orbits, facials, nasal
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
A Parietoacanthial view is describing the:
A. Position of the patient
B. Projection of the beam, entrance to exit site
C. Position of the tube
D. Baseline used
B. Projection of the beam, entrance to exit site
True or False: The Waters view will demonstrate a displaced fracture in the perpendicular plate/nasal septum?
A. True
B. False
A. True
What is the name of the spongy depressions where the teeth embed from?
A. Coronal process
B. Alveolar processes
C. Diploe
D. Turbinates
B. Alveolar processes
What 2 bones form the bony nasal septum?
A. Superior and Inferior nasal conchae
B. Ethmoid and Vomer
C. Vomer and Maxilla
D. Sphenoid and Ethmoid
B. Ethmoid and Vomer
What is the junction of the 2 halves of the mandible called?
A. Mandibular symphysis
B. Symphysis pubis
C. Midline
D. TMJ
A. Mandibular symphysis
The posterior aspect of the orbit is termed the:
A. Apex
B. Base
C. Sphenoid strut
D. Crown
A. Apex
What is the name of the L-shaped bone that makes up the majority of the roof of our mouth?
A. Malar
B. Vomer
C. Zygoma
D. Palatine
D. Palatine
What is the vertical portion of the mandible called?
A. Ramus/Rami
B. Symphysis
C. Body
D. Mentum
A. Ramus/Rami
What is another name for the Maxillary sinuses?
A. Pars Petrosa
B. Gonion
C. Malar
D. Antrum of Highmore
D. Antrum of Highmore
What is the name of the angle of the mandible?
A. Condyle
B. Coronoid
C. Rami
D. Gonion
D. Gonion
How many Nasal bones are there?
2
What facial bone is described as plow shaped?
Vomer
Which process of the mandible forms the TMJ joint with the temporal bone?
A. Condyloid
B. Coronoid
C. Alveolar
D. Gonion
A. Condyloid
The small bone at the base of the tongue that does not articulate with any other bone is the:
A. Hyoid bone
B. Alveolar bone
C. Cornu bone
D. Styloid process
A. Hyoid bone
On a lateral nasal bone, do you image the affected side only or both?
A. Both
B. Affected Side Only
A. Both
What is the FOV for all facial, nasal, and orbital imaging?
A. 10x12
B. 8x8
C. 8x10
D. 12x14
C. 8x10
Is a Towne's or SMV part of a nasal bone routine?
A. No
B. Yes
A. No
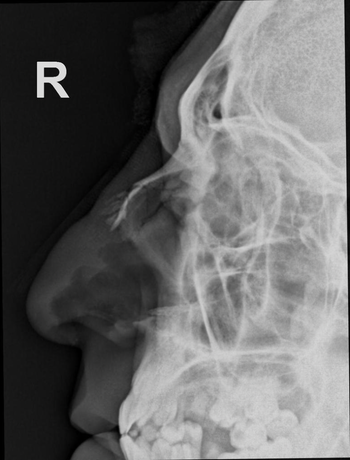
What pathology do you see in this image?
A. Fractured nasal bones
B. Orbital fracture
C. Frontal sinusitis
D. Maxillary sinusitis
A. Fractured nasal bones
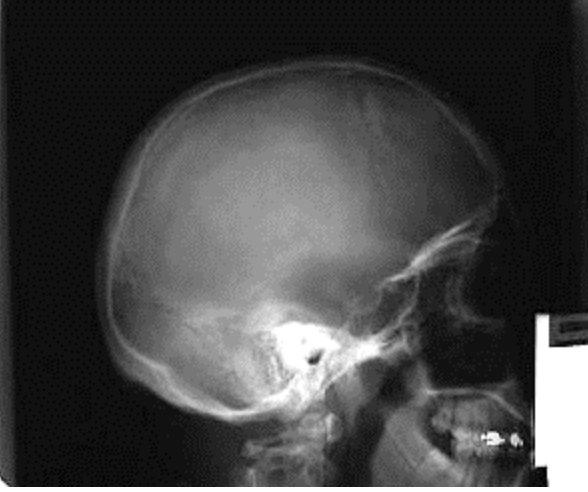
Which baseline is parallel to the longitudinal axis of the IR/FOV in the image below?
A. Infraorbital meatal line
B. Orbitomeatal line
C. Glabellomeatal line
D. Interpupillary line
A. Infraorbital meatal line
Which baseline is perpendicular to the IR in the image below?
