Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life — Campbell Biology Chapter 4
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms and concepts from carbon chemistry, the carbon cycle, and the functional groups essential for biomolecules.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Carbon cycle
The movement of carbon among the atmosphere, organisms, oceans, and earth, including photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and fossil fuel formation.
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
An inorganic gas in the atmosphere; raw material for photosynthesis; greenhouse gas contributing to warming.
Photosynthesis
Process by which photoautotrophs convert light energy and CO2 into organic sugars, storing energy in chemical bonds.
Carbon fixation
Incorporation of CO2 into organic molecules during photosynthesis.
Organic molecules
Carbon-based compounds produced by living organisms; the products of photosynthesis and respiration.
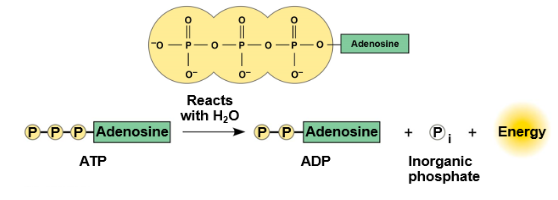
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
Cellular energy currency; formed from ADP and phosphate; drives most cellular reactions.
Fossil fuels
Coal, oil, and other energy-rich carbon compounds formed from ancient organisms; burning releases CO2.
Greenhouse gas
Gas in the atmosphere (e.g., CO2, methane) that traps heat and warms the planet.
Methane (CH4)
A simple hydrocarbon; potent greenhouse gas with high heat-trapping per molecule.
Hydrocarbons
Molecules composed only of carbon and hydrogen; typically nonpolar and hydrophobic.
Alkane
Saturated hydrocarbons with only single bonds; end in -ane (e.g., methane, ethane).
Methane
The simplest alkane (CH4) with one carbon and four hydrogens; tetrahedral geometry.
Ethane
C2H6; two carbons connected by a single bond; all other bonds to hydrogen.
Ethene (ethylene)
C2H4; an alkene with a carbon–carbon double bond; planar and non-rotatable.
Alkene
Hydrocarbon with at least one double bond; ends with -ene.
Double bond
Bond sharing two pairs of electrons; restricts rotation and changes molecule geometry.
Isomer
Molecules with the same molecular formula but different structures
Structural isomer
Isomers with same formula but different shape due to the way the atoms are linked together
Enantiomer
differ in special arrangement around the central asymmetric carbon
Cis-trans isomer (geometric isomer)
Isomerism around a double bond; cis = same side, trans = opposite sides; affects shape.
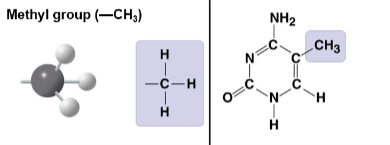
Methyl group
CH3 substituent; common side group in organic molecules.
Functional group
groups that change the molecule’s shape, chemistry, and function.
Hydroxyl group
–OH; forms alcohols; makes molecules polar and hydrophilic.
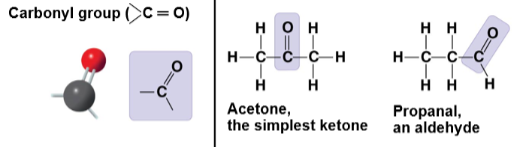
Carbonyl group
C=O; in aldehydes (terminal) or ketones (in the middle); increases polarity.
Aldehyde
Carbonyl group at the end of a carbon skeleton; terminal carbonyl compound.
Ketone
Carbonyl group within the carbon skeleton; internal carbonyl compound.
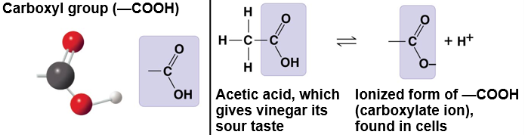
Carboxyl group
–COOH; acidic group that donates a proton in water, creating polarity.
Amino group
–NH2; acts as a base; present in amino acids; forms peptide bonds.
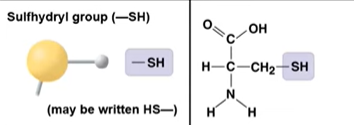
Sulfhydryl group
–SH; thiol group; can form disulfide bonds that influence protein structure.
Phosphate group
–PO4 (often as –PO4^3– in solution); negative, polar; key in energy transfer (ATP) and DNA backbone.
Methyl group (CH3)
Methyl substituent; modulates function and gene expression via methylation.
DNA sugar-phosphate backbone
Alternating sugar (deoxyribose in DNA, ribose in RNA) and phosphate groups forming the DNA backbone.
Deoxyribose
Five-carbon sugar in DNA; lacks the 2′-OH, differentiating DNA from RNA.
Ribose
Five-carbon sugar in RNA; contains a 2′-OH group.
Nucleic acids
DNA and RNA polymers built from nucleotides; store and transmit genetic information.
Nitrogenous base
Part of a nucleotide (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, uracil); paired in DNA/RNA.
Mitochondria
Organelle where cellular respiration occurs; produces ATP.
Polypeptide
Polymer of amino acids; folds into a protein with specific function.
Amino acids
Monomers of proteins; contain amino and carboxyl groups with a side chain.
Peptide bond
Bond between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of the next.
Biological energy transfer
ATP hydrolysis releases energy to drive non-spontaneous biological reactions.
ATP → ADP + Pi
Transfer of a phosphate from ATP to another molecule; energy is released in the process.
Base pairing and nucleotides
Knowledge of how nucleotides with different bases encode genetic information.
Hydrophilic
Molecule or region that interacts well with water due to polarity.
Hydrophobic
Nonpolar molecule or region that tends to repel water.
organic chemistry
the study of compounds that contain carbon, regardless of origin
4 ways carbon chains can vary
length
double bond position
branching
presence of rings