5: Data Collection and Sampling
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What are the 3 most popular methods of collecting primary data?
Direct observation
Experiments
Surveys
Direct observation
Collection of observational data – I.e., data that can be obtained by the senses.
- Pro: Inexpensive
- Con: Cannot assess causation and difficult to produce useful information due to the presence of dubious variables that cannot be controlled.
Experiments
Scientific procedure performed to determine something or support/refute a hypothesis.
- Pro: produces better quality data because design can limit influence of outside variables through controlling and manipulating the variables of interest
- Con: more expensive
Surveys
Solicitation of information from people, highly influenced by response rate aka the size of the sample of people who complete the survey. Administration includes personal interviews, telephone interviews, or self-administered surveys.
- Pro: can acquire answers from a larger spread of locations, telephone and self-administered surveys are inexpensive (not personal interviews).
- Cons: Personal interviews are expensive. Can be impacted by low response rates and incorrect answers.
Personal Interview
Best survey approach, has higher response rate and fewer incorrect answers.
Requires trained interviewer to avoid response bias
Telephone Interview
Less expensive but less personal + lower response rate. Cell phones are more difficult than landlines to include in survey.
Rationale: Landlines used to be fixed and tied to households, making it easy to reach a representative sample. With cell phones:
People can move across regions, so area codes don’t match location.
Numbers change more often.
Self-Administered survey
Mailed to a sample of people. It is inexpensive + attractive for large samples but suffers from low response rates and high rates of incorrect answers.
Questionnaire Design basic points (condensed):
Keep the questionnaire + question short and simple
Start w/ demographics to help comfortable start
Use dichotomous (yes/no) and multiple choice, be ecareful with open-ended
Avoid using leading questions
Pretest questionnaire w/ small sample
When making questionnaire, think about intention for collected data
Sampling
Process of selecting a subset of the population, often done for cost and practicality.
To be accurate, sampled populaton should be very close to target population
The larger the sample size, the better
Self-selected samples (volunteers) are prone to bias b/c participants are often already interested in the topic
Simple Random Sampling
Every possible sample of the same size has an equal chance to be chosen
Ex. picking 3 names from a hat containing all the names of the students in class (everyone has an equal shot of being chosen)
Ex. picking 40 tax returns out of 1,000 returns to estimate the proportion of dishonest returns
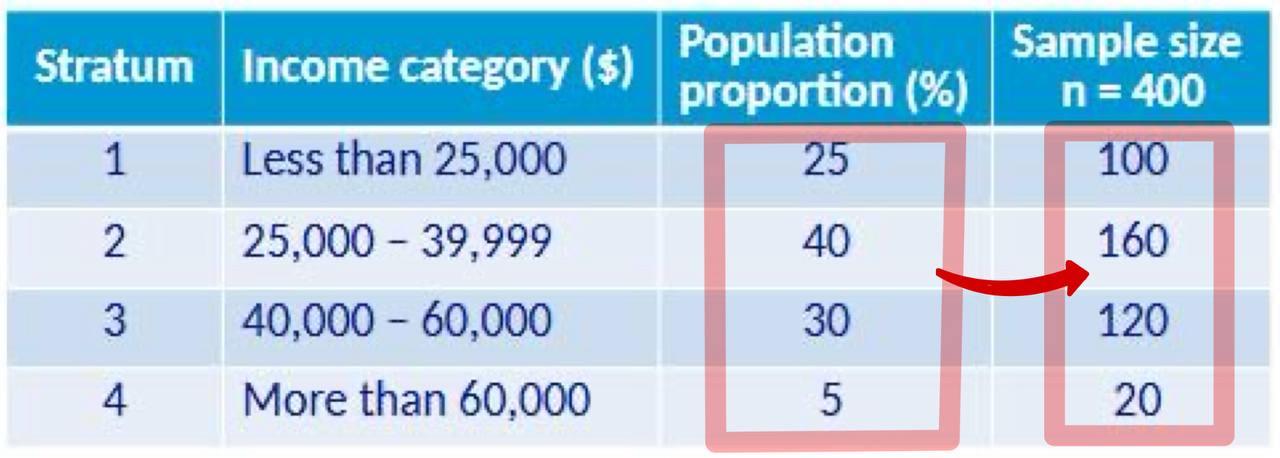
Stratified Random Sampling
Separate the population into strata then draw random samples from each stratum based on how their proportion to the sample.
Cluster Sampling
Divide the population into strata and pick entire group(s) to be sample. I.e. you don’t take samples from every strata.
Example: To estimate the average annual household income in a large city, we let each block within the city represent a cluster. A sample of a couple blocks (clusters) could then be randomly selected, and every household within these clusters could be questioned to determine income - notice that they did not sample a household from every block.
Sampling error
Difference or “gap” between the sample’s results and the true population value. The larger the sample, the less chance of error, as it is more proportional to the population.
Example:
If we want to know the average income of all North American blue-collar workers, we can’t ask everyone. Instead, we ask a sample.
Let’s say the true average income (population mean) is $50,000.
If we survey 100 workers, our sample might give an average of $48,500.
The sampling error is $48,500 – $50,000 = –$1,500
Nonsampling errors
Worse errors, mistakes made in the acquiring of data or due to improperly selected sample observations. 3 types:
Errors in data acquisition
Nonresponse errors
Selection bias
Errors in data acquisition
Mistakes made while gathering data; recording incorrect responses due to inaccurate measurements, transcription mistakes, inaccurate recording, or inaccurate responses to the questions
Nonresponse errors
Collected sample’s observations are not representative of the target population = biased results
Selection bias
Part of the target population is not included in the sampling plan