A. Glabellomeatal line
B. Infraorbitomeatal line
C. Orbitomeatal line
D. Acanthiomeatal line
C. Orbitomeatal line
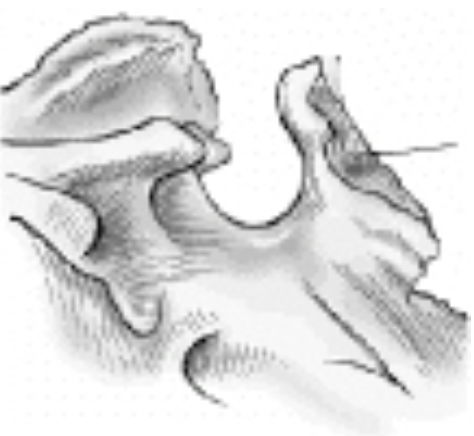
The part of the sphenoid bone identified by the line pointing to it in the figure below is the:
A. Sella Turcica
B. Clinoid processes
C. Dorsum Sellae
D. Clivus
C. Dorsum Sellae
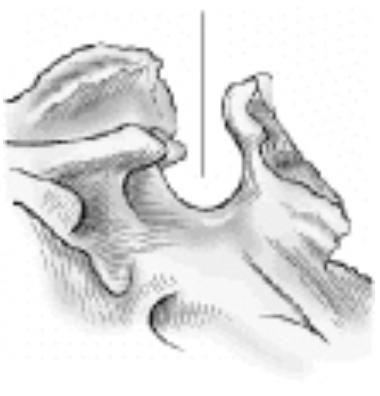
The part of the sphenoid bone identified by the line pointing to it in the figure below is the:
A. Foramen magnum
B. Clivus
C. Dorsum sellae
D. Sella turcica
D. Sella turcica
What is a blowout fracture?
A. Orbital floor fracture
B. Blow to the zygomatic bone (cheek bone)
C. Blow to mid face
D. Blow to back of head
A. Orbital floor fracture
Which of the following is not part of the routine images taken for facial bones?
A. PA axial (Caldwell method)
B. Parietoacanthial (Waters method)
C. Lateral
D. SMV
D. SMV
True or False: A modified Waters requires more extension of the chin than the regular Waters?
A. True
B. False
B. False
What image best evaluates FB (foreign bodies) or blowout fractures of the orbit?
Modified Waters
Basilar view demonstrates what of the facial bones?
Zygomatic arches
CR for lateral nasal bones is?
0.5 inches inferior to nasion
Schuller method, what is the relationship with the IOML to the IR?
Parallel
For lateral facial bones cr is where?
Between EAM and outer canthus. On the zygoma bone
What is the routine for nasal bones?
Bilateral laterals and waters
How many bones make up the bony orbit?
A. 4
B. 5
C. 6
D. 7
D. 7
How many bones of the face are there?
14
47 degrees for mesocephalic typical head. petrous ridges medial and anterior project
for reverse waters, what is the angle?
0 degree. no angle
the largest and most dense bone of the face is what?
mandible
what is the biggest sinus in the face?
maxillary
for lateral nasal bones, you can see
all sinuses
for lateral facial bones, you can see
all facial bones.
for waters view of the orbits, ioml is what degree to the IR?
50 degrees
What is another name for waters?
parietoacanthial
respiration phase for all facial bones
suspended
What bone are the two ethmoid sinuses located?
Ethmoid bone
Zygomatic processes are part of what bone
temporal
20-25 degree cephalic for mandubular rami 27:00:00
Tear duct is another name for what?
Lacrimal bone
Functions of the sinueses?
resonating chamber for voice, warm and moistent inhaled air, decrease weight of the skull
Whats true about lateral nasal bones?
midsaggital plane is parallel, you do bilateral lateral, IPL perpendicular IR
Lateral sinuses, what do you look for instead of sella tusica?
orbital roofs should be superimposed (same with Rami of mandible)
What is sinus is developed at birth and is visible radiographically?
maxillary
which reference line is positioned horizontal to show proper extension of the neck
IOML
What reference line is perpendicular for cadwell axial?
OML
which sinus is projected through the open mouth when doing modified waters method?
Sphenoid
What bone does the zygoma join with to form the Zygomatic Arches?
A. Maxilla
B. Sphenoid
C. Temporal
D. Mandible
C. Temporal
Which facial bone contains a foramen through which the tear duct passes?
