AP 2 Quiz 1
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
Plasma
A clear, light-yellow fluid constituting a little over half of the blood volume
Thrombopoiesis vs Thrombocytopenia
Thrombopoiesis: The process of platelet (thrombocyte) production from megakaryocytes in the bone marrow
Thrombocytopenia: A condition characterized by abnormally low platelet count in the blood
What is PDGF?
PDGF is a growth factor from platelets that stimulates fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells to repair damaged vessels after clotting
Difference between neutropenia, neutrophilia and leukopenia, leukemia
Neutropenia: WBC deficiency (low neutrophils)
Neutrophilia: WBC excess (high neutrophils)
Leukopenia: General low WBC count
Leukemia: High WBC count - Cancer of WBC-forming stem cells
WBC life history
Born: red bone marrow
Mature: marrow / thymus (T cells)
Die: tissues or lymphatic organs
How many polypeptides make up hemoglobin?
4:
2 alpha chains
2 beta chains
RBC life history
Made: red bone marrow
Lifespan: ~120 days
Destroyed: spleen & liver
Iron recycled
Heme → bilirubin → bile
What is the most common vs most rare WBC?
Common: Neutrophil
Rare: Basophil
In Kwashiorkor, low albumin =
Low albumin production by the liver results in hypoproteinemia
What happens to the water in a person with Kwashiorkor?
Reduced plasma proteins → ↓ blood osmotic pressure
Water moves out of blood vessels
Fluid accumulates in:
Interstitial spaces (edema)
Abdominal cavity (ascites)
Produces the characteristic swollen belly despite malnutrition
What is ascites?
Abnormal accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity
occurs when plasma osmotic pressure is too low to retain water in blood vessels
What happens if blood osmolarity drops?
Water moves out of the blood into surrounding tissues
Explain the significance of blood viscosity. How does viscosity relate to flow?
Blood viscosity = thickness of blood
High viscosity = low flow = high workload on heart = high RBC
What is thrombosis?
Formation of a blood clot (thrombus) in an unbroken blood vessel
blocks blood flow, can cause ischemia and tissue damage
What is embolus?
A detached thrombus or other material traveling through the bloodstream
lodges in smaller vessels, can cause stroke, pulmonary embolism, or heart attack
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells which are the heaviest components and settle first
Leukocytes
White blood cells and platelets that make up 1% total volume and buffy coat
In a centrifuged blood sample, how does RBC, WBC, and plasma sit?
RBC is heaviest so it is on the bottom
Buffy coat: leukocytes and platelets
Plasma (55% of whole blood)
Function of lymphocytes
destroy cells (cancer, foreign, and virally infected cells)
Present antigens to activate other immune cells
Coordinate actions of other immune cells
Secrete antibodies and provide immune memory
What is plasma made up of?
Complex mixture of water, proteins, nutrients, electrolytes, nitrogenous wastes, hormones, and gases
How many L of blood does a human hold?
5.5L
Blood plasma vs Blood serum?
Plasma is the liquid, cell-free part of the blood, that has been treated with anti-coagulants
Serum is the liquid part of blood after coagulation, therefore lacking clotting factors as fibrinogen
plasma - fibrinogen = serum
What is blood plasma made up of?
Proteins such as albumin and fibrinogen
Electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and calcium
Nutrients
Hormones and waste products
Dissolved O2, CO2, and nitrogen
Albumin and fibrinogen help maintain?
Osmotic pressure and blood clotting
Leukocytes are broken into what two groups?
Granulocytes and Agranulocytes
Granulocytes make up?
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Basophils
Agranulocytes make up?
Lymphocytes
Monocytes
What are the formed elements?
Erythrocytes
Leukocytes
Granulocytes
neutrophils
Eosinophils
Basophils
Agranulocytes
Lymphocytes
Monocytes
Platelets
Hematocrit
The percentage of blood volume that is composed of erythrocytes
WBCs and platelets settle into a?
Narrow cream- or buff-colored zone called the buffy coat
If plasma is separated, allowed to coagulate (clot), and centrifuged again, the clotting proteins (mainly fibrin) settle to the bottom of the tube and the overlying fluid is called?
