muscular system notes
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
tendons
muscle to bone
periosteum strengthens connection with this
made of dense regular connective fibrous tissue
epimysia covers
ligaments
bone to bone
3 types of muscles
smooth, skeletal, cardiac
smooth muscle
involuntary
walls of hollow visceral organs
slow, sustained movements
layers of smooth muscle
circular: squeezes
longitudinal: ripples down
squeeze at top and then ripple downward
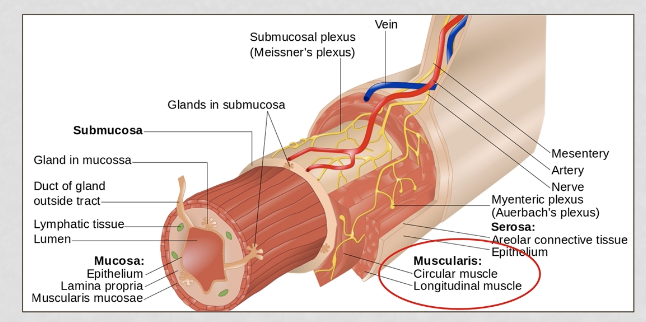
cardiac muscle
aka myocardium
intercalated discs are connections between the cells
skeletal muscle
multiple nuclei
one really long cell with multiple nuclei
muscle fiber
= one long muscle cell with lots of nuclei
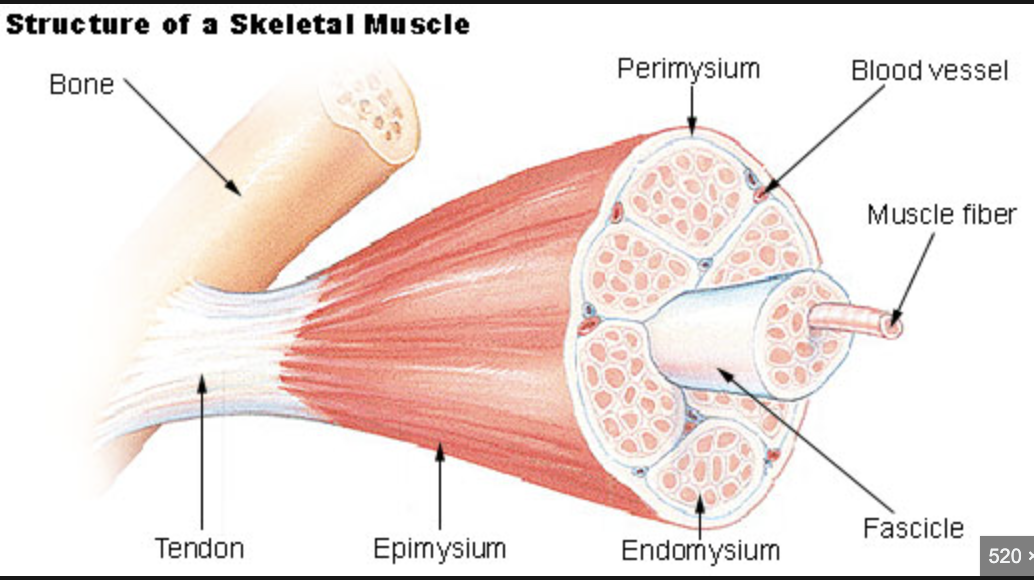
fibers are cells and fibers get packaged into fassicles and fassicles are bundled into muscles
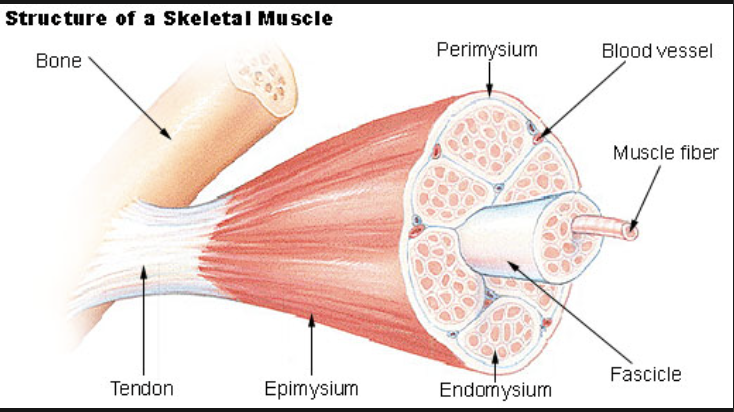
fassicles
bundle of muscle cells
AKA bundle of fibers
what protects muscle fibers
connective tissue wrapping:
endomysium: protects muscle fibers
perimysium: protects fassicle
epimysium: protects muscle
fassicle arrangements
diff shapes caused by how muscles are bundled
circular
convergent: come together
unipennate
parallel
bipennate
parallel fusiform
multipennate
pennate ones = many points of connection coming together
fusiform = come together
origin
point of attachment, anchor point, less moveable part
insertion
whichever bone has the most movement
what muscle naming is based off of
directional term, shape, points of attachment, etc.`
most body movements are the result of
2 or more muscles acting together or against each other
prime mover or agonist
muscle that produces a particular movement
antagonist
produces opposite effect on same bones
synergists
steady the area
stop from accidental movements
fixators
stabilizes the origin
for posture and balance
muscle cell membrane
aka sarcolema
fibers inside muscle cell
myofibrils
what are muscle cells stimulated by
electrochemical signals that travel along the sarcolemma (muscle cell membrane) AND THEN t-tubules carry signal to another muscle cell(fiber)
sarcomere explanation
actin and myosin are microfilaments that work together to contract and relax muscles
there can be lots of them in one fiber
causes striations in muscle
actin is blocked by tropomyosin which is held on by troponin; meanwhile, the myosin has an atp binded to it and whenever that atp releases its energy AND there’s a high enough calcium concentration for the troponin change shape and fall off of the actin, the myosin connects to the actin and pulls the actin closer to the midline which causes the muscle contraction
irritability
allows muscles to respond to a stimulus
more so neurological
losing it means you’re not responding
contractility
allows muscles to shorten
actual muscle issue
functions of muscle
movement, posture, heat generating, moving stuff
why can you bend partially
bc you don’t tell all your cells to move