A. Nasal
B. Palatine
C. Maxillae
D. Lacrimal
D. Lacrimal
Which of the sinuses is developed at birth and visible radiographically?
A. Maxillary
B. Ethmoidal
C. Sphenoidal
D. Frontal
A. Maxillary
Which line is positioned horizontal to ensure proper extension of the head during a lateral projection of the sinuses?
A. AML
B. OML
C. IOML
D. MML
C. IOML
For the Waters method, the orbitomeatal line is placed at what angle to the IR?
A. 30 degrees
B. 35 degrees
C. 37 degrees
D. 55 degrees
C. 37 degrees
For the open-mouth modification of the Waters method, the central ray should exit the:
A. Nasion
B. Glabella
C. Acanthion
D. Open mouth
D. Open mouth
How many bones comprise the bony orbit?
A. 5
B. 7
C. 9
D. 11
B. 7
How many bones make up the face?
A. 6
B. 10
C. 12
D. 14
D. 14
In a typically shaped head, the petrous pyramids project anteriorly and medially at what angle?
A. 37 degrees
B. 40 degrees
C. 47 degrees
D. 54 degrees
C. 47 degrees
The central-ray angulation for the reverse Waters method is:
A. 0 degrees
B. 15 degrees
C. 30 degrees to the AML
D. 37 degrees to the AML
A. 0 degrees
The largest and most dense bone of the face is the:
A. Maxilla
B. Mandible
C. Frontal
D. Sphenoid
B. Mandible
The largest sinus is the:
A. Frontal
B. Maxillary
C. Ethmoidal
D. Sphenoidal
B. Maxillary
The modified Waters method requires less angulation of the facial bones. The OML is adjusted to:
A. 30 degrees to the IR
B. 37 degrees to the IR
C. 55 degrees to the IR
D. 60 degrees to the IR
C. 55 degrees to the IR (50-55)
The small bone situated at the base of the tongue is the:
A. Hyoid
B. Alveolar
C. Cornu
D. Styloid
A. Hyoid
The zygomatic processes are a part of which bone?
A. Frontal
B. Parietal
C. Temporal
D. Sphenoid
C. Temporal
Where is the CR for a Towne's view for mandible imaging?
A. 2.5" above the Glabella
B. At the Glabella
C. At the Nasion
D. At the Acanthion
B. At the Glabella
Where is the CR for a PA projection of the mandible?
A. Nasion
B. Acanthion
C. Junction of the lips
D. Mental point
C. Junction of the lips
What is the angle for the axiolaterals of the Mandible?
A. 10 degrees cephalic
B. 10 degrees caudad
C. 15 degrees cephalic
D. 20 degrees cephalic
D. 20 degrees cephalic
How is the mandibular body placed for an axiolateral view in relation to the IR to see it in profile?
A. Perpendicular
B. Parallel
C. 20 degree rotation
D. 45 degree rotation
B. Parallel
What position is described here? Head true lateral, Angle Caudally 25-30 degrees to separate each TMJ from the other.
A. Towne
B. Schuller Method
C. Law's
D. Axiolateral mandible
B. Schuller Method
What is the name of the junction of the two halves of the mandible at the midline?
1. Mental point
2. Symphysis
3. Mental protuberance
4. Mentum
A. 1 and 3
B. 1 and 2
C. 1, 2 and 3
D. All of the above
A. 1 and 3
What is the name of the vertical portions on each side of the mandible?
A. Zygomatic processes
B. Alveolar processes
C. Condyles
D. Rami
C. Condyles
What is the name of the vertical portions on each side of the mandible?
A. Zygomatic processes
B. Alveolar processes
C. Condyles
D. Rami
D. Rami
Where are the petrous ridges seen on a parietoacanthial Waters radiograph?
A. Middle of maxillary sinuses
B. Superior to maxillary sinuses
C. Inferior to floor of maxillary sinuses
D. Lower third of the maxillary sinuses
C. Inferior to floor of maxillary sinuses
Which sinus is located immediately below the sella turcica?
A. Frontal
B. Maxillary
C. Ethmoidal
D. Sphenoidal
D. Sphenoidal
What are the four divisions of the temporal bone?
