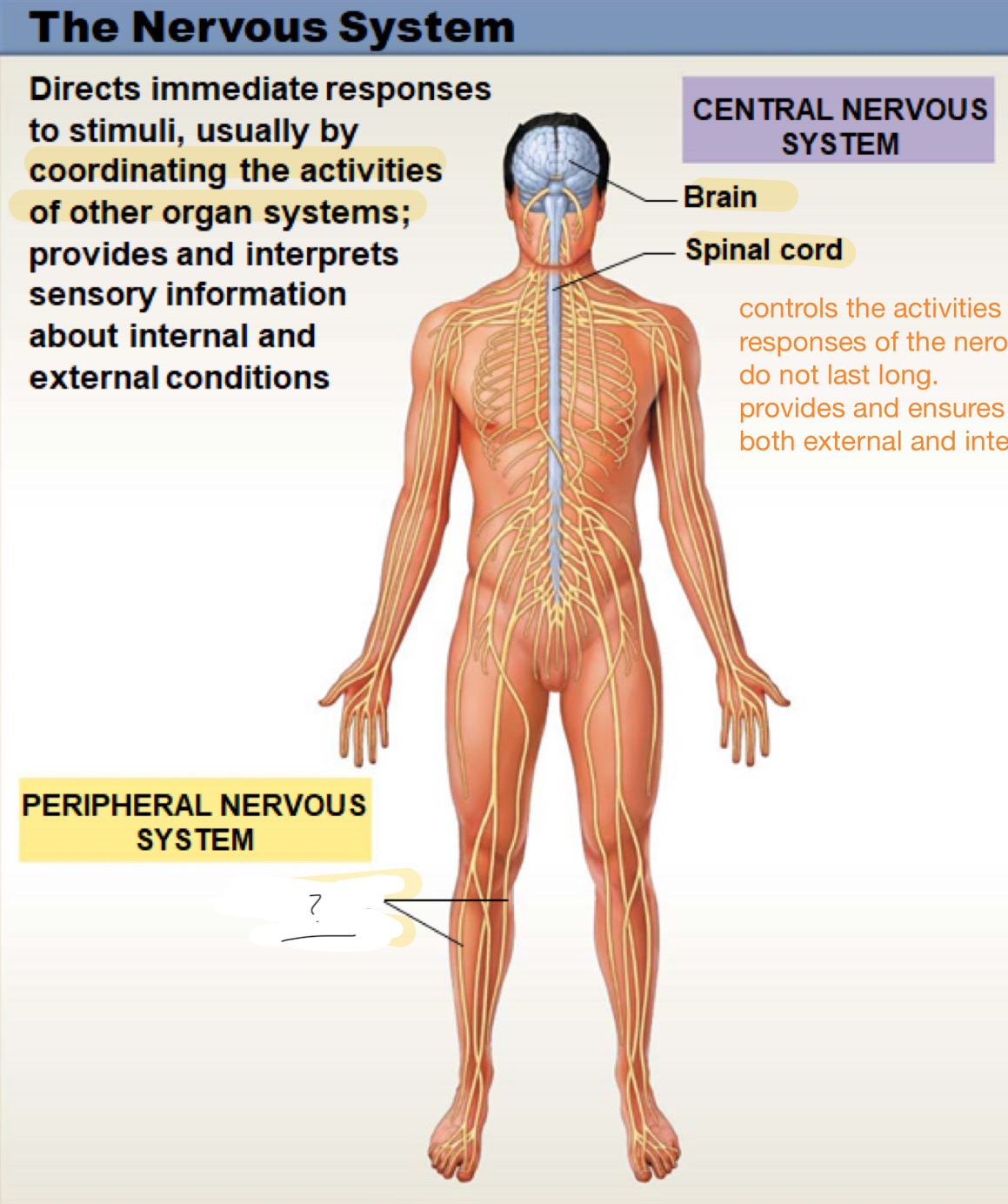
brain
spinal cord