Blood serum
Functions of albumin
Osmotic pressure
Blood viscosity
Transports lipids, hormones, calcium, and other solutes
Buffers blood pH
Blood pressure
Flow and balance
Functions of globulins
Transport and defense functions as itemized below
Functions of fibrinogen
Becomes fibrin
The major component of blood clots
What is albumin?
Maintains blood osmotic pressure, keeps water inside blood vessels, prevents edema and fluid loss into tissues
Smallest and most abundant plasma protein in the liver
What are the three subclasses of globulins? What do they do?
Smallest to largest in MW:
Alpha (a) - transport proteins
Beta (B) - transport proteins
Gamma (y) - clotting protein
What are globulins?
Antibodies that provide immune system functions
What is fibrinogen?
Precursor of fibrin threads that help form blood clots
What is plasminogen?
Precursor to plasma which dissolves blood clots
Plasma proteins are formed by the?
Liver
Globulins are formed by?
Produced by plasma cells, a type B lymphocyte
Kwashiorkor is?
A disease marked by severe protein malnutrition and bilateral extremity swelling.
affects infants and children
severe cases of starvation and poverty-stricken regions
What is the most abundant nitrogenous waste?
Urea, a product of amino acid catabolism
What is Hypoproteinemia
Condition where the total protein levels in the blood fall below the normal range
can cause edema in the abdomen
Osmosis
A process by which molecules of a solvent tend to pass through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated solution into a more concentrated one, thus equalizing the concentrations on each side of the membrane.
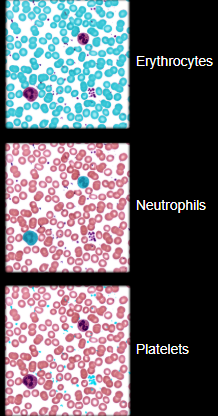
Label the erythrocytes, neutrophils, and platelets:
The biggest component of blood in terms of volume is?
Plasma
What are platelets?
Cell fragments from special cell (megakaryocyte) in bone marrow
What are the stained colors of the 3 granulocytes?
Basophils (stained blue/purple)
Eosinophils (stained red/pink/orange)
Neutrophils (neutral balance of colors above)
What are the stained colors of the agranulocytes?
Lymphocytes (B & T cells)
Monocytes
Function of erythrocytes?
Transport O2 and CO2 (mainly O2)
Function of neutrophils
Phagocytes that engulf bacteria and debris
Function of eosinophils
Attack parasitic worms; important in allergic reactions
Function of basophils
Release histamine, which is important in allergic reactions, and heparin, which helps clear fat from the blood
Function of monocytes
Leave bloodstream and transform into macrophages
Phagocytize pathogens and debris
Present antigens to activate other immune cells
The first hematopoietic tissues of the human embryo form in the?
Yolk sac, a membrane associated with all vertebrate embryos
Hemoglobin
The red gas transport pigment of an erythrocyte
Function of B and T lymphocytes
B lymphocytes: produce antibodies
T lymphocytes: cell-mediated immune responses
Function of platelets
Homeostasis
Blood formation in the bone marrow and lymphoid organs is called?
myeloid and lymphoid hematopoiesis
What are the characteristics of RBC’s?
Disc-shaped cell with thick rim
7.5 um diameter and 2.0 um thick at rim
lose nearly all organelles during development
anaerobic fermentation to produce ATP
lack nucleus and DNA
no protein synthesis or mitosis
Erythropoiesis
The production of erythrocytes
How does erythropoiesis begin?
When a hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) becomes an erythrocyte colony-forming unit (CFU)
Erythropoietin
A hormone that is secreted by the kidneys and liver in response to hypoxemia and stimulates erythropoiesis
Hypoxemia
A deficiency of oxygen in the bloodstream
When hypoxemia occurs, what do the kidneys do?
The kidneys detect this and increase their EPO output. 3-4 days later, the RBC count begins to rise and reverse the hypoxemia
Hemopoietic tissues produce?
Blood cells
When does the liver stop producing blood cells?
At birth
Yolk sac (of the embryo) produces?
Stem cells for the first blood cells
What stimulates more RBC production?
