STAT 250 - Chapter 5
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Normal Distribution
A symmetric and bell-shaped curve.
Probability
Of an event, is the long run frequency or proportion of times the event would occur if the process was repeated many, many times.
Law of Large Numbers
As the number of repetitions of a random process increases, the proportion with which a certain outcome is observed gets closer to the probability of that outcome.
Empirical Probability
Relative frequencies based on observations to estimate probability. Relies on running an actual experiment.
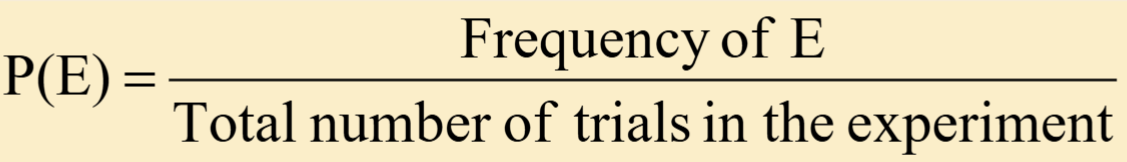
Theoretical Probability
The relative frequency at which an event happens after infinitely many repetitions. It tells us how many times an event would occur if a random process were repeated an infinite number of times. We cannot actually run the probability experiment.

Random Variable (rv)
A variable whose value is a numerical outcome of a random process.
Discrete Random Variable
A random variable that can take on a countable number of observations and has a finite number of values.
Continuous Random Variable
A random variable whose values are uncountable.
Probability Distribution
Of a random variable X, tells us what values X can take and how to assign probabilities to those values.
Density Curve
A theoretical model for a distribution of a continuous random variable.
Central Limit Theorem
For a large enough sample size (depending on the parameter), the distribution of many common sample statistics (such as means, proportions, difference in means, and difference in proportions) can be approximated with a normal distribution.