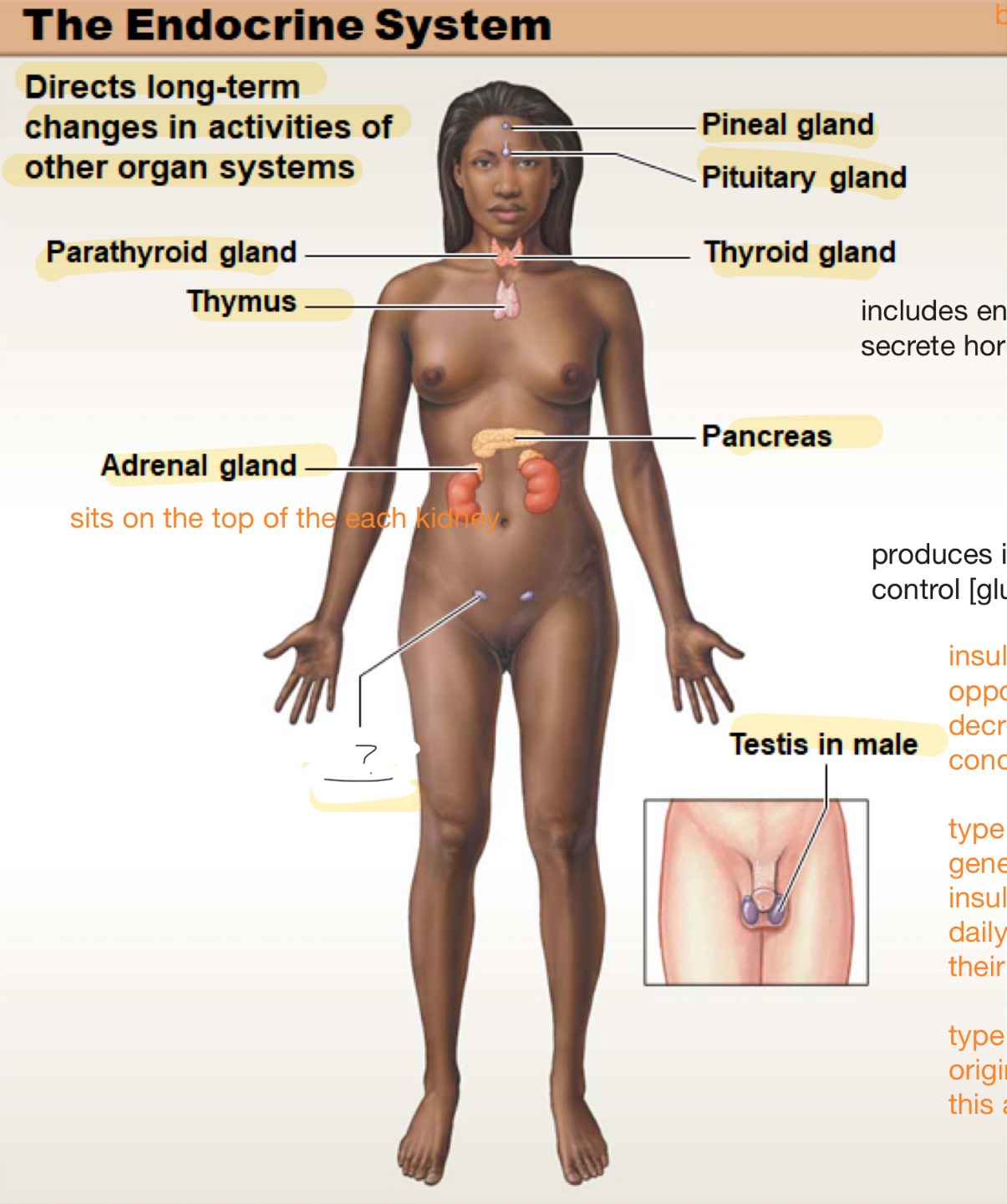
endocrine system
directs long-term changes in activities