EPO = Erythropoietin
Primary polycythemia (polycythemia vera) is?
An RBC excess due to cancer of the erythropoietic line of the red bone marrow
RBC count can be as high as 11 million RBCs/uL
Hematocrit as high as 80%
Secondary polycythemia is
RBC counts as high as 11 million RBCs/uL due to dehydration, emphysema, high altitude, or physical conditioning
Relative polycythemia
RBC count up to 8 million RBCs/uL due to low plasma volume
Dangers of polycythemia
Increases blood volume, pressure, viscosity
can lead to embolism, stroke, or heart failure
Causes of anemia fall into 3 categories, they are?
Inadequate erythropoiesis or hemoglobin synthesis
Hemorrhagic anemia from bleeding
Hemolytic anemia from RBC destruction
What are examples of inadequate erythropoiesis or hemoglobin synthesis
Kidney failure & insufficient erythropoietin
Iron-deficiency anemia
Pernicious anemia
Hypoplastic anemia
Aplastic anemia
Porphyria
Porphyria
Lack enzymes to synthesize heme
Aplastic anemia
Complete cessation of erythropoiesis and all other blood cells (WBCs & platelets)
Hypoplastic anemia
Slowing of erythropoiesis
Pernicious anemia
Autoimmune attack of stomach tissue leads to inadequate vitamin B12 absorption
What is anemia caused by?
Too few RBCs or low Hb
What are the 3 consequences of anemia?
Tissue hypoxia and necrosis
Blood osmolarity is reduced, producing tissue edema
Blood viscosity is low
What is sickle-cell?
A hereditary hemoglobin defect found mostly among people of sub-Saharan Africa, the Mediterranean basin, the Middle East, and India.
Caused by recessive alleles that modifies structure of Hb (makes HbS)
What causes the pain in sickle-cell patients?
HbS does not bind O2 well, erythrocytes are sticky; they agglutinate and block small blood vessels, causing intense pain in oxygen-starved tissues
What can sickled cell lead to? What advantage does it have?
Kidney or heart failure, stroke, joint pain, or paralysis
Heterozygote “advantage” are resistant to malaria
What is the heme group?
The heme group consists of a porphyrin ring with an iron (Fe2+) ion at its center
allows it to bind oxygen molecules reversibly
4 total heme groups for each polypeptide
The antibody that reacts against antigen B is
Beta agglutinin or anti-B
The antibody that reacts against antigen A is
Alpha agglutinin or anti-A
A person who is type A is?
Anti-B, so should never get type B or AB transfusion
A person with a type B is
Anti-A, so should never get type A or AB blood
Type O is?
Anti-A and Anti-B, so they cannot safely receive type A, B, or AB blood
Those who have genotype DD or Dd (D antigen) are? Those who do not have it?
Rh+
Rh-
Agglutinogen vs Agglutinin
Agglutinogen: Specific antigens found on the surface of cells, such as red blood cells. They stimulate an immune response when recognized as foreign by the body
they determine blood groups
called Antigen A and B
Agglutinin: These are antibodies produced by the immune system in response to agglutinogens. They bind to corresponding agglutinogens, leading to agglutination, which is the clumping of cells
found in plasma
Anti-A and anti-B
Universal donor is?
Type O: most common bloody type
lacks RBC antigens
Donor’s plasma may have both antibodies against recipient’s RBC’s
May give packed cells
Universal recipient is?
Type AB: rarest blood type
lacks plasma antibodies; no anti-A or anti-B
What is hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN)?
Can occur if Rh- mother has formed antibodies and is pregnant with second Rh+ child
anti-D antibodies can cross placenta and attack fetal blood causing severe anemia and toxic brain syndrome
What are the preventions for HDN?
RhoGAM, given to pregnant Rh- women to bind fetal agglutinogens in her blood so she will not form anti-D antibodies
Anti-D agglutinin are present when?
Forms in Rh- individuals exposed to Rh+ blood
What is the relative abundance of WBCs?
Most abundant to least abundant
Neutrophils
Lymphocytes
Monocytes
Eosinophils
Basophils
Hemostasis
The stopping of blood flow from a damaged blood vessel