A. Tympanic, Clivus, TEA, Petrous
B. Squamosal, Tympanic, Mastoid, Petrous
C. Mastoid, Sphenoid, Ethmoid, EAM
D. Tympanic, Parietal, Zygomatic, Squamosal
B. Squamosal, Tympanic, Mastoid, Petrous
What is another name for the petrous pyramids?
A. Pars interarticularis
B. Pars petrosa
C. Pers Petrosa
D. Petrous peaks
B. Pars petrosa
Which bone contains the cribriform plate?
A. Frontal
B. Occipital
C. Ethmoid
D. Sphenoid
C. Ethmoid
What is the relationship between the mentomeatal line and the IR for a Waters view?
A. 30 degrees
B. 37 degrees
C. 90 degrees
D. 45 degrees
C. 90 degrees
What projection requires the petrous ridges be in the lower third of the orbits?
A. PA
B. Waters view
C. Acanthioparietal projection
D. 15 degree Caldwell
D. 15 degree Caldwell
What is the smallest facial bone?
A. Lacrimal
B. Nasal
C. Palatine
D. Vomer
A. Lacrimal
What is the name of the spongy depressions where the teeth embed from?
A. Coronal process
B. Alveolar processes
C. Diploe
D. Turbinates
B. Alveolar processes
What is another name for the nasal conchae?
A. Malar bones
B. Antrum of Highmore
C. Turbinates
D. Crista galli
C. Turbinates
The anterior nasal spine is also known as the:
A. Vomer
B. Acanthion
C. Palatine
D. Malar bone
B. Acanthion
What is the name of the L-shaped bone that makes up the majority of the roof of our mouth?
A. Malar
B. Vomer
C. Zygoma
D. Palatine
D. Palatine
What is another name for the zygoma bones?
A. Malar bones
B. Maxillary bones
C. Antrum of Highmore
D. Malabar
A. Malar bones
What is the other name for the facial bone also known as the Antrum of Highmore?
A. Mandible
B. Maxilla
C. Lacrimal
D. Zygoma
B. Maxilla
What is the only facial bone that does not articulate with any other bone in the body?
A. Ethmoid
B. Zygoma
C. Mandible
D. Hyoid
D. Hyoid
What position/method is used for the best evaluation of orbital foreign bodies and blowout fractures of the orbit?
A. Waters
B. Modified Waters
C. PA
D. PA Caldwell
B. Modified Waters
For a Basilar/Schuller's image, what is the relationship of the IOML and IR?
A. Parallel
B. Perpendicular
C. Oblique
D. Inferior
A. Parallel
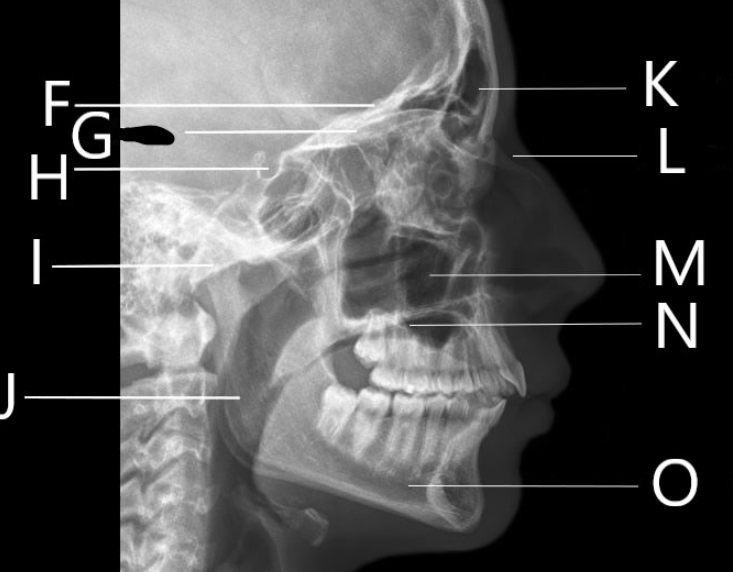
What bone is F identifying?