of other organ systems
parathyroid gland
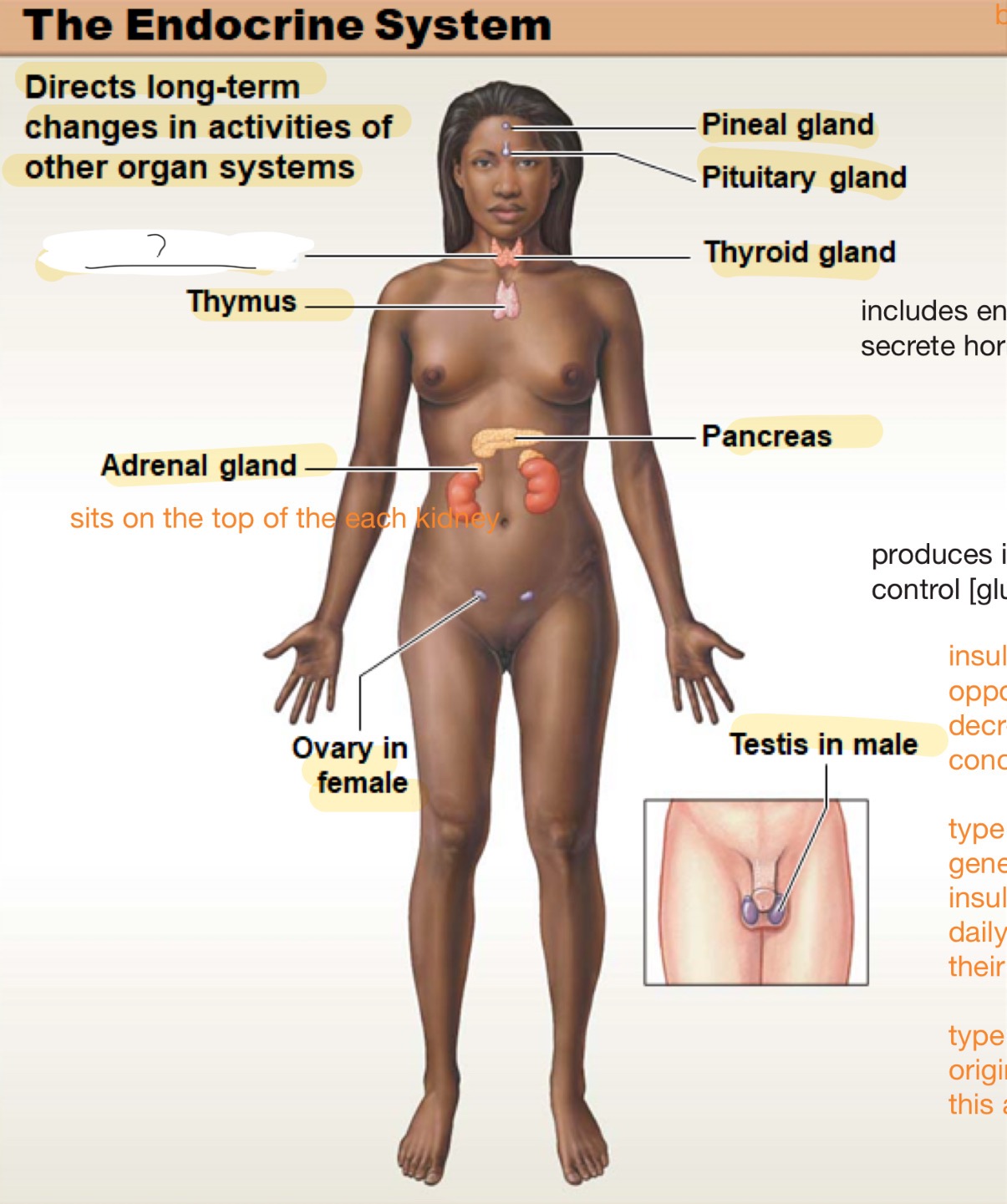