bc if you tell one fiber to contract it will contract completely
motor unit
muscle cell + nerve cell
each muscle needs to be activated by a nerve but one can activate more than just one cell
neuromuscular junction
neuron forms a tiny space between it and the muscle fiber/cell which is called the synapse
the neuron releases neurotransmitters in vesicles in exocytosis which binds to receptor proteins and tells the muscle cell to move
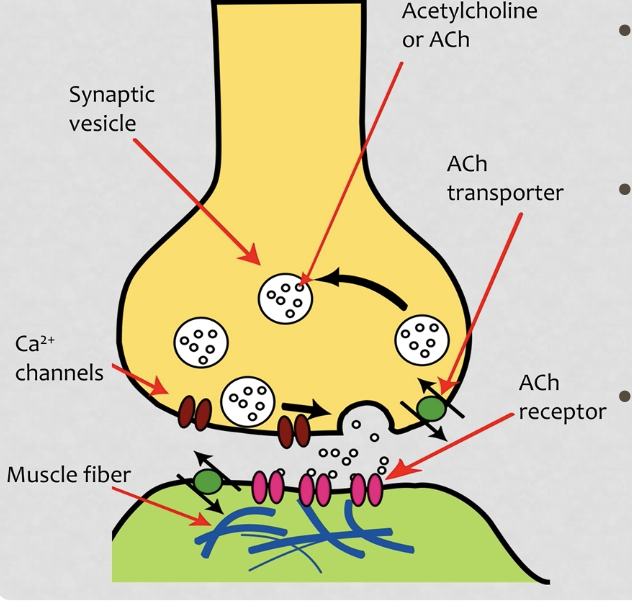
acetylcholine
neurotransmitter that tells muscles to contract
acetylcholinesterase
breaks down ACh to prevent futher contraction of a muscle
not enough of this enzyme —> muscle cell keeps contracting
action potential
charge difference
signal that tells muscle cells to contract
this stimulates the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium ions which attaches to troponin and allows myosin to attach to actin (which creates a crossbridge)
crossbridges
they’re the attachments of myosin heads to binding sites of actin
rigor mortis
example of it taking energy to release but not bind
muscles let go (needs energy) and then it gains energy when it (myosin) releases
when you die, your muscle releases all the calcium so the troponin releases and allows the myosin to attach which causes your muscles to contract
sliding filament theory
filaments bind to each other and pull and overlap
creates contraction
steps to muscle contractoin

incomplete tetanus
muscle relaxes a little bit and then contracts some more
more time between signals
more jerking motions
what happens after a muscle contraction
everything goes back
sodium potassium pump puts ions back (reabsorbed)
troopomyosin covers actin binding sites so that myosin can’t form crossbridges anymore
muscle relaxes
graded responses
different degrees of shortening or contraction
more muscle cells = stronger response
can be produced by:
changing frequency of muscle stimulation
changing number of muscles stimulated
how to create atp
breaking creatine phosphate (from food)
aerobic respiration
anaerobic glycolysis
muscle fatigue
caused by not enough oxygen to create a complete contraction to release
if you’re anemic, you don’t have enough rbcs to carry oxygen
isotonic movements
muscle shortening
isometric
muscles don’t shorten, they are held in one place
ex. planlk
muscle tone
little contractions
muscles are always just ready to go
muscle atrophy
disuse of muscles
losing tone bc not using
aerobic exercise
increases endurance and becomes stronger
muscle size stays the same
more fatigue resistant
resistance training
grows muscle fibers and increases endurance
cramp
where you get a contraction and you just don’t let go
causes: overuse, dehydration, strain, staying in one position
muscle pull
strain, pull, or tear = damage to tendons by tearing muscle fibers
paralysis
nervous system not telling muscle to contract so it won’t
muscular dystrophy
defects in proteins that form filaments in muscle
not structurally sound
caused by genes