Orbital Roof
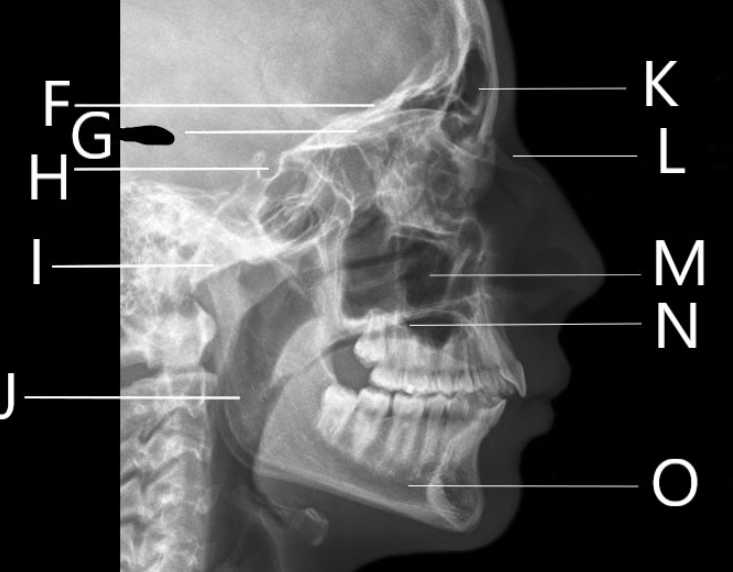
What is G identifying?
A. Horizontal plates of the frontal bone
B. Greater wing of the sphenoid
C. Sella Turcica
D. Vomer
B. Greater wing of the sphenoid
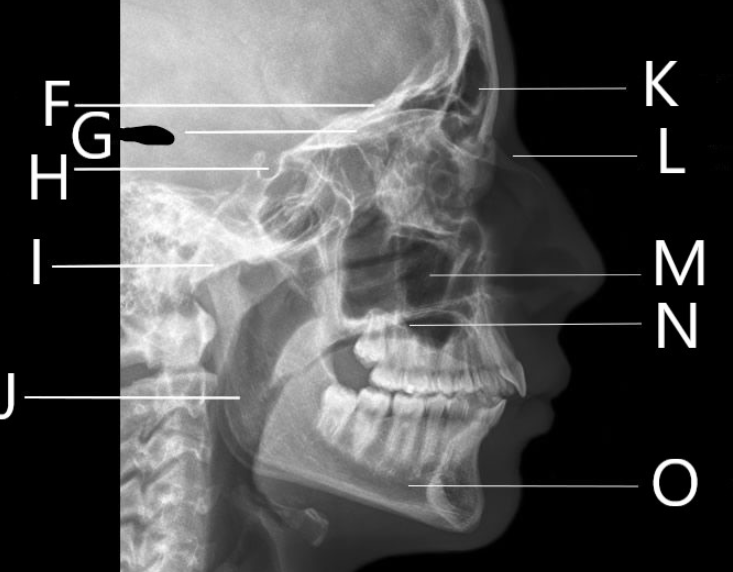
Identify letter H
Sella Turcica
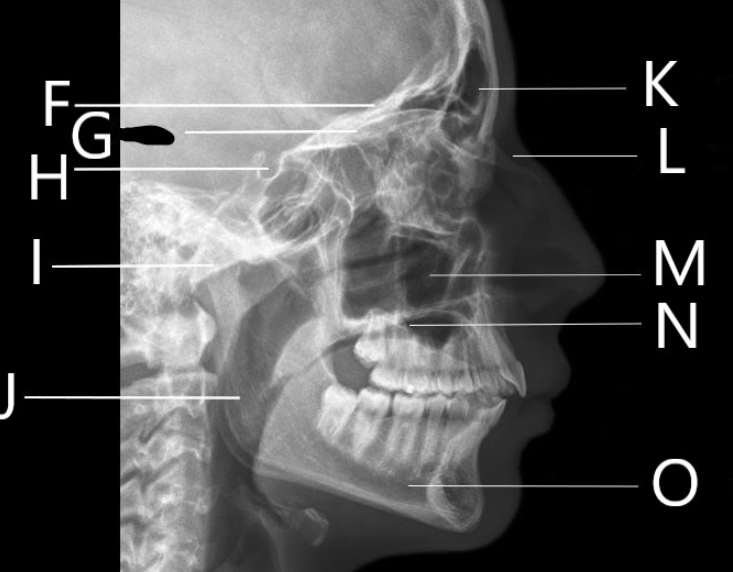
Identify letter I
A. Mandibular condyle
B. Greater wing of the sphenoid
C. Mastoid air cells
D. Sella Turcica
A. Mandibular condyle
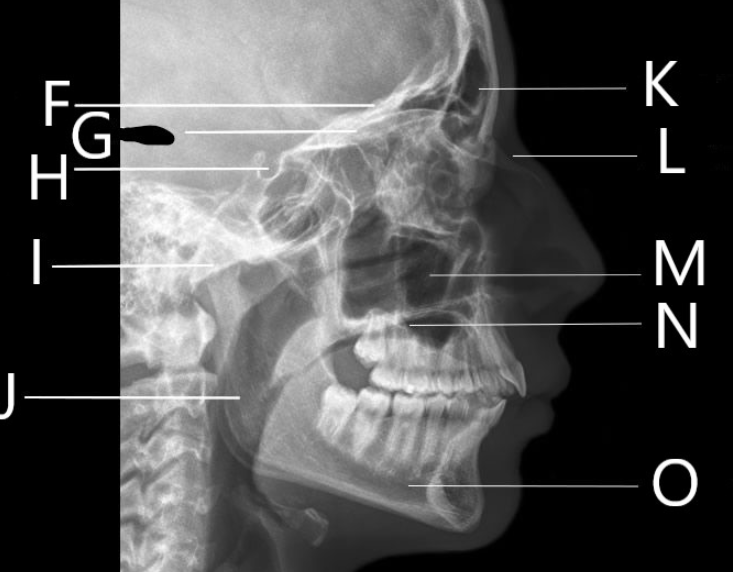
What bone is J identifying?