thymus
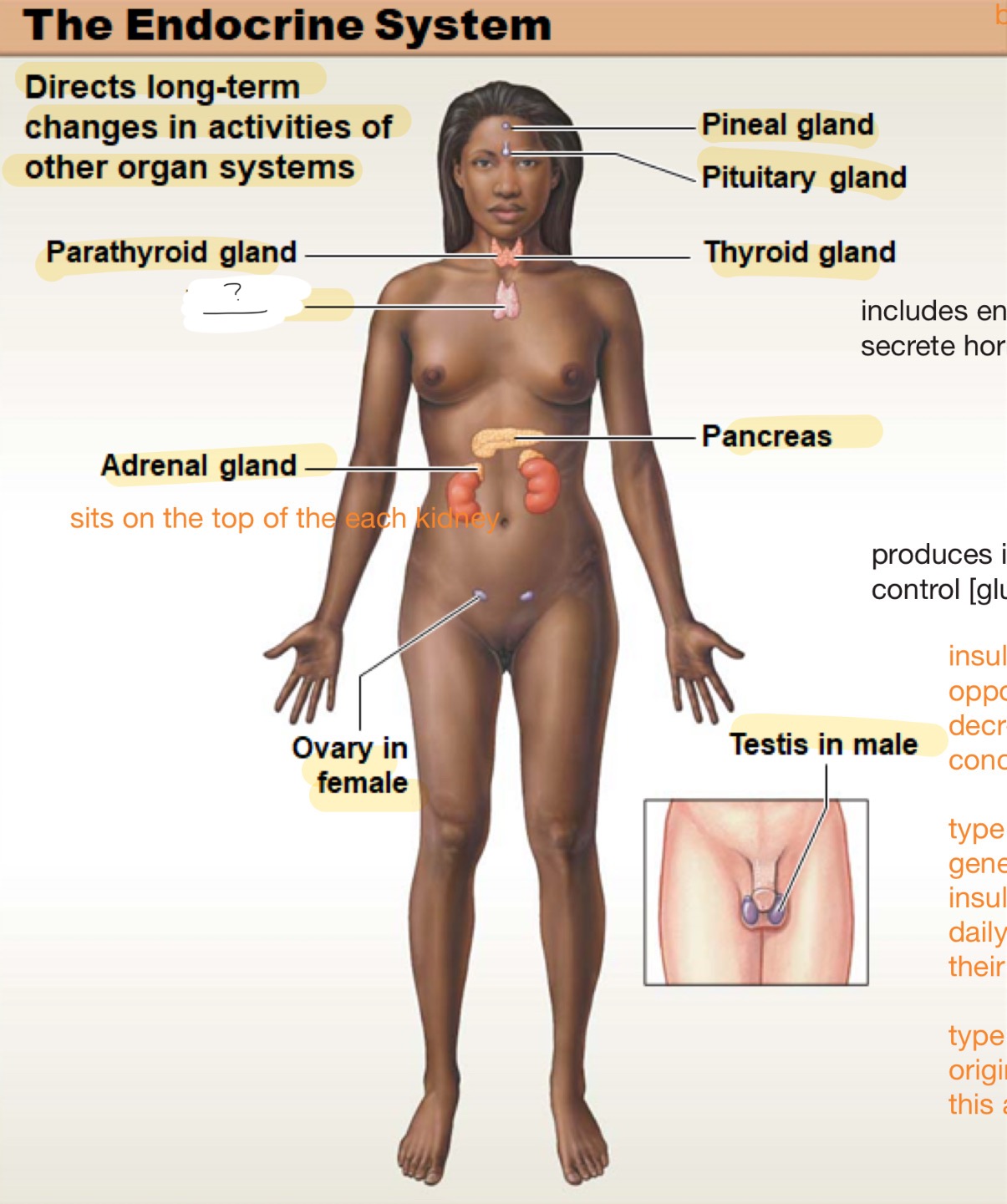
adrenal gland