Ramus
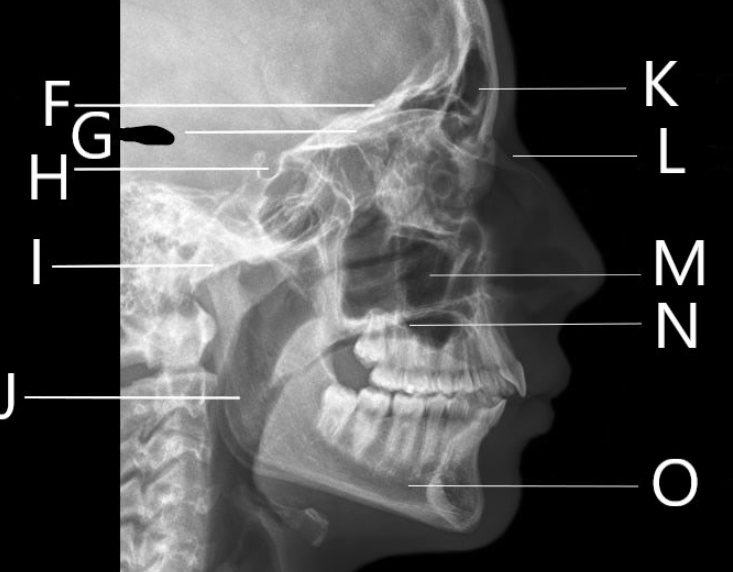
1. Identify letter K
A. Maxillary sinus
B. Frontal bone
C. Frontal sinus
D. Zygoma
C. Frontal sinus
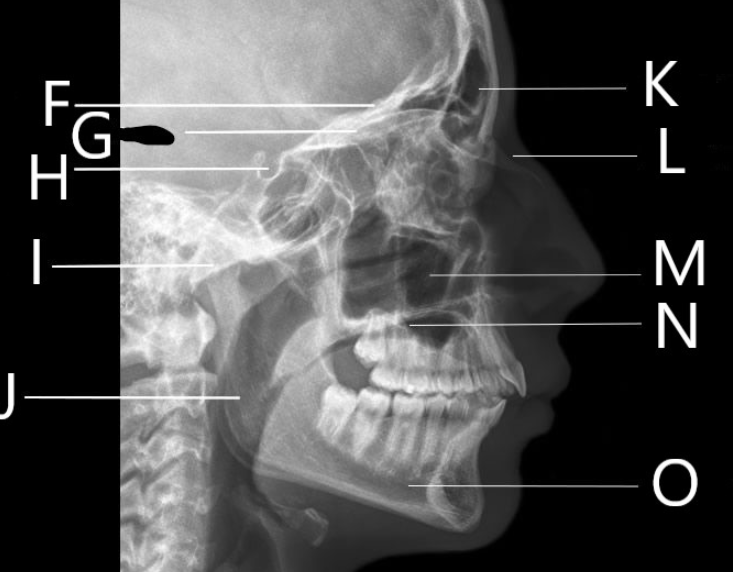
What bone is L identifying?
Nasal Bone