sits on top of each kidney
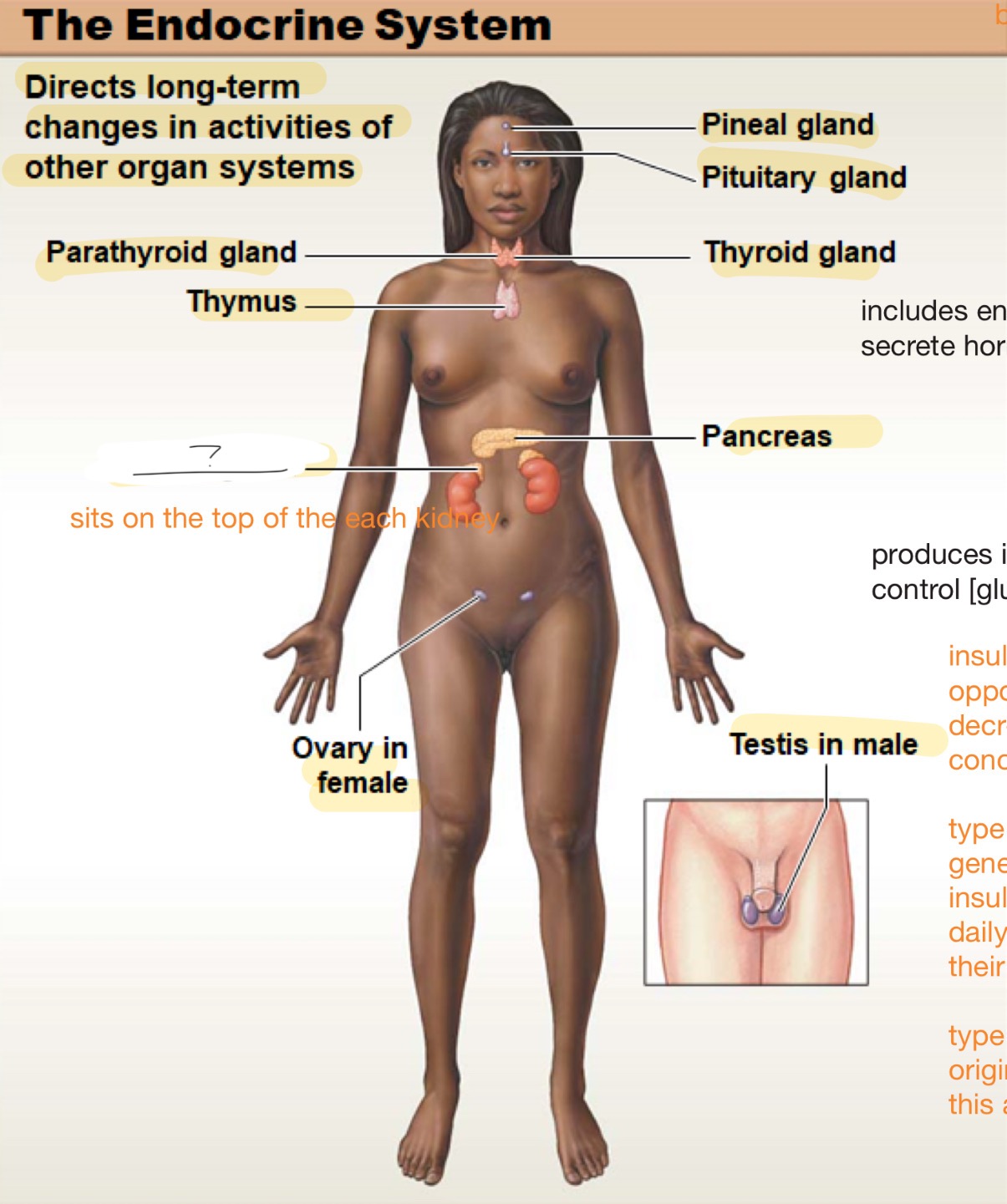
ovary in female